Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Article
- [Korean]
- Maternal home meal replacement use and attitudes, and young children’s preferences by usage frequency in meals for young children: a cross-sectional study
- Bo-Yeon Kim, Mi-Hyun Kim, Jee-Young Yeon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):163-172. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00066
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
With the increase in women’s workforce participation and changing family eating habits, home meal replacements (HMRs) have become more prevalent. However, research on how mothers incorporate HMR into meals of young children remains limited. This study examined mothers’ attitudes toward and use of HMR, as well as their association with young children’s HMR preferences.
Methods
A survey was conducted between June 1 and July 3, 2020, involving 337 mothers of 5-year-old children in Sejong, South Korea. The questionnaire assessed mothers’ perceptions of HMR, consumption patterns, and their children’s preferences for HMR.
Results
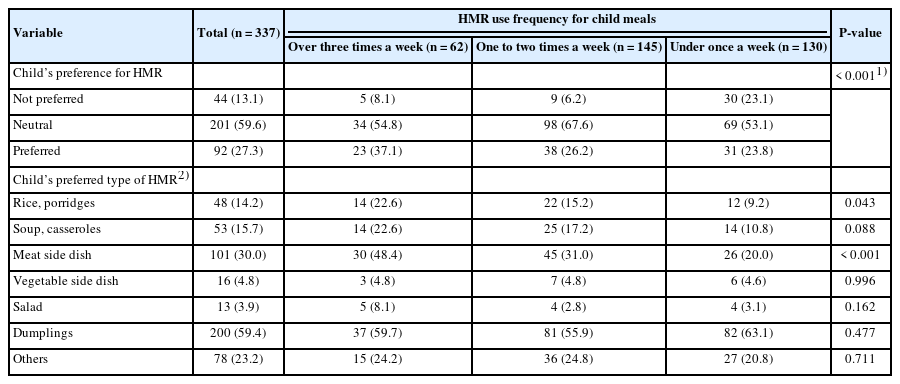
The average age of participating mothers was 38.3 years, with 93.2% living in nuclear families. Full-time homemakers constituted 40.1% of the respondents and showed lower HMR usage among them. HMR was primarily consumed as late-night snacks, side dishes, and dinners, with large discount stores (81.6%) being the primary purchase location. The high HMR consumption group exhibited more positive attitudes toward HMR (P < 0.001). HMR types varied in consumption frequency. Among ready-to-eat foods, kimbap (38.3%) was the most common, followed by meat side dishes (11.3%) and salads (11.0%). Among the heat-and-eat items, dumplings were the most frequently consumed. Simple cooking kits for Korean street food were used by 56.5% of mothers in the high-frequency HMR group, compared to 38.6% and 29.2% in the lower consumption groups (P < 0.01). Children’s preference for HMR was significantly associated with maternal HMR consumption frequency (P < 0.001). The most preferred items among children were rice porridge (P < 0.05) and meat side dishes (P < 0.001).
Conclusion
Higher maternal HMR consumption was associated with increased acceptance by children. Mothers who frequently used HMR exhibited more positive attitudes toward its palatability, convenience, nutritional value, and variety. While HMR offers diverse and tasty meal options, overreliance on processed foods warrants caution. Importantly, high HMR consumption during early childhood may influence long-term dietary behaviors, including a continued preference for HMRs.
- 1,370 View
- 34 Download

Original Articles
- [English]
- The Development and Validation of Eating Behavior Test Form for Infants and Young Children
- Youngshin Han, Su An Kim, Yoonna Lee, Jeongmee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(1):1-10. Published online February 28, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to develop and validate Eating Behaviors Test form (EBT) for infants and young children, including eating behaviors of their parents and parental feeding practices.
METHODS
Draft version of EBT form was developed after a pretest on 83 mothers. It was consisted of 42 questions including 3 components; eating behavior of children, eating behavior of parents, and parental feeding practices. Using these questionnaires, the first survey was conducted on 320 infants and children, 1 to 6 year old, for exploratory factor analysis, and the second survey was collected on 731 infants and children for confirmatory factor analysis.
RESULTS
Exploratory factor analysis on 42 questions of EBT form resulted in 3 factor model for children's eating behavior, 3 factor model for parents' eating behavior, and 1 factor model for parental feeding practices. Three factors for children's eating behavior could be explained as follows; factor 1, pickiness (reliability alpha=0.89; explanation of variance=27.79), factor 2, over activity (alpha=0.80, explanation of variance=16.51), and factor 3, irregularity (alpha=0.59, explanation of variance=10.01). Three factors for mother's eating behavior could be explained as follows; factor 1,irregularities (alpha=0.73, explanation of variance=21.73), factor 2, pickiness (alpha=0.65, explanation of variance= 20.16), and factor 3, permissiveness (alpha=0.60, explanation of variance=19.13). Confirmatory factor analysis confirmed an acceptance fit for these models. Internal consistencies for these factors were above 0.6.
CONCLUSIONS
Our results indicated that EBT form is a valid tool to measure comprehensive eating and feeding behaviors for infants and young children. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Parents' needs and perceptions of dietary and nutrition education in early childhood education institutions in South Korea: a mixed methods study
Jounghee Lee, Sookyung Choi, Minseo Kim, Seonghyun Lim, Jeong-Weon Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(6): 441. CrossRef - A study on the factors affecting the omnivorous diet of adolescents and the typology: focusing on inherited and acquired cultural capital
Hyewon Lee, Rando Kim
Journal of Families and Better Life.2024; 42(1): 81. CrossRef - Assessment of Dietary Characteristics and Eating Behavior in Children Using a Dietary Screening Test
Sun-Im Won
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(6): 557. CrossRef - Associations between maternal comprehensive feeding practices and dietary practices in preschool children
Myeongil Cho, Seunghee Kye
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(1): 141. CrossRef - The effect of the mother's modeling and feeding practices on the eating behavior of young children
Hyeonmi Sim, Youngshin Han, Kyung A Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(2): 296. CrossRef - The influence of parental eating behaviors, child-feeding practices, and infants’ temperaments upon infants’ eating behaviors
Goh Woon Lim, Kyoung Min Shin
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics.2022; 65(9): 466. CrossRef - The status of food allergy and parental burden of preschoolers in Jeju area
Jeong Eun Oh, Eunyoung Kim, Yunkyoung Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(6): 664. CrossRef - MAMAS: Supporting Parent--Child Mealtime Interactions Using Automated Tracking and Speech Recognition
Eunkyung Jo, Hyeonseok Bang, Myeonghan Ryu, Eun Jee Sung, Sungmook Leem, Hwajung Hong
Proceedings of the ACM on Human-Computer Interaction.2020; 4(CSCW1): 1. CrossRef - Analysis of the types of eating behavior affecting the nutrition of preschool children: using the Dietary Behavior Test (DBT) and the Nutrition Quotient (NQ)
Hyeon Mi Sim, Youngshin Han, Kyung A Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(6): 604. CrossRef - The Infant and Child Growth Assistance System Based on a Smartphone
Ki-Won Byun, Joon-Gyu Kang
Journal of the Korea Society of Computer and Information.2016; 21(8): 95. CrossRef - Evaluation of a Nutrition Education Program Designed to Reduce Sugar Intake in Preschool Children
Ma-Young Yeom, Youn-Ok Cho
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2016; 22(3): 179. CrossRef - The Development of Sugar Intake Reduction Test for Young Children
Nam-Hee Kim, Jee-Young Yeon, Mi-Hyun Kim
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(5): 818. CrossRef
- Parents' needs and perceptions of dietary and nutrition education in early childhood education institutions in South Korea: a mixed methods study
- 1,373 View
- 5 Download
- 12 Crossref

- [English]
- Recommended Dietary Allowances for Young Children and Food Guideline for Preschool Children in Sweden
- Eun Sook Park, Young Hwan Yee, Jin Sook Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2004;9(6):742-752. Published online December 31, 2004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study is to offer information related to recommended dietary allowances for young children and food guidelines for preschool children in Sweden. Sweden, located in Europe, is the most developed country for young child care system. Swedish nutrition policy background, Swedish recommended dietary allowances for young children, and food guidelines of early childhood education center in Sweden were used. The number of Swedish child care centers increased from 70,000 in 1970 to 700,000 in 2000. The Swedish Institute of Public Health promoted children's indoor and outdoor activity. The aim of the Swedish public health contains children's safety, good food habits, and eating food safely. Swedish Food Administration made recommended dietary allowance and food guidelines for children care centers. The aim of food guidelines was to increase energy, calcium, iron, and dietary fiber intake. Swedish RDA contains minimum and maximum intake as well as mean intake for macro and micro nutrients. The fat intake ratio of energy is increased for younger children. For preschool children, the food guideline is determined by dietary allowances for breakfast, lunch, and snack respectively. Food guideline contains meal time schedule, menu for each meal using food model, amount of food for age group, and recommended dietary allowance for each meal. It is recommended for Korean early childhood education center: 1) Korean RDA for young children should be made range of intake, minimum and maximum intake. 2) Food guideline should be make for Korean child care center. 3) Korean child care centers should offer an afternoon snack twice for children who retun home late. 4) Nutrition education program for preschool teachers should be developed for children's good eating habits and health promotion.
- 402 View
- 3 Download

- [English]
- Study on the Establishment of Nutrient Requirements for Commercial Supplementary Foods for Infants and Young Children
- Dong Yeon Kim, Kyung Hee Kim, Haymie Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 1997;2(4):624-632. Published online October 31, 1997
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to evaluated the nutrition quality of the commercial supplementary foods for infants and young children and to seek a solution to the establishment of standards of nutrient requirements for supplementary foods in Korea. Information on food ingredients, nutrient contents, claims about usefulness of food components and instructions for feeding preparation were obtained from the labels of 33 commercial supplementary foods manufactured by 4 different domestic companies. According to the standard of supplementary foods for infants and young children described in the Korean Food Code, the commercial supplementary foods were categorized into two different types, weaning food and baby food. All the commercial weaning foods were in powder form and mainly composed of cereals, whereas all the baby foods were mainly composed of fruits in the form of canned juice. The weaning foods contained more nutrients than the baby foods did, and the nutrient levels of the weaning foods expressed as nutrient density on energy basis were higher than the RDA for infants aged 5 to 11 months, suggesting that the commercial weaning foods provide adequate amounts of nutrients. If one followed the instructions for feeding preparation appearing on the label, however, recommended amounts of intake of the weaning foods would provide too much energy as well as nutrients. There were many differences in nutrient standards of weaning foods between the Korean Food Code and Codex international food standard. In conclusion, the establishment of standards for nutrient requirements for the supplementary foods requires significant scientific studies on what nutrients are the most inadequate in Korean infants and young children feeds and what levels of nutrients should be added to the foods in order to supplement their nutrition. In addition, it is very important to have a strong scientific basis to support our standard when discrepancies exist between our standard and the international standard.
- 416 View
- 2 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



