Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Korean J Community Nutr > Volume 23(5); 2018 > Article
-
Research Article
- Development of a Food Exchange Table and Food Pattern for Nutritionally Balanced Menu Planning
-
Yun Ahn, Ikhyun Yeo, Sangyun Lee, Kisun Nam

-
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition 2018;23(5):411-423.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.5.411
Published online: October 31, 2018
1Health & Nutrition Research Center, Corporate Technology Office, Pulmuone Co., Ltd. Seoul, Korea, Senior Researcher.
2Corporate Technology Office, Pulmuone Co., Ltd. Seoul, Korea, Director.
3Corporate Technology Office, Pulmuone Co., Ltd. Seoul, Korea, Head.
4Health & Nutrition Research Center, Corporate Technology Office, Pulmuone Co., Ltd. Seoul, Korea, Head.
- Corresponding author: Kisun Nam. Corporate Technology Office, Pulmuone Co., Ltd., 50 Yonsei-ro, Seodaemun-Gu, Seoul 03722, Korea. Tel: (02)3277-8553, Fax: (02)6499-0129, ksnama@pulmuone.com
Copyright © 2018 The Korean Society of Community Nutrition
This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 2,507 Views
- 8 Download
- 4 Crossref
Abstract
-
Objectives
- The purpose of this study was to develop new meal planning tools for a nutritionally balanced diet.
-
Methods
- Based on the food exchange list for diabetes, we adjusted the food group classification system to reflect the suggested nutritional factors for chronic disease prevention and health promotion. We developed a nutritionally balanced dietary profile for adults and compared it with the dietary reference intakes for Koreans (KDRIs) and the food pattern recommended by the Korean Diabetes Association.
-
Results
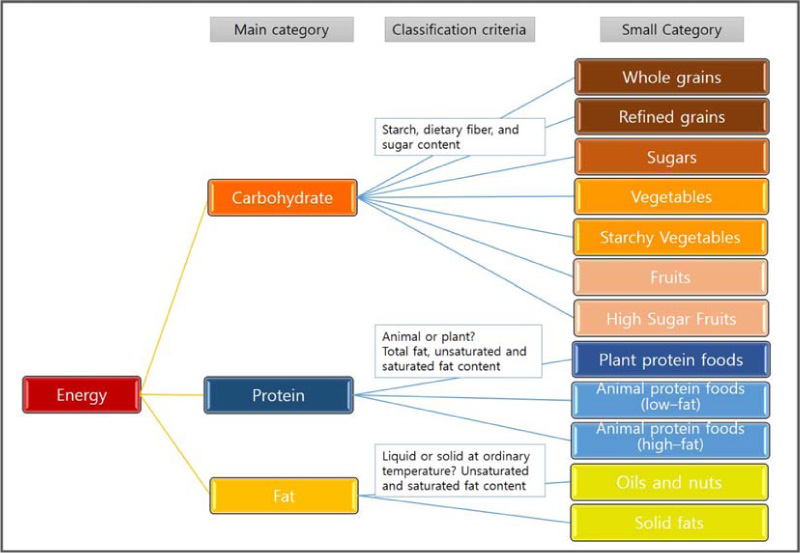
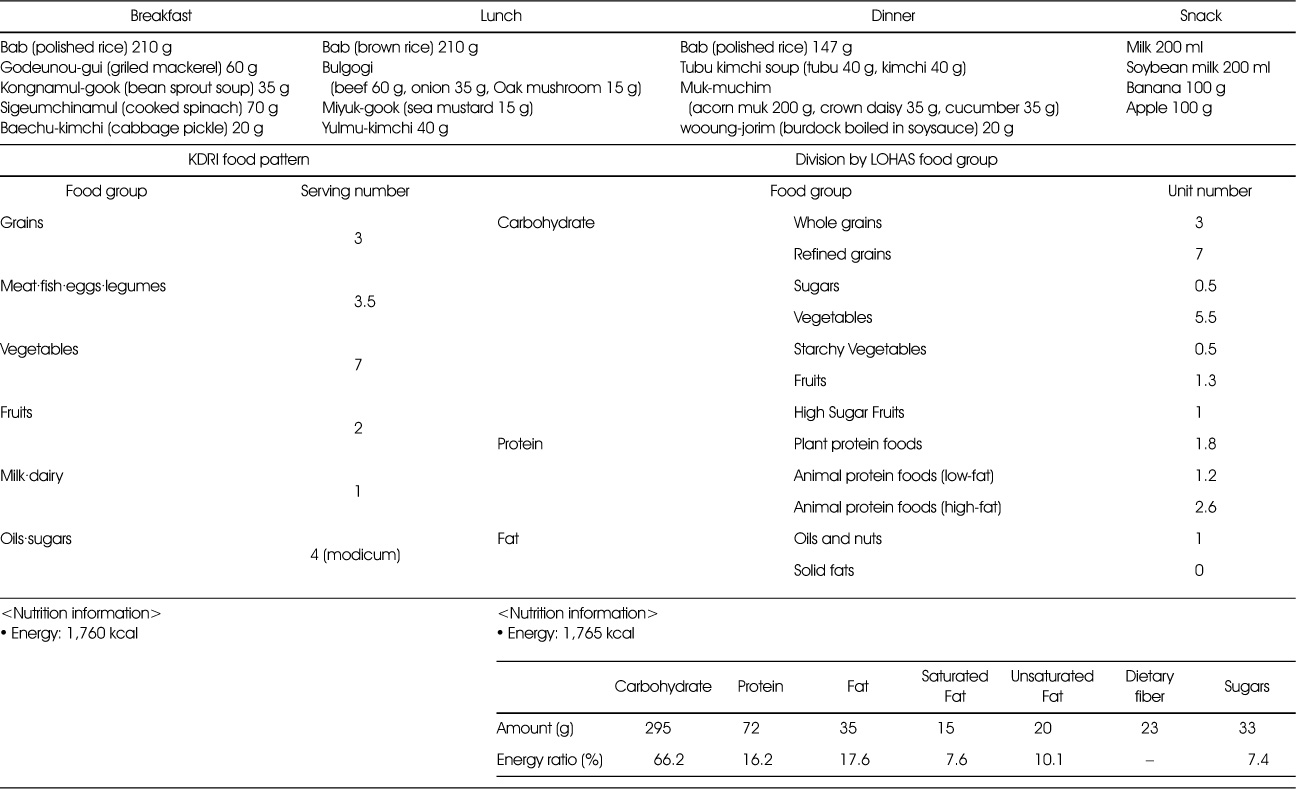
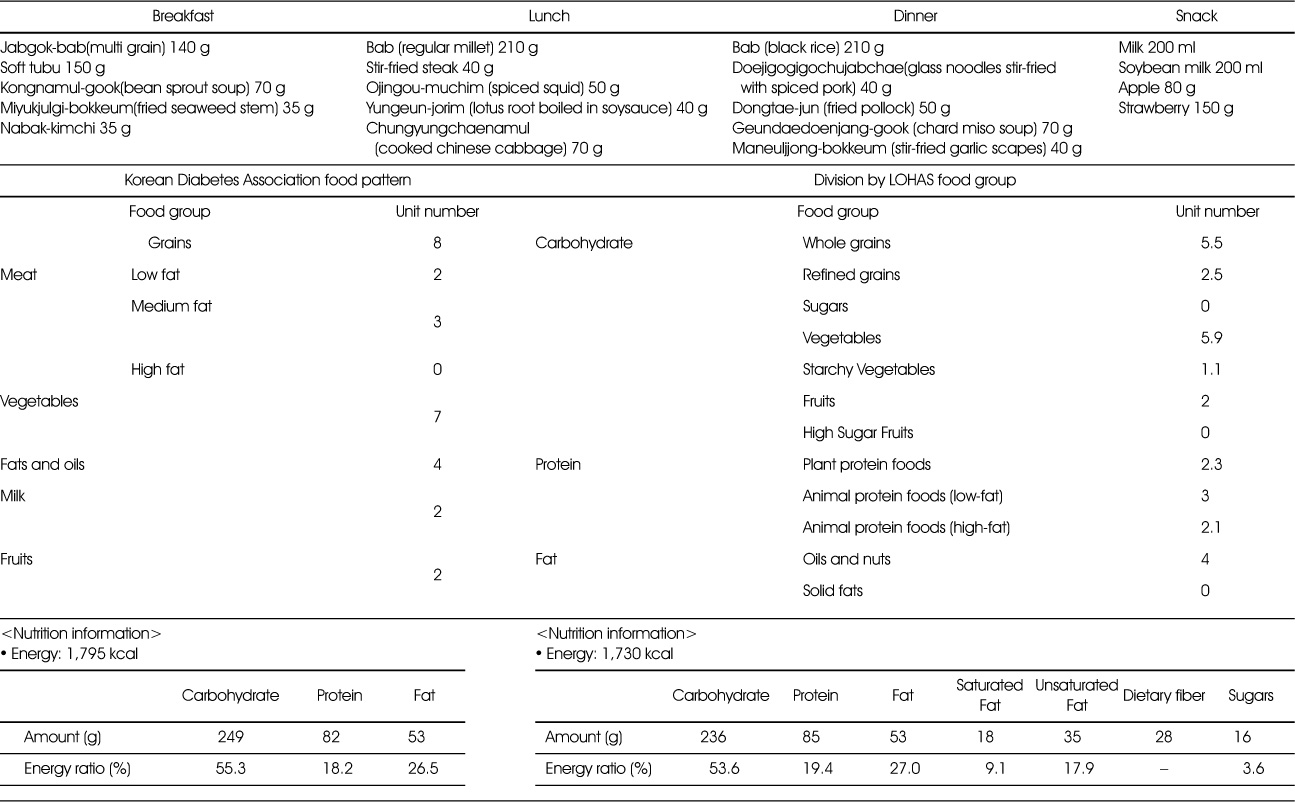
- The newly developed menu planning tools are the LOHAS food exchange table and the LOHAS food pattern. Our recommended daily 1,800 kcal dietary composition for adults is as follows: The carbohydrate food group consists of 4 ‘whole grains’, 3 ‘refined grains’, 2 ‘sugars’, 9 ‘vegetables’, 3 ‘starchy vegetables’, 2 ‘fruits’ and 1 ‘high sugar fruits’. The protein food group includes 3 ‘plant protein foods’, 3 ‘animal protein foods (low-fat)’, and 1 ‘animal protein foods (high-fat)’. The fat food group consists of 2 ‘oils and nuts’ and 1 ‘solid fats’. The total number of calories is estimated at 1,840 kcal and the energy ratio is 62% carbohydrate, 18% protein, 20% fat, 6.8% saturated fat and 13.2% sugars. Using the LOHAS food exchange table, it is possible to estimate values of saturated fat, unsaturated fat, dietary fiber, and sugars besides carbohydrate, protein and fat. It is also possible to compose a dietary design considering carbohydrate, sugars, saturated fat and dietary fiber. The LOHAS food pattern provides benefits for the management of both institutional food services and individual meals, as it can help reduce the levels of saturated fat and sugar intake and help develop healthy meals rich in unsaturated fats and dietary fiber.
-
Conclusions
- The LOHAS food exchange table and LOHAS food pattern are expected to be practical tools for designing and evaluating nutritionally balanced diets.
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgments
- 1. Korean Statistical Information Service. Annual report on the cause of death statistics [internet]. Statistics Korea; 2016; cited 2018 Apr 25]. Available from: http://kosis.kr/publication/publicationThema.do?pubcode=YD.
- 2. Ministry of Health & Welfare, Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Korea Health Statistics 2016: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES VII-1) [internet]. Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention; 2017; cited 2018 Apr 25]. Available from: https://www.cdc.go.kr/CDC/contents/CdcKrContentView.jsp?cid=60949&menuIds=HOME001-MNU1130-MNU1639-MNU1749-MNU1761..
- 3. Lee J, Shin AS. Vegetable and fruit intake in one person household: The Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2010~2012). J Nutr Health 2015; 48(3): 269-276.Article
- 4. Choi MK, Bae YJ. A study on blood lipids and blood pressure of adult men and women according to vegetable intake. Korean J Community Nutr 2007; 12(6): 761-772.
- 5. Kim SJ, Choi MK. Factors associated with fruit and vegetable consumption of subjects having a history of stroke: Using 5th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2010, 2011). Korean J Community Nutr 2014; 19(5): 468-478.Article
- 6. Song S, Paik HY, Song YJ. The relationship between intake of nutrients and food groups and insulin resistance in Korean adults: Using the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES IV, 2007-2009). Korean J Nutr 2013; 46(1): 61-71.Article
- 7. Lee HS, Kwon SO, Yon MY, Kim DH, Lee JY, Nam JW, et al. Dietary total sugar intake of Koreans: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), 2008-2011. J Nutr Health 2014; 47(4): 268-276.Article
- 8. Ko YS, Kim EM, Chae IS, Lee HS. A study of total sugar intake by middle school students in Jeju province. J Nutr Health 2015; 48(3): 248-257.Article
- 9. Ministry of Health & Welfare. The Korean Nutrition Society. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. Dietary reference intakes for Koreans. 1st revision. Seoul: The Korean Nutrition Society; 2010. p. 531.
- 10. Ministry of Health & Welfare. The Korean Nutrition Society. Dietary reference intakes for Koreans 2015. Sejong: Ministry of Health & Welfare; 2015. p. 939.
- 11. Korean Diabetes Association. Korean food exchange lists for diabetes. 3rd ed. Seoul: Gold' Planning and Development; 2010. p. 1-64.
- 12. Ahn Y, Bae JH, Kim HS. Development of web-based u-Health self-nutrition management program for diabetic patients. Korean J Community Nutr 2014; 19(4): 372-385.Article
- 13. Hong SM, Cho JY, Lee JH, Kim G, Kim MC. NutriSonic web expert system for meal management and nutrition counseling with nutrient time-series analysis, e-food exchange and easy data transition. Nutr Res Pract 2008; 2(2): 121-129.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 14. Ju DL, Jang HC, Cho YY, Cho JW, Yoo HS, Choi KS, et al. Korean food exchange lists for diabetes: revised 2010. Korean J Nutr 2011; 44(6): 577-591.Article
- 15. National Institute of Agricultural Sciences. Rural Development Administration. Food composition table. 8th revision. Wanju-gun: National Institute of Agricultural Sciences; Rural Development Administration; 2011.
- 16. The Korean Nutrition Society. CAN-Pro 4.0 CD. Seoul: The Korean Nutrition Society; 2011.
- 17. U.S. Department of Agriculture. USDA food composition databases [internet]. U.S. Department of Agriculture Agricultural Research Service; 2013; cited 2018 Apr 25]. Available from: https://ndb.nal.usda.gov/ndbhttps://ndb.nal.usda.gov/ndb.
- 18. Song S, Choi HN, Lee SY, Park JM, Kim BR, Paik HY, et al. Establishing a table of glycemic index values for common Korean foods and an evaluation of the dietary glycemic index among the Korean adult population. Korean J Nutr 2012; 45(1): 80-93.Article
- 19. U.S. Department of Agriculture. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Dietary guidelines for Americans 2010. 7th ed. Washington, DC: U.S. Government printing office; 2010. p. 59-94.
- 20. Natural Marketing Institute. Understanding the LOHAS consumer report - A focus on energy efficient electronics and appliances. Natural Marketing Institute; 2000.
- 21. Korea LOHAS. Overview of LOHAS [internet]. Korean Standards Association; 2006; cited 2018 Apr 25]. Available from: http://www.korealohas.or.kr/korealohas/1630/subview.do.
- 22. Kang HJ, Kim KJ, Kim I. A study on the menu planning program by food exchange group. Korean J Nutr 1998; 31(7): 1192-1205.
- 23. Choi J, Moon HK. Nutrients and dish intake by fasting blood glucose level. Korean J Nutr 2010; 43(5): 463-474.Article
- 24. Lee Y, Kim MY, Chung HK, Kim HR, Shim JB, Cho HY, et al. Evaluation of traditional aspects of school lunch menus in Korea by analyzing dish group composition. Korean J Community Nutr 2013; 18(4): 386-401.Article
- 25. Hong H, Lee JS. The relationship between food and nutrient intakes, glycemic index, glycemic load, and body mass index among high school girls in Seoul. Korean J Nutr 2010; 43(5): 500-512.Article
- 26. Kim SH, Chung HK. Sugar supply and intake of Koreans. Korean J Nutr 2007; 40: Suppl. 22-28.
- 27. Park YK, Lee YJ, Lee SS. The intake of food and nutrient by the elderly with chronic disease in the Seoul area. Korean J Nutr 2012; 45(6): 531-540.Article
- 28. Ministry of Health & Welfare. Korea Health Promotion Foundation. Health plan 2020 (2016-2020). Seoul: Korea Health Promotion Foundation; 2015.
- 29. Suh YS, Park MS, Chung YJ. An evaluation of chronic disease risk based on the percentage of energy from carbohydrates and the frequency of vegetable intake in the Korean elderly: Using the 2007-2009 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Korean J Community Nutr 2015; 20(1): 41-52.Article
- 30. Kim JY, Kim OY, Yoo HJ, Kim TI, Kim WH, Yoon YD, et al. Effects of fiber supplements on functional constipation. Korean J Nutr 2006; 39(1): 35-43.
- 31. Lee HJ, Kim YA, Lee HS. Annual changes in the estimated dietary fiber intake of Korean during 1991-2001. Korean J Nutr 2006; 39(6): 549-559.
- 32. Ryu JH, Yim JE, Suk WH, Lee HSY, Ahn HJ, Kim YS, et al. Sugar composition and glycemic indices of frequently consumed fruits in Korea. Korean J Nutr 2012; 45(2): 192-200.Article
- 33. Youn HJ, Han YH, Hyun TS. Amounts and food sources of nutrients of elementary school lunch menus by the type of foodservice and the percent energy from fat. Korean J Community Nutr 2007; 12(1): 90-105.
- 34. Lee HY, Kim YN. Revision and application of the target pattern in food guidance system: Administered to 2nd grade middle school students. Korean J Community Nutr 2014; 19(3): 274-282.Article
- 35. Park MJ, Kim YN. Proposition and application of a dish-based target pattern for Korean adolescent girls. Korean J Community Nutr 2015; 20(2): 87-95.Article
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- The association between COVID-19 and changes in food consumption in Korea: analyzing the microdata of household income and expenditure from Statistics Korea 2019–2022
Haram Eom, Kyounghee Kim, Seonghwan Cho, Junghoon Moon
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(1): 153. CrossRef - Development of a food exchange atlas for Sri Lankan adults
Ranil Jayawardena, Dhanushya T. Jeyakumar, Manoja Gamage
Journal of Food Composition and Analysis.2023; 118: 105154. CrossRef - Development and validation of a nutrition literacy assessment tool for young adults
Seokyoung Ahn, Bogyeong Kim, Mihyang Um, Yookyung Park, Seunghee Kye
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(2): 175. CrossRef - A Study on Decision Making by Visualization with Food Nutrition Information
Sang-heon Oh, Sung-Hee Kim
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2020; 21(2): 357. CrossRef

Fig. 1
LOHAS food exchange table: specific characteristics and foods of food group
1) GI: Glycemic Index
LOHAS food exchange table: the amount of nutritions and foods in 1 exchange
LOHAS food pattern(1,800kcal diet per day for adult)
Assessment of 1,800 kcal (A pattern) recommended diet for Korean adult (KDRIs)
Assessment of 1,800kcal recommended diet for diabetic patient (Korean Diabetes Association)
Comparison of 1,800kcal LOHAS food pattern with KDRIs and Diabetes Association 1,800 kcal recommended diet : division by LOHAS food group
1) GI: Glycemic Index

 KSCN
KSCN




 Cite
Cite


