Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [English]
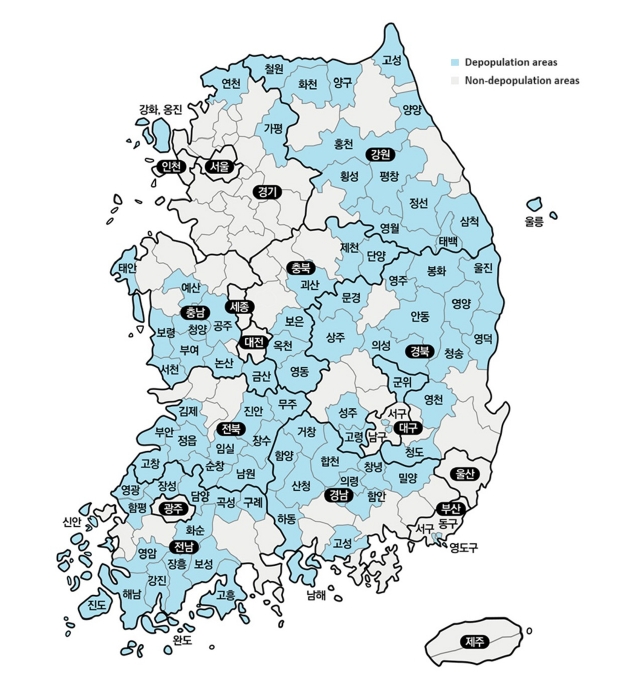
- Analysis of health behavior changes among residents in depopulation areas in Korea: a cross-sectional study based on Community Health Survey data from 2010 to 2019
- Miyong Yon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):348-357. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00001
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The total population of Korea began to decline in 2019; in particular, the population in rural areas has been rapidly decreasing and is aging. Therefore, the government has designated depopulation areas and is seeking ways to support them. To assess whether health disparities exist between areas with population decline and those without, this study used community health survey data to observe temporal changes in health behaviors between the two types of areas. Methods: The analysis used Community Health Survey data from 2010 to 2019, and regional classification was divided by depopulation areas designated by the Ministry of the Interior and Safety. Trends in health behavior and chronic disease prevalence between depopulation and non-depopulation areas were analyzed. All analyses were conducted using complex sample analysis procedures in SAS 9.4 software. Results: The smoking rate steadily decreased in both depopulation and non-depopulation areas, whereas the high-risk drinking rate increased slightly. The walking practice rate did not improve in depopulation areas compared to non-depopulation areas. Furthermore, nutritional labeling usage rate was consistently lower in depopulation areas than in non-depopulation areas, with the gap being the largest. The prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and hypertension showed that the gap between depopulation and non-depopulation areas is continuously increasing. Conclusions: Health behaviors in depopulation areas have not improved, and the prevalence of chronic diseases is increasing rapidly. Therefore, the demand for health care services that support healthy lifestyle practices and chronic disease management in these areas is expected to increase.
- 2,843 View
- 28 Download

- [Korean]
- Trends in Dietary Behavior Changes by Region using 2008 ~ 2019 Community Health Survey Data
- Yun-Hui Jeong, Hye-Young Kim, Hae-Young Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(2):132-145. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.2.132
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined trends in the health status and dietary behavior changes by region using the raw data from the 2008 ~ 2019 Community Health Survey.
Methods
This study analyzed the data of 2,738,572 people among the raw data of the Community Health Survey from 2008 to 2019. The regional differences in health status and dietary behavior were examined by classifying the regions into capital and non-capital regions, and the non-capital regions were classified into metropolitan cities and provinces. A chi-square test was conducted on the body mass index (BMI), diagnosis of diabetes and hypertension, frequency of eating breakfast, salty taste in usual diet, recognition of nutrition labeling, reading of nutrition labeling, and utilization of nutrition labeling.
Results
In determining obesity using the BMI, the normal weight by year decreased, and the obesity rate by year was 34.6% in 2019, which increased by 13% compared to 2008. In addition, the diabetes diagnosis rate and hypertension diagnosis rate continued to increase with the year. Both diabetes and hypertension diagnosis rates were higher in the non-capital regions than in the capital region. Eating breakfast five to seven times per week was most common and showed a significant decreasing trend by year (P < 0.001). The percentage of respondents who said they eat slightly bland foods increased from 19.5% in 2008 to 19.9% in 2010 and then to 22.1% in 2013. The percentage then decreased to 19.9% in 2019, but showed an overall increasing trend (P < 0.001). According to the region, the capital region had a higher percentage than the non-capital region. The nutrition labeling's recognition rate and utilization rate increased yearly, whereas the reading rate decreased.
Conclusions
The study results presented the primary data necessary to develop nutrition education programs and establish strategies for local nutrition management projects to improve disease prevention and dietary problems. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on the Eating Out Behavior and the Status of Meal Delivery and Take-Out Consumption according to the Food-related Lifestyles of Adolescents : Using the Consumption Behavior Survey for Food in 2020
Eun Jung Lee, Hyeon Min Yang, Yeong Ju Lee, Sun A Choi, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(4): 284. CrossRef - Comparison of the levels of energy intake from dish and food groups by gender and age among Korean obese adults: data obtained from the 2013-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Cheongmin Sohn, Woori Na, Chaeryeon Kim, Seunghee Choi, Oh Yoen Kim, Jounghee Lee, Mi Ock Yoon, Myoungsook Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(6): 670. CrossRef
- Study on the Eating Out Behavior and the Status of Meal Delivery and Take-Out Consumption according to the Food-related Lifestyles of Adolescents : Using the Consumption Behavior Survey for Food in 2020
- 1,303 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Article
- [English]
- Development and Effects' Analysis of Nutrition Education Program for Diabetes Mellitus at Community Health Center: Focused on Individual Daily Energy Requirements and Food Exchange Units
- Ji Yoon Oh, Sook Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(4):485-497. Published online August 31, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate effects of the developed nutrition education program focused on individual daily energy requirements and food exchange units using Food Exchange System for diabetes mellitus at a community health center. Developed the nutrition education program, four weeks' nutrition education including provided twice individual meal as diet therapy (2 hour/lesson/week, 4 week), was provided to 20 diabetic elderly (12 male, 8 female, 50-75 yrs): 1st lesson "Introduction: management of diabetes mellitus", 2nd lesson "6 Food groups and sources of 6 food groups", 3rd lesson "Individual daily energy requirements and food exchange units", and 4th lesson "Food choice for diabetes mellitus". For effects' analysis of the developed program, we assessed the changes in anthropometric characteristics; biochemical characteristics and nutrient intakes using 24 hr recall method. Effects of the developed nutrition education program were as follows: weight was significantly decreased, blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) were significantly decreased, and distribution of subjects in BUN and HbA1c was significantly changed. In protein : fat : carbohydrate (PFC) ratio, it was significantly changed from 15.98 : 16.30 : 66.69 to 17.51 : 18.94 : 64.10. In evaluation of nutrient intakes by Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans (KDRI), protein, fiber, fat, vitamin E, niacin, folic acid, calcium and zinc were shown significantly positive changes in distribution of subjects according to intake level. The index of nutrition quality (INQ), nutrition adequacy ratio (NAR) and mean nutrition adequacy ratio (MAR) were significantly increased. In conclusion, the developed 4 weeks' nutrition education program focused on individual daily energy requirements and food exchange units using Food Exchange System for diabetes mellitus at community health center may improve the symptom of diabetes mellitus.
- 276 View
- 1 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



