Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Article
- [Korean]
- Analysis of the relationship between sugar intake and cancer prevalence: a cross-sectional study using the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Hye-Ryun Kim, Soo-Kyung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):89-102. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00339
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
This study aimed to analyze the association between sugar intake and cancer risk among Korean adults aged 19 years and older.
Methods
A total of 13,016 adults aged 19 years and older who participated in the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2019 to 2021 were included. Sugar intake was assessed in terms of both absolute intake and sugar energy rate. Sugar intake was divided into quartiles, while sugar energy rate was categorized into three groups (< 10%, 10%–20%, > 20%) based on the 2020 Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans and into two groups (< 10%, ≥ 10%) based on WHO recommendations. Cancer prevalence was determined using cancer-related survey questions. The association between sugar intake and cancer prevalence was analyzed by sex and cancer type using logistic regression. All statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS statistics 29.0 (IBM Co.).
Results
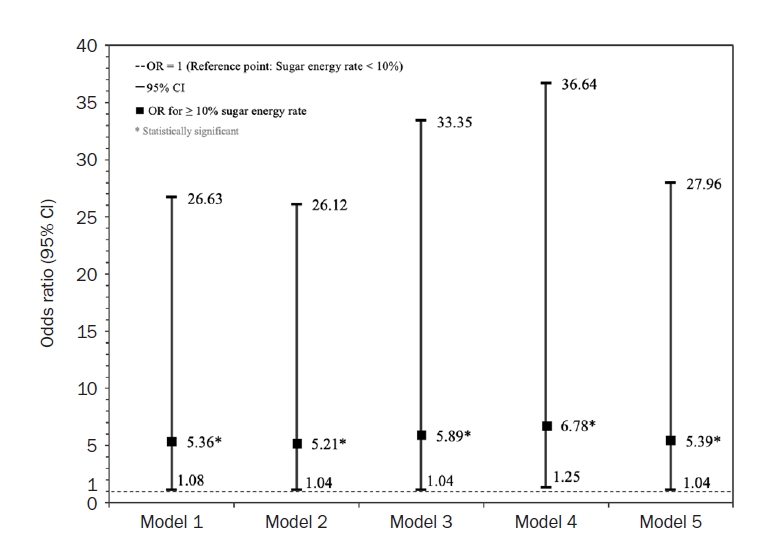
From 2019 to 2021, sugar intake significantly declined with age in both men and women (P for trend < 0.001), with the highest intake observed in the 19–29 age group (61.38 g). Men consumed significantly more sugar than women across all age groups except for the 50–64 and 65–74 groups (P < 0.05). However, the sugar energy rate was significantly higher in women than in men (P < 0.05). While the association between sugar intake and cancer prevalence varied across regression models and cancer types, cervical cancer consistently showed a significant association with sugar intake (P < 0.05).
Conclusion
The association between sugar energy rate and the prevalence of premenopausal cervical cancer was consistent and significant. Given that women had a higher sugar energy rate than men, the relationship between sugar intake and cancer prevalence in women warrants further investigation. Longitudinal studies with more detailed sugar intake assessments are needed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A study on hypertension relevant nutritional knowledge and dietary practices in Chinese college students studying in South Korea
Zhe Sun, Wookyoun Cho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(5): 441. CrossRef - Influence of the Size of the Spoon on the Eating rate, Energy Intake and the Satiety Levels of Female College Students
Yang Hee Hong, Young Suk Kim, Hyun Jung Kwon, Do Seok Chang, Dong Geon Kim, Un Jae Chang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(5): 375. CrossRef - Dietary behavior and nutritional status among Chinese female college students residing in Korea
Gaowei, Soyeon Kim, Namsoo Chang, Ki Nam Kim
Korean Journal of Nutrition.2013; 46(2): 177. CrossRef
- A study on hypertension relevant nutritional knowledge and dietary practices in Chinese college students studying in South Korea
- 2,618 View
- 90 Download
- 3 Crossref


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



