Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Korean J Community Nutr > Volume 17(5); 2012 > Article
-
Original Article
- Development of Nutrition Education Program for Hypertension Based on Health Belief Model, Applying Focus Group Interview
- Seoyun Park, Jong-Sook Kwon, Cho-il Kim, Yoonna Lee, Hye-Kyeong Kim
-
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition 2012;17(5):623-636.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.5.623
Published online: October 31, 2012
Department of Food Science & Nutrition, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon, Korea.
1Department of Food & Nutrition, Shingu College, Songnam, Korea.
2Nutrition Policy & Promotion Team, Korea Health Industry Development Institute, Chungbuk, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Hye-Kyeong Kim, Department of Food Science & Nutrition, The Catholic University of Korea, 43-1, Yeokgok 2-dong, Wonmi-gu, Gyeonggi-do 420-743, Korea. Tel: (02) 2164-4314, Fax: (02) 2164-4314, hkyeong@catholic.ac.kr
Copyright © 2012 The Korean Society of Community Nutrition
- 1,594 Views
- 11 Download
- 21 Crossref
Abstract
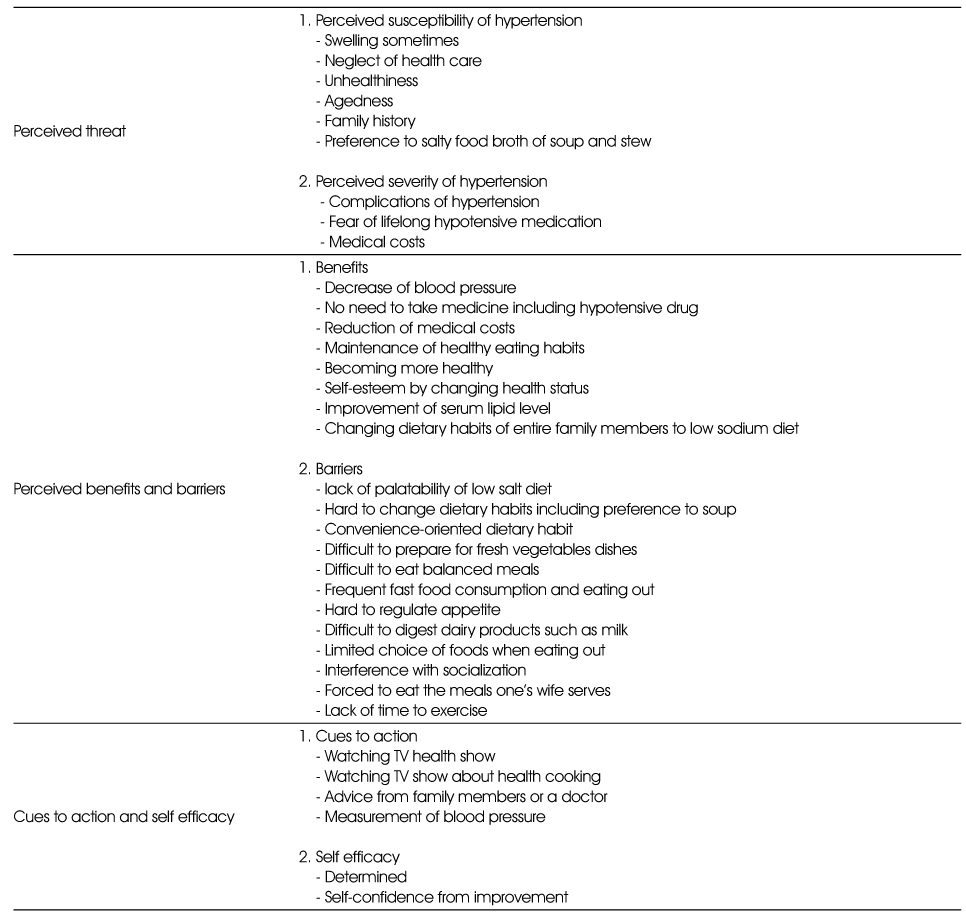
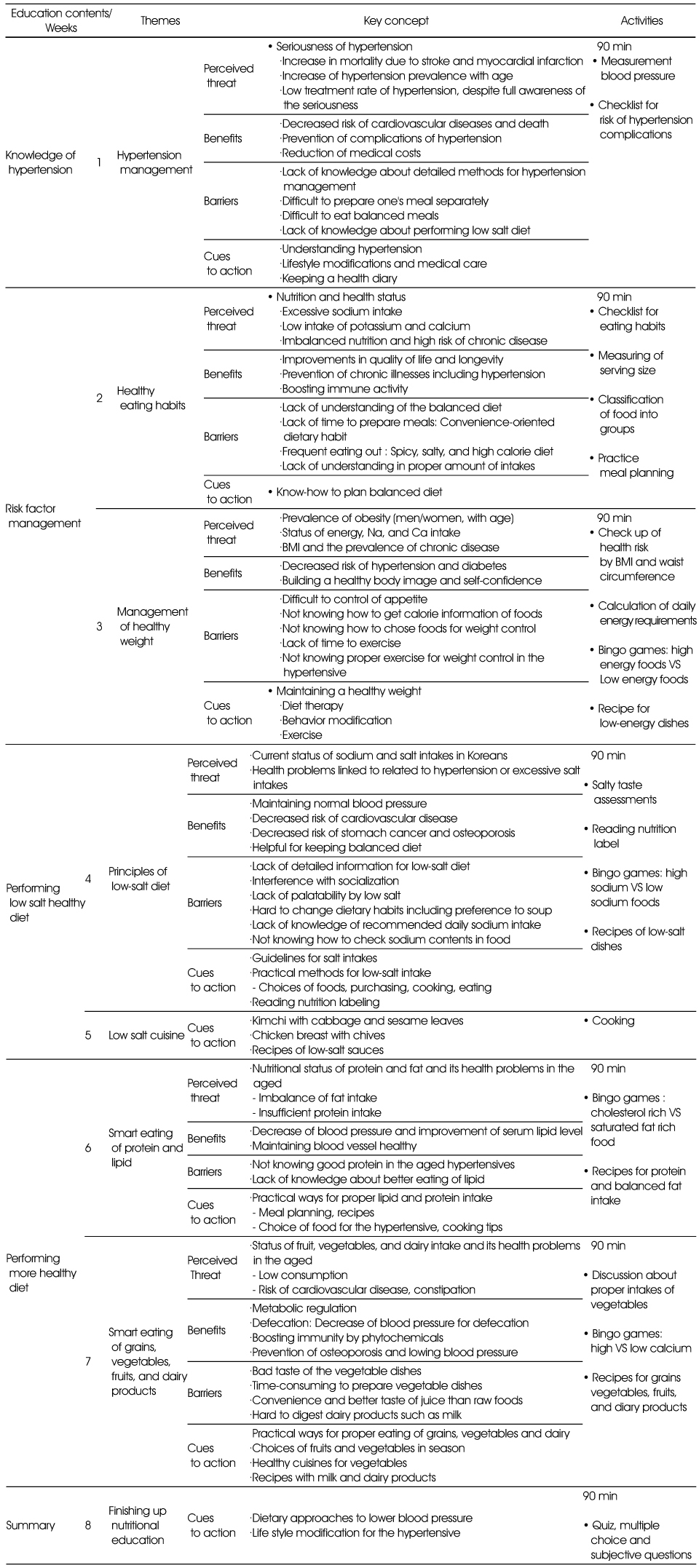
- Health Belief Model is a socio-psychological theory of decision making to individual health-related behaviors. This study was aimed to develop an effective education program for hypertension based on health belief model. The main factors of health belief model were investigated by focus group interview (FGI) with 23 hypertensive or prehypertensive subjects aged over fifty years. 'Perceived susceptibility' to hypertension was family history, neglect of health care, preference for salty food, broth of soup and stew. Lifelong medication, complications, and medical costs were reported as 'perceived severity' of hypertension. 'Perceived benefits' of hypertension management were decrease of medicinal dose, reduction of medical costs, and healthy eating habits of the family, while 'perceived barriers' were lack of palatability of low salt diet, convenience-oriented dietary habits, and limited choice of foods when eating out. Subjects mentioned TV health programs, public health center programs, and advice from doctors and family as 'cues to action' of hypertension management. These qualitative information provided basis for developing a nutrition education program for hypertension which could be implemented in the public health center. Eight week program was composed of understanding hypertension, risk factor management (eating habits, weight), low salt diet (principles, cooking), advanced management for healthy diet in 2 sessions, and summary. Each session was designed to alert the susceptibility and severity, to emphasize the benefits, and to reduce the barriers by providing dietary monitoring, practical advice, and action tips.
-
This research was supported by grants from Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI-Food-2010-97).
NOTES
- 1. Abood DA, Black DR, Diane F. Nutrition education worksite intervention for university staff: application of the health belief model. J Nutr Educ Behav. 2003; 35(5): 260-267.ArticlePubMed
- 2. American Heart Association. Blood pressure risk calculator. 2012; cited 2012 May 1. Available from http://www.heart.org.
- 3. Catholic University of Korea & Management Center for Health promotion. Integrated health promotion service in community health center. 2010; cited 2011 March 1. Available from http://research.hp.go.kr.
- 4. Choi-Kwon S, Kim JS. Lifestyle factors and risk of stroke in Seoul, South Korea. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 1998; 7(6): 414-420.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Cho SN, Lee HJ, Joo YJ, Kim NY. Qualitative research design & practice. 2011; Seoul: Green; 95-116.
- 6. Ellis J, Johnson MA, Fischer JF, Hargrove JL. Nutrition and health education intervention for whole grain foods in the georgia older Americans nutrition program. J Nutr Elder. 2005; 24(3): 67-83.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Glanz K, Rimer BK, Viswanath K. Health behavior and health education: theory, research and practice. 2008; SF: Joseey-Bass; 45-62.
- 8. Health Insurance Policy Institute. Analysis of health insurance increasing factor. 2010; cited 2011 March 1. Available from http://www.nhic.or.kr/.
- 9. He FJ, Macgregor GA. Reducing population salt intake worldwide: from evidence to implementation. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2010; 52(5): 363-382.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Huh GY. Analysis of the risk factors related to hypertension and development of FFQ and nutrition education program. 2003; The Catholic University of Korea; 120-148 Dissertation.
- 11. Inui TS, Yourtee EL, Williamson JW. Improved outcomes inhypertension after physician tutorials. Ann Intern Med. 1976; 84(6): 646-651.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Jo HS, Kim CB, Lee HW, Jeong HJ. A meta-analysis of health related behavior study based on health belief model in Korean. Korean J Health Psychol. 2004; 9(1): 69-84.
- 13. Jung EJ. The effect of salt reduction education program combined with DASH on blood pressure and salt intake of adults. 2008; Catholic University of Korea; 9-20 MS thesis.
- 14. Korea Food & Drug Administration. Reduce sugar, natrium and fat intakes. 2012; cited 2011 May 1. Available from http://www.foodnara.go.kr.
- 15. Kim MK, Han JI, Chung YJ. Dietary behavior related to salty food intake of adults living in a rural area according to saline sensitivity. Korean J Nutr. 2011; 44(6): 537-550.Article
- 16. Lee KJ, Park SH, Park KO. Health counseling. 2008; Seoul: Ewha Womans University Press; 115-122.
- 17. Ministry of Health & Welfare, Korea Centers for Disease Control & Prevention. Korea National Health & Nutrition Examination Survey. 2011; cited 2011 March 1. Available from http://knhanes.cdc.go.kr.
- 18. Moon EH, Kim KY. Evaluation of nutrition education for hypertension patients age 50 years and over. Korean J Community Nutr. 2011; 16(1): 62-74.Article
- 19. National Hypertension Center. Hypertension. 2012; cited 2012 May 1. Available from http://www.hypertension.or.kr.
- 20. Nelson EC, Stason WB, Neutra RR, Solomon HS, Mcardle PJ. Impact of patient perceptions on compliance with treatment for hypertension. Med Care. 1978; 16(11): 893-906.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Park YS, Son SM, Lim WJ, Kim SB, Chung YS. Comparison of dietary behaviors related to sodium intake by gender and age. Korean J Community Nutr. 2008; 13(1): 1-12.
- 22. Rosenstock IM. Historical origins of the health belief model. Health Educ Monogr. 1974; 2: 328-335.ArticlePDF
- 23. Salt Reduction Center. Salt down, health up. 2012; cited 2011 March 1. Available from http://www.saltdown.com.
- 24. Silverman D. Doing qualitative research. 2010; third edition. London: SAGE; 131-132. 192-199.
- 25. Son SM, Huh GY. Dietary risk factor, hypertension, urinary sodium. Korean J Community Nutr. 2006; 11(5): 661-672.
- 26. Statistics Korea. Annual report on the cause of death statistics. 2010; cited 2011 March 1. Available from http://kostat.go.kr.
- 27. Sullivan KA, White KM, Young RM, Chang A, Roos C, Scott C. Predictors of intention to reduce stroke risk among people at risk of stroke: an application of an extended health belief model. Rehabil Psychol. 2008; 53(4): 505-512.Article
- 28. The Canadian Hypertension Education Program. Hypertension Canada. 2012; cited 2011 March 1. Available from http://www.hypertension.ca.
- 29. Yim KS, Min YH, Lee TY. Evaluations of the Elderly Nutrition Improvement Program in the community health center: Effects of nutrition counseling and education program on elderly dietary behavior. J Korean Diet Assoc. 1997; 3(2): 197-210.
- 30. Yim KS. The Effects of a nutrition education program for hypertensive female elderly at the public health center. Korean J Community Nutr. 2008; 13(5): 640-652.
- 31. Yoon HS, Lee H, Lee S. Factors associated with the use of health promotion program -Seoul community health center-. Health Soc Welf Rev. 2008; 28(2): 157-184.Article
- 32. Glanz K, Rimer BK, Lewis FM. Yoo T, Yoo HR, translators. Behavior and health education: Theory, research, and practice. 2009; 3rd edition. Seoul: Koonja; 43-69.
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Educational Materials for Block Programming-Based Data Structures to Enhance Teacher Competence in Software Classes
Sook-Young Yoon, Hyun-Jong Choi, Seung-Hyun Kim
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2023; 24(4): 743. CrossRef - Dietary habits and nutrient intake status of university students according to obesity risk based on body mass index and percent body fat
Chae Hong Lee, Kyung A Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(6): 714. CrossRef - A Qualitative Study of the Awareness and Influencing Factors of the Dietary Habits of the Male and Female Workers' at a Manufacturing Facility in Gwangju
Ji Suk Yim, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(1): 12. CrossRef - Consumption of Weight-control or Health Functional Foods, Dietary Habits, and Weight Perceptions According to the Body Mass Index of Adult Women in the Chungcheong Area
Gayoung Seong, Munkyong Pae
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(2): 81. CrossRef - Comparison of low-salt preference trends and regional variations between patients with major non-communicable diseases and the general population
Eun Young Choi, Young-Kwon Park, Minsu Ock, Masaki Mogi
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(10): e0276655. CrossRef - Comparison of the health and nutritional status of Korean elderly considering the household income level, using the 2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jin Mo Khil
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(1): 39. CrossRef - Effects of Gender and Age on Dietary Intake and Body Mass Index in Hypertensive Patients: Analysis of the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination
Hyunju Dan, Jiyoung Kim, Oksoo Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(12): 4482. CrossRef - A study on the experience of mHealth based on health belief model: Focus group interview
Na Young Park, Jeong Hae Hwang, Yun-Kyoung Choi, Seong-Hi Park, Yeon Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2019; 36(3): 97. CrossRef - Association between Sodium Excretion and Obesity of Adults in Gwangju
Mijin Jo, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(1): 38. CrossRef - Effect of a public health center-based nutrition education program for hypertension in women older than 50 years of age
Seoyun Park, Jong-Sook Kwon, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(3): 228. CrossRef - Perception on Optimal Diet, Diet Problems and Factors Related to Optimal Diet Among Young Adult Women Using Focus Group Interviews: Based on Social Cognitive Theory
Hye Jin Kim, A Reum Lee, Kyung Won Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(4): 332. CrossRef - Status and Need Assessment on Nutrition & Dietary Life Education among Nutrition Teachers in Elementary, Middle and High Schools
Na Gyeong Oh, Su Jin Gwon, Kyung Won Kim, Cheong Min Sohn, Hae Ryun Park, Jung Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(2): 152. CrossRef - Evaluation of Obesity and Nutritional Status by Age among Low-income Women aged over 20 -Using Data from the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey-
Hee-Kyung Jang
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(2): 246. CrossRef - Patient and Healthcare Provider Barriers to Hypertension Awareness, Treatment and Follow Up: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Qualitative and Quantitative Studies
Rasha Khatib, Jon-David Schwalm, Salim Yusuf, R. Brian Haynes, Martin McKee, Maheer Khan, Robby Nieuwlaat, Noel Christopher Barengo
PLoS ONE.2014; 9(1): e84238. CrossRef - Development of Nutrition Education Program for Consumers to Reduce Sodium Intake Applying the Social Cognitive Theory: Based on Focus Group Interviews
So-Hyun Ahn, Hye-Kyeong Kim, Kyung Min Kim, Jin-sook Yoon, Jong Sook Kwon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(4): 342. CrossRef - Factors affecting Weight-Control Behavior Intention in Female College Students: Based on the Theory of Planned Behavior
Eun Ju Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2013; 24(2): 195. CrossRef - Comparison of practice of dietary guidelines and health beliefs according to stage of weight loss behavior change among male workers
Su Jeong Song, HongSeok Ahn, Jinmo Khil
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2013; 46(3): 276. CrossRef - A Study on the Health and Nutritional Characteristics according to Household Income and Obesity in Korean Adults Aged over 50 -Based on 2005 KNHANES-
So Hyun Ahn, Sook Mee Son, Hye Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(4): 463. CrossRef - Estimation of Sodium Intake of Adult Female by 24-Hour Urine Analysis, Dietary Records and Dish Frequency Questionnaire (DFQ 55)
Eun-Kyung Shin, Hye-Jin Lee, Jung-Jeung Lee, Moon-Young Ann, Sook-Me Son, Yeon-Kyung Lee
The Korean Journal of Nutrition.2010; 43(1): 79. CrossRef - Effects of Weight Control Program on Dietary Habits and Blood Composition in Obese Middle-Aged Women
Hye-Kyung Kim, Mi-Jeong Kim
The Korean Journal of Nutrition.2010; 43(3): 273. CrossRef - Diet Quality Index-International Score is Correlated with Weight Loss in Female College Students on a Weight Management Program
Hee Kyung Yun, Hyesook Kim, Namsoo Chang
The Korean Journal of Nutrition.2009; 42(5): 453. CrossRef
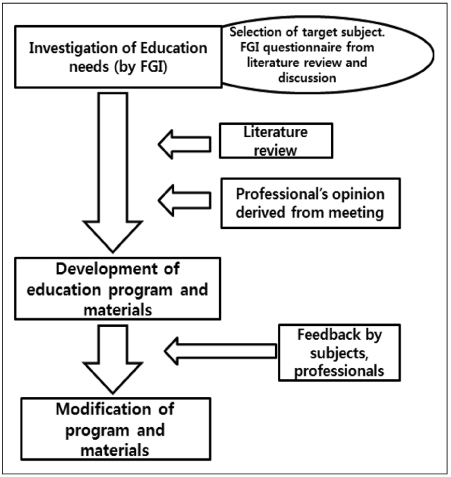

Figure 1
Figure 2
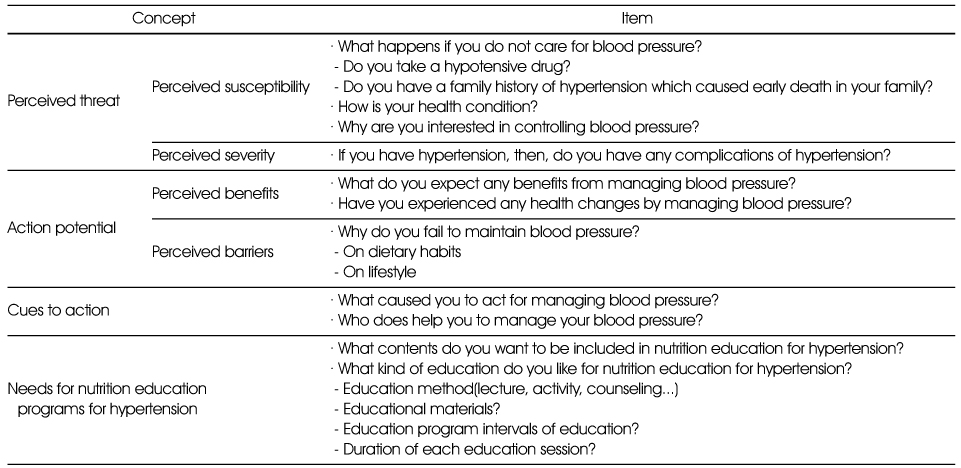
Questions used for focus group interview based on health belief model
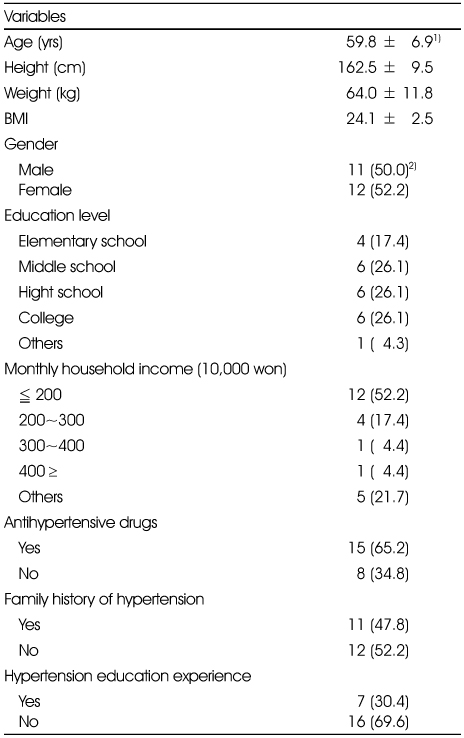
General characteristics of the subjects
1) Mean ± SD
2) N (%)
Major themes and subthemes for Health belief model in focus group interview
Major themes and subthemes for needs of nutrition education programs of hypertension
Nutrition education program for hypertension based on health belief model
1) Mean ± SD 2) N (%)

 KSCN
KSCN


 Cite
Cite


