Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Analysis of the relationship between sugar intake and cancer prevalence: a cross-sectional study using the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Hye-Ryun Kim, Soo-Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):89-102. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00339
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
This study aimed to analyze the association between sugar intake and cancer risk among Korean adults aged 19 years and older.
Methods
A total of 13,016 adults aged 19 years and older who participated in the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2019 to 2021 were included. Sugar intake was assessed in terms of both absolute intake and sugar energy rate. Sugar intake was divided into quartiles, while sugar energy rate was categorized into three groups (< 10%, 10%–20%, > 20%) based on the 2020 Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans and into two groups (< 10%, ≥ 10%) based on WHO recommendations. Cancer prevalence was determined using cancer-related survey questions. The association between sugar intake and cancer prevalence was analyzed by sex and cancer type using logistic regression. All statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS statistics 29.0 (IBM Co.).
Results
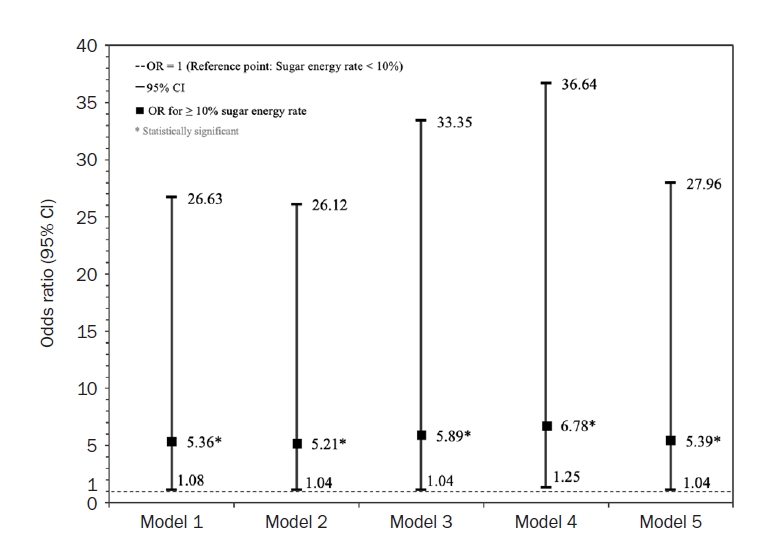
From 2019 to 2021, sugar intake significantly declined with age in both men and women (P for trend < 0.001), with the highest intake observed in the 19–29 age group (61.38 g). Men consumed significantly more sugar than women across all age groups except for the 50–64 and 65–74 groups (P < 0.05). However, the sugar energy rate was significantly higher in women than in men (P < 0.05). While the association between sugar intake and cancer prevalence varied across regression models and cancer types, cervical cancer consistently showed a significant association with sugar intake (P < 0.05).
Conclusion
The association between sugar energy rate and the prevalence of premenopausal cervical cancer was consistent and significant. Given that women had a higher sugar energy rate than men, the relationship between sugar intake and cancer prevalence in women warrants further investigation. Longitudinal studies with more detailed sugar intake assessments are needed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A study on hypertension relevant nutritional knowledge and dietary practices in Chinese college students studying in South Korea
Zhe Sun, Wookyoun Cho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(5): 441. CrossRef - Influence of the Size of the Spoon on the Eating rate, Energy Intake and the Satiety Levels of Female College Students
Yang Hee Hong, Young Suk Kim, Hyun Jung Kwon, Do Seok Chang, Dong Geon Kim, Un Jae Chang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(5): 375. CrossRef - Dietary behavior and nutritional status among Chinese female college students residing in Korea
Gaowei, Soyeon Kim, Namsoo Chang, Ki Nam Kim
Korean Journal of Nutrition.2013; 46(2): 177. CrossRef
- A study on hypertension relevant nutritional knowledge and dietary practices in Chinese college students studying in South Korea
- 2,926 View
- 115 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Current Status of Sanitary and Nutritional Food Service in Elderly Day Care Center
- Jeong hyeon Woo, Yoo Kyoung Park, Mi-Hyun Kim, Soo-Kyung Lee, Kyung hee Song, Hye-Kyeong Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(5):374-385. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.5.374
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to examine the status of foodservice management, with special interest on sanitary and nutritional food service in elderly day care centers. Methods A total of 79 employees who managed foodservice facilities in elderly day care centers were included in the survey. The contents of the questionnaire consisted of general characteristics, importance and performance of sanitary and nutrition management, the reasons for poor performance, factors necessary for improvement, and the employee's demand for support. Data analysis was conducted using the SPSS v25.0. Results Sanitary management showed an average importance score of 4.84 ± 0.40 and a performance score of 4.70 ± 0.61 (t-value: 8.260). The item with the lowest performance score was personal sanitary management (4.58 ± 0.71). In nutrition management, the average importance score was 4.52 ± 0.68, and the performance score was 4.20 ± 1.00 (t-value: 9.609). There were significant differences between the average score of importance and performance in both areas. As a result of an Importance-Performance Analysis, items that were recognized as important but had relatively low performance was “personal hygiene”, “ventilation” and “food storage”. Also in the nutritional management area, “menu planning for disease management” and “checking the saltiness in the soup” etc. had very low performance with low importance recognition. The items shown in the “low priority” quadrant were those that required professional management skills. In the areas that demanded support in foodservice management, education about sanitary and safe institutional food service had the highest score (4.42 ± 0.74), and all other items showed a demand of 4 points or more. Conclusions Foodservice managers recognize the importance of foodservice facility management but performance is relatively low. Institutional support is, therefore, needed to improve performance. For items with low importance, it seems necessary to improve awareness of the necessity of these items and to provide education in this regard. To gradually improve foodservice management, continuous provision of education and training in these areas are of great importance. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Importance-performance analysis of hygiene and nutrition management in social welfare meal service facilities in selected regions of Jeollanam-do
Do Hee Kim, Hee Kyong Ro
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(4): 421. CrossRef - A study on the diet and nutrition management status and educational needs in elderly care facilities in Korea: focus group interviews with staff from children’s and social welfare meal management support centers and elderly care facilities
Seo Young Choi, Hyun joo Ryou, Jieun Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(4): 286. CrossRef - Development of Protein Enhanced Diet for Socially Vulnerable Elderly
Jihye Hong, Hyung-Geun Jeon, Seulgi Kim, Gitae Park
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(1): 39. CrossRef - Snack Provision Practice in Long-Term Care Hospitals and Facilities in Korea
Dayeong Yeo, Hae Jin Kang, Hyejin Ahn, Yoo Kyoung Park
Clinical Nutrition Research.2024; 13(2): 108. CrossRef - Factors associated with malnutrition in demented and non-demented elderly residing in the community of Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive and analytical study
Jinhee Kwon, Jung Hee Kim, Hyeonjin Jeong, Jung Suk Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(5): 359. CrossRef - Sanitation Management Performance According to the Characteristics of Coffee Franchise Shops and Sanitation Knowledge According to the Characteristics of Employees
Suk-Kyoung Gu, Sunyoon Jung, Inyong Kim, Yoonhwa Jeong
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2021; 50(11): 1248. CrossRef - Analysis of Awareness, Knowledge, and Behavior about Food Hygiene·Safety Among the elderly
Mi Sook Lee, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(3): 200. CrossRef
- Importance-performance analysis of hygiene and nutrition management in social welfare meal service facilities in selected regions of Jeollanam-do
- 1,175 View
- 13 Download
- 7 Crossref


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



