Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Korean J Community Nutr > Volume 18(5); 2013 > Article
-
Original Article
- Evaluation of the Quality Attribute and Satisfaction on School Foodservice in 2010
- Il-Sun Yang, Bo-Sook Yi, Moon-Kyung Park, Seung-Hee Baek, Yoo-Sun Chung, Jin-Yi Jeong, Yoon-Ji Kim, Hye-Young Kim
-
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition 2013;18(5):491-504.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.5.491
Published online: October 31, 2013
Department of Food & Nutrition, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
1Department of Foodservice Industry, Hanyang Woman's University, Seoul, Korea.
2Department of Food & Nutrition, Shingu University, Kyeonggi, Korea.
3Research Center for Food, Nutrition and Foodservice Management, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Hye-Young Kim, Research Center for Food, Nutrition and Foodservice Management, Yonsei University, 50 Yonsei-ro, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul 120-749, Korea. Tel: (02) 2123-4276, Fax: (02) 363-3430, tilooc@chol.com
Copyright © 2013 The Korean Society of Community Nutrition
This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 1,425 Views
- 3 Download
- 14 Crossref
Abstract
- The purposes of this study were to analyze the quality attributes, quality factors and customer satisfaction in school foodservice and to provide suggestions for improving school foodservice environments. The survey was distributed to different respondents (5,771 students, 2,045 parents, and 1,981 faculty members) at different types of schools (elementary school, middle school, and high school) on September 2010 in 16 cities and provinces. The data were analyzed using SPSS for descriptive analysis, one-way ANOVA, t-test and multiple linear regression analysis. First, all foodservice quality attributes were significant different by respondents and the faculty had higher scores than parents and students. A comparison of scores by respondents and distribution place demonstrated that classroom of student and parents had a higher score for quality attributes. The overall satisfaction with school foodservice was significant different by respondents and higher for classroom than for dining hall for student and parents. In comparison of annual data, there was decreased overall satisfaction and quality attributes in student and parents. Second, in the regression results, which showed the effects of the foodservice quality attributes on overall satisfaction by respondents and distribution place, improvements of 'food taste', 'pleasant foodservice environment', and 'kindness of employee' would increase satisfaction in most of the respondents. Third, the overall satisfaction with school foodservice was higher for nutrition teachers than dietitians for students and faculty. Therefore, the operators will need to make different efforts based on each customer needs to improve the overall satisfaction on school foodservice.
- 1. Choo YJ, Ryu SH, Yoon JH. Dietitian's job satisfaction and perception of foodservice quality in elementary schools. Korean J Nutr 2006; 39(2): 192-200.
- 2. Jang HR, Kim HYL. Survey on the satisfaction degree for school lunch program of elementary school students in Yongin. Korean J Food Nutr 2005a; 18(2): 155-160.
- 3. Jang MR, Kim JY. Comparison of importance and performance to the school lunch service according of male and female middle school students in the Gangwon province. J Korean Diet Assoc 2005b; 11(1): 95-104.
- 4. Kim KA, Kim SJ, Jung LH, Jeon ER. Degree of satisfaction on the school foodservice among the middle school students in Gwangju and Chonnam area. Korean J Soc Food Cookery Sci 2002; 18(6): 579-585.
- 5. Yi BS. Comparative analysis of the quality attributes affecting students' satisfaction on school lunch service of middle school by year. Korean J Community Nutr 2012; 17(4): 479-493.Article
- 6. Lee HS, Jang MH. Survey of students satisfaction with school food-service programs in Gangwon province. Korean J Food Nutr 2005; 18(3): 175-191.
- 7. Lee KH, Park ES. School foodservice satisfaction and menu preferences of high school students: Focused on Iksan, Cheonbuk. Korean J Community Nutr 2010; 15(1): 108-123.
- 8. Ministry of Education, Science and Technology. Survey on satisfaction with school foodservice. 2009. p. 6-8.
- 9. Ministry of Education, Science and Technology. School meals hygiene guidelines. 2010. p. 27-41.
- 10. Mo SJ, Suh JS, Lyu ES. The evaluation of the perception of students and employees for foodservice characteristics of in high schools in the Busan area. Korean J Food Cookery Sci 2005; 21(2): 250-262.
- 11. Oh YM, Kim MH, Chung JS. The study of satisfaction, meal preference and improvement on school lunch program of middle school boys and girls in Jeonju. J Korean Diet Assoc 2006; 12(4): 358-368.
- 12. Parasuraman A, Zeothmal VA, Berry LL. SERVQUAL: A multiple-item scale for measuring consumer perceptions of service quality. J Retailing 1985; 64(1): 12-40.
- 13. Park MK, Yang IS, Yi BS, Kim YS. Analysis of the quality attributes and the customer satisfaction in school foodservice by school type and distribution place. J Korean Diet Assoc 2010; 16(2): 83-99.
- 14. Park KJ, Jang MR. Survey on satisfaction of fifth and sixth grade students from elementary school foodservice in Won-ju. J Korean Diet Assoc 2008; 14(1): 13-22.
- 15. Song HJ, Moon HK. Comparing school lunch program served at dining room with program at classroom for sanitation and contentment at one middle school. Korean J Community Nutr 2010; 15(3): 369-378.
- 16. Teas RK. Expectation, performance evaluation, and consumers' perception of quality. J Market 1993; 57(4): 18-34.
- 17. Yang IS, Park MK. Identifying the quality attributes affecting customers satisfaction of school foodservice by city and province: student, parents, and faculty. J Korean Diet Assoc 2008; 14(3): 302-318.
- 18. Yang IS, Yi BS, Cha JA, Han KS, Chae IS, Lee JM. Foodservice in institution. Paju: Kyomunsa; 2010. p. 39-40.
- 19. Yi BS, Yang IS, Park MK. Annual analysis on quality attributes and customer satisfaction in school foodservice. Korean J Nutr 2009; 42(8): 770-783.Article
- 20. Yoon J, Choo YJ, Chung SJ, Ryu SH. Satisfaction of elementary students earing school lunch; Association with level of involvement in school lunch service. Korean J Community Nutr 2005; 10(5): 668-676.
REFERENCES

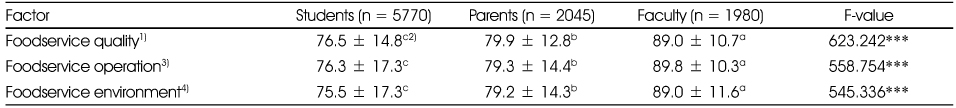
1) Foodservice quality: food taste, proper food temperature, adequate food quantity, menu variety, nutritional foods, food sanitation, quality of food ingredients
2) Mean ± SD
3) Foodservice operation: teacher's guidance on foodservice behavior, entertains suggestions offered to foodservice, providing information on foodservice
4) Foodservice environment: steady distribution, pleasant foodservice environment, kindness of employees
abc: Duncan's multiple comparison
***: p < 0.001

1) Foodservice quality: food taste, proper food temperature, adequate food quantity, menu variety, nutritional food, food sanitation, quality of food ingredients
2) Mean ± SD
3) Foodservice operation: teacher's guidance on foodservice behavior, entertains suggestions offered to foodservice, providing information on foodservice
4) Foodservice environment: steady distribution, pleasant foodservice environment, kindness of employees
** p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Acceptability of School Menus: A Systematic Review of Assessment Methods
Síntia Almeida Santana, Sueny Andrade Batista, Dayanne da Costa Maynard, Verônica Cortez Ginani, Renata Puppin Zandonadi, Raquel Braz Assunção Botelho
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(3): 2242. CrossRef - School Foodservice Employees’ Perception on Food Waste Generation and Needs to Improve Foodservice for Plate Waste Reduction in Gyeonggi Province
Kyung-Eun Lee, Jiyeon Choi
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2019; 29(5): 408. CrossRef - Development of Model for 「The Survey on School Foodservice Program」
Hae-Young Lee, Bo-Sook Yi, Jina Cha, Sun-Ok Ham, Moon-Kyung Park, Mi-Nam Lee, Hye-Young Kim, Haeng-Hwa Kang, Jin-Wook Kwon, Yun-Hui Jeong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(1): 60. CrossRef - Perception of Use of Environment-friendly Agricultural Products during School Foodservice of Mothers of Elementary School Students in Gyeonggi
Young-Un An, Myung-Hee Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi, Mi-Hyun Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(3): 234. CrossRef - Effects of students' satisfaction with school meal programs on school happiness in South Korea
Sooyoun Kwon, Oksun Kim, Youngmi Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2018; 12(4): 342. CrossRef - Improving Perception and Satisfaction on Middle and High School Foodservice: The Role of Student Participation Program in Serving School Meals
Jeong-Eun Park, Kyung-Suk Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(3): 243. CrossRef - Exploratory study on effect of eco-friendly program in high school foodservice on adolescents' dietary behavior and satisfaction with foodservice
Seyoung Ju, Deokhee Song, Hyeja Chang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(5): 494. CrossRef - Analysis of Perception and Satisfaction of Military Foodservice that are Provided According to the Ranks of the Soldiers
Jun-Hee Kim, Se-Jeong Bae
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(1): 53. CrossRef - Dietary Habits and Satisfaction of School Foodservice by High School Type in Chungnam Area
Myung-Hee Kim, Su-Mi Lim, Jee-Young Yeon
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(2): 213. CrossRef - Evaluation of Foodservice Hygiene in Middle School Students by Meal Service Area in Busan
Yeo Kyeong Kim, Hee Sun Choi, Eun Soon Lyu
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2015; 44(1): 145. CrossRef - Students’ Satisfaction of School Lunch According to the Dietary Habit and Educational Experience of Nutrition and Food
Sung Hee Park, Young Chan Choe
Family and Environment Research.2015; 53(4): 425. CrossRef - Use and Assessment of Home-Delivered Meal Service for Children from Low-Income Families
Jeong-A Moon, Chang-Hee Yoo, Kyung-Eun Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2015; 44(6): 935. CrossRef - A Study on the Foodservice Quality Factors and Satisfaction of Community Children Center
Seong Hee Ko, Kyung-Yeoun Lee
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(5): 914. CrossRef - Perception and Satisfaction of Free Foodservice in Male Middle School Students in Chungnam
Yu-Rin Kim, Eun-Jin Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2014; 20(2): 87. CrossRef


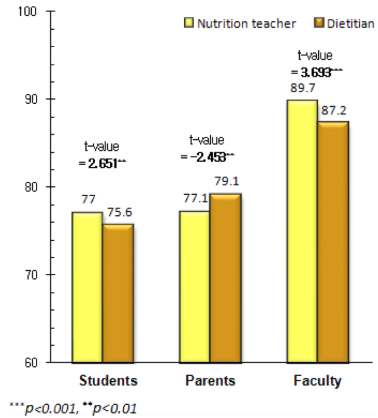
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Comparison of the quality attributes by respondents
1) Mean ± SD
abc: Duncan's multiple comparison, ***: p < 0.001
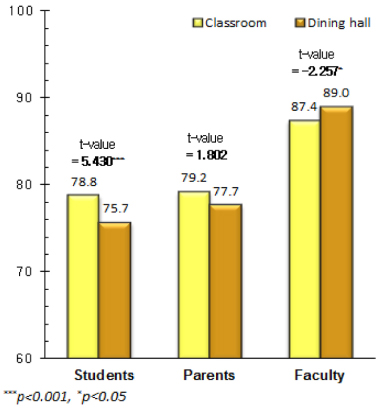
Comparison of the quality attributes by respondents and distribution place
1) Mean ± SD
*: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
Comparison of the quality factors by respondents
1) Foodservice quality: food taste, proper food temperature, adequate food quantity, menu variety, nutritional foods, food sanitation, quality of food ingredients
2) Mean ± SD
3) Foodservice operation: teacher's guidance on foodservice behavior, entertains suggestions offered to foodservice, providing information on foodservice
4) Foodservice environment: steady distribution, pleasant foodservice environment, kindness of employees
abc: Duncan's multiple comparison
***: p < 0.001
Comparison of the quality factors by respondents and distribution place
1) Foodservice quality: food taste, proper food temperature, adequate food quantity, menu variety, nutritional food, food sanitation, quality of food ingredients
2) Mean ± SD
3) Foodservice operation: teacher's guidance on foodservice behavior, entertains suggestions offered to foodservice, providing information on foodservice
4) Foodservice environment: steady distribution, pleasant foodservice environment, kindness of employees
** p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
Comparison of overall satisfaction by respondents
1) Mean ± SD
abc: Duncan's multiple comparison, ***: p < 0.001
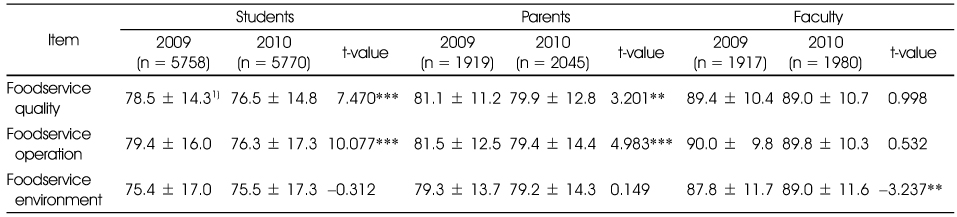
Comparison of annual quality attributes by respondents
1) Mean ± SD
*: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
Comparison of annual quality factors by respondents
1) Mean ± SD
**: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
The effect of quality attributes on students' overall satisfaction in school foodservice
Independent variable: Quality attributes, Dependent variable: Overall satisfaction
β1: Unstandardized coefficient β / β2: Standardized coefficient β
*: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
The effect of quality factors on overall satisfaction in school foodservice by distribution place
Independent variable: Quality attributes, Dependent variable: Overall satisfaction
β1: Unstandardized coefficient β / β2: Standardized coefficient β
*: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
Comparison of quality attributes by foodservice competent type: dietitians vs. nutrition teachers
1) Mean ± SD
abc: Duncan's multiple comparison
**: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
1) Mean ± SD abc: Duncan's multiple comparison, ***: p < 0.001
1) Mean ± SD *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
1) Foodservice quality: food taste, proper food temperature, adequate food quantity, menu variety, nutritional foods, food sanitation, quality of food ingredients 2) Mean ± SD 3) Foodservice operation: teacher's guidance on foodservice behavior, entertains suggestions offered to foodservice, providing information on foodservice 4) Foodservice environment: steady distribution, pleasant foodservice environment, kindness of employees abc: Duncan's multiple comparison ***: p < 0.001
1) Foodservice quality: food taste, proper food temperature, adequate food quantity, menu variety, nutritional food, food sanitation, quality of food ingredients 2) Mean ± SD 3) Foodservice operation: teacher's guidance on foodservice behavior, entertains suggestions offered to foodservice, providing information on foodservice 4) Foodservice environment: steady distribution, pleasant foodservice environment, kindness of employees ** p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
1) Mean ± SD abc: Duncan's multiple comparison, ***: p < 0.001
1) Mean ± SD *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
1) Mean ± SD **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
Independent variable: Quality attributes, Dependent variable: Overall satisfaction β1: Unstandardized coefficient β / β2: Standardized coefficient β *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
Independent variable: Quality attributes, Dependent variable: Overall satisfaction β1: Unstandardized coefficient β / β2: Standardized coefficient β *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
1) Mean ± SD abc: Duncan's multiple comparison **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001

 KSCN
KSCN








 Cite
Cite


