Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Application of a living lab model to an evidence-based reduced-sodium healthy eating practice program in Korea: a pre-post study
- Jung-Hyun Kim, Eugene Shim, Min Sook Kyung, Sooyoun Kwon, Hyoung Su Park, Jae-Heon Kang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):53-63. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00346
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
To apply a healthy dietary program with reduced sodium intake, developed using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), focusing on the sodium intake level and eating patterns.
Methods
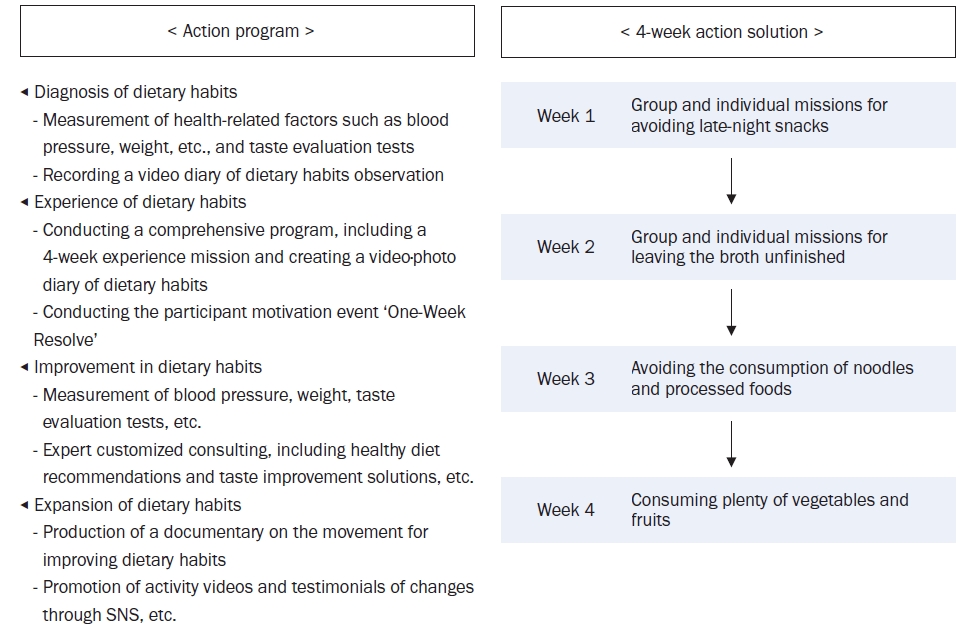
The program was implemented using a living lab model, an open innovation ecosystem for user-centered problem-solving. Analysis of the KNHANES data revealed that older age groups had a low energy intake but a high sodium intake, particularly among those who frequently dined out. The program was designed to improve sodium-reduction literacy and enhance practical competency. Over four weeks, 40 participants tracked their dietary intake and worked with a clinical nutritionist through a process of diagnosis, experience, improvement, and expansion. A self-administered survey was conducted before and after the program to assess effectiveness.
Results
Participants were four teenagers (10%), 26 in their twenties (65%), and 10 aged ≥ 30 years (25%), with eight males (20%) and 32 females (80%). Post-program analysis showed significant improvements in sodium-related nutrition knowledge (P < 0.01), with increased agreement on adopting low-sodium intake practices (e.g., interest in sodium content, choosing lower-sodium foods). Nutrient intake analysis showed a decrease in energy, carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins (P < 0.001), with sodium intake decreasing from 3,382.37 mg/d to 2,119.05 mg/d (P < 0.001).
Conclusion
The community-based, living lab model for the sodium-reduction program effectively improved participant sodium-reduction literacy and practical competency, suggesting that step-by-step, autonomous learning, can reduce sodium intake and promote healthier eating habits. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of food literacy on short- and long-term healthy eating intentions among adolescent and adult convenience store users: An application of the extended theory of planned behavior
Wonyeong Park, Hae Jin Park, Suah Moon, Jieun Oh
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(6): 917. CrossRef
- Influence of food literacy on short- and long-term healthy eating intentions among adolescent and adult convenience store users: An application of the extended theory of planned behavior
- 1,818 View
- 55 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Program Evaluation using the RE-AIM Framework: A Systematic Review and Application to a Pilot Health Promotion Program for Children
- Ji-Eun Lee, Jae Eun Shim, Kirang Kim, Jae-Heon Kang, Ji-Yun Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(4):296-308. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.4.296
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to develop evaluation criteria for the elementary-school-based health promotion program using the RE-AIM framework and to examine their feasibility.
Methods
Previous evaluation studies on health interventions for elementary-school students using the RE-AIM framework were reviewed systematically to identify appropriate evaluation criteria. A diet and physical activity intervention based on the transtheoretical model was implemented in a pilot study using the “Happy Me” application. The feasibility of using the RE-AIM framework to evaluate it was examined.
Results
The review yielded the following evaluation criteria: “reach,” the ratio of participants out of the total target population; “efficacy/effectiveness,” the difference in outcomes between the intervention and control groups, or between a pre- and post-test; “adoption,” the rate of use of the program and participation in the next stage of the program; “implementation,” the progress on the program components; “maintenance,” the participants’ and teachers’ intention to continue using the program. The pilot study reached 76.6% of the targeted population. The intake of sugar-sweetened beverages decreased (P < 0.0001), and the duration of walking increased (P < 0.0001). Other indicators could not be evaluated; therefore, potential indicators were suggested.
Conclusions
This study produced feasible evaluation criteria for elementary-school-based health promotion using the RE-AIM framework. Nevertheless, the feasibility needs to be validated with a broader range of studies and long-term interventions.
- 1,836 View
- 32 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



