Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Food purchase patterns, food policy recognition, and food environment satisfaction among adults in Jeju, Korea, according to food security: a cross-sectional study
- Sumin Kim, Youjeong Jang, Hyunji Ham, Hanbin Ko, Insuk Chai, Kyungho Ha
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):406-417. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00012

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
Recently, food insecurity has been a major public health issue along with the food crisis caused by COVID-19, climate change, and the polarization of food supply due to socioeconomic disparities. Food insecurity is known to be related to the food choices and environment of the consumer. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the food security statuses of adults in Jeju and investigate their food purchase patterns, food policy recognition, and food environment satisfaction.
Methods
Based on data from the 2022 Jeju Food Survey, 346 adults aged ≥19 years in Jeju were classified into food security and insecurity groups (quantitatively and qualitatively) using the questionnaire. Food purchase patterns, including purchasing frequency, items, and reasons, were surveyed for local and eco-friendly foods. The recognition and necessity of several food policies and satisfaction with diet and food environment (availability, accessibility, affordability, accommodation, and acceptability) were measured using the Likert scale.
Results
Among the total participants, 47.4% were in the food insecurity group. The frequency of purchasing local and eco-friendly foods did not significantly differ by food security status. The insecurity group exhibited a higher recognition rate of basic rights to food (36.0%) than the security group (24.7%, P = 0.023). The recognition and necessity of specific food policies did not significantly differ by food security status, except for the policy of promoting food communities, for which the food security group exhibited higher recognition than the food insecurity group did (P = 0.004). The food insecurity group exhibited significantly lower scores regarding satisfaction toward diet and food environment factors (P < 0.05 for all).
Conclusions
Overall, the food security group reported higher satisfaction with their diet and food environment than the food insecurity group. Further in-depth studies to investigate the determinants of food insecurity and effective promotional strategies for food policies are needed.
- 2,283 View
- 51 Download

- [Korean]
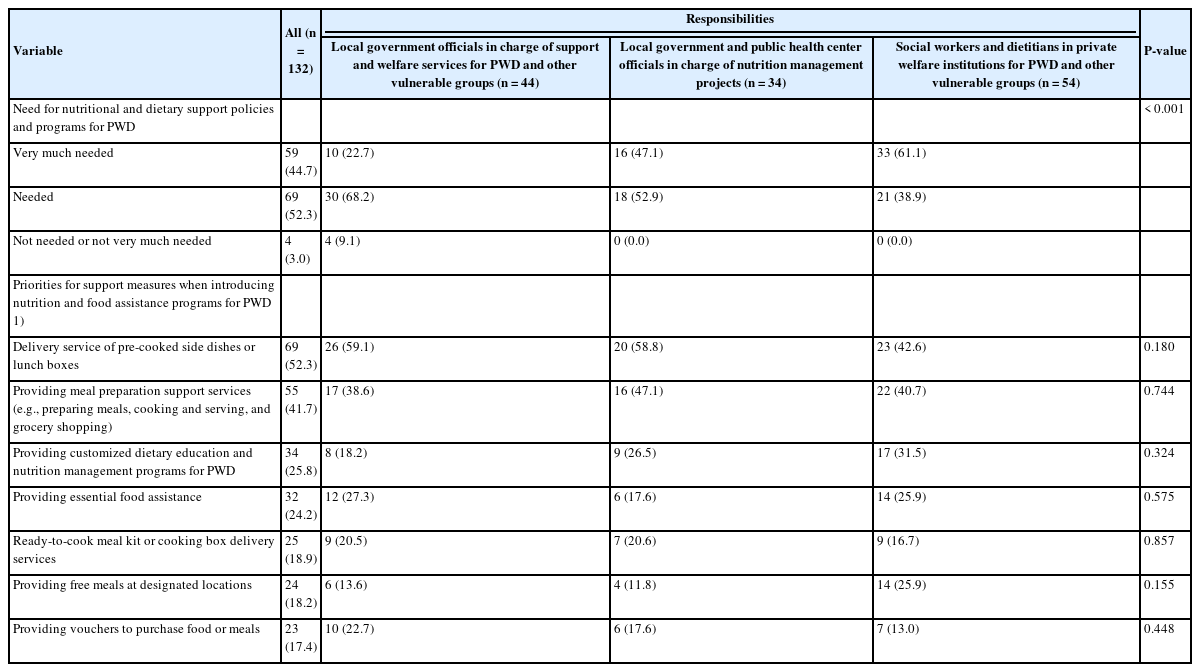
- The needs and prioritization of nutrition and dietary support for individuals with disabilities: an exploratory study
- Jong Eun Park, Yu Jin Kim, So Young Kim, Jong Hyock Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):431-443. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Based on a survey of officers, social workers, and dietitians involved in managing nutrition and welfare policies or projects for vulnerable groups in local governments or private welfare institutions, this study aimed to assess the need for nutritional and dietary support policies and programs for persons with disabilities (PWD), as well as to identify appropriate support measures. Methods: An online survey was conducted from March 2 to 15, 2021. The survey included 20 questions exploring perspectives on the nutritional status of PWD, their need for nutritional and dietary support policies and programs, and the prioritization of appropriate support measures. A total of 132 responses were analyzed. Results: Approximately 68.9% of the respondents rated the nutritional status of PWD as “bad” or “very bad.” A substantial number identified “difficulty in purchasing ingredients, cooking, and preparing meals independently due to disability,” and “limited knowledge about nutrition and recipes necessary for maintaining a healthy and balanced diet” as the primary challenges in the dietary and nutritional management of this population. Additionally, 97.0% of the respondents deemed that the introduction of nutritional and dietary support policies and programs for PWD was “needed” or “very much needed.” Priority strategies to implement and strengthen these policies and systems included the “development of customized programs and services tailored to the needs and demands of the target population” and the “establishment of a dedicated department with specialized personnel.” Conclusion: Comprehensive nutritional and dietary support policies and programs should be actively implemented to ensure a healthy and stable diet for PWD, tailored to meet their actual needs and demands. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a standard nutrition management model algorithm for personalized care in social welfare facilities for the disabled
Su-Jin Lee, Ji-Won Kang, Sil Ah Kim, Kirang Kim, Sohyun Park, Jieun Oh, Hyunjoo Ryou, Ji-Yun Hwang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(5): 498. CrossRef - Factors associated with nutritional risk among disabled persons in the Republic of Korea: a cross-sectional study using 2020 Disability and Life Dynamics Panel
Seong-Ah Kim, Seul Ki Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(5): 364. CrossRef
- Development of a standard nutrition management model algorithm for personalized care in social welfare facilities for the disabled
- 2,840 View
- 125 Download
- 2 Crossref


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



