Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [English]
- Associations between diet quality and regional factors in Korea vary according to individuals’ characteristics: a cross-sectional study
- Hyunmi Han, Clara Yongjoo Park, Jeonghwa Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(4):274-285. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00157

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
Although diet quality is known to be associated with environment and individuals’ characteristics, these have not been studied together. We determined the association of diet quality with regional factors stratified by individuals’ sociodemographic characteristics.
Methods
This study used nationally representative survey data on regional factors (2010–2020) and the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data on individuals’ sociodemographic characteristics (2013–2018). Community-dwelling Koreans aged ≥ 20 were included (n = 26,853). Regions were categorized into metropolitan cities or provinces and subsequently according to regional factors (level of educational attainment, income per capita, food security status, physical activity facilities, time to the nearest large retailer, and internet use of the region). Individuals’ sociodemographic characteristics included age, education status, income, and number of household members. Diet quality was assessed using the Korean Healthy Eating Index (KHEI).
Results
In the entire population, education status of metropolitan cities was positively associated with the KHEI. Shorter time to retailers and higher internet use were positively associated with the KHEI in metropolitan residents with higher income levels but negatively associated with the KHEI in those with lower income status. Among provincial residents with a low education status or income, regional physical activity facilities were positively associated with the KHEI.
Conclusion
The association between diet quality and regional factors varied depending on the resident’s sociodemographic characteristics. Both regional and individual sociodemographic factors must be considered to address gaps in nutritional equity.
- 1,540 View
- 25 Download

- [Korean]
- Food purchase patterns, food policy recognition, and food environment satisfaction among adults in Jeju, Korea, according to food security: a cross-sectional study
- Sumin Kim, Youjeong Jang, Hyunji Ham, Hanbin Ko, Insuk Chai, Kyungho Ha
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):406-417. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00012

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
Recently, food insecurity has been a major public health issue along with the food crisis caused by COVID-19, climate change, and the polarization of food supply due to socioeconomic disparities. Food insecurity is known to be related to the food choices and environment of the consumer. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the food security statuses of adults in Jeju and investigate their food purchase patterns, food policy recognition, and food environment satisfaction.
Methods
Based on data from the 2022 Jeju Food Survey, 346 adults aged ≥19 years in Jeju were classified into food security and insecurity groups (quantitatively and qualitatively) using the questionnaire. Food purchase patterns, including purchasing frequency, items, and reasons, were surveyed for local and eco-friendly foods. The recognition and necessity of several food policies and satisfaction with diet and food environment (availability, accessibility, affordability, accommodation, and acceptability) were measured using the Likert scale.
Results
Among the total participants, 47.4% were in the food insecurity group. The frequency of purchasing local and eco-friendly foods did not significantly differ by food security status. The insecurity group exhibited a higher recognition rate of basic rights to food (36.0%) than the security group (24.7%, P = 0.023). The recognition and necessity of specific food policies did not significantly differ by food security status, except for the policy of promoting food communities, for which the food security group exhibited higher recognition than the food insecurity group did (P = 0.004). The food insecurity group exhibited significantly lower scores regarding satisfaction toward diet and food environment factors (P < 0.05 for all).
Conclusions
Overall, the food security group reported higher satisfaction with their diet and food environment than the food insecurity group. Further in-depth studies to investigate the determinants of food insecurity and effective promotional strategies for food policies are needed.
- 2,106 View
- 50 Download

- [Korean]
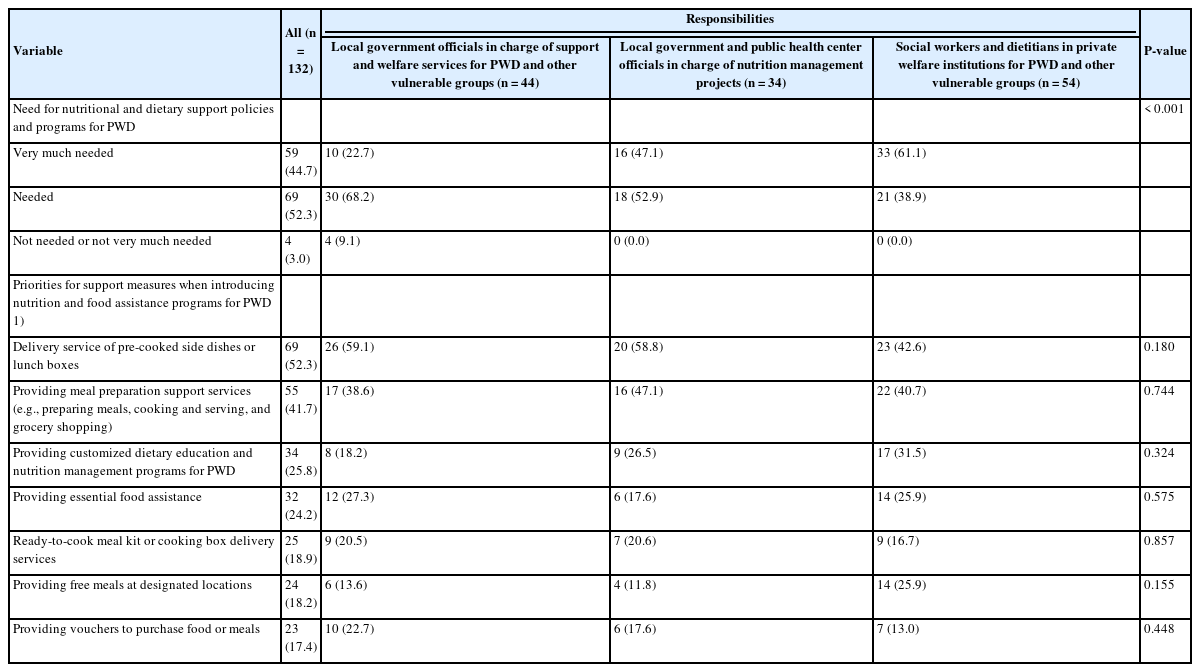
- The needs and prioritization of nutrition and dietary support for individuals with disabilities: an exploratory study
- Jong Eun Park, Yu Jin Kim, So Young Kim, Jong Hyock Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):431-443. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Based on a survey of officers, social workers, and dietitians involved in managing nutrition and welfare policies or projects for vulnerable groups in local governments or private welfare institutions, this study aimed to assess the need for nutritional and dietary support policies and programs for persons with disabilities (PWD), as well as to identify appropriate support measures. Methods: An online survey was conducted from March 2 to 15, 2021. The survey included 20 questions exploring perspectives on the nutritional status of PWD, their need for nutritional and dietary support policies and programs, and the prioritization of appropriate support measures. A total of 132 responses were analyzed. Results: Approximately 68.9% of the respondents rated the nutritional status of PWD as “bad” or “very bad.” A substantial number identified “difficulty in purchasing ingredients, cooking, and preparing meals independently due to disability,” and “limited knowledge about nutrition and recipes necessary for maintaining a healthy and balanced diet” as the primary challenges in the dietary and nutritional management of this population. Additionally, 97.0% of the respondents deemed that the introduction of nutritional and dietary support policies and programs for PWD was “needed” or “very much needed.” Priority strategies to implement and strengthen these policies and systems included the “development of customized programs and services tailored to the needs and demands of the target population” and the “establishment of a dedicated department with specialized personnel.” Conclusion: Comprehensive nutritional and dietary support policies and programs should be actively implemented to ensure a healthy and stable diet for PWD, tailored to meet their actual needs and demands. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a standard nutrition management model algorithm for personalized care in social welfare facilities for the disabled
Su-Jin Lee, Ji-Won Kang, Sil Ah Kim, Kirang Kim, Sohyun Park, Jieun Oh, Hyunjoo Ryou, Ji-Yun Hwang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(5): 498. CrossRef - Factors associated with nutritional risk among disabled persons in the Republic of Korea: a cross-sectional study using 2020 Disability and Life Dynamics Panel
Seong-Ah Kim, Seul Ki Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(5): 364. CrossRef
- Development of a standard nutrition management model algorithm for personalized care in social welfare facilities for the disabled
- 2,597 View
- 117 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Relationship between the Intake of Children's Favorite Foods and Policy based on Special Act on Safety Control of Children's Dietary Life
- Taejung Woo, Jihye Yoo, Kyung Hea Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(2):106-116. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.2.106
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the status of children's favorite foods intake and the relationship with the policy environment based on the Special Act on Safety Control of Children's Dietary Life for suggesting a supportive policy strategy.
METHODS
The subjects were 4th grade students (n=1,638) in elementary school from 45 schools collected from seven areas (Seoul, Daegu, Daejeon, Gyeonggi, Chungnam, Jeonbuk, and Gyeongnam). The children participated in a self-administered questionnaire survey in class under the supervision of the teacher. The questionnaire consisted of items, such as social demographic characteristics, frequency of intake of the children's favorite foods, and policy cognition. A t-test and ANOVA were applied to explore the relationship between the frequency of children's favorite foods intake and policy cognition. The survey was implemented from August 2016 to September 2016.
RESULTS
For the boys, the frequency of ‘high-calorie low nutrient foods intake’ (HCLN) was significantly higher than that of the girls (p<0.01). For the children who received information on their favorite foods from the internet, the frequency of HCLN was higher than the other sources (p<0.01). The time of TV viewing and computer usage, and smartphone usage was associated with a higher frequency of HCLN, and a lower healthy favorite food intake (all p<0.001). The intake frequency of healthy favorite foods indicated a positive correlation with the policy cognition, including policy perception, usefulness, necessity and buying intention, and educational experience.
CONCLUSIONS
This study showed a correlation with the frequency of children's favorite foods intake and policy. In particular, the frequency of children's healthy favorite foods intake indicated a meaningful relationship with the policy than the frequency of HCLN. This study also found that the consumption of children's healthy favorite foods was positively correlated with the educational experience. To develop a supportive policy for a good dietary environment for children, there is a need to focus on how to collaborate with multiple levels of influences, such as the national level, school level, and family. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Correlation between adolescents’ dietary safety management competency and value recognition, efficacy, and competency of convergence using dietary area: a descriptive study
Yunhwa Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(4): 317. CrossRef
- Correlation between adolescents’ dietary safety management competency and value recognition, efficacy, and competency of convergence using dietary area: a descriptive study
- 1,188 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Analysis of Nutrition Teachers' Awareness of Necessity for an Operating School Meal Support Center in Chungnam
- Jonghwa Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(6):506-515. Published online December 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.6.506
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
We investigated the operation needs of school meal support centers (SMSC) in Chungnam-do based on analysis of nutrition teachers' perception of them.
METHODS
The Chungnam government established the first SMSC in 2012. Thirteen SMSCs are currently being operated in Chungnam-do. To analyze the results quantitatively, we investigated nutrition teachers opinions regarding the necessity for SMSCs as a dependent variable and derived the independent variables based on the causal relationships with dependent variables using the ordered logit model. Those independent variables included region, school type, number of students, attitude regarding free meal policy, satisfaction with school meal policy, and preference for local food.
RESULTS
Briefly, teachers in the region in which the SMSC was located more strongly supported the SMSC. In addition, teachers in public schools with a smaller number of students believed that having a SMSC is more beneficial, and that other variables also affected the necessity for SMSCs. Moreover, nutrition teachers preferred local foods rather than organic foods because of the unstable supply of organic foods.
CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of this study, it was recommended that the local government implement the policy consistently. Moreover, it was recommended that the government operate the SMSC more efficiently, enhance the roles of the SMSC as the local organization responsible for student nutritional planing and expand the coverage of agricultural products.
- 785 View
- 0 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



