Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Korean J Community Nutr > Volume 20(1); 2015 > Article
-
Research Article
- The Development and Validation of Eating Behavior Test Form for Infants and Young Children
- Youngshin Han, Su An kim, Yoonna Lee, Jeongmee Kim
-
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition 2015;20(1):1-10.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.1.1
Published online: February 28, 2015
1Environmental Health Center for Atopic Diseases, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
2Shingu College, Department of Food and Nutrition, Seongnam, Korea.
3Hansol Education Research Center, Hansol Education Co. Ltd., Seoul, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Jeongmee Kim. 6F Hansol Education Bldg., 361 Worldcup buk-ro, Mapo-gu, Seoul 121-914, Korea. Tel: (02) 2001-5765, Fax: (02) 2001-5335, jeongmeex@eduhansol.co.kr
Copyright © 2015 The Korean Society of Community Nutrition
This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 648 Views
- 4 Download
- 11 Crossref
Abstract
-
Objectives
- This study was conducted to develop and validate Eating Behaviors Test form (EBT) for infants and young children, including eating behaviors of their parents and parental feeding practices.
-
Methods
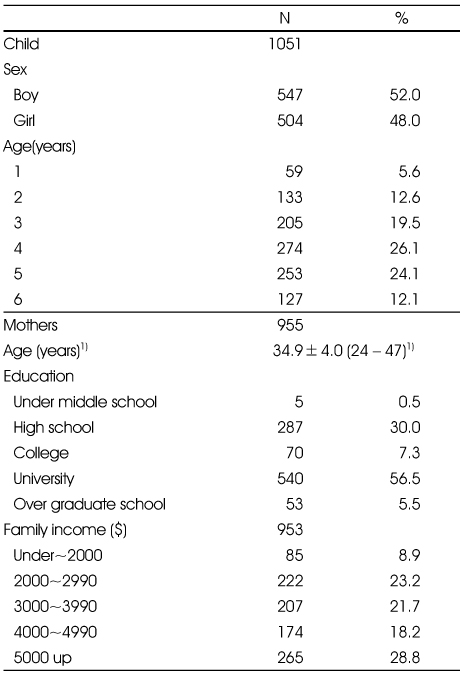
- Draft version of EBT form was developed after a pretest on 83 mothers. It was consisted of 42 questions including 3 components; eating behavior of children, eating behavior of parents, and parental feeding practices. Using these questionnaires, the first survey was conducted on 320 infants and children, 1 to 6 year old, for exploratory factor analysis, and the second survey was collected on 731 infants and children for confirmatory factor analysis.
-
Results
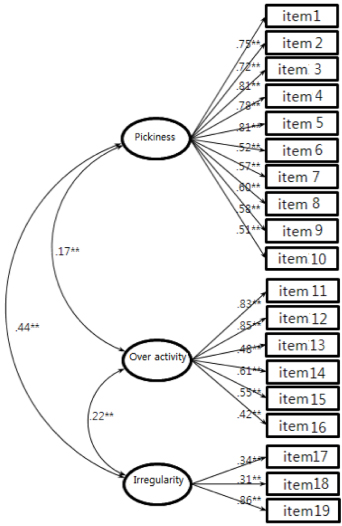
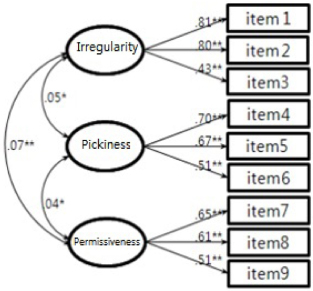
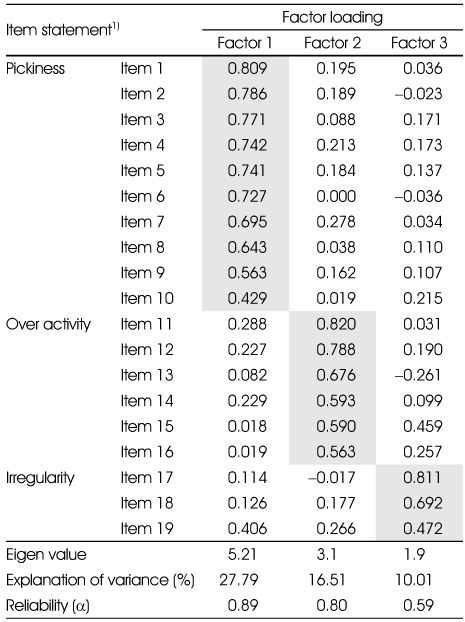
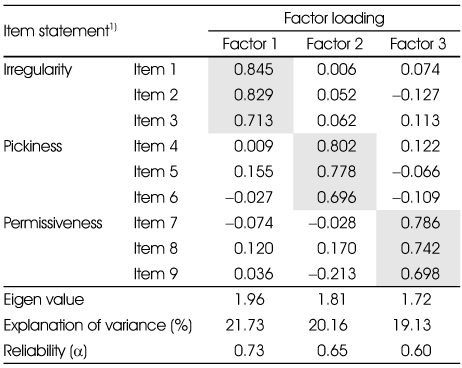
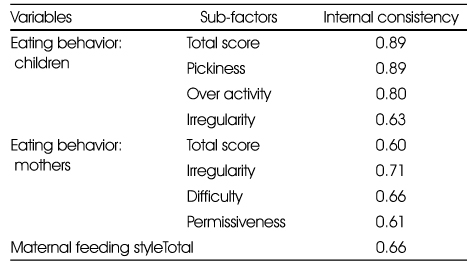
- Exploratory factor analysis on 42 questions of EBT form resulted in 3 factor model for children's eating behavior, 3 factor model for parents' eating behavior, and 1 factor model for parental feeding practices. Three factors for children's eating behavior could be explained as follows; factor 1, pickiness (reliability α=0.89; explanation of variance=27.79), factor 2, over activity (α=0.80, explanation of variance=16.51), and factor 3, irregularity (α=0.59, explanation of variance=10.01). Three factors for mother's eating behavior could be explained as follows; factor 1,irregularities (α=0.73, explanation of variance=21.73), factor 2, pickiness (α=0.65, explanation of variance= 20.16), and factor 3, permissiveness (α=0.60, explanation of variance=19.13). Confirmatory factor analysis confirmed an acceptance fit for these models. Internal consistencies for these factors were above 0.6.
-
Conclusions
- Our results indicated that EBT form is a valid tool to measure comprehensive eating and feeding behaviors for infants and young children.
Supplements
- 1. Baek KS. A study on children's adjustment to full-time daycare center. Doctorate Thesis. Sookmyung Women's University; 1996.
- 2. Bentler PM. Comparative fit indexes in structural models. Psychol Bull 1990; 107(2): 238-246.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Birch LL, Fisher JO. Development of eating behaviors among children and adolescents. Pediatrics 1998; 101(3 Pt 2): 539-549.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 4. Blissett J, Fogel A. Intrinsic and extrinsic influences on children's acceptance of new foods. Physiol Behav 2013; 121: 89-95.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Chatoor I, Ganiban J, Hirsch R, Borman-Spurrell E, Mrazek DA. Maternal characteristics and toddler temperament in infantile anorexia. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2000; 39(6): 743-751.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Chess S, Thomas A. Temperamental individuality from childhood to adolescence. J Am Acad Child Psychiatry 1977; 16(2): 218-226.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Dunn W. The impact of sensory processing abilities on the daily lives of young children and their families: a conceptual model. Infants Young Child 1997; 9(4): 23-35.Article
- 8. Farrow CV, Coulthard H. Relationships between sensory sensitivity, anxiety and selective eating in children. Appetite 2012; 58(3): 842-846.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Fullard W, McDevitt SC, Carey WB. The relationship between parental literacy level and perception of emergent literacy. J Read Behav 1984; 23(2): 191-213.
- 10. Gibson EL, Wardle J, Watts CJ. Fruit and vegetable consumption, nutritional knowledge and beliefs in mothers and children. Appetite 1998; 31(2): 205-228.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Hagekull B, Bohlin G, Rydell AM. Maternal sensitivity, infant temperament, and the development of early feeding problems. Infant Ment Health J 1997; 18(1): 92-106.Article
- 12. Harper LV, Sanders KM. The effect of adults' eating on young children's acceptance of unfamiliar foods. J Exp Child Psychol 1975; 20(2): 206-214.Article
- 13. Hendy HM, Raudenbush B. Effectiveness of teacher modeling to encourage food acceptance in preschool children. Appetite 2000; 34(1): 61-76.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Hetherington MM, Schwartz C, Madrelle J, Croden F, Nekitsing C, Vereijken CM, Weenen H. A step-by-step introduction to vegetables at the beginning of complementary feeding. The effects of early and repeated exposure. Appetite 2015; 84: 280-290.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Johnson SL, Birch LL. Parents' and children's adiposity and eating style. Pediatrics 1994; 94(5): 653-661.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 16. Kim Y, Han Y, Chung S, Lee Y, Lee S, Choi H. Characteristics of infants' temperaments and eating behaviors, mothers' eating behaviors and feeding practices in poor eating infants. Korean J Community Nutr 2006; 11(4): 449-458.
- 17. Kim YJ, Chung S, Han Y, Lee Y, Lee S, Byun K, Choi H. The characteristics of infants' temperament, maternal feeding behavior and feeding practices in picky eaters. Korean J Community Nutr 2005; 10(4): 462-470.
- 18. Kwon SH. Multivariate data analysis-using SPSS. Daejeon: Hannam University Press; 2005.
- 19. Lee MS. The effects of temperament and peer-support on the self-evaluation of early adolescents. Dissertation. Yonsei University; 1994.
- 20. Moding KJ, Birch LL, Stifter CA. Infant temperament and feeding history predict infants' responses to novel foods. Appetite 2014; 83: 218-225.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 21. Morrison H, Power TG, Nicklas T, Hughes SO. Exploring the effects of maternal eating patterns on maternal feeding and child eating. Appetite 2013; 63: 77-83.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Pliner P, Hobden K. Development of a scale to measure the trait of food neophobia in humans. Appetite 1992; 19(2): 105-120.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Pliner P, Loewen ER. Temperament and food neophobia in children and their mothers. Appetite 1997; 28(3): 239-254.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Putnam SP, Gartstein MA, Rothbart MK. Measurement of fine-grained aspects of toddler temperament: the early childhood behavior questionnaire. Infant Behav Dev 2006; 29(3): 386-401.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 25. Rollins BY, Loken E, Savage JS, Birch LL. Effects of restriction on children's intake differ by child temperament, food reinforcement, and parent's chronic use of restriction. Appetite 2014; 73: 31-39.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 26. Saslow ER. Temperament and day care: an examination of differences in expression across settings. Dissertation. Temple University; 1993.
- 27. Steiger JH. Structural model evaluation and modification: aninterval estimation approach. Multivariate Behav Res 1990; 25(2): 173-180.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Stunkard AJ, Messick S. The three-factor eating questionnaire to measure dietary restraint, disinhibition and hunger. J Psychosom Res 1985; 29(1): 71-83.ArticlePubMed
- 29. Sullivan SA, Birch LL. Infant dietary experience and acceptance of solid foods. Pediatrics 1994; 93(2): 271-277.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 30. Windle M. Temperament and social support in adolescence: interrelations with depressive symptoms and delinquent behaviors. J Youth Adolesc 1992; 21(1): 1-21.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 31. Wright DE, Radcliffe JD. Parents' perceptions of influences on food behavior development of children attending day care facilities. J Nutr Educ 1992; 24(4): 198-201.Article
- 32. Yang BH. Understanding multivariate data analysis. Seoul: Communication Books; 2006.
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- A study on the factors affecting the omnivorous diet of adolescents and the typology: focusing on inherited and acquired cultural capital
Hyewon Lee, Rando Kim
Journal of Families and Better Life.2024; 42(1): 81. CrossRef - Assessment of Dietary Characteristics and Eating Behavior in Children Using a Dietary Screening Test
Sun-Im Won
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(6): 557. CrossRef - Associations between maternal comprehensive feeding practices and dietary practices in preschool children
Myeongil Cho, Seunghee Kye
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(1): 141. CrossRef - The effect of the mother's modeling and feeding practices on the eating behavior of young children
Hyeonmi Sim, Youngshin Han, Kyung A Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(2): 296. CrossRef - The influence of parental eating behaviors, child-feeding practices, and infants’ temperaments upon infants’ eating behaviors
Goh Woon Lim, Kyoung Min Shin
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics.2022; 65(9): 466. CrossRef - The status of food allergy and parental burden of preschoolers in Jeju area
Jeong Eun Oh, Eunyoung Kim, Yunkyoung Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(6): 664. CrossRef - MAMAS: Supporting Parent--Child Mealtime Interactions Using Automated Tracking and Speech Recognition
Eunkyung Jo, Hyeonseok Bang, Myeonghan Ryu, Eun Jee Sung, Sungmook Leem, Hwajung Hong
Proceedings of the ACM on Human-Computer Interaction.2020; 4(CSCW1): 1. CrossRef - Analysis of the types of eating behavior affecting the nutrition of preschool children: using the Dietary Behavior Test (DBT) and the Nutrition Quotient (NQ)
Hyeon Mi Sim, Youngshin Han, Kyung A Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(6): 604. CrossRef - The Infant and Child Growth Assistance System Based on a Smartphone
Ki-Won Byun, Joon-Gyu Kang
Journal of the Korea Society of Computer and Information.2016; 21(8): 95. CrossRef - Evaluation of a Nutrition Education Program Designed to Reduce Sugar Intake in Preschool Children
Ma-Young Yeom, Youn-Ok Cho
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2016; 22(3): 179. CrossRef - The Development of Sugar Intake Reduction Test for Young Children
Nam-Hee Kim, Jee-Young Yeon, Mi-Hyun Kim
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(5): 818. CrossRef
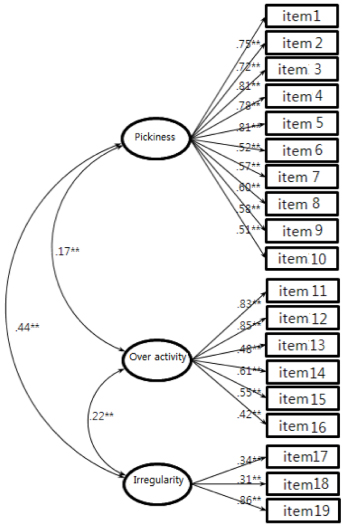
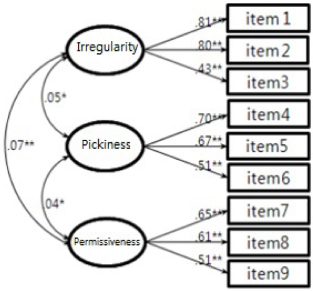
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Warning: simplexml_load_file(): /home/virtual/kjcn/journal/../xmls/kjcn-20-1.xml:938: namespace error : Namespace prefix xlink for href on media is not defined in /home/virtual/kjcn/journal/journal/include.viewer.php on line 76
Warning: simplexml_load_file(): <media mimetype="application" mime-subtype="pdf" xlink:href="kjcn-20-1-s001.pdf" in /home/virtual/kjcn/journal/journal/include.viewer.php on line 76
Warning: simplexml_load_file(): ^ in /home/virtual/kjcn/journal/journal/include.viewer.php on line 76
Warning: simplexml_load_file(): /home/virtual/kjcn/journal/../xmls/kjcn-20-1.xml:945: namespace error : Namespace prefix xlink for href on media is not defined in /home/virtual/kjcn/journal/journal/include.viewer.php on line 76
Warning: simplexml_load_file(): <media mimetype="application" mime-subtype="pdf" xlink:href="kjcn-20-1-s002.pdf" in /home/virtual/kjcn/journal/journal/include.viewer.php on line 76
Warning: simplexml_load_file(): ^ in /home/virtual/kjcn/journal/journal/include.viewer.php on line 76
Demographic characteristic of the study participants (N=1051)
1) Mean±SD (Range)
Exploratory factor analysis of eating behavior test for the early childhood (N=320)
1) Refer to Supplement 1
Exploratory factor analysis of eating behavior test for mothers (N=320)
1) Refer to Supplement 2
Internal consistency of eating behavior test for early childhood (N=731)
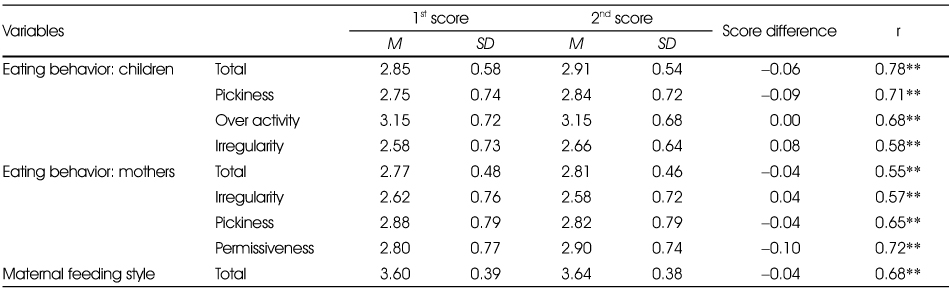
Test-retest reliability of eating behavior test (N=113)
**: p < 0.01
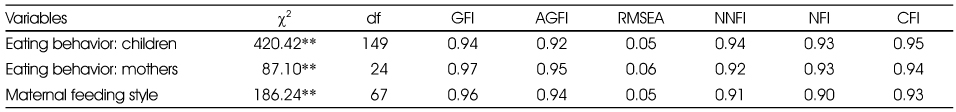
Goodness of fit measures of eating behavior test (N=731)
**: p < 0.01
1) Mean±SD (Range)
1) Refer to Supplement 1
1) Refer to Supplement 2
**:
**:

 KSCN
KSCN
 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite


