- [Korean]
-
Application of a living lab model to an evidence-based reduced-sodium healthy eating practice program in Korea: a pre-post study
-
Jung-Hyun Kim, Eugene Shim, Min Sook Kyung, Sooyoun Kwon, Hyoung Su Park, Jae-Heon Kang
-
Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):53-63. Published online February 28, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00346
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Objectives
To apply a healthy dietary program with reduced sodium intake, developed using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), focusing on the sodium intake level and eating patterns.
Methods
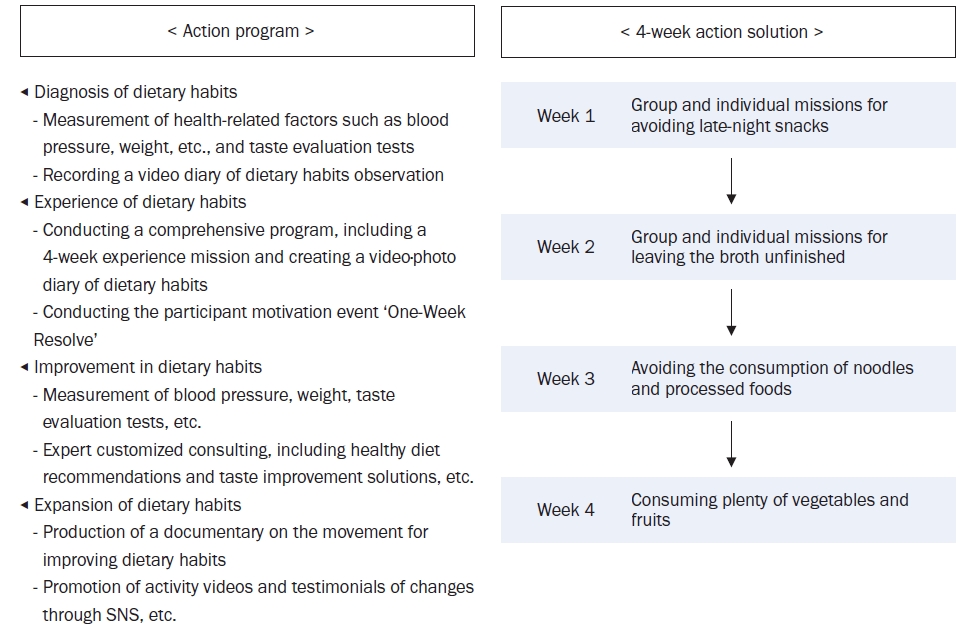
The program was implemented using a living lab model, an open innovation ecosystem for user-centered problem-solving. Analysis of the KNHANES data revealed that older age groups had a low energy intake but a high sodium intake, particularly among those who frequently dined out. The program was designed to improve sodium-reduction literacy and enhance practical competency. Over four weeks, 40 participants tracked their dietary intake and worked with a clinical nutritionist through a process of diagnosis, experience, improvement, and expansion. A self-administered survey was conducted before and after the program to assess effectiveness.
Results
Participants were four teenagers (10%), 26 in their twenties (65%), and 10 aged ≥ 30 years (25%), with eight males (20%) and 32 females (80%). Post-program analysis showed significant improvements in sodium-related nutrition knowledge (P < 0.01), with increased agreement on adopting low-sodium intake practices (e.g., interest in sodium content, choosing lower-sodium foods). Nutrient intake analysis showed a decrease in energy, carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins (P < 0.001), with sodium intake decreasing from 3,382.37 mg/d to 2,119.05 mg/d (P < 0.001).
Conclusion
The community-based, living lab model for the sodium-reduction program effectively improved participant sodium-reduction literacy and practical competency, suggesting that step-by-step, autonomous learning, can reduce sodium intake and promote healthier eating habits.
- [Korean]
-
Development and application of a dietary program to reduce sugar intake using a living lab approach in Korea: an intervention study
-
Jung-Hyun Kim, Min Sook Kyung, Seul Ki Choi
-
Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(6):504-513. Published online December 31, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00318
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Objectives
This study aimed to develop and apply a dietary program to reduce sugar intake among community residents using a Living Lab approach.
Methods
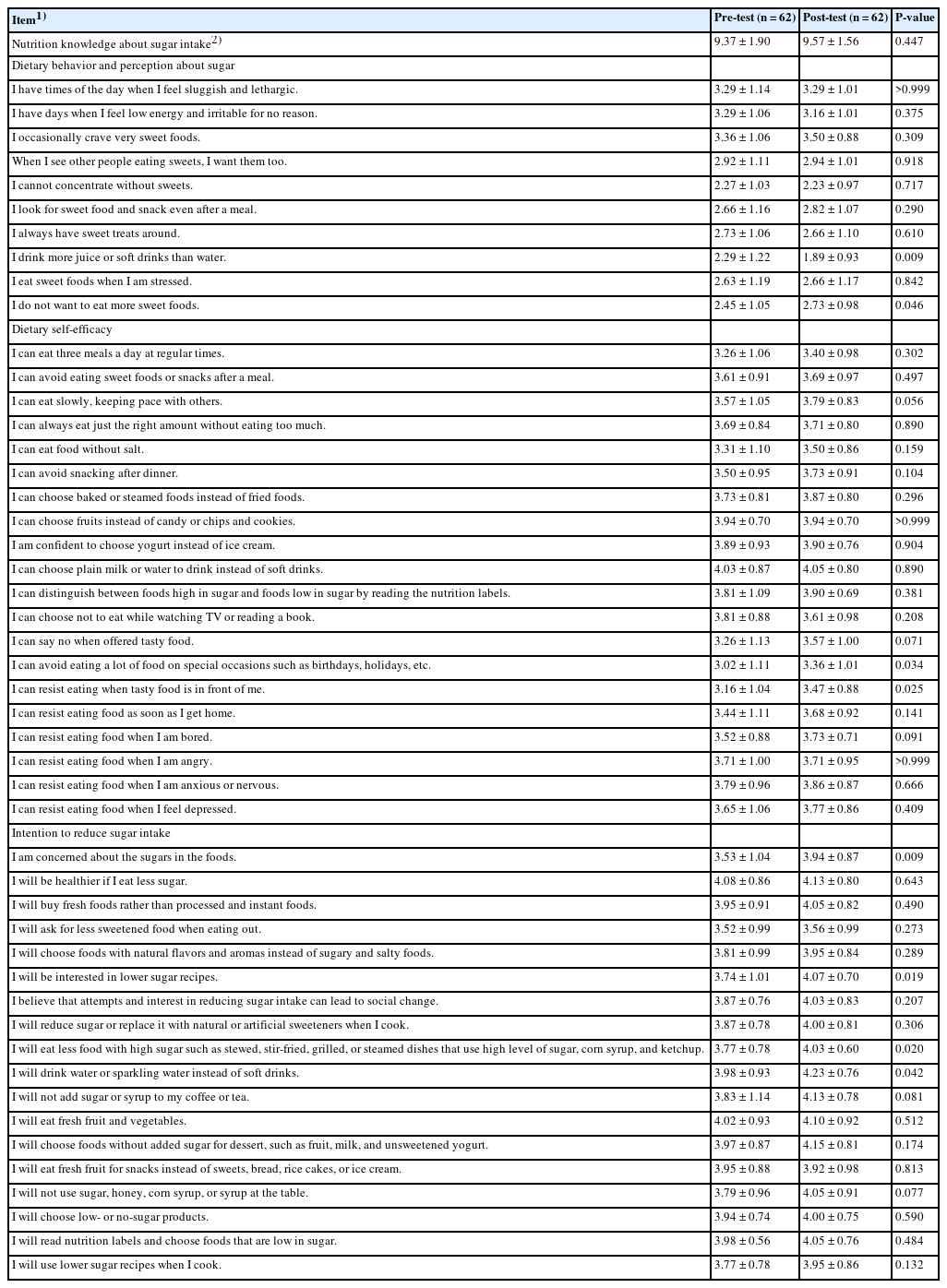
We developed and applied a community-based dietary program to reduce sugar intake. Participants were recruited from community organizations, including a children’s food service management center, elementary to high schools, a university, a family center, a community health center, and an elderly welfare center. The dietary program was conducted in two phases; start and next levels. The start level included a pre-assessment of dietary behaviors and participation in educational platforms, whereas the next level included activities using educational platforms, tailored mission and feedback, and pre- and post-surveys. Extension educators at each community organization implemented the dietary program following organization-specific guidelines. Changes in participants’ nutrition knowledge, dietary behaviors and perceptions, self-efficacy, intention to reduce sugar intake, and participants’ program satisfaction were analyzed using paired t-tests.
Results
In total, 1,238 and 339 individuals participated in the start and next level, respectively. Participants reported significantly lower scores on dietary behavior items regarding drinking more juice or soft drinks after program participation (P = 0.009) and craving sweet foods (P = 0.046). They reported a higher intention to take interest in sugar content in food (P = 0.009) and lower-sugar recipes (P = 0.019), eat less food with high sugar content (P = 0.020), and drink water or sparkling water instead of soft drinks (P = 0.042). Nutrition knowledge did not significantly change after program participation. Program satisfaction significantly increased from the start level to the next level (P<0.050).
Conclusion
This study showed the potential of using a Living Lab approach to implement community-wide dietary interventions. Further research is required to evaluate the effectiveness of the Living Lab approach in various community settings.
- [Korean]
-
Systematization of food and nutrition education content based on national kindergarten curriculum: a qualitative formative study
-
Jung-Hyun Kim, Eugene Shim, Eunyoung Baik
-
Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(6):509-522. Published online December 31, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.6.509
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Objectives
This study is intended to develop a curriculum for kindergarten food and nutrition education aimed at preschool children, reflecting government policy and meeting the demands of preschool settings.
Methods
Existing educational materials were analyzed, and key elements of the 2019 Revised Nuri Curriculum (“Nuri Curriculum”) and Guidelines for Nutrition and Food Education in Kindergartens, Elementary, Middle, and High Schools (“Guidelines”) were examined as foundational information for developing the curriculum for food and nutrition education.
Results
Basing ourselves on the five domains of the Nuri Curriculum, “Physical Activity and Health,” “Communication,” “Social Relationships,” “Art Experience,” and “Natural Science Inquiry,” we integrated three areas from the Guidelines, namely “Dietary Habits and Health,” “Dietary Habits and Safety,” and “Dietary Habits and Culture,” to structure the curriculum for kindergarten food and nutrition education. Three specific domains, “Nutrition and Health,” “Food and Culture,” and “Safe Dietary Practices,” were tailored for preschool children, each comprising core concepts, content elements, and educational materials. In the “Nutrition and Health” domain, core concepts such as “nutrition” were addressed through content elements such as “balanced eating” and “vegetables and fruit,” while “health” included elements such as “eating regularly” and “nutrients for disease prevention,” each with two educational content components. The “Food and Culture” domain focused on “food” with content on “local foods (vegetable-garden experience)” and “food culture” with content on “our dining table (rice and side dishes),” “our agricultural products,” “global cuisine (multiculture),” and “considerate dietary practices,” each with four educational content components. The “Safe Dietary Practices” domain included core concepts such as “hygiene” with content on “hand-washing habits” and “food poisoning management,” and “safety” with content on “food labeling.”
Conclusions
The systematized curriculum for kindergarten food and nutrition education aligns with the Nuri Curriculum and is interconnected with the Guidelines. This curriculum can be used as foundational material for developing educational resources tailored to the characteristics of preschoolers, contributing to effective implementation in early childhood education.
|