- [English]
-
Comparison of clinical characteristics and dietary intakes according to phenotypes of type 2 diabetes mellitus in South Korea: a cross-sectional study
-
Mi-Jin Kim, Ji-Sook Park, Sung-Rae Cho, Daeung Yu, Jung-Eun Yim
-
Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):127-139. Published online April 29, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00059
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Objectives
Clinical nutrition treatment is the central part of diabetes management, such as prevention, treatment, and self-management of diabetes, and personalized clinical nutrition treatment, which enables improvement in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Our study aimed to contribute to the improvement of appropriate nutrition management in personalized treatment for obese and non-obese diabetes patients.
Methods
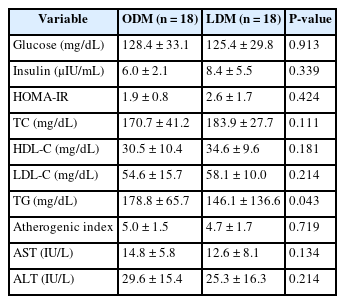
T2DM patients were recruited as participants, and 36 final participants were assigned to the lean diabetes mellitus group (LDM; body mass index [BMI] < 25 kg/m2) and the obese diabetes mellitus group (ODM; BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2). We assessed the dietary intakes, body composition, dietary habits, the Korean version of obesity-related quality of life, and biochemical indices.
Results
According to the phenotype’s comparison, the ODM group had a high prevalence of T2DM complications and hypertension, had a dietary habit of less than 10 minutes of mealtime duration and preferred fast food intake, and had a low obesity-related quality of life. However, the LDM group had a high choice of Korean dishes at the time of eating out and a high intake of vitamin C, and iodine because of the intake of vegetables and seaweeds.
Conclusion
We observed differences in diet, nutrient intake, and clinical characteristics according to the phenotype of T2DM patients. In particular, obese diabetes patients have an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, bad dietary habits, and low obesity-related quality of life. Therefore, personalized nutrition treatment is needed in consideration of the risk of cardiovascular disease and dietary habits for patients in the ODM group, as well as determining the energy requirements of Korean patients with T2DM.
- [English]
-
Serum branch chain amino acids and aromatic amino acids ratio and metabolic risks in Koreans with normal-weight or obesity: a cross-sectional study
-
Ji-Sook Park, Kainat Ahmed, Jung-Eun Yim
-
Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(3):212-221. Published online June 30, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.3.212
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Objectives
Metabolic disease is strongly associated with future insulin resistance, and its prevalence is increasing worldwide. Thus, identifying early biomarkers of metabolic-related disease based on serum profiling is useful to control future metabolic disease. Our study aimed to assess the association of serum branched chain amino acids (BCAAs) and aromatic amino acids (AAAs) ratio and metabolic disease according to body mass index (BMI) status among Korean adults.
Methods
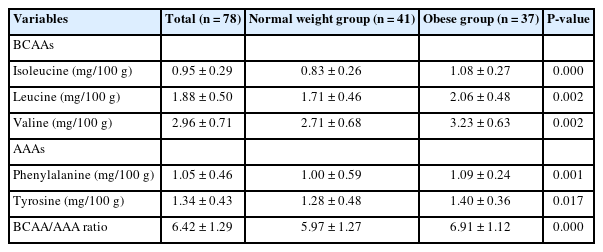
This cross-sectional study included 78 adults aged 20–59 years in Korea. We compared serum amino acid (AA) levels between adults with normal-weight and adults with obesity and investigated biomarkers of metabolic disease. We examined serum AA levels, blood profile, and body composition. We also evaluated the association between serum AAs and metabolic-related disease.
Results
The height, weight, BMI, waist circumference, hip circumference, waist-hip-ratio, body fat mass, body fat percent, skeletal muscle mass, systolic blood pressure, and diastolic blood pressure were higher in the group with obesity compared to normal weight group. The group with obesity showed significantly higher levels of BCAA, AAA, and BCAA and AAA ratio. Further, BCAA and AAA ratio were significantly positively correlated with triglyceride, body weight, and skeletal muscle mass. The evaluation of metabolic disease risks revealed an association between the ratios of BCAAs and AAAs, hypertension, and metabolic syndrome.
Conclusions
Our study is showed the associations between BCAA and AAA ratio, obesity, and obesity-related diseases using various analytical approaches. The elevated BCAA and AAA ratio could be early biomarkers for predicting future metabolic diseases in Korean population.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The Role of Aromatic Amino Acids in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome through Patients’ Blood Metabolic Profiling: A Systematic Review of the Past Five Years
Apostolos Gkantzos, Stavros Kalogiannis, Olga Deda
Journal of Proteome Research.2025; 24(5): 2208. CrossRef - Current Data on the Role of Amino Acids in the Management of Obesity in Children and Adolescents
Diana Zamosteanu, Nina Filip, Laura Mihaela Trandafir, Elena Ţarcă, Mihaela Pertea, Gabriela Bordeianu, Jana Bernic, Anne Marie Heredea, Elena Cojocaru
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(15): 7129. CrossRef
-
1,857
View
-
23
Download
-
2
Crossref
- [English]
-
Nutrition Quotient and nutrient intake among older adults in a rural Korean community: a cross-sectional study
-
Ji-Sook Park, Hyeon-Mi Bae, Jung-Eun Yim
-
Received September 25, 2025 Accepted November 6, 2025 Published online November 21, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00283
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
- Objectives
Korea is experiencing rapid population aging, with older adults forming a large proportion of rural communities. Aging leads to physiological and functional declines, resulting in lower physical activity, poor diet quality, and higher risk of chronic diseases. Although the Nutrition Quotient for the Elderly (NQ-E) is a validated tool to assess dietary quality, few studies have applied it to rural populations. This study aimed to compare nutrient intake and NQ-E scores by age and sex and examine their associations with lifestyle factors.
Methods
This study investigated the relationship between nutrient intake and NQ-E scores among older adults in rural Korean community, considering age, sex, and lifestyle factors. A cross-sectional study was conducted with 79 community-dwelling older adults (24 male and 55 female; mean age: 76.3 years) residing in Geochang-gun, Gyeongsangnam-do, Korea. Participants were recruited from community centers and health posts between June 2024 and December 2024. Data collection included general characteristics, 24-hour dietary recalls, and NQ-E questionnaires.
Results
Female aged > 75 years had significantly lower intakes of energy, protein, fat, vitamin E, riboflavin, folate, and zinc than their male counterparts (P < 0.05). The mean NQ-E score was 55.01, which was lower than the national average reported for urban older adults (57.6). Participants with higher NQ-E grades had significantly higher intakes of dietary fiber, vitamin A, thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, potassium, and magnesium, and regular physical activity and dietary supplement use were positively associated with higher NQ-E grades (P < 0.01).
Conclusion
These findings suggest that older female in rural communities are particularly vulnerable to inadequate nutrient intake and lower dietary quality, and that the NQ-E is a useful screening tool for identifying nutritional risk in this population. Community-based nutrition interventions promoting physical activity, supplement use, and dietary diversity are warranted to improve dietary quality and support healthy aging.
|