Evaluation of the Quality Attribute and Satisfaction on School Foodservice in 2010
Article information
Abstract
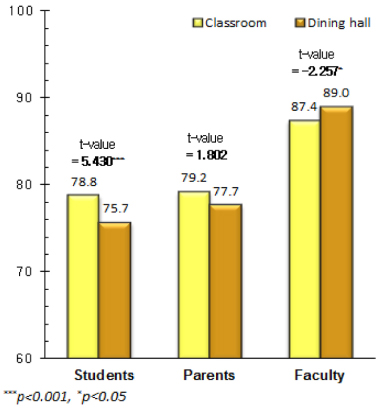
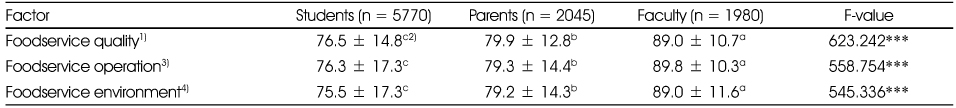
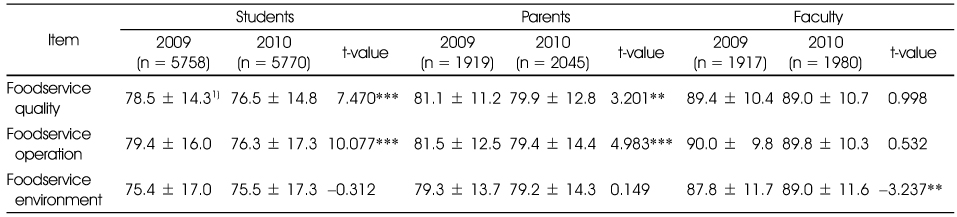
The purposes of this study were to analyze the quality attributes, quality factors and customer satisfaction in school foodservice and to provide suggestions for improving school foodservice environments. The survey was distributed to different respondents (5,771 students, 2,045 parents, and 1,981 faculty members) at different types of schools (elementary school, middle school, and high school) on September 2010 in 16 cities and provinces. The data were analyzed using SPSS for descriptive analysis, one-way ANOVA, t-test and multiple linear regression analysis. First, all foodservice quality attributes were significant different by respondents and the faculty had higher scores than parents and students. A comparison of scores by respondents and distribution place demonstrated that classroom of student and parents had a higher score for quality attributes. The overall satisfaction with school foodservice was significant different by respondents and higher for classroom than for dining hall for student and parents. In comparison of annual data, there was decreased overall satisfaction and quality attributes in student and parents. Second, in the regression results, which showed the effects of the foodservice quality attributes on overall satisfaction by respondents and distribution place, improvements of 'food taste', 'pleasant foodservice environment', and 'kindness of employee' would increase satisfaction in most of the respondents. Third, the overall satisfaction with school foodservice was higher for nutrition teachers than dietitians for students and faculty. Therefore, the operators will need to make different efforts based on each customer needs to improve the overall satisfaction on school foodservice.
Notes
This research was supported by a Ministry of Education and Science Technology.