Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Article
- [English]
- Effects of a nutrition education program on metabolic syndrome risk factors in middle-aged Korean adults: an intervention study
- Minji Kang, Young-Hee Park, Subeen Kim, Eunyoung Tak, Hyun Wook Baik, Hee Young Paik, Hyojee Joung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):265-277. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study was conducted to evaluate the effects of a nutrition education program on metabolic syndrome in middle-aged Korean adults.
Methods
A total of 411 Korean adults 30–59 years of age were allocated randomly into three groups: the nutrition education group for promoting Han-sik consumption (HG), the nutrition education group for eating balanced diet (EG), and the control group (CG). The HG and EG received four face-to-face nutrition education sessions over 16 weeks to improve nutritional problems based on the individual’ usual diet. Effectiveness of the program was evaluated with the differences of self-reported dietary behaviors, dietary intakes, anthropometric measurements and biochemical indices between the baseline and the end of the nutrition education program. The changes within groups were analyzed using paired t-test and McNemar test and effectiveness among three groups was analyzed by repeated analysis of variance.
Results
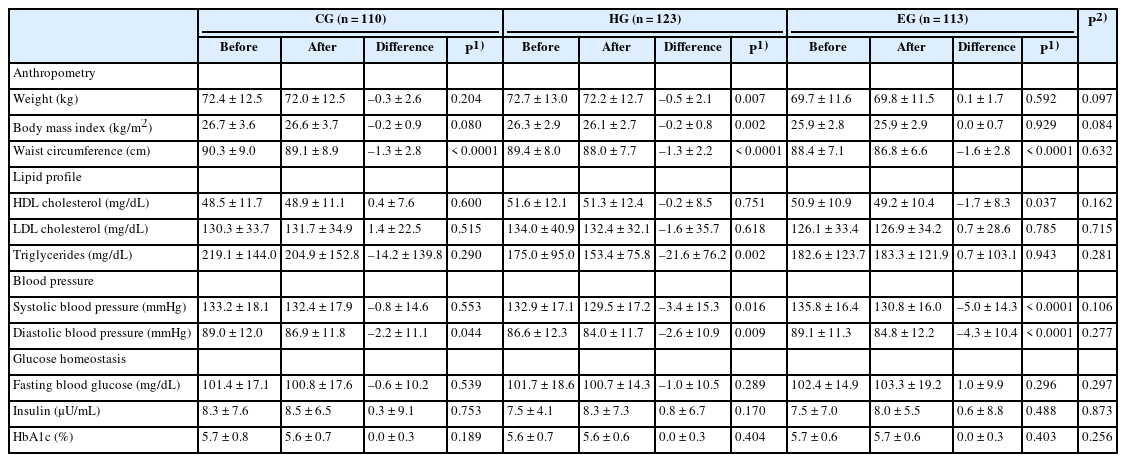
After the nutrition education, the percentages of participants who achieved the recommended food group consumption in the Korean Food Guidance Systems significantly increased in HG (P = 0.022). Body weight (P = 0.007), body mass index (P = 0.002), and triglycerides (P = 0.002) significantly decreased in HG. Waist circumference and diastolic blood pressure decreased in all three groups (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
This study found that tailored nutrition education program for middle aged Korean adults showed beneficial effects on improving dietary behaviors and metabolic syndrome risk factors. Further studies are needed to assess the long-term effects of the nutrition education programs on metabolic syndrome risks.
- 1,347 View
- 65 Download

Original Article
- [English]
- Consumption of Han-sik and its Association with Socioeconomic Status among Filipino Immigrant Women: the Filipino Women's Diet and Health Study (FiLWHEL)
- Nayeon Kim, Minji Kang, Grace Abris, Sherlyn Mae P Provido, Hyojee Joung, Sangmo Hong, Sung Hoon Yu, Chang Beom Lee, Jung Eun Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(6):475-487. Published online December 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.6.475
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the consumption of Han-sik and its association with the years of residence in Korea and the socioeconomic status among Filipino immigrant women of the Filipino Women's Diet and Health Study (FiLWHEL).
METHODS
A total of 474 Filipino women married to Korean men were included in the analysis. Their dietary intake was assessed using a single-day 24-hour recall. The participants provided information on the demographics, socioeconomic, and health-related factors through face-to-face interviews. The generalized linear model and logistic regression model were used to examine the association between the socioeconomic status and consumption of Han-sik.
RESULTS
The mean age of the participants was 34.3 years old, and the average duration of residence in Korea was 8.2 years. Among 474 Filipino women, a total of 467 consumed Han-sik, with an average of 6.8 food items per day. The Han-sik foods that the participants consumed most frequently were rice, cabbage kimchi, mixed-grain rice, and fried eggs. The average ratio of Han-sik was 58.57%. The ratio of Han-sik showed no significant associations with the years of residence, years of living together with their husband, education levels, total annual family income, or linguistic competence of Korean. However, the ratio of Han-sik use was associated with cohabitation with parents-in-law; the odds ratio (95% confidence interval) was 2.41 (1.18–4.92, p-trend = 0.002) comparing the fourth quartile with the first quartile of the Han-sik ratio.
CONCLUSIONS
Filipino immigrant women in the FiLWHEL study consumed a larger number of Han-sik than Philippine foods. In addition, cohabitation with their parents-in-law was associated with the consumption of Han-sik. Further epidemiologic studies will be needed to determine how the diet affects the health and wellbeing of immigrant women in Korea.
- 499 View
- 8 Download


 KSCN
KSCN
 First
First Prev
Prev



