Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Article
- [English]
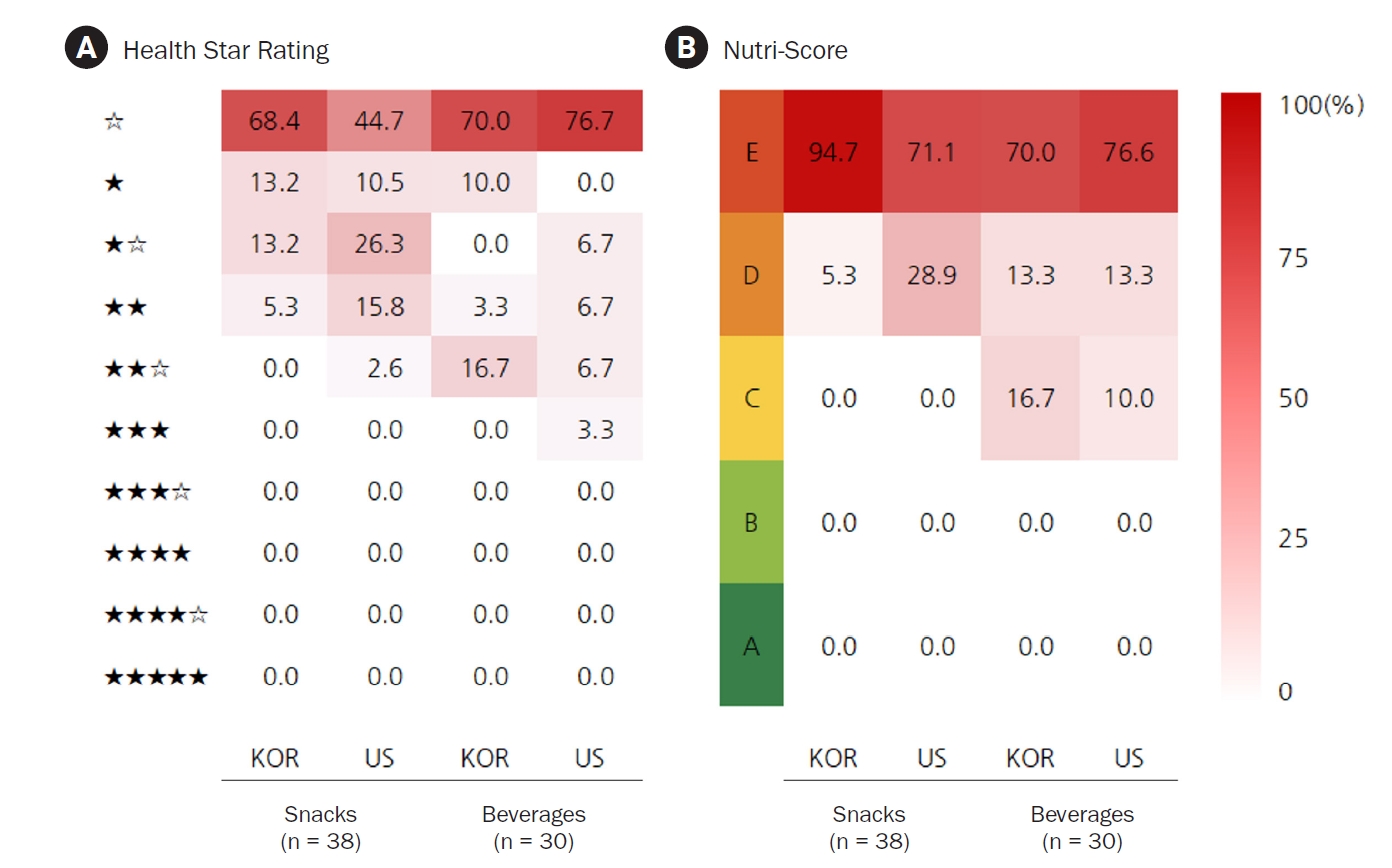
- Nutritional content and healthiness in sweet and salty snacks and beverages popular in South Korea and the United States assessed by nutrition labels: a cross-sectional comparative study
- Bo Jeong Gong, Segovia Lucas, Diewo Camara, Pauline E. Jolly, Chandrika Piyathilake, Taisun Hyun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(6):467-479. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00290
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated the nutritional differences between sweet and salty snacks and beverages in South Korea (Korea) and the United States (US). Nutritional content and healthiness were determined using back- and front-of-package nutrition labeling (FoPNL) systems.
Methods
Three snack and three beverage categories popular in Korea and the US were selected. Statistical data were used to determine the top 10–15 best-selling products in each category in each country. The selected products included chips (n = 15), cookies (n = 10), chocolate (n = 13), carbonated drinks (n = 10), fruit juices/drinks (n = 10, 5/5), and energy drinks (n = 10). The study excluded products that were artificially sweetened. Nutritional information and percentages of fruit and vegetable content in each product were collected from brand websites and grocery stores in each country. The FoPNL system was used to assess the healthiness of the products, which included multiple traffic light labels, a Health Star Rating, and a Nutri-Score.
Results
Overall, Korean snacks contained significantly more protein, total fat, saturated fat, and cholesterol than US snacks. However, the US chips and carbonated drinks contained more sodium, while the US energy drinks contained more caffeine than Korean products. The serving size of US carbonated drinks was significantly larger than that of Korean drinks, whereas the serving size of US chips was smaller than that of Korean products. The FoPNL system classified the majority of products as ‘less healthy.’
Conclusion
Our results suggest that Korean and US food manufacturers should improve the nutritional quality and/or serving size of commonly consumed food products. Policymakers in both countries should work to improve the presentation of ingredient and nutrient information on nutritional labels to assist consumers in making healthier food choices.
- 6,472 View
- 56 Download

Original Articles
- [English]
- Relationship between Snack Intake and Oral Health Behavior of Middle School Students in Gyeonggi Area
- Hyunsook Kang, Kyunghee Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(4):336-346. Published online August 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.4.336
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The study was performed to investigate the relationship between snack intake and oral health behavior in middle school students in Gyeonggi-do area.
METHODS
The survey questionnaire was recorded by middle school students from July 6 to August 24, 2011. The questionnaire included items on general characteristics, snack intake status, and oral health behavior. Among collected survey questionnaire, a total of 620 questionnaires (320 males and 300 females) were analyzed using SPSS 15.0 program.
RESULTS
Frequencies of snack and beverage intakes were significantly higher in males than in females (p < 0.001). Oral health behavior was significantly higher in students with lower snack intake compared to those with higher or average snack intake (p < 0.05). Oral health behavior for tooth brushing and toothbrush care were significantly higher in females than in males (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
Oral health behavior score that reflected better oral health of the subjects were higher as the snack intake was lower. Oral health behavior score was higher in females than in males. We conclude that the contents for oral health and nutrition education focused on snack intake need to be developed to induce changes in oral health behavior in middle school students. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of night eating on oral health characteristics and symptoms of poor oral health in adolescents: a cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Seung–Hee Hong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(2): 150. CrossRef - Evaluation of frequency of consumption of cariogenic snacks by freshmen versus the senior dental students in Tehran and the related factors: a cross-sectional study
Mahdia Gholami, Simin Z Mohebbi, Milad Mafakheri, Houra Shahhosseini
BMJ Open.2024; 14(9): e086041. CrossRef
- Effects of night eating on oral health characteristics and symptoms of poor oral health in adolescents: a cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- 1,439 View
- 8 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Relationship among Life Stress, Dietary Behaviors and High-fat Snack Intake in High School Students in Gyeonggi Area
- Seorin Doo, Youngmi Lee, Haeryun Park, Kyunghee Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(4):289-297. Published online August 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.4.289
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Stress during adolescence is related to undesirable nutritional intake and negatively affects the growth and development. This study was performed to investigate the relationship among life stress, dietary behaviors and the intake of high-fat containing snacks in male and female high school students in Gyeonggi-do area.
METHODS
The subjects were 700 high school students (350 males, 350 females) in Gyeonggi-do from July to September 2014 and the survey was performed by using questionnaire that included general characteristics, dietary behaviors, high-fat containing snacks intake, and daily life stress.
RESULTS
There was a gender difference in health-related life style and dietary behaviors, and the life stress was significantly higher in female students than in male students. For health-related life style, exercise frequency, hours of sleep and conversation time with parents had significantly negative correlations with life stress, while smoking and perceived stress had significantly positive correlations with life stress. For dietary behaviors, the frequency of eating-out had a significantly negative correlation with life stress, while the changes in amount of meal intake under stress had a significantly positive correlation with life stress. The fat intake of ‘high-stress group’ was significantly higher and high-fat containing snacks consumed by this group consisted of cookies, honey bread and fried foods.
CONCLUSIONS
It is necessary to develop appropriate programs for the emotional stability and stress relief of adolescents that provide continuous nutrition education focused on proper snack intake, desirable dietary behaviors and nutritional aspects. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos on adolescents’ dietary habits and mental health: cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Seung-Hee Hong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 156. CrossRef - Study on the relationship between dietary habits and the quality of life of some high school students in Seoul based on the nutrition quotient for adolescents (NQ-A)
Ho-Jung Kim, Jung-Sug Lee, Yookyung Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(3): 320. CrossRef - Life stress, dietary attitudes, and frequency of snack intake for college students in Seoul and Gyeonggi area: the difference between male and female students
Hyun Seung Oh, Yu bin Kim, Soyoung Park, Kyunghee Song
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(1): 91. CrossRef - Actual Status of Mukbang Viewing and Food Habits of University Students in Wonju Area
Seung-Lim Lee, Sun Hee Lee
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2022; 33(4): 631. CrossRef - Assessment of Sugar and Sodium Contents and Their Intakes in Snack Food Groups : A Focus on Cookies, Nuts, Fruits, Dairy Products, and Beverages
Yun-Jung Bae, Kyoung-A Choi, Yu-Mi Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2022; 32(4): 263. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of the Dietary Behavior of Adults Aged 20 and Over according to theMukbangViewing Time
Ha-Yan Nam, Bok-Mi Jung
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(2): 93. CrossRef - Relationship between Dietary Habits, Life Stress and Nutrition Knowledge of High School Students in Gyeonggi Area
Kyung Ae Park, Hongmie Lee, Kyunghee Song
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(2): 126. CrossRef - Association between Stress and Nutritional status of High School Students in Chungbuk using Nutrition Quotient for Korean Adolescents
In Young Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(5): 361. CrossRef - Relationship between Dietary Behaviors and Life Stress of Middle School Students in Gyeonggi Area
Kyung Ae Park, Myoung Sook Lee, Kyung Hee Song
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(5): 384. CrossRef - Body Image Perception and Eating Behaviors among Male Middle and High School Students according to Weight Status in Seoul
Bo-Mi Kim, Kyung-Hee Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2018; 28(2): 123. CrossRef
- Effects of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos on adolescents’ dietary habits and mental health: cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- 1,170 View
- 1 Download
- 10 Crossref

- [English]
- Lifestyle, Dietary Behavior and Snack Preference of Upper-grade Elementary School Students in Cheongju according to the Usage Time of Smartphones
- Hayeon Kim, Munkyong Pae
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(1):40-52. Published online February 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.1.40
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to examine the length of exposure to smartphone and its association with dietary behavior toward snacks, lifestyle, and nutrition knowledge in elementary school students.
METHODS
Subjects were 372 5th and 6th grade schoolchildren in Cheongju, Korea, and data was collected by a self-administered questionnaire. They were divided into two groups by the time spent using smartphone: moderate (< 2 hours/day) and overexposure (≥ 2 hours/day). Data was analyzed using frequency analysis, χ²-test, and independent t-test as well as analysis of covariance when necessary.
RESULTS
Approximately half of subjects (41.4%) reported spending ≥ 2 hours/day using smartphone. That habit was more frequent among students in the 6th grade, those who received more monthly allowance, and who has a working mother. 63.4% of the subjects reported that they consumed snacks while watching television, using a computer and/or a smartphone and 48.1% said that they consumed snacks while they use a smartphone. Both situations were most prevalent among those with overexposure to smartphone (≥ 2 hours/day). We also observed that a higher percentage of subjects from the overexposure group spent more money on snack foods with the preference for ice cream, fast food, and carbonated drinks. Further, those in the overexposure group consumed more ice cream, cookies, and carbonated drinks. In addition, they had less desirable dietary behavior and health-related lifestyle (sleep duration and frequency of regular exercise) compared to those with moderate smartphone usage (< 2 hours/day). However, there was no statistical difference in nutrition knowledge among children with different degrees of smartphone usage.
CONCLUSIONS
Our results showed that longer smartphone use was associated with less desirable snack preference/consumption and other dietary behavior in elementary school students. Thus interest and positive attitudes towards healthy snacks and diet should be reinforced in nutrition education programs, especially for those who are prone to use smartphones. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the association between nomophobia, mindful eating, and nutritional status
Aliye Kuyumcu, Müberra Yıldız, Kadriye Toprak
Turkish Journal of Clinics and Laboratory.2025; 16(2): 349. CrossRef - The impact of maladaptive perfectionism on college students' bedtime procrastination: The chain mediating effects of nomophobia and physical exercise
Yong Jiang, Chuanyang Jiang
Acta Psychologica.2025; 260: 105504. CrossRef - The relationship between smartphone usage and eating behavior for elementary school students in Gangneung, South Korea: cross-sectional study
Minji Kim, Meera Jang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(4): 278. CrossRef - Screen time, mealtime media use, and dietary behaviors in Korean preschoolers: a cross-sectional study
Young-Hee Han, Saerom Shin, Eun Yeol Woo, Hye-Kyung Park, Taisun Hyun
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(3): 206. CrossRef - Comparing the Mediating Effect of Adolescent Lifestyle Profiles on the Relationship between Smartphone Addiction and Health-related Quality of Life Among Male and Female Senior High School Students in the Philippines
Danilo B. Buctot, Nami Kim, Sun Hee Kim
International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction.2023; 21(1): 511. CrossRef - The Effects of Smartphone and Internet Gaming Addiction on Eating Attitudes Among University Students
Bahar Yeşil Örnek, İbrahim Gündoğmuş
Psychiatry Investigation.2022; 19(1): 1. CrossRef - The role of nomophobia and smartphone addiction in the lifestyle profiles of junior and senior high school students in the Philippines
Danilo B. Buctot, Nami Kim, Sun Hee Kim
Social Sciences & Humanities Open.2020; 2(1): 100035. CrossRef - Relationship between the Intake of Children's Favorite Foods and Policy based on Special Act on Safety Control of Children's Dietary Life
Taejung Woo, Jihye Yoo, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(2): 106. CrossRef - Health Behavior Factors Associated with Sugar-sweetened Beverage Intake among Adolescents
Hyae Min Gu, Jong Park, So Yeon Ryu
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(3): 193. CrossRef - A Study on Weight Control Behaviour, Eating Habits and Health-related Life Habits According to Obesity Degree of University Students in Jeonbuk
Hye-Soon Chang
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2016; 25(1): 73. CrossRef - Weight loss effects of Bariatric Surgery after nutrition education in extremely obese patients*
Eun-Ha Jeong, Hong-Chan Lee, Jung-Eun Yim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(1): 30. CrossRef - A Study of Nutrient Intakes, Blood Lipids and Bone Mineral Density according to Obesity Degree by Percentage of Body Fat and Age between Male and Female Teacher in Jeonbuk Province, Korea
Hye-Soon Chang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(1): 49. CrossRef - A Study of Glycemic Index, Glycemic Load and Food Sources according to Body Mass Index in Female College Students
Jee-Young Yeon, Eun-Young Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(4): 429. CrossRef
- Evaluation of the association between nomophobia, mindful eating, and nutritional status
- 1,415 View
- 6 Download
- 13 Crossref

- [English]
- Interrelations Among Snack Preference, Purchasing Behaviors and Intake in Upper Grade Elementary School Students: Compared by the Gender and TV Watching Time
- Eun Sil Her
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(5):429-441. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.5.429
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to examine the interrelations among snack preference, purchasing behavior and intake of fifth and sixth grade students in elementary schools in Gyeongnam province. Frequency of snack intake was the highest in those who reported 'once a day' (45.6%) snack habit. Longer-time television viewers also showed higher frequency of snack intake than shorter-time viewers. Thirty-three percent of students purchased snacks by themselves and the frequency of snack purchasing had a significant positive relationship with TV watching time (p < 0.01). The main reason, place and time of eating snacks were 'hunger' (79.2%), their home environment (50.9%) and 'after school hours' (89.7%). The favorite snack was 'ice cream' and, this snack habit was significantly different by gender of the child (p < 0.01) and TV watching time (p < 0.01). 'Milk and dairy products' scored highest (3.47) in snack intake frequency among longer-time TV viewers (> 2hr) compared to shorter-time TV viewers and this difference was statistically significant (p < 0.001). The snack preference score was correlated positively (r = 0.454) with the intake frequency for snack and its explanation power (R2) was 20.5%. With regard to snack purchase behaviors, the scores of 'checking the expiration date' and 'comparing the price with similar products' were high (in what group?). Female students (p < 0.001) and shorter-time TV viewers (< 2hr) (p < 0.01) had a more reasonable purchasing behavior. The total score of preference was significantly higher (p < 0.05) in shorter-timeTV viewers (< 2hr). In the correlation between snack purchasing behaviors and intake frequency, attractiveness (r = 0.208, p < 0.001) and preference (r = 0.330, p < 0.001) showed significant positive correlations. The result of regression analysis, preference only was selected (R2= 0.108).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The relationship between smartphone usage and eating behavior for elementary school students in Gangneung, South Korea: cross-sectional study
Minji Kim, Meera Jang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(4): 278. CrossRef - Association between eating habits, sweet taste assessment, and high-sugar food consumption among elementary school students in Daegu: a descriptive study
Min-Jung Kim, Eun-Kyung Shin, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(2): 104. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of the Dietary Behavior of Adults Aged 20 and Over according to theMukbangViewing Time
Ha-Yan Nam, Bok-Mi Jung
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(2): 93. CrossRef - A Study on the Development of the Goals and Contents System of Healthy Dietary Education Program for After-School Care in Lower Grade in Elementary School
Jung-Hyun Kim, Myoung Hee Lee, Okjin Park, Kyung Sook Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(1): 24. CrossRef - Eating patterns of children's favorite foods and its related factors among elementary, middle, and high school students in Korea
YuJin Lee, Seungmin Lee, KyoungAe Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee, Inkyung Baik
Nutrition Research and Practice.2017; 11(6): 517. CrossRef - Lifestyle, Dietary Behavior and Snack Preference of Upper-grade Elementary School Students in Cheongju according to the Usage Time of Smartphones
Hayeon Kim, Munkyong Pae
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(1): 40. CrossRef - Association of Interpersonal Relationships with Preference and Intake Frequency of Snack with a Focus on Obesity Index and Snack Preparations in Upper Grade Elementary School Students
Eun Sil Her
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2015; 28(2): 178. CrossRef - Perceptions and Use of Premium Snacks and Associated Factors in School Aged Children and Their Mothers in Kyung-Ki Area
Hye-Young Yang, Hyo-Suk Lee, Jayong Chung
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2014; 14(3): 121. CrossRef
- The relationship between smartphone usage and eating behavior for elementary school students in Gangneung, South Korea: cross-sectional study
- 1,414 View
- 3 Download
- 8 Crossref

- [English]
- Effects of Occasional Mid-Morning Snacks on Dietary Behaviors and School Life in Elementary School Students
- Eun Ji Park, Yuri Kim, Yunsook Lim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(6):661-671. Published online December 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.6.661
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of occasional mid-morning snacks (MMS) on dietary behaviors and school life among elementary students. The students, mothers, and teachers from two elementary schools in Seoul were selected. The schools have been provided a steamed sweet-potato or potato, or a piece of ricecake or cake with a pack of milk as MMS 3-4 times a month for more than 3 years. Most students were satisfied with the MMS. Mothers and teachers reported that their children or students were happier, more active, and more energetic in school with MMS. Furthermore, the students answered that they could drink milk better on the day when the school provided MMS. Many students felt that it was relevant to serve a simple menu at lunch time if they were served MMS. Also, students became more interested in school meals or foods with MMS. In addition, mothers who had jobs wanted more frequent MMS. The degree of satisfaction about MMS of the teachers was higher than that of students or mothers. Many teachers thought that their students drank milk better with MMS and further, that it made students to drink more milk on other days. In conclusion, MMS had positive effects on the dietary behavior and school life of elementary students. Therefore, it can be a good option for eliminating skipping breakfast because it provides more nutrition, makes students drink more milk, and allows students to enjoy school activities more.
- 928 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Nutrition Label Use, Self-Efficacy, Snacking and Eating Behavior of Middle School Students in Kyunggi Area
- Seo Yeon Ko, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(4):513-524. Published online August 31, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was designed to examine nutrition label use, self-efficacy, snacking and eating behaviors of middle school students, and to investigate if these characteristics were different by nutrition label use. A cross-sectional survey was conducted to 348 middle school students in Kyunggi, Korea. About a third of subjects read nutrition labels when they purchased snacks/packaged foods. Most nutrition label users were interested in reading information on calories, fat and trans-fat. Self-efficacy of eating/selecting snacks or general nutrition behavior was moderate (mean score: 44.4 out of 60), with significantly higher score in nutrition label users compared to nonusers (p < 0.001). Nutrition label users felt more confident in 9 items out of 15 items of self-efficacy, such as "taking fruits instead of cookies/candy for snack" (p < 0.001), "choosing milk instead of soft drink" (p < 0.01), "not having snacks after dinner" and "avoiding processed foods for snacks" (p < 0.05). Subjects had snacks 1.3 times a day, and nutrition label nonusers consumed snacks more frequently than the counterparts (p < 0.01). About 55% of nutrition label users and 64.7% of nonusers mainly purchased snacks for themselves (p < 0.05). Commonly purchased snacks by adolescents were ice cream, cookies/chips, breads and ramen. Major considerations in purchasing snacks were taste (46.9%) and price (34.6%). In selecting snacks, the influence of friends and parents was greater than the other sources. Based on eating frequency of snacks, nutrition label users were more likely to consume healthy snacks, such as fruit juices, vegetables, milk, yogurt, and potato/sweet potato than nonusers (p < 0.05). Eating behaviors measured by 15 items scored 33.6 out of 45. Nutrition label users showed better eating behaviors, such as "eating meals slowly", "eating foods cooked with plant oil", and "eating out less frequently" (p < 0.05). Study results showed that majority of adolescents did not read nutrition labels, selected snacks for themselves and had somewhat unhealthy foods for snacks. This study also showed the differences in self-efficacy, snacking and eating behaviors between nutrition label users and nonusers. In nutrition education, it is necessary to stress the importance and skills for reading nutrition labels. It is also needed to help adolescents to select healthy snacks and have desirable eating behaviors, as well as increasing self-efficacy.
- 369 View
- 6 Download

- [English]
- Snack Consumption Behaviors and Nutrition Knowledge among Elementary School Students in Siheung-si
- Eun A Cho, Soo Kyung Lee, Gyu Jin Heo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(2):169-179. Published online April 30, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Good snack consumption behaviors are important among elementary students because snack provides additional energy and nutrients and because good dietary behaviors should be formed during early stages of life. This study investigated, among elementary school students, 1) snack consumption behaviors, 2) snack-related nutrition knowledge level, and 3) relationships between snack behaviors and snack-related nutrition knowledge. A convenience sample (N = 372), drawn from 5th and 6th graders of an elementary schools in Siheung-si, Gyeonggi-do, completed a pre-tested questionnaire. More than 85% of the participants snacked more than once per week. Most (77%) had their snacks at home. Fruit and fruit juice were the most frequently consumed and the most liked snack items. Taste was the most important in choosing a snack item closely followed by health/nutrition. Snack-related knowledge level was relatively high and the participants obtained their nutrition knowledge through mass media (30.4%) and family/friends (29.0%). Snack-related nutrition knowledge level and snack consumption behaviors showed positive relationships in various areas such as choosing more nutritious snack items and checking nutrition labels. Although this study was limited by its cross-sectional study design, these positive relationships suggest that better nutrition knowledge could result in better behaviors. Results of this study indicated that factual nutritional knowledge has been well transmitted to students. Therefore, future nutrition education on snacking could focus more on providing problem-solving and operational knowledge.
- 498 View
- 11 Download

- [English]
- Survey of Cookie Consumption and Nutrition Labelling of Cookie Consumed in High School Students
- Ji Yeon Yoo, Youngnam Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(2):147-157. Published online April 30, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to find out the information on nutrition labeling and how many calories and nutrients the high school students consumed for 1 day from cookies. A total of 74 male and female high school students in Suwon were surveyed and 56 cookies that they consumed were examined. Background data were collected by questionnaire, cookie intake by 24-hr recall, and the calories and nutrients content in cookies and the amount of intake by nutrition information on the wrapping paper of cookie. The statistical analysis for the data was done by SPSS 12.0. Energy contents in 1 serving size of cookie were 90~315 kcal, average of 170 kcal. The protein contents were 0~7 g, fat 2~20 g, cholesterol 0~55 mg, and sodium 30~390 mg in 1 serving size of cookie. Most of the cookies (80%) examined contained no trans fat at all, which is desirable. Among the types of cookies, snacks contained higher quantities of calories and sodium, the pie contained more sugar and cholesterol, and the biscuit had more trans fat. One fourth of the cookies examined belonged to 'high calorie, low nutritious food' according to the criteria proposed by The Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs. Thus the excessive intake of cookies might result in nutritional imbalance. There were large differences in calorie intake among students, from zero who did not intake any cookies at all to maximum 818 kcal/day, an average of 75 kcal/day. When the students who did not intake cookies were excluded, energy 205 kcal. fat 10g, sodium 177mg were consumed from the cookie for a 1 day on average.
- 390 View
- 5 Download

- [English]
- The Daily Intakes of Nutrients and Snacks of High School Smokers and Non-Smokers
- Young Mi Song, Jang Il Han, Seong Ai Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2008;13(4):476-488. Published online August 31, 2008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigates the relationship of smoking on daily intake of nutrients and snacks in the Chungnam and Daejeon high school students. Up to date scientific nutrition education and counseling programs in the regular school system is needed for a professional nutrition education teacher. The primary objective of this study was to provide useful information to nutrition education teachers. A survey was conducted with 400 high school students in the Chungnam and Daejeon areas. 381 out of 400 questionnaires were analyzed with SPSS 12.0K. The subjects were composed of 49.8% male, 50.1% female and 40.9% regular high school students, 59.1% business high school students and smokers 43.1%, non-smokers 56.9%. 43.4% of smokers had been smoking since middle school. On analysis of daily nutrient intakes, 16 out of 19 nutrients except animal calcium, Vitamin A and Vitamin C were much more consumed by the smoking group than the non-smoking group non-significantly. Especially vegetable fat and Vitamin E were higher in the smoking group than the non-smoking group(p < 0.05). The intake ratio of carbohydrates: protein: fat was similar in the two groups (smoking group 55 : 15 : 29, nonsmoking group 56 : 15 : 28). Intakes of Vitamin B1 and potassium in comparison with the Korean dietary reference intakes (KDRI) were under 50% in both groups. However, sodium was taken over 200% compared to KDRI in both groups. Intakes of Vitamin C in the smoking group were as low as 76.5% in comparison to KDRI. Smokers need to increase the intakes of Vitamin C considering that smokers need to intake Vitamin C two times than non-smokers. Nutrient intakes from snacks in the smoking group were higher than the non-smoking group. Nutrients that originated from snacks which took over 20% among daily nutrient intakes were 12 nutrients (energy, fat, carbohydrate, calcium, P, Fe, K, Vitamin B1, Vitamin B2, Vitamin C, Vitamin E, dietary fiber) in the smoking group compared to 7 nutrients (energy, vegetable protein, fat, carbohydrate, calcium, Vitamin B2, Vitamin C) in the non-smoking group. The smoking group was significantly paying more money for snacks each month than the non-smoking group was (p < 0.01). Periods of consumption were irregular in the smoking group(p < 0.05) and the smoking group was used to taking snacks in the morning compared to the non-smoking group. The smoking group preferred sweets and high calorie food over other snacks in comparison of the non-smoking group. The nonsmoking group had better eating habits than the smoking group
- 319 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Snacking Behaviors of Middle and High School Students in Seoul
- Seul Ki Choi, Hyeon Jeong Choi, Nam Soo Chang, Sung Hee Cho, Young Sun Choi, Hye Kyung Park, Hyo Jee Joung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2008;13(2):199-206. Published online April 30, 2008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate snacking behavior in adolescents. We selected one middle school and one high school in 11 school districts in Seoul. The subjects were 1,813 students (904 boys and 909 girls) in 21 schools (11 middle schools and 10 high schools). Subjects reported their snacking behavior: snack frequency, snack type, snack time, with whom to eat snack, place to purchase snack. The subjects were classified into four groups by gender and schooling. The mean snack frequency was 2.8. Girls ate snacks more frequently than boys (p < 0.001). More than half of subjects ate 1 to 3 snacks a day. Only 9.3% of them did not eat any snack. Tangerine was highly ranked in snack type. Each subject groups had different snack time (p < 0.01) and type of snack (p < 0.001). Most snack was consumed alone (46.6%), however they mainly ate fruits and other foods with family. 46.9% of snacks were purchased outside. A typical snack time was 'before dinner' for most snacks except fruits. Unhealthy foods like soft drinks, cookies, chips, candies, chocolates, ice creams had relatively high proportion in snack consumption with friends. In conclusion, adolescents had different snacking behaviors by their age and gender. These results indicate necessities of multi-dimensional efforts at home, school, media and government level considering adolescents' age and gender for their healthy snacking behavior.
- 374 View
- 6 Download

- [English]
- Analysis of Weight Maintenance Behavior among Female University Students
- Seolhyang Baek, Eunjeong Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2007;12(2):150-159. Published online April 30, 2007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Since the 1980's, despite the conclusion of a number of studies in Western countries focusing upon weight maintenance there has been no similar research in Korea which takes into account the contrasts of culture and eating habits between east and west. In order to identify eating, snacking and exercise behaviors, 24 female university students who have maintained weight for at least a year were enrolled for an 11 day study. Participants were required to sign into the program and complete the questionnaire, answering questions by concerning what they ate and did everyday. After excluding unanswered questions, data over 11 days were exported into the Microsoft Excel spreadsheet, then both ANOVA and Kendall's tau correlation were applied with SPSS. 75% of weight maintainers had normal BMI (18-23.5) in relation to Korean standard, and appeared to eat a main meal smaller than moderate in portion size. Only two days showed that amount of breakfast eaten negatively correlated with lunch (p < 0.05), while no correlations between amounts of lunch and dinner eaten over all study period. Compared with breakfast or lunch, dinner was usually larger in portion size, but some variables such as TV viewing, restaurant meals, number of people at dinner table seemed not correlated with amount of dinner eaten. In addition, the weight-maintainers reported they rarely consumed snacks or sweetened beverages. Unlike their western counterparts, few participants reported that they took part in regular exercise during the day, which may lead us to the conclusion that these young female weight maintainers seem to maintain their weight with eating behaviours such as 'eat small portion', 'avoid snacking' and 'avoid soft drinks' rather than doing regular exercise. The study did not include a control group, and was foreshortened due to technical difficulties so it may be necessary to repeat the study while considering these two points.
- 299 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Comparison of Weight Control Behavior and Self-esteem between Healthy Weight and Obese Children
- Seolhyang Baek, Junghee Yeo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2006;11(5):562-574. Published online October 31, 2006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The study compared eating and physical activity related behaviors and self-esteem between healthy weight and obese children by presenting 175 primary school students in Busan City and Gyeongsang province with a self-reported questionnaire and Coopersmith's self-esteem inventory. The questionnaire was composed of 25 items, weighted primarily by a Likert scale. The self-esteem inventory presented to the students comprised 25 "Yes" or "No" response questions to different statements. The study found obese children were more likely to think they always had to control their weight (p = 0.000), reportedly measuring their weights significantly more than the healthy weight children. Also the study found that obese children are significantly more likely than healthy weight children to go on a diet, however neither group were successful in losing weight as the duration of the diet in 79.5% of the total sample lasted no longer than one week. In comparison to healthy weight children, obese children reported that they consumed fewer snacks during the day, avoided snacking subsequent to an evening meal and exercised more frequently for as long as physically possible. Interestingly, we found no difference of reported self-esteem between groups, though the obese group were more likely to answer that their parents did not understand them (p = 0.055). Based on these findings, we concluded that the obese children who participated in the study were more aware of their body weights than the healthy weights children. It may be necessary to investigate further the relationship between self-esteem and participants' weights while considering other variables such as personality and body image.
- 367 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- The Different View Point Of Child Education Center Food Service Program between the Parents and the Teachers
- Youngmee Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(5):654-667. Published online October 31, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To survey the different view points about food service programs among parents and teachers, 2 types of questionnaires, which consisted of attitude, perception, satisfaction and demand of the food service program in child education centers, were used. The data was collected from 2450 parents and 450 teachers who attended a child education center in 16 provinces, nationwide. SPSS was used for descriptive analysis and ANOVA test and chi2-test. The finding results were as follows. 1. The average serving size of meal (lunch) were 80 meals per day and 167 meals per day at large institutions. Mean cost of snacks was 14,709 won per month and mean costs of lunch were 29,319 won per month. The mean price was not significantly different according to the scale of institution. The numbers of servings of lunch, morning snack and afternoon snack were 5, 3.4 and 3.5 times per week each. 56.4% of the institutions served meals to children in classrooms, but the national/public institutions, which were attending elementary school, served meals in a dining place in the elementary school. 2. Teacher controlled serving portion size of snacks (79.6%) and lunch (88.8%) and 30.1% of teacher did not allow leaving lunch food. The ratio of knowing about preserved meals of the teacher who worked at a small institution was significantly higher than the teacher who worked at large institutions (p < 0.01). 3. Between parents and teachers, several different view points about school lunch programs were detected. Most parents and teachers wanted that the school lunch to be fully cooked and served at the child education institution itself, but 12.2% of parents and 14.4% of teachers wanted a catering service. The teachers group preferred 'lunch box from home' and 'home partially prepared lunch' as an ideal meal serving type than the parent groups (p < 0.01). And there were significantly different view points about price factors in school meals, teachers group highly answered that operating expenses must be added in meal prices. 4. The teacher groups' priorities of education activities during meal time were a significantly lower score than parents group in overall education activities. Teacher and parent groups pointed out that individual sanitation activities were most important of the education activities during meal time, but promoting good eating habits was the lowest score in both groups. 5. 'Improving taste and food quality' was most urgent in food service at child education centers, but there were significantly different view points between parent groups (64.5%) and teacher groups (43.8%)(p < 0.05). They answered at a lower percent in 'employee qualified person' and 'cost control' point to improve food service, but there were also different opinions between the two groups (p < 0.01). 6. As to the matter of the advantages and disadvantages of catering services, two group answered that the advantages of a catering service were 'convenience' and 'to solve facilities and labor problems', disadvantages were 'lower in food freshness' and 'sanitation problems'. There were also several different view pionts in catering services, the parents groups were more anxious about food sanitation than teachers. This study found several different view points about school food services among parents and teachers. To improve food services at child education institutions, there is a need to adjust the differences between the two groups through interactive communication channels and education and to employ dietitians as taking charge of adjusting roles between the two groups.
- 336 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- A Study of the Frequency of Food Purchase for Snacking and Its Related Ecological Factors on Elementary School Children
- Seock Ah Kang, Joung Won Lee, Kyeung Eun Kim, Jae Ok Koo, Dong Yean Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2004;9(4):453-463. Published online August 31, 2004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In order to investigate food purchase frequency of elementary school children and its related ecological factors, 4314th, 5th and 6th grade elementary school children and their mothers, living in Seoul and Daejon, small city and rural area of Chungnam Province, were participated in this study. The subjects and their parents were surveyed by a selfrecording questionnaire about food purchase frequency and some ecological factors. Average height and weight of the subjects by gender and grade were similar to or a little bit more than the 1998 Korean Growth Standard. According to relative body weight, 30.6% and 10.8% of the subjects belonged to under-weight and obesity categories, respectively. Of the subjects, 46.9% used PC telecommunication or internet, 53.8% of them used it for less than an hour per day, and 46.4% watched TV for 2 to 4 hours a day. About 42% of the subjects spent 500 Won or less daily to buy snacks. A half of the subjects took snacks once a day because of hunger. Mothers' nutrition knowledge score was averagely 8.16 out of 13 full score and the average attitude score was 43.22 out of 50 full score. Foods purchased more than once a week were milk and yoghurt, cookies, ice-cream, ramyun, and gum in order. Family income, parents' education level, mothers' nutrition knowledge and food attitude score, students' snacking frequency and TV watching time showed significant correlations with purchase frequencies of some individual food items. In conclusion, the elementary school children considered taste most important rather than nutrition in buying snacks and most frequently bought carbohydrate foods and concentrated sugars except milk. Ecological factors such as mothers' nutritional knowledge and food attitude, TV watching time and snacking frequency had influenced the children's food purchase frequency. Accordingly, it is necessary to educate both children and their mothers about good food purchase and the importance of snacking.
- 554 View
- 9 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



