Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Korean J Community Nutr > Volume 22(4); 2017 > Article
-
Research Article
- Nutritional Adequacy Analysis of Recommended Menu in Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans 2015
-
Youngnam Kim

-
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition 2017;22(4):279-288.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.4.279
Published online: August 31, 2017
†Department of Home Economics Education, Korea National University of Education, Cheongju, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Youngnam Kim. Department of Home Economics Education, Korea National University of Education, 250, Taeseongtabyeon-ro, Cheongjusi, Chungcheongbuk-do 28173, Korea. Tel: (043) 230-3709, Fax: (043) 231-4087, youngnam@knue.ac.kr
Copyright © 2017 The Korean Society of Community Nutrition
This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 1,497 Views
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- A Causal Relationship between Vitamin C Intake with Hyperglycemia and Metabolic Syndrome Risk: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study
Meiling Liu, Sunmin Park
Antioxidants.2022; 11(5): 857. CrossRef - Inverse association of a traditional Korean diet composed of a multigrain rice-containing meal with fruits and nuts with metabolic syndrome risk: The KoGES
Min Jung Kim, Haeng Jeon Hur, Dai Ja Jang, Myung-Sunny Kim, Sunmin Park, Hye Jeong Yang
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef

Fig. 1
Number of dishes listed in Recommended Menu as meal
1) N/3 meals/10 age groups
Number of dishes listed in Recommended Menu as between-meal
1) Green tea in Recommended Menu is excluded, 2) N/10 age groups
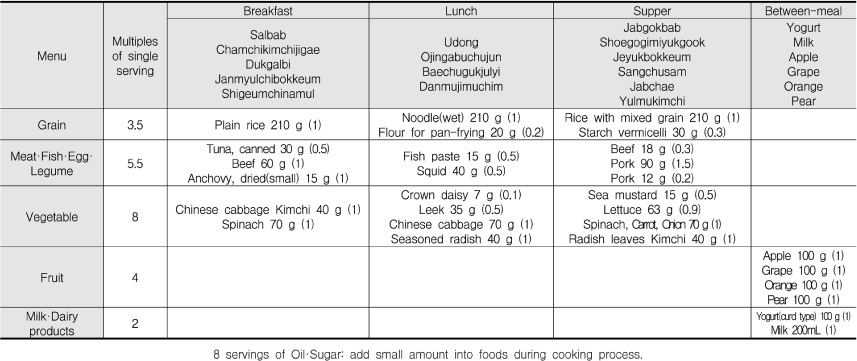
Multiples of single serving in Recommended Menu
1) Multiples of single serving, 2) N (%)
Energy and Nutrients contents of the Target Pattern calculated based upon food weights and food composition table by Multiples of Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans 2015
1) Recommended Intake, 2) Adequate Intake, 3) 65 − 74/≥ 75 years
Number of Recommended Menu with less than Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans
Percent of energy derived from protein, fat, and carbohydrate in Recommended Menu
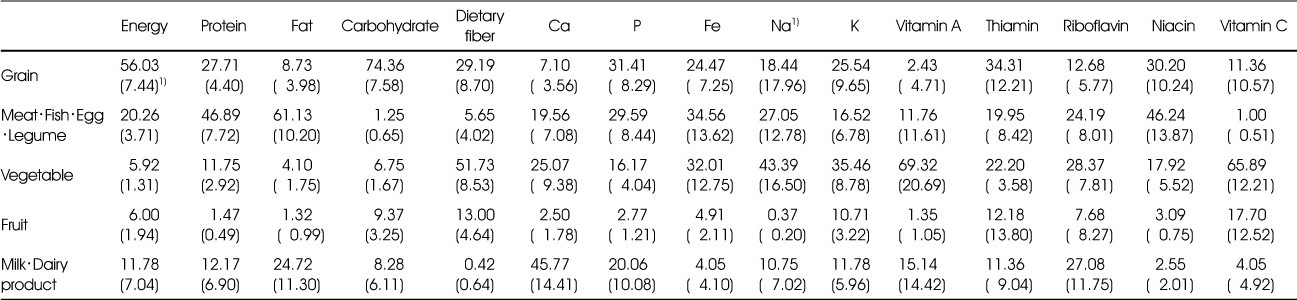
Percentage of energy and nutrients from 5 food groups in Recommended Menu
1) Mean (SD)
Calculation of energy content for condiment in Recommended Menu
1) Assigned serving×45 kcal/serving
1) N/3 meals/10 age groups
1) Green tea in Recommended Menu is excluded, 2) N/10 age groups
1) Multiples of single serving, 2) N (%)
1) Recommended Intake, 2) Adequate Intake, 3) 65 − 74/≥ 75 years
1) Mean (SD)
1) Assigned serving×45 kcal/serving

 KSCN
KSCN







 Cite
Cite


