Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Korean J Community Nutr > Volume 23(1); 2018 > Article
-
Research Article
- Awareness and Consumption of Energy Drinks and Associated Factors among College Students in Cheongju
-
Tae Yang Kim, Soo Min Kim, Ji Yeon Kim, Jeong Yeon Im, Hui Yu, Young-Hee Han, Taisun Hyun

-
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition 2018;23(1):60-72.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.1.60
Published online: February 28, 2018
Department of Food and Nutrition, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Taisun Hyun. Department of Food and Nutrition, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Chungbuk 28644, Korea. Tel: (043) 261-2790, Fax: (043) 267-2742, taisun@cbnu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2018 The Korean Society of Community Nutrition
This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 2,094 Views
- 20 Download
- 7 Crossref
Abstract
-
Objectives
- This study was conducted to investigate the awareness of energy drinks, energy drink consumption behaviors, and associated factors among college students.
-
Methods
- A total of 536 students from three universities in Cheongju completed a self-administered questionnaire regarding awareness and consumption of energy drinks as well as general characteristics, health-related characteristics, and eating habits.
-
Results
- Approximately half of the respondents reported they knew what energy drinks were, while 45.7% had heard of energy drinks but did not know what they were. However, 76.9% had experience in using energy drinks. The main reason for using energy drinks was to stay awake, and the main place that they were used was on campus or at the library. More than 70% of energy drink users did not read the caffeine contents of energy drinks. After consuming energy drinks, 31.3% experienced adverse effects, the most serious being sleep disturbance. Approximately 33% of students consumed energy drinks once a month or more frequently, and men consumed energy drinks more frequently than females. Energy drink users who consumed at least one drink each month were more likely to be natural science major or drink more milk for male students, and to have more allowances or consume less meat for female students, compared with non-users.
-
Conclusions
- Our study showed that 33% of students consumed at least one energy drink each month, and there were a small number of students consumed energy drinks almost every day or energy drinks mixed with alcohol. Accordingly, college students should be taught potential health hazards of energy drinks mixed with alcohol as well as energy drinks alone. In addition, reading labels about caffeine and sugar contents in energy drinks is encouraged.
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgments
- 1. Korean Consumer Agency. A survey on current safety issues of energy drinks [Internet]. 2013; updated 2013 Nov 15]. cited 2017 Dec 1]. Available from: http://www.kca.go.kr/brd/m_46/view.do?seq=792&itm_seq_1=3.
- 2. Heckman M, Sherry K, Mejia D, Gonzalez E. Energy drinks: an assessment of their market size, consumer demographics, ingredient profile, functionality, and regulations in the United States. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 2010; 9(3): 303-317.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Lee YM. Energy drinks, emerged as a new blue ocean [Internet]. Next economy; 2010; updated 2010 Aug 24]. cited 2018 Jan 30]. Available from: http://www.nexteconomy.co.kr/news/articleView.html?idxno=6208.
- 4. Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs·Korea Agro-Fisheries & Food Trade Corporation. A report on consumption trend of processed food: focused on functional beverages [Internet]. 2014; updated 2014 Oct 11]. cited 2017 Dec 1]. Available from: http://www.atfis.or.kr/article/M001040000/view.do?articleId=1247.
- 5. Yoo SY. Energy drinks, too much is harmful [Internet]. Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information; 2012; updated 2012 Nov 5]. cited 2018 Jan 30]. Available from: http://scent.ndsl.kr/site/main/archive/article/에너지-음료-과하면-독?cp=1&sv=에너지음료&pageSize=8&sortDirection=DESC&listType=list&catId=11&artClass=100.
- 6. Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs·Korea Agro-Fisheries & Food Trade Corporation. Situation in segmental market of processed food: beverages [Internet]. 2017; updated 2017 Oct 15]. cited 2017 Dec 1]. Available from: http://www.atfis.or.kr/article/M001050000/view.do?articleId=2659&page=&searchKey=&searchString=&searchCategory=.
- 7. Reissig CJ, Strain EC, Griffiths R. Caffeinated energy drinks: a growing problem. Drug Alcohol Depend 2009; 99(1): 1-10.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Seifert SM, Schaechter JL, Hershorin ER, Lipshultz SE. Health effects of energy drinks on children, adolescents, and young adults. Pediatrics 2011; 127(3): 511-528.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 9. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. Changes in safety policy of food, medicine and medical supplies since 2013 [Internet]. 2013; updated 2013 Jan 7]. cited 2017 Dec 1]. Available from: http://www.mfds.go.kr/index.do?mid=675&seq=19445&cmd=v.
- 10. Ministry of Health and Welfare, The Korean Nutrition Society. Dietary reference intakes for Koreans 2015. Sejong: Ministry of Health and Welfare; 2015.
- 11. Lee HS, Kwon SO, Yon M, Kim D, Lee JY, Nam J. Dietary total sugar intake of Koreans: based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), 2008-2011. J Nutr Health 2014; 47(4): 268-276.Article
- 12. Malik VS, Popkin BM, Bray GA, Despres JP, Hu FB. Sugar-sweetened beverages, obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disease risk. Circulation 2010; 121(11): 1356-1364.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 13. Marczinski CA, Fillmore MT. Energy drinks mixed with alcohol: what are the risks? Nutr Rev 2014; 72(S1): 98-107.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Striley CW, Khan SR. Review of the energy drink literature from 2013: findings continue to support most risk from mixing with alcohol. Curr Opin Psychiatry 2014; 27(4): 263-268.PubMed
- 15. Park S, Onufrak S, Blanck HM, Sherry B. Characteristics associated with consumption of sports and energy drinks among US adults: National Health Interview Survey, 2010. J Acad Nutr Diet 2013; 113(1): 112-119.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Larson N, Laska MN, Story M, Neumark-Sztainer D. Sports and energy drink consumption are linked to health-risk behaviours among young adults. Public Health Nutr 2015; 18(15): 2794-2803.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 17. Poulos NS, Pasch KE. Energy drink consumption is associated with unhealthy dietary behaviours among college youth. Perspect Public Health 2015; 135(6): 316-321.ArticlePubMedLink
- 18. Yun H, Kim SH, Lee CY. An analysis of factors affecting energy drink consumption college students. Korean J Health Educ Promot 2013; 30(3): 1-12.
- 19. Lee J, Huh W, Choi EJ. Pattern analysis of high-caffeine energy drink consumption and adverse effects among college students in a university. Yakhak Hoeji 2013; 57(2): 110-118.
- 20. Park JS, Lee EJ, Lee CY, Jung HS. Consumption status, risk awareness and experience of adverse effects of high-caffeine energy drink among university students. J Korean Public Health Nurs 2015; 29(1): 102-114.Article
- 21. Yoo HS, Sim KH. Survey on the high-caffeine energy drink consumption status of university students in Seoul. J East Asian Soc Diet Life 2014; 24(3): 407-420.Article
- 22. Kim YJ, Jeon EM, Shim SB, Seo HJ. Effects of awareness and knowledge of energy drinks on consumption patterns among college students. Korean J Health Promot 2015; 15(1): 31-38.Article
- 23. Lee HY, Hwang EJ, Hyun T. Development of an eating habit checklist for screening college students at risk of inadequate nutrient intake. J Hum Ecol 2015; 19(2): 67-79.
- 24. Ra JS, Yun HK, Kim HS, Ryu JL. Associated factors on energy drink consumption among Korean high school students. J Korean Soc Sch Health 2017; 30(1): 48-58.Article
- 25. Picard-Masson M, Loslier J, Paquin P, Bertrand K. Consumption of energy drinks among Quebec college students. Can J Public Health 2017; 107(6): e514-e519.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 26. Malinauskas BM, Aeby VG, Overton RF, Carpenter-Aeby T, Barber-Heidal K. A survey of energy drink consumption patterns among college students. Nutr J 2007; 6(1): 35.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 27. Attila S, Cakir B. Energy-drink consumption in college students and associated factors. Nutrition 2011; 27(3): 316-322.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Cabezas-Bou E, De León-Arbucias J, Matos-Vergara N, Álvarez-Bagnarol Y, Ortega-Guzmán J, Narváez-Pérez K. A survey of energy drink consumption patterns among college students at a mostly Hispanic university. J Caffeine Res 2016; 6(4): 154-162.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 29. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. Increase in high risk drinking and bomb cocktail drinking. Survey results of alcoholic beverage consumption in 2013 [Internet]. 2014; updated 2014 Dec 23]. cited 2017 Dec 1]. Available from: http://www.mfds.go.kr/index.do?mid=675&seq=25988&cmd=v.
REFERENCES
Eating habits of the study participants

1) N (%)
2) Diagnosed using eight questions above based on the previous study [23]
*: p<0.05, ***: p<0.001 Significantly different by χ2-test
Eating habits among energy drink users1) and non-users

1) Students who consume energy drink once a month or more frequently
2) N (%)
3) Diagnosed using eight questions above based on the previous study [23]
*: p<0.05 Significantly different by χ2-test
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- The Impact of Promotional Activities on the Purchase and Repurchase Intention of Energy Drinks in Yemen Under Different Levels of Awareness of the Potential Adverse Effects
Majid Mapkhot Goaill, Mohammed A. Al-Hakimi, Hamood Mohammed Al-Hattami, Mohsen Ali Murshid, Amal Al-Mogahed, Sharf Obad
Sage Open.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of Usage, Preference, and Satisfaction for Convenience
Store Dessert among University Students in Chungbuk Area
Go Eun Lee, Hye-In Yang, Yun-Jung Bae
Journal of Biotechnology and Bioindustry.2021; 9: 63. CrossRef - Energy drinks
Towhid Hasan, Marjia Sultana, Md. Tareq Hossain, Lima Khatun, Md. Alauddin
Journal of Health Research.2020; 34(3): 221. CrossRef - Energy Drink Consumption and Dietary-, Lifestyle-, and Mental Health-Related Behaviors in Korean Adolescents: Based on the 10th–13th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-Based Survey
Jiwon Oh, Jayong Chung
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2019; 19(3): 145. CrossRef - Sleep Quality and Its Association with the Dietary Behavior and Lifestyle of University Students in Cheongju
Sewhan Jin, Munkyong Pae
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(5): 395. CrossRef - Consumption of energy drink and associated factors
Towhid Hasan, Marjia Sultana, Lincon Chandra Shill, Sara Sultana
Nutrition & Food Science .2019; 50(1): 131. CrossRef - Consumption Behaviors of Energy Drinks and Comparison of Associated Factors Among College Students in Gwangju
DaWun Seo, Bok Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(4): 289. CrossRef
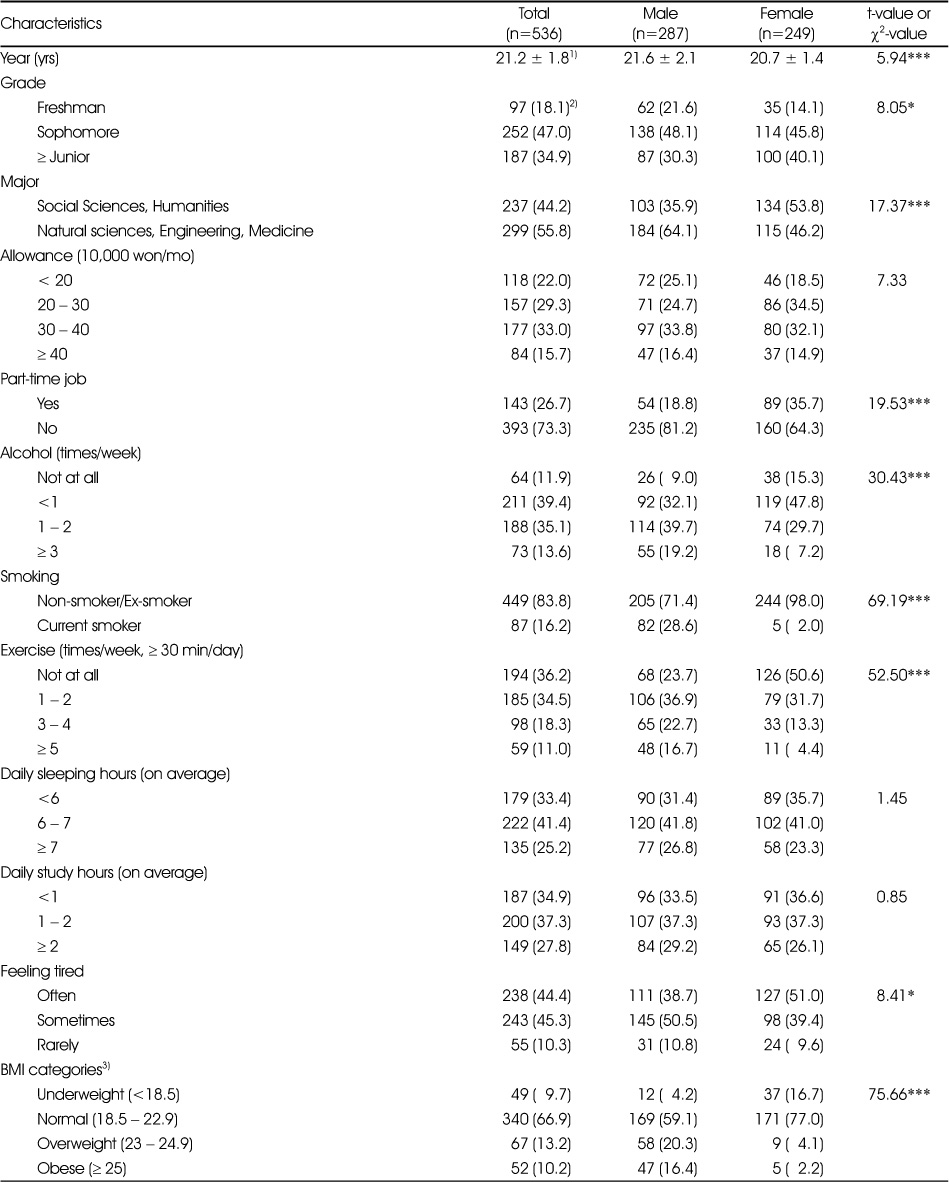
Characteristics of the study participants
1) Mean ± SD
2) N (%)
3) n=508, 286, 222 for total, male and female, respectively due to missing data
*: p<0.05, ***: p<0.001 Significantly different by χ2-test
Eating habits of the study participants
1) N (%)
2) Diagnosed using eight questions above based on the previous study [23]
*: p<0.05, ***: p<0.001 Significantly different by χ2-test
Awareness and use of energy drinks
1) N (%)
2) Among those who knew or had heard of energy drinks (n=517, 287, 249 for total, male, and female)
3) Multiple responses, A percentage of each response was calculated out of a total of participants.
*: p<0.05, **: p<0.01 Significantly different by χ2-test
Energy drink consumption behaviors among users
1) N (%)
2) Multiple responses, A percentage of each response was calculated out of a total of participants.
*: p<0.05, ***: p<0.001 Significantly different by χ2-test
Consumption frequency of energy drinks
1) N (%)
**: p<0.01 Significantly different by χ2-test
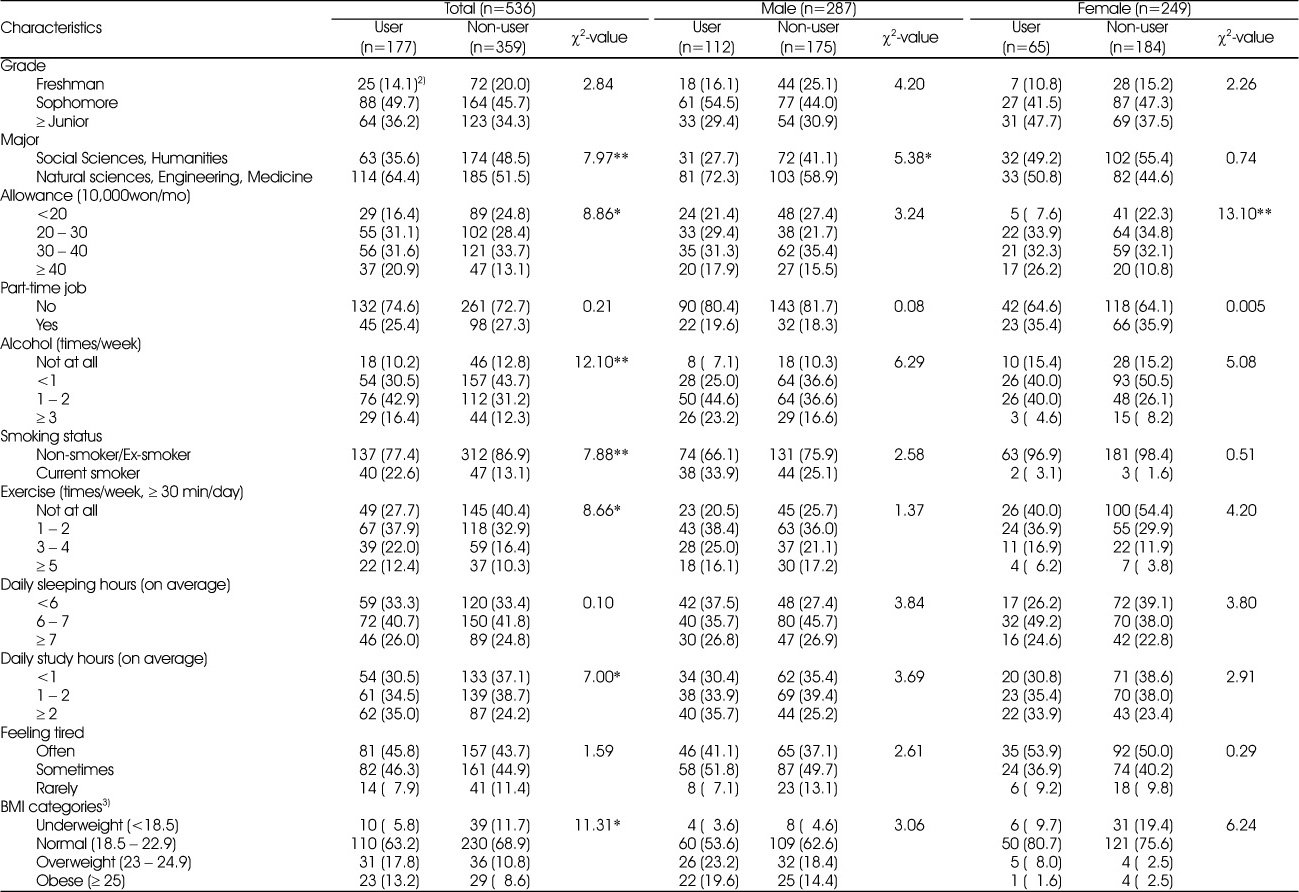
Characteristics among energy drink users1) and non-users
1) Students who consume energy drink once a month or more frequently, 2) N (%), 3) n=508, 286, 222 for total, male and female, respectively due to missing data
*: p<0.05, **: p<0.01 Significantly different by χ2-test
Eating habits among energy drink users1) and non-users
1) Students who consume energy drink once a month or more frequently
2) N (%)
3) Diagnosed using eight questions above based on the previous study [23]
*: p<0.05 Significantly different by χ2-test
1) Mean ± SD 2) N (%) 3) n=508, 286, 222 for total, male and female, respectively due to missing data *: p<0.05, ***: p<0.001 Significantly different by χ2-test
1) N (%) 2) Diagnosed using eight questions above based on the previous study [ *: p<0.05, ***: p<0.001 Significantly different by χ2-test
1) N (%) 2) Among those who knew or had heard of energy drinks (n=517, 287, 249 for total, male, and female) 3) Multiple responses, A percentage of each response was calculated out of a total of participants. *: p<0.05, **: p<0.01 Significantly different by χ2-test
1) N (%) 2) Multiple responses, A percentage of each response was calculated out of a total of participants. *: p<0.05, ***: p<0.001 Significantly different by χ2-test
1) N (%) **: p<0.01 Significantly different by χ2-test
1) Students who consume energy drink once a month or more frequently, 2) N (%), 3) n=508, 286, 222 for total, male and female, respectively due to missing data *: p<0.05, **: p<0.01 Significantly different by χ2-test
1) Students who consume energy drink once a month or more frequently 2) N (%) 3) Diagnosed using eight questions above based on the previous study [ *: p<0.05 Significantly different by χ2-test

 KSCN
KSCN



 Cite
Cite


