Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Korean J Community Nutr > Volume 17(1); 2012 > Article
-
Original Article
- Beliefs Regarding Vegetable Consumption, Self-Efficacy and Eating Behaviors according to the Stages of Change in Vegetable Consumption among College Students
- Yun Ahn, Kyung Won Kim
-
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition 2012;17(1):1-13.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.1.1
Published online: February 29, 2012
Department of Food & Nutrition, Seoul Women's University, Seoul, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Kyung Won Kim, Department of Food & Nutrition, College of Natural Sciences, Seoul Women's University, 621 Hwarangro, Nowon-gu, Seoul 139-774, Korea. Tel: (02) 970-5647, Fax: (02) 976-4049, kwkim@swu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2012 The Korean Society of Community Nutrition
- 1,146 Views
- 5 Download
- 20 Crossref
Abstract
- The purpose of this study was to examine beliefs, self-efficacy and eating behaviors by the stages of change in vegetable consumption among college students (n = 297). A survey was conducted to examine study variables, and subjects were categorized into three groups based on the stages of change: precontemplation/contemplation stage (PC/C), preparation stage (P), action/maintenance stage (A/M). Subjects had 3.7 servings of vegetables a day, and vegetable consumption was significantly different by stages of change (p < 0.001). The A/M group showed higher score on beliefs regarding vegetable consumption (p < 0.001) than the other groups, and perceived benefits of vegetable consumption (e.g. cancer prevention) more strongly (p < 0.05). The PC/C group felt more barriers than the A/M group, such as disliking cooking methods, texture of vegetables (p < 0.001), bad taste and bad experience of eating vegetables (p < 0.05). Self-efficacy score was 27.2, with decreasing self-efficacy from A/M to P, PC/C (p < 0.001). The A/M group showed more confidence in nine behaviors such as "eating vegetables during meals" and "replacing menu at home with more vegetable dishes" (p < 0.001) than the other groups. The A/M group had more desirable eating behaviors (e.g, having a variety of foods, eating regularly, consumption of food groups). This study suggests that target population for education and educational strategies be different based on the stages of change. For those in the PC/C stage, education might focus on reducing barriers and increasing self-efficacy. For those in the A/M stage, it is necessary to use strategies to maintain and reinforce behaviors for enough vegetable consumption.
- 1. Ahn Y, Ko SY, Kim KW. Evaluation of a nutrition education program for elementary school children. Korean J Community Nutr. 2009; 14(3): 266-276.
- 2. Ahn YK, Ro HK. A survey on preferences for vegetable cooking methods and vegetable-aversion-related factors among elementary school students in Kwangju and Chonnam regions. Korean J Community Nutr. 2009; 14(5): 531-544.
- 3. Bandura A. Foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA. 1986.
- 4. Cho HS, Kim MH, Choi MK. A study on vegetable intakes and dietary habits of middle school students in Chungnam. Korean J Community Nutr. 2010; 15(4): 525-535.
- 5. Choi MY, Kim HY. Nutrition knowledge, dietary self-efficacy and eating habits according to student's stage of regular breakfast or exercise. Korean J Community Nutr. 2008; 13(5): 653-662.
- 6. Contento IR. Nutrition education - Linking research, theory, and practice. 2007; Sudbury, MA, USA: Jones and Barlett Publishers.
- 7. Hong HO, Lee JS. Survey on Korean food preference of college students in Seoul - focused on the staple food and snack -. Korean J Nutr. 2006; 39(7): 699-706.
- 8. Hwang JH, Lee HM. A study on lifestyles, dietary habits, nutrition knowledge and dietary behaviors of male university students according to residence type. Korean J Community Nutr. 2007; 12(4): 381-395.
- 9. Jang HB, Lee HW, Han YH, Song JH, Kim KN, Hyun TS. Changes in food and nutrient intakes of college students between 1999 and 2009. Korean J Community Nutr. 2011; 16(3): 324-336.Article
- 10. Janis IL, Mann L. Decision making-A psychological analysis of conflict, choice and commitment. 1977; New York: free press.
- 11. Kang HJ, Byun KW. Effect of two-year course of food and nutrition on improving nutrition knowledge, dietary attitudes and food habits of junior college female students. Korean J Community Nutr. 2010; 15(6): 750-759.
- 12. Kang JY, Kim SY, Lee MS, Ahn HS. Effect of vegetable juice supplementation on serum lipid profile and antioxidant activity in college women. Korean J Community Nutr. 2005; 10(2): 183-188.
- 13. Kim KH. A study of the dietary habits, the nutritional knowledge and the consumption patterns of convenience foods of university students in the Gwangju area. Korean J Community Nutr. 2003; 8(2): 181-191.
- 14. Kim KW, Ahn Y, Kim HM. Fast food consumption and related factors among university students in Daejeon. Korean J Community Nutr. 2004; 9(1): 47-57.
- 15. Ko MS. The comparison in daily intake of nutrients and dietary habits of college students in Busan. Korean J Community Nutr. 2007; 12(3): 259-271.
- 16. Korean Nutrition Society. Dietary reference intakes for Koreans. 2010; 530-535.
- 17. Ku UH, Seo JS. The status of nutrient intake and factors related to dislike of vegetables in elementary school students. Korean J Community Nutr. 2005; 10(2): 151-162.
- 18. Kwon SY, Han JI, Chung YJ. Relationship of nutritional knowledge, dietary self efficacy and change of dietary behavior of nutrition professional. Korean J Nutr. 2008; 41(6): 550-560.
- 19. Lee JS, Ha BJ. A study of the dietary attitude, dietary self-efficacy and nutrient intake among middle school students with different obesity indices in Gyeong-nam. Korean J Community Nutr. 2003; 8(2): 171-180.
- 20. Lee KA, Jeong BY, Moon SK, Kim IS, Nakamura S. Comparisons of Korean adults' eating habits, food preferences and nutrient intake by generation. Korean J Nutr. 2006; 39(5): 494-504.
- 21. Chuan Ling AM, Horwath C. Perceived benefits and barriers of increased fruit and vegetable consumption: validation of a decisional balance scale. J Nutr Educ. 2001; 33(5): 257-265.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Na SY, Ko SY, Eom SH, Kim KW. Intakes and beliefs of vegetables and fruits, self-efficacy, nutrition knowledge, eating behavior of elementary school students in Kyunggi area. Korean J Community Nutr. 2010; 15(3): 329-341.
- 23. Ministry of Health and Welfare. Korean Health Statistics 2009 - Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES -3). 2010.
- 24. Park MS, Kim SA. Effect of nutrition education on improving diet behavior of university students. Korean J Community Nutr. 2005; 10(2): 189-195.
- 25. Prochaska JO, Diclemente CC. Stage and process of self-change in smoking - Towards an integrative model of change. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1983; 51: 390-395.PubMed
- 26. Prochaska JO, Redding CA, Evers KE. In: Glanz K, Rimer BK, Viswanath K, editors. The transtheoretical model and stages of change. Health behavior and health education. 2008; 4th ed. CA: Jossey-Bass; 97-108.
- 27. Shaikh AR, Yaroch AL, Nebeling L, Yeh MC, Resnicow K. Psychosocial predictors of fruit and vegetable consumption in adults - a review of the literature. Am J Prev Med. 2008; 34(6): 535-543.PubMed
- 28. Sorensen G, Stoddard AM, Dubowitz T, Barbeau EM, Bigby J, Emmons KM, Berkman LF, Peterson KE. The influence of social context on change in fruit and vegetable consumption -results of the healthy directions studies. Am J Public Health. 2007; 97(7): 1216-1227.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 29. Suh YS, Chung YG. Comparison of mineral and vitamin intakes according to the stage of change in fruit and vegetable intake for elementary school students in Chungnam province. Korean J Nutr. 2008; 41(7): 658-666.
- 30. Suh YS, Chung YG. The effect of nutrition education on the improvement of psychosocial factors related to vegetable and fruit intake of elementary school children in pre-action stage. Korean J Nutr. 2010; 43(6): 597-606.Article
- 31. Thompson VJ, Bachman CM, Baranowski T, Cullen KW. Self-efficacy and norm measures for lunch fruit and vegetable consumption are reliable and valid among fifth grade students. J Nutr Educ Behav. 2007; 39(1): 2-7.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 32. Wolf RL, Lepore SJ, Vandergrift JL, Wetmore-Arkader L, Mcginty E, Pietrzak G, Yaroch AL. Knowledge, barriers, and stage of change as correlates of fruit and vegetable consumption among urban and mostly immigrant black men. J Am Diet Assoc. 2008; 108(8): 1315-1322.ArticlePubMedPMC
REFERENCES

N (%)
*: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by ANOVA
1) Each item was measured by 4-point scales ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 4 (strongly agree)
For items 1-7, the higher score showed the more favorable beliefs regarding eating vegetables
For items 8-20, the higher score showed the less favorable beliefs regarding eating vegetables
2) Mean ± SE
3) Different alphabets with superscripts at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple range test
4) Total score of 20 items (possible score: 20-80). To calculate the total score, the items of 8-20 were scored reversely

***: p < 0.001 by ANOVA
1) Each item was measured by 4-point scales ranging from 1 (very difficult) to 4 (very easy). The higher score showed the higher self-efficacy
2) Mean ± SE
3) Different alphabets with superscripts at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple range test
4) Total score of 10 items (possible score: 10 - 40)
N (%)
*: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by χ2-test, 1) no response: 1
2) Total score of 15 items (possible score: 15 - 45). Each item was measured by 3-point scales ranging from 1 (0 - 2days/week) to 3 (6 - 7days/week). To calculate the total score, the items from 12 to 15 were scored reversely
3) Mean ± SE, ***: p < 0.001 by ANOVA. Different alphabets with superscripts at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple range test
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Outcome expectations, self-efficacy, eating environment, and eating behaviors by the stages of change in adequate sodium intake among university students: a cross-sectional study
Yeon Gyu Im, Kyung Won Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(5): 382. CrossRef - Barriers influencing purchase behaviour of green personal care products – integrating innovation resistance theory perspective and stages of change model
Marta Szaban, Magdalena Stefańska
Economics and Environment.2023; 85(2): 420. CrossRef - Investigation of Millennials' Perception of Vegan Trends and Future Needs
Eun-Hye Song, Bok-Mi Jung
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(5): 373. CrossRef - Psychosocial factors and eating behaviors according to the stages of change in nutrition management among elementary and middle school athletes
Ji Yeon Kim, Seong Suk Cho, Kyung Won Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2021; 15(6): 732. CrossRef - Comparative Study of Eating Habits and Lifestyle by Gender among College Students in Pyeongtaek Region
Seo Hyeon Ahn, Seong Yeong Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2020; 30(2): 117. CrossRef - Dietary Life, Vitamin D Status and Blood Clinical Indices of University Laboratory Workers
Jung Hyun Hwang, Hong Mie Lee, Jung Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(3): 245. CrossRef - Factors affecting preference of vegetable in elementary school students: based on social cognitive theory
Su Hyeon Cha, Ho Kyung Ryu
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(3): 285. CrossRef - Relationship between Bone Density, Eating Habit, and Nutritional Intake in College Students
Hee-Sook Lim, Sung-In Ji, Hyeonji Hwang, Jeongmmok Kang, Yoon-Hyung Park, Hae-Hyeog Lee, Tae-Hee Kim
Journal of Bone Metabolism.2018; 25(3): 181. CrossRef - Factors affecting vegetable preference in adolescents: stages of change and social cognitive theory
Taejung Woo, Kyung-Hea Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2017; 11(4): 340. CrossRef - Coffee consumption behaviors, dietary habits, and dietary nutrient intakes according to coffee intake amount among university students
Sun-Hyo Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(3): 270. CrossRef - Gender Differences in Adolescents' Dietary Perceptions and Practices
Taejung Woo, Hye-Jin Lee, Kyoung Ae Lee, Seung Min Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(2): 165. CrossRef - Comparison of Dietary Self-efficacy, Obesity Stress, and Obesity-related Quality of Life According to BMI and Stages of Change in Vegetable Consumption for Nursing Students
Myoung Sook Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2015; 21(1): 65. CrossRef - A comparison of Dietary Habits and Influencing Factors for Vegetable Preferences of Adolescents in Gyeongnam Province
Suhyang Kwak, Taejung Woo, Kyoung Ae Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(4): 259. CrossRef - Factors associated with nutrition label use among female college students applying the theory of planned behavior
Hyun Jeong Lim, Min Ju Kim, Kyung Won Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2015; 9(1): 63. CrossRef - Nutrition knowledge, outcome expectations, self-efficacy, and eating behaviors by calcium intake level in Korean female college students
Min Ju Kim, Kyung Won Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2015; 9(5): 530. CrossRef - Nutrition knowledge, eating attitudes, nutrition behavior, self-efficacy of childcare center foodservice employees by stages of behavioral change in reducing sodium intake
Yun Ahn, Kyung Won Kim, Kyungmin Kim, Jinwon Pyun, Ikhyun Yeo, Kisun Nam
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(5): 429. CrossRef - Study on the Salt-Related Dietary Behaviors according to the Stage of Change Model for Salt-Related Intake of Middle School Students in Gyeongsangbuk-do Area
So-Young Park, Kyung-A Lee
Korean journal of food and cookery science.2014; 30(6): 687. CrossRef - Factors influencing on intention to intake fruit: moderating effect of fruit intake habit
Hyesoo Kim, Sunhee Seo
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2014; 47(2): 134. CrossRef - Comparison of practice of dietary guidelines and health beliefs according to stage of weight loss behavior change among male workers
Su Jeong Song, HongSeok Ahn, Jinmo Khil
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2013; 46(3): 276. CrossRef - Study on the Eating Habits and Practicability of Guidelines for Reducing Sodium Intake according to the Stage of Change in Housewives
So-Hyun Ahn, Jong-Sook Kwon, Kyungmin Kim, Jin-Sook Yoon, Baeg-Won Kang, Jong wook Kim, Seok Heo, Hea-Young Cho, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(6): 724. CrossRef
General characteristics of subjects
N (%)
***: p < 0.001 by t-test
1) Mean ± SE, 2) no response: 1, 3) no response: 7
Consumption of vegetables of subjects (servings/day)
*: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by ANOVA
1) Mean ± SE. Frequency of eating vegetables per day based on a serving size (Korean Nutrition Society 2010)
2) Different alphabets with superscripts at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple range test
Preference of vegetables of subjects
N (%)
1) Subjects were asked to choose five vegetables from 30 vegetable items
Beliefs regarding eating vegetables
N (%)
*: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by ANOVA
1) Each item was measured by 4-point scales ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 4 (strongly agree)
For items 1-7, the higher score showed the more favorable beliefs regarding eating vegetables
For items 8-20, the higher score showed the less favorable beliefs regarding eating vegetables
2) Mean ± SE
3) Different alphabets with superscripts at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple range test
4) Total score of 20 items (possible score: 20-80). To calculate the total score, the items of 8-20 were scored reversely
Self-efficacy regarding eating vegetables
***: p < 0.001 by ANOVA
1) Each item was measured by 4-point scales ranging from 1 (very difficult) to 4 (very easy). The higher score showed the higher self-efficacy
2) Mean ± SE
3) Different alphabets with superscripts at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple range test
4) Total score of 10 items (possible score: 10 - 40)
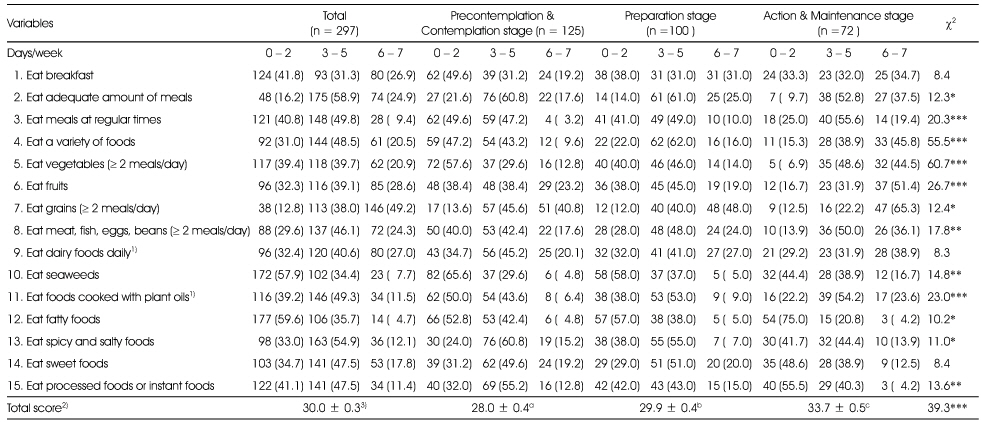
Eating behavior of subjects
N (%)
*: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by χ2-test, 1) no response: 1
2) Total score of 15 items (possible score: 15 - 45). Each item was measured by 3-point scales ranging from 1 (0 - 2days/week) to 3 (6 - 7days/week). To calculate the total score, the items from 12 to 15 were scored reversely
3) Mean ± SE, ***: p < 0.001 by ANOVA. Different alphabets with superscripts at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple range test
N (%) ***: p < 0.001 by t-test 1) Mean ± SE, 2) no response: 1, 3) no response: 7
*: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by ANOVA 1) Mean ± SE. Frequency of eating vegetables per day based on a serving size (Korean Nutrition Society 2010) 2) Different alphabets with superscripts at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple range test
N (%) 1) Subjects were asked to choose five vegetables from 30 vegetable items
N (%) *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by ANOVA 1) Each item was measured by 4-point scales ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 4 (strongly agree) For items 1-7, the higher score showed the more favorable beliefs regarding eating vegetables For items 8-20, the higher score showed the less favorable beliefs regarding eating vegetables 2) Mean ± SE 3) Different alphabets with superscripts at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple range test 4) Total score of 20 items (possible score: 20-80). To calculate the total score, the items of 8-20 were scored reversely
***: p < 0.001 by ANOVA 1) Each item was measured by 4-point scales ranging from 1 (very difficult) to 4 (very easy). The higher score showed the higher self-efficacy 2) Mean ± SE 3) Different alphabets with superscripts at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple range test 4) Total score of 10 items (possible score: 10 - 40)
N (%) *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by χ2-test, 1) no response: 1 2) Total score of 15 items (possible score: 15 - 45). Each item was measured by 3-point scales ranging from 1 (0 - 2days/week) to 3 (6 - 7days/week). To calculate the total score, the items from 12 to 15 were scored reversely 3) Mean ± SE, ***: p < 0.001 by ANOVA. Different alphabets with superscripts at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple range test

 KSCN
KSCN



 Cite
Cite


