Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Article
- [Korean]
- Biochemical characteristics, nutrient intakes, and chronic disease risk according to the dietary fat energy ratio in middle-aged Korean: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Ga-Hyeon Jeong, Sook-Bae Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(6):528-540. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00304
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to examine health-related characteristics and chronic disease risk in middle-aged Koreans based on their fat energy intake ratio.
Methods
We analyzed data from 7,274 Koreans aged 40–64 years using the 7th (2016–2018) Koreans National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Participants were classified into three groups based on their fat energy intake ratio: insufficient (< 15%), adequate (15%–30%), and excessive (> 30%). We assessed their socio-demographic characteristics; lifestyle characteristics; biochemical characteristics; quantitative and qualitative nutrient intakes, measured using dietary reference intakes for Koreans and index of nutrition quality (INQ); and chronic disease risk.
Results
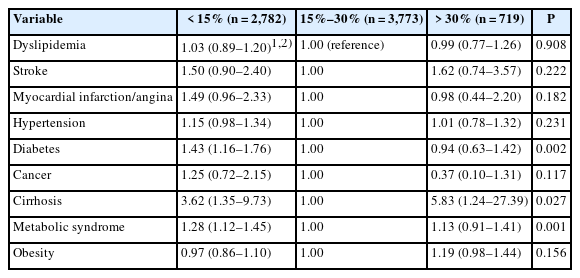
Significant differences were observed between the groups in age, gender, income, education, and residence region. The insufficient group had the highest proportion of older adults, male, lower income, rural residents, and lower education levels. The groups differed significantly in lifestyle characteristics, with the insufficient group having the highest rates of no walking, heavy drinking, smoking, and poor subjective health perception. Biochemical characteristics in the insufficient group exhibited the lowest levels for fasting blood glucose, hemoglobin A1c, and triglycerides. Significant differences were found in both the quantitative and qualitative intake of nutrients. The insufficient group had the lowest intake of most nutrients except fiber, whereas the excessive group had the lowest fiber intake. Based on the INQ, vitamin A and Ca were the lowest in the insufficient group, and vitamin C and folic acid were the lowest in the excessive group. The risk of diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome was highest in the deficient group, and the risk of liver cirrhosis was highest in the excessive group.
Conclusion
Insufficient or excessive fat energy intake ratio negatively affects nutrient intake and chronic disease risk. Fat energy intake of 15%–30% is important for improving nutrient intake and managing chronic diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, and liver cirrhosis. We suggest that education and an appropriate social environment are necessary to ensure this fat energy intake. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on the Optimization of Manufacturing Conditions for Traditional Potato Bugak Using Response Surface Methodology
Yu Hyeon Jo, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2025; 35(1): 60. CrossRef - Nutritional risk assessment using estimated usual nutrient intake in Korean adults: analysis of the 8th (2019–2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Woojin Byeon, Cho-il Kim, Sung Ok Kwon, Jihyun Yoon, Linxi Huang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 799. CrossRef
- Study on the Optimization of Manufacturing Conditions for Traditional Potato Bugak Using Response Surface Methodology
- 1,407 View
- 48 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Article
- [English]
- Evaluation of Total Fat and Fatty Acids Intakes in the Korean Adult Population using Data from the 2016–2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
- SuJin Song, Jae Eun Shim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(3):223-231. Published online June 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.3.223
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study evaluated dietary intakes of total fat and fatty acids among the Korean adult population.
METHODS
This cross-sectional study used the 2016–2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data. A total of 10,772 subjects aged ≥19 y for which dietary data were available were selected. Data pertaining to energy and nutrient intakes were obtained by a 24-h recall method. Total fat and fatty acids intakes were evaluated based on the Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Ranges (AMDR) of 2015 Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans by sex and age groups. All statistical analyses accounted for the complex sampling design effect and sampling weights.
RESULTS
The mean intakes of energy and total fat were 1,952 kcal (95% CI: 1928–1977) and 46.1 g (45.2–47.1), respectively, and about 21% of the energy was obtained from fat in this study population (21.7% in men and 20.2% in women). The mean percentages of energy from saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fatty acids were 6.4%, 6.7%, and 5.2%, respectively. About 18% of adults exceeded the AMDR for fat (30% of energy), whereas 37.6% exceeded the AMDR for saturated fatty acids (7% of energy). The proportions of subjects who consumed more than the AMDR for fat and saturated fatty acids decreased across age groups in both sexes. Among young adults (19–29 y), about 63% of the subjects obtained ≥7% of their energy from saturated fatty acids. About 61% of older adults obtained less than 15% of their energy from total fat.
CONCLUSIONS
Increased intake of fat energy was prominent in saturated fatty acids. Our findings suggest current information on total fat and fatty acids intakes in Korean adults and can be used to provide dietary guidelines for the improvement of public health. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary patterns derived by reduced rank regression are associated with lipid disorders among Korean adults: a cross-sectional analysis
Hyun Ah Kim, Hye Ran Shin, SuJin Song
Lipids in Health and Disease.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Dietary intake and food sources of essential fatty acids among Korean adolescents: a cross-sectional study based on the 2016–2021 KNHANES data
Enkhgerel Erdenetsetseg, Hye Ran Shin, SuJin Song
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 144. CrossRef - Nutrition and food intake status among adults in Jeju according to sociodemographic characteristics and obesity
Hyunji Ham, Hanbin Ko, Sumin Kim, Youjeong Jang, Jong-Seok Byun, Yoonsuk Jekal, Insuk Chai, Kyungho Ha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(6): 667. CrossRef - Biochemical characteristics, nutrient intakes, and chronic disease risk according to the dietary fat energy ratio in middle-aged Korean: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ga-Hyeon Jeong, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 528. CrossRef - Evaluation of Nutritional Content of Snacks for Smart Snack Choices
Chae Young Yoon, Eunju Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2023; 33(4): 264. CrossRef - Trends in dietary intake and food sources of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids among Korean adults between 2007 and 2018
Jae Eun Shim, Youngmi Lee, SuJin Song
Epidemiology and Health.2023; 45: e2023069. CrossRef - Diabetes and Dietary Fats
Jae Won Cho
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 154. CrossRef - Association of Saturated Fatty Acid Intake and Its Food Sources With Hypercholesterolemia in Middle-Aged Korean Men and Women
In Young Jeong, Jae Eun Shim, SuJin Song
CardioMetabolic Syndrome Journal.2022; 2(2): 142. CrossRef - Increasing trends in dietary total fat and fatty acid intake among Korean children: using the 2007–2017 national data
SuJin Song, Jae Eun Shim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2022; 16(2): 260. CrossRef - Substitution of Carbohydrates for Fats and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes among Korean Middle-Aged Adults: Findings from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Hye-Ah Lee, Hyesook Park
Nutrients.2022; 14(3): 654. CrossRef - Food behaviors accounting for the recent trends in dietary fatty acid profiles among Korean adults
SuJin Song, Jae Eun Shim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2022; 16(3): 405. CrossRef - Current status of nutrient intake in Korea: focused on macronutrients
Seung-Won Oh
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2022; 65(12): 801. CrossRef - Regional Differences in Dietary Total Fat and Saturated Fatty Acid Intake and Their Associations with Metabolic Diseases among Korean Adults: Using the 2016~2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
SuJin Song, Jae Eun Shim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(6): 495. CrossRef - The number of teeth is associated with diet quality in Korean adult population
Hye-Sun Shin
Archives of Oral Biology.2020; 118: 104882. CrossRef - Trends in Dietary Intake of Total Fat and Fatty Acids Among Korean Adolescents from 2007 to 2017
SuJin Song, Jae Eun Shim
Nutrients.2019; 11(12): 3073. CrossRef
- Dietary patterns derived by reduced rank regression are associated with lipid disorders among Korean adults: a cross-sectional analysis
- 1,547 View
- 6 Download
- 15 Crossref


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



