Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Article
- [English]
- The dietary factors associated with sleep duration in postmenopausal middle-aged women: a cross-sectional study using 2019–2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
- Eugene Shim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(3):197-213. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00052
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to analyze dietary factors associated with sleep duration in postmenopausal middle-aged women using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), with particular emphasis on the postmenopausal period.
Methods
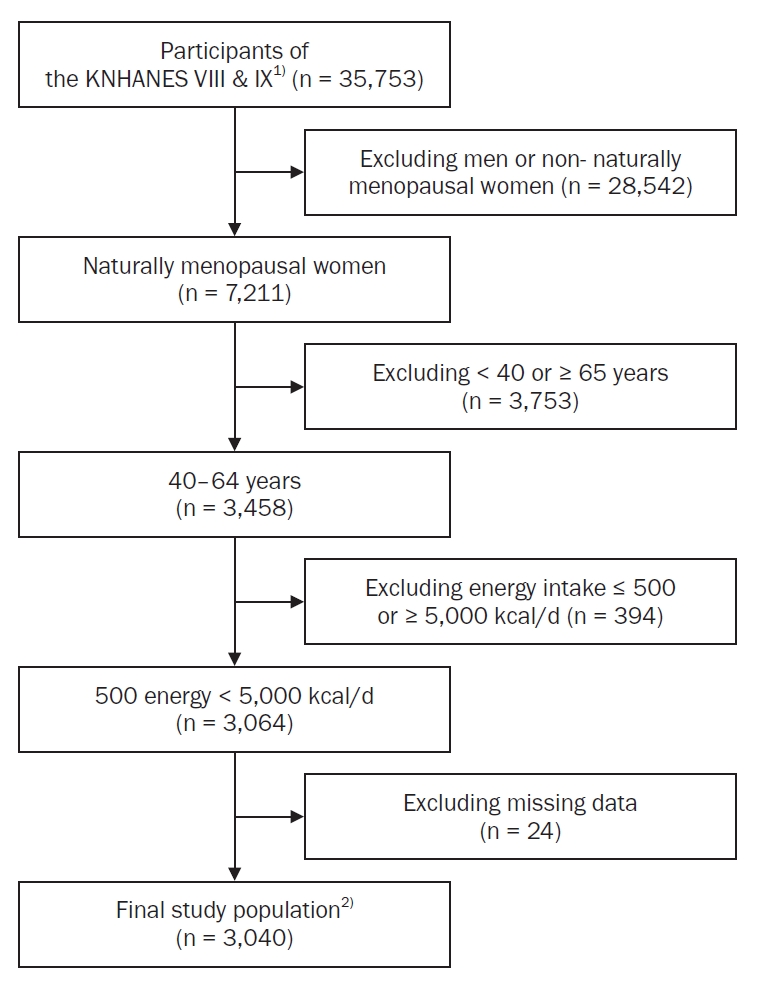
A total of 3,040 postmenopausal women aged 40–64 years from the 2019–2023 KNHANES were included. Sleep duration was classified into four categories: “appropriate sleep duration” (ASD; 7–9 hours), “short sleep duration” (6–7 hours), “very short sleep duration” (VSSD; < 6 hours), and “long sleep duration” (LSD; > 9 hours). Nutrient and food intake were compared among groups using analysis of covariance. Multinomial logistic and polynomial regression models assessed associations, adjusting for demographic and health covariates.
Results
The VSSD group had higher body mass index and waist circumference than the ASD group, despite lower total energy intake, and also consumed more snack energy and skipped breakfast and dinner more often. This group also had lower intakes of monounsaturated fatty acids and nuts and seeds. In the late menopausal group, greater consumption of cereal grains, fish and shellfish, and beverages was associated with elevated LSD risk. Conversely, higher folate intake in the early menopausal group was inversely associated with VSSD risk. Cholesterol intake was positively associated with LSD risk in both groups. A negative nonlinear association between sleep duration and dietary intake was observed in the early menopausal group when polyunsaturated fatty acid intake exceeded 19.86 g/day and riboflavin intake exceeded 1.76 mg/day. In the late menopausal group, riboflavin intake was strongly correlated with increased LSD risk (odds ratio = 4.776, P = 0.004). Sugar and beverage intake showed a positive linear relationship with sleep duration at average intake levels.
Conclusion
Dietary factors associated with sleep duration differed by postmenopausal period, with specific nutrients and food groups exhibiting variable associations with sleep duration above mean intake levels.meS
- 4,092 View
- 54 Download

Original Article
- [English]
- Relationship between Nutrient Intake and Biochemical Markers of Bone Metabolism in Korean Postmenopausal Women
- Haeng Shin Lee, Da Hong Lee, Chung Ja Sung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2001;6(5):765-772. Published online December 31, 2001
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To delineate the relationship between the nutrient intake from diet and the serum biochemical markers of bone metabolism, 56 postmenopausal women of 50 to 77 years of age were recruited. The biochemical markers including osteocalcin, calcium, phosphorus, estradiol and free testosterone were measured in fasting blood. Bone mineral density(BMD) was measured also by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry, and the nutrient intake of earth individual subject was estimated by 24-hour recall of 3 days. The age of the subjects was 64.8 +/- 7.7 years, and the BMDs of the subject were 0.86 +/- 0.26g/cm2(Lumbar spine), 0.60 +/- 0.10g/cm2 (Femoral neck), 0.49 +/- 0.10g/cm2(Trochanter), and 0.41 +/- 0.14g/cm2(Ward's triangle). There were no significant differences among age and nutrient intake level groups due to the small sample size. The biochemical markers showed certain degree of relationship with nutrient intake levels. The results were compared among 3 groups with different nutrient intake level classified by the percentage of Recommended Daily Allowances(RDA) for Koreans as follows low < 75% RDA, 75% RDA < or = adequate< 125% RDA, high > or = 125% RDA. The low energy and low riboflavin groups showed significantly higher serum osteocalcin levels than those of the high intake groups(p<0.05). On the other hand, there was a trend for serum Ca level to be higher with high nutrient intake. In this case, protein and thiamin were the only nutrients that reached a statistical significance(p<0.05). And the groups with low intake for protein and Ca showed significantly lower serum free testosterone levels than that of other intake groups(p<0.05). This study suggests an important role of nutrient intake levels on blood biochemical markers of bone metabolism.
- 340 View
- 1 Download


 KSCN
KSCN
 First
First Prev
Prev



