Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Korean J Community Nutr > Volume 23(2); 2018 > Article
-
Research Article
- Effects of an Intensive Management Program for Diabetic Patients on a Blood Biochemical Profile and Diabetes Knowledge
-
Su-Jeong Yeo, Bok-Hee Kim

-
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition 2018;23(2):148-161.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.2.148
Published online: April 30, 2018
1Department of Nutrition Services, Chosun University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
2Department of Food & Nutrition, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Bok-Hee Kim. Department of Food and Nutrition, Chosun University, 309 Pilmun-daero, Dong-gu, Gwangju 61452, Korea. Tel: (062) 230-7721, Fax: (062) 225-7726, kimbh@chosun.ac.kr
Copyright © 2018 The Korean Society of Community Nutrition
This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 502 Views
- 1 Download
- 4 Crossref
Abstract
-
Objectives
- This study examined the effects of nutrition education and exercise therapies on the hematological status and diabetes knowledge of diabetic patients. For this purpose, a 12-week intensive management program was provided to diabetic patients participating in an exercise program in S health subcenter in Kwangju city and the effects were analyzed.
-
Methods
- The subjects were 26 diabetic patients, who provided written informed consent. As a preliminary survey, this study examined the general characteristics, physical status, obesity, blood pressure, hematological status, daily activity level, diabetes knowledge, diet performance, and barriers to diet therapy. After the 12-week intensive management program was completed, a post-test was conducted in the same way as the preliminary test. The data were analyzed with using SPSS 18.0. The data from this study are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. A paired t-test was conducted to compare differences in the means before and after the program. Statistical significance was set to p<0.05.
-
Results
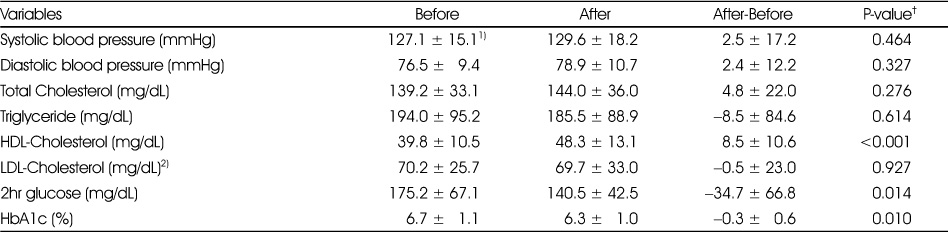
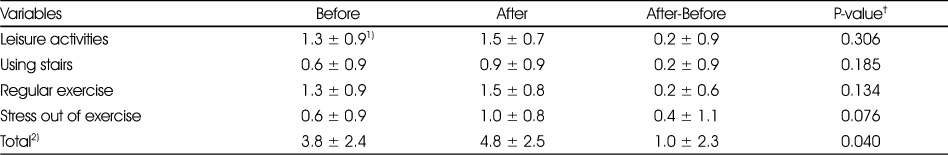
- The results of the program are presented as follows. The HDL-cholesterol levels changed from 39.8 ± 10.5 mg/dL to 48.3 ± 13.1 mg/dL, showing a significant increase (p<0.001). The blood sugar 2 hours after a meal changed from 175.2 ± 67.1 mg/dL to 140.5 ± 42.5 mg/dL, showing a significant decrease (p=0.014). The glycosylated hemoglobin levels decreased significantly from 6.7 ± 1.1% to 6.3 ± 1.0% (p=0.010). The total scores of the daily activity levels increased significantly from 3.8 ± 2.4 to 4.8 ± 2.5 (p=0.040). The scores of knowledge on diabetes increased from 11.5 ± 3.6 to 14.0 ± 3.8 (p=0.001). The scores of knowledge on diet therapy changed from 6.7 ± 2.2 to 7.9 ± 1.7, showing a significant increase (p=0.027).
-
Conclusions
- The 12-week intensive management program intervened by nutrition education and exercise therapies induced positive changes to the HDL-cholesterol, blood sugar 2 hours after a meal, glycosylated hemoglobin, daily activity levels, and knowledge on diabetes.
- 1. Cho KO. A comparative study assessing metabolic profile and diet quality in college women according to their mother's diabetes mellitus. J Korean Diet Assoc 2009; 15(1): 1-9.
- 2. Park YS, Lee JW, Seo JS, Lee BK, Lee SH. Nutrition education and counseling. 3th ed. Paju: Kyomunsa; 2011. p. 4-374.
- 3. International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas Eighth Edition 2017 [internet]. 2017; Available from: http://www.diabetesatlas.org/across-the-globe.html.
- 4. Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes fact sheet. Seoul: Korean Diabetes Association; 2016.
- 5. Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service, National Health Insurance Service. 2016 National Health Insurance Statistical Yearbook 2017 [internet]. 2017; cited 2017 October 17]. Available from: http://www.hira.or.kr/bbsDummy.do?pgmid=HIRAA020045010000&brdScnBltNo=4&brdBltNo=2293&pageIndex=1#none.
- 6. Tuomilehto J, Lindstrom J, Eriksson JG, Valle TT, Hamalainen H, Ilanne-Parikka P. Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med 2001; 344(18): 1343-1350.Article
- 7. Boule NG, Haddad E, Kenny GP, Wells GA, Sigal RJ. Effects of exercise on glycemic control and body mass in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of controlled clinical trial. JAMA 2001; 286(10): 1218-1227.Article
- 8. Song MS, Song KH, Ko SH, Ahn YB, Kim JS, Shin JH. The long-term effect of a structured diabetes program for uncontrolled type 2 diabetes mellitus patients - a 4-year follow-up. J Korean Diabetes Assoc 2005; 29(2): 140-150.
- 9. Lee JY, Kim CB. Direction of community health promotion in Korea. Korean J Health Promot 2000; 2(1): 3-12.
- 10. Kim SY, Kim SB. Effects of nutrition education at a community health center on overweight and obese middle-aged women in Jeonbuk area: Focused on personalized daily energy requirement and food exchange units. Korean J Community Nutr 2017; 22(4): 307-322.ArticlePDF
- 11. Kim MJ, Kwon SJ, Lee SY. Effects of low glycemic index nutrition education on the blood glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Korean J Nutr 2010; 43(1): 46-56.Article
- 12. Kang HJ, Sin EM, Kim KW. Evaluation of nutrition education for diabetes mellitus management of older adults. Korean J Community Nutr 2009; 14(6): 734-745.
- 13. Kim TY, Um SH, Kim WY, Chang NS. Group lunch visits are public health center improve glycemic control in older adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Korean J Nutr 2004; 37(4): 302-309.
- 14. Oh JY, Kim SB. Development and effects' analysis of nutrition education program for diabetes mellitus at community health center: Focused on individual daily energy requirements and food exchange units. Korean J Community Nutr 2010; 15(4): 485-497.
- 15. Lee YA, Kim KN, Chang NS. The effect of nutrition education on weight control and diet quality in middle-aged women. Korean J Nutr 2008; 41(1): 54-64.
- 16. Yim KS, Min YH, Lee TY. Evaluation of effect on nutrition counseling and nutrition education program at a public health center. J Korean Diet Assoc 1997; 3(2): 192-210.
- 17. Meloche J. Cooking with class: participation soars with hands-on learning and take-aways. J Nutr Educ Behav 2003; 35(2): 107-108.Article
- 18. Korean Diabetes Association. 2015 Treatment guideline for diabetes. Seoul: Korean Diabetes Association; 2015. p. 2-147.
- 19. Kim TY, Um SH, Kim WH, Chang NS. Group lunch visits at the public health center improve glycemic control in older adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Korean J Nutr 2004; 37(4): 302-309.
- 20. An SY. Effect of intensive health management program on knowledge, self-care behaviors and glycemic control in diabetic patients [master's thesis]. Chungju National University; 2011.
- 21. Norris SL, Lau J, Smith SJ, Schmid CH, Engelgau MM. Self-management education for adults with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of the effect on glycemic control. Diabetes Care 2002; 25(7): 1159-1171.
- 22. Korean Diabetes Association. Glycosiatrics. 3th ed. Seoul: Golyeouihag; 2005. p. 189-190.
- 23. Kim TY. Group lunch visits at the public health center improve glycemic control in older adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus [master's thesis]. Ewha Womans University; 2003.
- 24. Shim WS, Hong SB, Choi YS, Choi YJ, Ahn SH, Min KY. Development of two parallel diabetes knowledge tests. J Korean Diabetes Assoc 2006; 30(6): 476-486.Article
- 25. Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes diet selection screening (beginner) [internet]. Korean Diabetes Association; 2014; cited 2014 April 18]. Available from: http://www.diabetes.or.kr/pro/news/index.php?code=board&mode=view&number=1040.
- 26. Kwon YW. Development and validation of an evaluation instrument to measure diabetic patients' compliance with diet therapy [master's thesis]. Seoul National University; 2009.
- 27. Park Y, Park HH, Ryu SY. Factors associated with active participation in health promotion programs at a public health center. J Agric Med Community Health 2010; 35(3): 287-300.Article
- 28. Son SM, Kim HJ. Effect of 12-week low calorie diet and behavior modification on the anthropomeric indices and biochemical nutritional status of obese women. Korean J Community Nutr 2005; 10(4): 525-535.
- 29. Shin EY, Kim CH, Yoo WS, Kim HG, Kim CY. The effect of case management program for diabetic patients in Korean community. J Korean Community Nurs 2003; 14(4): 559-567.
- 30. Koproski J, Pretto Z, Poretsky L. Effect of an intervention by a diabetes team in hospitalized patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care 1997; 20(10): 1553-1555.
- 31. Engelgau MM, Thompson TJ, Herman WH, Boyle JP, Aubert RE, Kenny SJ. Comparison of fasting and 2-hour glucose and HbA1c levels for diagnosing diabetes: diagnostic criteria and performance revisited. Diabetes Care 1997; 20(5): 785-791.ArticlePDF
- 32. Lowe LP, Liu K, Greenland P, Metzger BE, Dyer AR, Stamler J. Diabetes, asymptomatic hyperglycemia, and 22-year mortality in black and white men: the Chicago Heart Association Detection Project in Industry Study. Diabetes Care 1997; 20(2): 163-169.ArticlePDF
- 33. Hanefeld M, Fischer S, Julius U, Schulze J, Schwanebeck U, Schnechel H. Risk factors for myocardial infarction and death in newly detected NIDDM: the Diabetes Intervention Study, 11-year follow-up. Diabetologia 1996; 39(12): 1577-1583.ArticlePDF
- 34. Kim JH, Chang SA. Effect of diabetes education program on glycemic control and self management for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Korean Diabetes J 2009; 33(6): 518-525.Article
- 35. Koev DJ, Tankova TI, Kozlovski PG. Effect of structured group education on glycemic control and hypoglycemia in insulin-treated patient. Diabetes Care 2003; 26(1): 251.
- 36. Moon SJ, Shon CY, Kim JH, Kim HS, Lim HS, Lee HC. Measurement of nutrition counseling effects for diabetes mellitus patients. Korean J Nutr 1994; 27(10): 1070-1077.
- 37. Kim MJ, Kwon SJ, Ly SY. Effect of low glycemic index nutrition education on the blood glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Korean J Nutr 2010; 43(1): 46-56.
- 38. Lee MR, Song MS. Long term effects of a self-care education program promoting self-efficacy for elderly people with diabetes. J Korean Gerontol Nurs 2003; 5(1): 91-101.
- 39. Howe CJ, Jaward AF, Tuttle AK, Moser JT, Peris C, Buzby M. Education and telephone case management for children with type 1 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. J Pediatr Nurs 2005; 20(2): 83-95.
- 40. Kang HJ, Shin EM, Kim KW. Evaluation of nutrition education for diabetes mellitus management of older adults. Korean J Community Nutr 2009; 14(6): 734-745.
- 41. Yang SO, Ahn SY, Yim ES, Kwon MS. The effects of customized home visiting health service in Gangwon-do: Focused on hypertension and DM clients. J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs 2008; 19(1): 88-100.
- 42. Seo HJ, Jung MS, Park GH. Diabetic knowledge, perceived stress, response patterns of health locus of control and sick-role behavior compliance in diabetic patients. J Kyungpook Nurs Sci 2003; 7(2): 1-18.
- 43. Kim YS, Seung JJ, Kim DM, Kim SB, Yoo HJ. A study on the evaluation of diet-education program of diabetes. Diabetes Metab J 1986; 10(2): 191-195.
- 44. Olson JC, Sims LS. Assessing nutrition knowledge from an information processing perspective. J Nutr Educ 1980; 12(3): 157-161.
- 45. Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes fact sheet. Seoul: Korean Diabetes Association; 2013.
- 46. McCulloch DK, Mitchell RD, Ambler J, Tattersall RB. Influence of imaginative teaching of diet on compliance and metabolic in insulin dependent diabetes. Br Med J 1983; 287(6408): 1858-1861.
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Impact of a public health center nutrition education program on patients with type 2 diabetes in a primary care-based chronic disease management project: a pilot intervention study
Haerim Yang, Yoo Kyoung Park, Ji-hyun Lee, Hee-Sook Lim, Heejoon Baek, Hyejin Lee, Haeran Park, Pyunghwa Lee, Jooyoun Chung, Won Gyoung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 492. CrossRef - The Associated Factors of Medical Treatment in Diabetic Patients
Sun Ju Choi, So Yeon Ryu, Jong Park, Seong Woo Choi
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2021; 46(3): 302. CrossRef - Association between diabetes mellitus and anemia among Korean adults according to sex: a cross-sectional analysis of data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2010–2016)
Mihye Kim, Sook-Hyun Lee, Kyoung Sun Park, Eun-Jung Kim, Sujung Yeo, In-Hyuk Ha
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Nutrition Counseling by Nutrition Care Process on Diet Therapy Practice and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Tae-Jeong Bae, Na-Eun Jeon, Soo-Kyong Choi, Jung-Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(3): 214. CrossRef
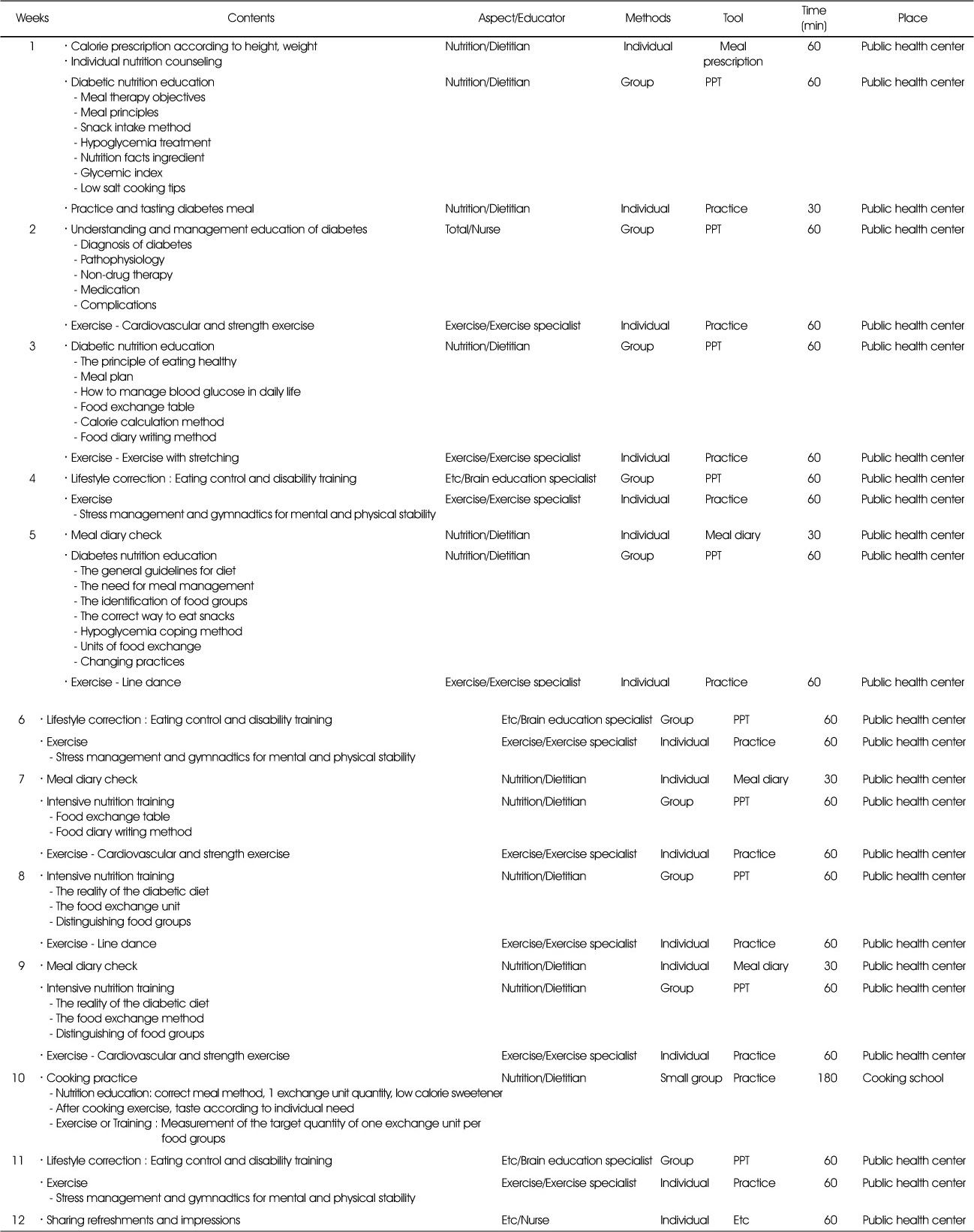
Contents of intensive management program
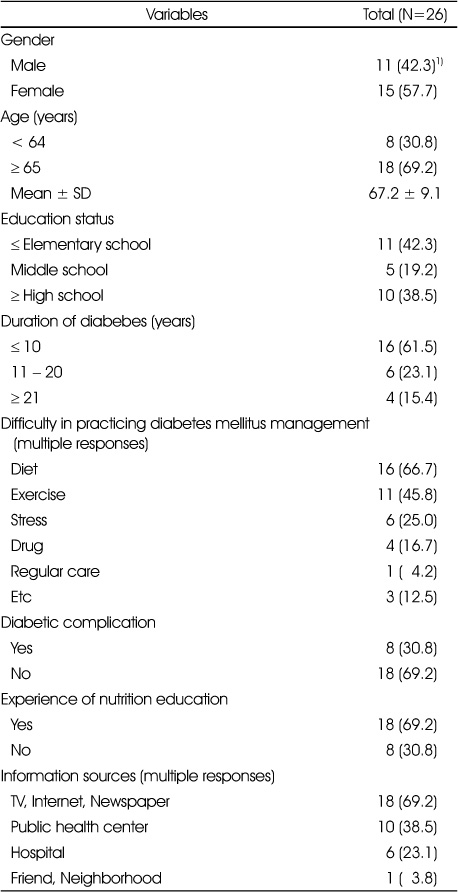
General characteristics of subjects
1) N (%)
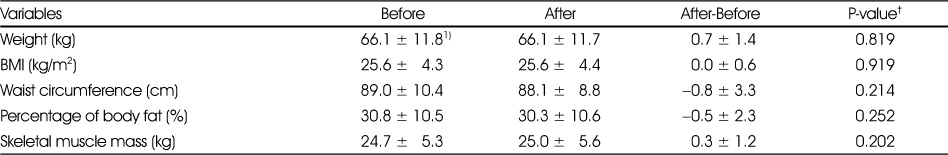
Changes in anthropometric characteristics by intensive management program
†: Tested by paired t-test
1) Mean ± SD
Changes in blood pressure and biochemical characteristics by intensive management program
†: Tested by paired t-test
1) Mean ± SD
2) Sample size: 18
Effect of intensive management program on daily activity
†: Tested by paired t-test
1) Mean ± SD
2) Total(Maximum) score was 8 score
Effect of intensive management program on knowledge of diabetes and diet therapy
†: Tested by paired t-test
1) Mean ± SD
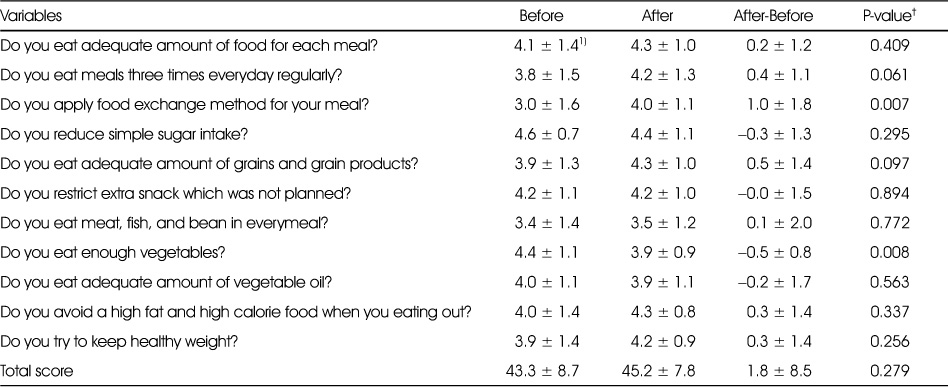
Effect of intensive management program on meal behavior
†: Tested by paired t-test
1) Mean ± SD
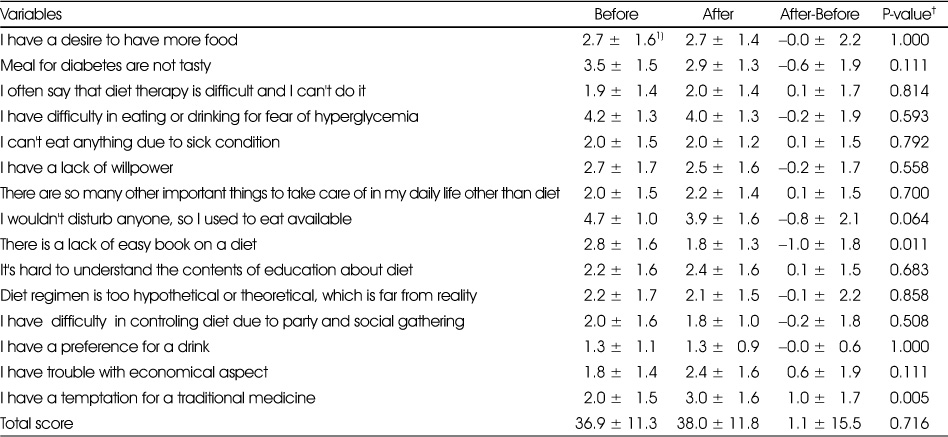
Effect of intensive management program on barriers of meals
†: Tested by paired t-test
1) Mean ± SD
1) N (%)
†: Tested by paired t-test 1) Mean ± SD
†: Tested by paired t-test 1) Mean ± SD 2) Sample size: 18
†: Tested by paired t-test 1) Mean ± SD 2) Total(Maximum) score was 8 score
†: Tested by paired t-test 1) Mean ± SD
†: Tested by paired t-test 1) Mean ± SD
†: Tested by paired t-test 1) Mean ± SD

 KSCN
KSCN

 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite


