Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Korean J Community Nutr > Volume 19(1); 2014 > Article
-
Original Article
- Association of Food and Nutrient Intakes with Periodontitis by Smoking Status among Korean Adults
- Sunghee Kim, Areum Yu, Yoon Jung Yang
-
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition 2014;19(1):84-94.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.1.84
Published online: February 28, 2014
Department of Clinical Nutrition, Dongduk Women's University, Seoul, Korea.
1Department of Food and Nutrition, Dongduk Women's University, Seoul, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Yoon Jung Yang, Department of Food and Nutrition, Dongduk Women's University, 13 Hwarang-ro, Seongbukgu, Seoul 136-714, Korea. Tel: (02) 940-4465, Fax: (02) 940-4193, yjyang@dongduk.ac.kr
Copyright © 2014 The Korean Society of Community Nutrition
This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 1,287 Views
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
- Periodontal disease is one of the most common chronic inflammatory diseases in the oral cavity, and this is the leading cause of loss of teeth. Studies on the association between diet and periodontal diseases are very limited. The purpose of this study was to investigate the association between food and nutrient intakes and the prevalence of periodontitis. Subjects were 13,391 adults participating in the 2008-2010 Korea Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Periodontitis was diagnosed by dentists using the Community Periodontal Index. Nutrient intakes were estimated by the 24-hour dietary recall. Consumption frequencies of foods were from the food frequency questionnaire. Subjects were categorized into 'smoking' or 'non-smoking' groups. Multiple logistic regression analysis was applied to determine the association between diet and periodontitis. The proportions of subjects having periodontitis were 26% in the non-smoking group and 37.5% in the smoking group. In the non-smoking group, intakes of fruits, dairy products, green tea, energy and vitamin C were inversely associated with the prevalence of periodontitis, but fish and coffee intakes were positively associated with the prevalence of periodontitis after adjusting for covariates. In the smoking group, protein and retinol intakes were inversely associated with the prevalence of periodontitis after adjusting for covariates. These results suggest that certain food and nutrient intakes such as fruits, dairy products, green tea, vitamin C, protein, or retinol intakes may affect the prevalence of periodontitis among Korean adults. Further studies are required to confirm these findings in other research settings.
- 1. Almeida Abdo J, Cirano FR, Casati MZ, Ribeiro FV, Giampaoli V, Viana Casarin RC, Pimentel SP. Influence of dyslipidemia and diabetes mellitus on chronic periodontal disease. J Periodontol 2013; 84(10): 1401-1408.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Adegboye AR, Christensen LB, Holm-Pedersen P, Avlund K, Boucher BJ, Heitmann BL. Intake of dairy products in relation to periodontitis in older danish adults. Nutrients 2012; 4(9): 1219-1229.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 3. Araghizadeh A, Kohanteb J, Fani M. Inhibitory activity of green tea (Camellia sinensis) extract on some clinically isolated cariogenic and periodontopathic bacteria. Med Princ Pract 2013; 22(4): 368-372.ArticlePubMedPMCLink
- 4. Bae KH, Lee BJ, Jang YK, Lee BR, Lee WJ, Chang DS, Moon HS, Paik Di, Kim JB. Published erratum : The effect of mouthrinse products containing sodium fluoride, Cetylpyridinium Chloride (CPC), pine leaf extracts and green tea extracts on the plaque, gingivitis, dental caries and halitosis. J Korean Acad Oral Health 2001; 25(2): 227-227.
- 5. Baek YR, Park JW, Lee JM, Suh JY. The effect of vitamin-c containing neutraceutical on periodontal wound healing as an adjunct to non-surgical or surgical periodontal treatment. J Korean Acad Periodontol 2009; 39(2): 157-166.ArticleLink
- 6. Barnett CC Jr, Moore EE, Mierau GW, Partrick DA, Biffl WL, Elzi DJ, Silliman CC. ICAM-1-CD18 interaction mediates neutrophil cytotoxicity through protease release. Am J Physiol 1998; 274(6 Pt 1): C1634-C1644.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Bassani DG, da Silva CM, Oppermann RV. Validity of the Community Periodontal Index of Treatment Needs' (CPITN) for population periodontitis screening. Cad Saude Publica 2006; 22(2): 277-283.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Bergström J, Bostrom L. Tobacco smoking and periodontal hemorrhagic responsiveness. J Clin Periodontol 2001; 28(7): 680-685.ArticlePubMedLink
- 9. Bergström J, Persson L, Preber H. Influence of cigarette smoking on vascular reaction during experimental gingivitis. Scand J Dent Res 1988; 96(1): 34-39.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Bezerra JP, da Silva LR, de Alvarenga Lemos VA, Duarte PM, Bastos MF. Administration of high doses of caffeine increases alveolar bone loss in ligature-induced periodontitis in rats. J Periodontol 2008; 79(12): 2356-2360.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Chae GC, Auh QS, Chun YH, Hong JP. Antibacterial activity of artemisa capillaris THUNB on oral bacteria. Korean J Oral Med 2009; 34(2): 169-177.
- 12. Chang HS, Hwang HJ, Kang EH, Lee JH, Chung DJ, Yang WJ, Chung WH, Kim DH, Park WD, Kim HY. Original the effect of green tea bag in dogs with periodontal disease. J Vet Clin 2009; 26(1): 41-47.
- 13. Chang YY, Jang YJ, Jung IH, Um YJ, Jung UW, Kim CS, Kim BI, Choi SH. Clinical effect of vitamin C, vitamin E, lysozyme, carbazochrome complex medicine (IGATAN®) in periodontal disease : Double blind, randomized control study. J Korean Dent Assoc 2009; 47(12): 830-837.ArticlePDF
- 14. Chapple IL, Milward MR, Ling-Mountford N, Weston P, Carter K, Askey K, Dallal GE, De Spirt S, Sies H, Patel D. Adjunctive daily supplementation with encapsulated fruit, vegetable and berry juice powder concentrates and clinical periodontal outcomes: A double-blind RCT. J Clin Periodontol 2012; 39(1): 62-72.PubMedPMC
- 15. Daglia M, Tarsi R, Papetti A, Grisoli P, Dacarro C, Pruzzo C, Gazzani G. Antiadhesive effect of green and roasted coffee on streptococcus mutans' adhesive properties on salivacoated hydroxyapatite beads. J Agric Food Chem 2002; 50(5): 1225-1229.ArticlePubMed
- 16. de Souza BD, Lückemeyer DD, Felippe WT, Alves AM, Simões CM, Felippe M. Effect of milk renewal on human periodontal ligament fibroblast viability in vitro. Dent Traumatol 2012; 28(3): 214-216.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Deas DE, Mackey SA, McDonnell HT. Systemic disease and periodontitis: manifestations of neutrophil dysfunction. Periodontol 2000 2003; 32: 82-104.ArticlePubMedLink
- 18. Demmer RT, Desvarieux M, Holtfreter B, Jacobs DR, Wallaschofski H, Nauck M, Vlzke H, Kocher T. Periodontal status and A1C change longitudinal results from the study of health in pomerania (SHIP). Diabetes Care 2010; 33(5): 1037-1043.PubMedPMC
- 19. DeWitte SN. Sex differences in periodontal disease in catastrophic and attritional assemblages from medieval London. Am J Phys Anthropol 2012; 149(3): 405-416.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Dietrich T. Increased dairy intake may be associated with lower prevalence of periodontal disease. J Evid Based Dent Pract 2007; 7(2): 84-85.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Dietrich T, Bernimoulin J, Glynn RJ. The effect of cigaret smoking on gingival bleeding. J Periodontol 2004; 75(1): 16-22.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Drisko CL. Periodontal self-care: Evidence-based support. Periodontol 2000 2013; 62(1): 243-255.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Dye BA, Tan S, Smith V, Lewis BG, Barker LK, Thornton-Evans G, Eke PI, Beltran-Aguilar ED, Horowitz AM, Li CH. Trends in oral health status: United states, 1988-1994 and 1999-2004. Vital Health Stat 11 2007; (248): 1-92.PubMed
- 24. Eggert F, McLeod MH, Flowerdew G. Effects of smoking and treatment status on periodontal bacteria: Evidence that smoking influences control of periodontal bacteria at the mucosal surface of the gingival crevice. J Periodontol 2001; 72(9): 1210-1220.PubMed
- 25. Enwonwu C. Interface of Malnutrition and Periodontal Diseases. Am J Clin Nutr 1995; 61(2): 430S-436S.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Haffajee A, Socransky S. Relationship of cigarette smoking to the subgingival microbiota. J Clin Periodontol 2001; 28(5): 377-388.ArticlePubMedLink
- 27. Huttner EA, Machado DC, De Oliveira RB, Antunes AGF, Hebling E. Effects of human aging on periodontal tissues. Spec Care Dentist 2009; 29(4): 149-155.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Inoue K, Kobayashi Y, Hanamura H, Toyokawa S. Association of periodontitis with increased white blood cell count and blood pressure. Blood Press 2005; 14(1): 53-58.ArticlePubMed
- 29. Iwasaki M, Taylor GW, Moynihan P, Yoshihara A, Muramatsu K, Watanabe R, Miyazaki H. Dietary ratio of N-6 to N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and periodontal disease in community-based older Japanese: A 3-Year Follow-Up Study. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 2011; 85(2): 107-112.ArticlePubMed
- 30. Iwasaki M, Yoshihara A, Moynihan P, Watanabe R, Taylor GW, Miyazaki H. Longitudinal relationship between dietary Omega-3 fatty acids and periodontal disease. Nutrition 2010; 26(11-12): 1105-1109.ArticlePubMed
- 31. Jang JH, Park YD, Ryu DY. The effect of garlic extract on antibacterial activity of periopathogens. J Korean Soc Dent Hyg 2012; 12(3): 631-640.Article
- 32. Johnson GK, Guthmiller JM. The impact of cigarette smoking on periodontal disease and treatment. Periodontol 2000 2007; 44: 178-194.ArticlePubMed
- 33. Kamagata-Kiyoura Y, Ohta M, Cheuk G, Yazdani M, Saltzman MJ, Nakamoto T. Combined effects of caffeine and prostaglandin E2 on the proliferation of osteoblast-like cells (UMR106-01). J Periodontol 1999; 70(3): 283-288.ArticlePubMed
- 34. Kang HK, Sung MK, Lee MK, Lee BH, Lee JY. Periodontics for the dental hygienist. Paju: soomoonsa; 2013. p. 32-107.
- 35. Kim GY. Effect of naringin to dental caries and periodontal disease. J Food Hyg Saf 1997; 12(2): 102-106.
- 36. Kim JK, Lee JH, Kim IG. The effect of Korean red ginseng saponin on the growth and differentiation of periodontal ligament cell in culture. J Korean Acad Periodontol 1995; 25(1): 55-66.
- 37. Kim TI, Choi EJ, Jung JP, Han SB, Gu Y. Antimicorbial effect of zea mays L. and magnoliae cortex extract mixtures on periodontal pathogen and effect on human gingival fibroblast cellular activity. J Korean Acad Periodontol 2002; 32(1): 249-255.
- 38. Lee DJ, Han IM, Kim WJ, Cho IS. Anti-microbial, anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects of herbal medicine extracts as anti-gingivitis ingredients. J Dent Hyg Sci 2010; 10(1): 25-29.
- 39. Lee J, Yi H, Bae K. The association between periodontitis and dyslipidemia based on the fourth Korea national health and nutrition examination survey. J Clin Periodontol 2013; 40(5): 437-442.ArticlePubMedLink
- 40. Leggott P, Robertson P, Rothman D, Murray P, Jacob R. The effect of controlled ascorbic acid depletion and supplementation on periodontal health. J Periodontol 1986; 57(8): 480-485.PubMed
- 41. Lei L, Li H, Yan F, Xiao Y. Hyperlipidemia impaired innate immune response to periodontal pathogen porphyromonas gingivalis in apolipoprotein E knockout mice. PLoS One 2013; 8(8): e71849.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 42. Linden GJ, Linden K, Yarnell J, Evans A, Kee F, Patterson CC. All-cause mortality and periodontitis in 60-70-year-old Men: A prospective cohort study. J Clin Periodontol 2012; 39(10): 940-946.PubMed
- 43. Merchant AT, Pitiphat W, Franz M, Joshipura KJ. Whole-grain and fiber intakes and periodontitis risk in men. Am J Clin Nutr 2006; 83(6): 1395-1400.ArticlePubMed
- 44. Ministry of Health & Welfare. Korea Centers for Disease Control & Prevention. Guidelines of the 5th National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey. 2010.
- 45. Nair P, Sutherland G, Palmer R, Wilson R, Scott D. Gingival bleeding on probing increases after quitting smoking. J Clin Periodontol 2003; 30(5): 435-437.ArticlePubMedLink
- 46. Naqvi AZ, Buettner C, Phillips RS, Davis RB, Mukamal KJ. N-3 Fatty acids and periodontitis in US adults. J Am Diet Assoc 2010; 110(11): 1669-1675.PubMedPMC
- 47. Nugala B, Namasi A, Emmadi P, Krishna PM. Role of green tea as an antioxidant in periodontal disease: The asian paradox. J Indian Soc Periodontol 2012; 16(3): 313-316.PubMedPMC
- 48. Ojima M, Hanioka T, Tanaka K, Inoshita E, Aoyama H. Relationship between smoking status and periodontal conditions: Findings from national databases in Japan. J Periodontal Res 2006; 41(6): 573-579.PubMed
- 49. Palmer RM, Wilson RF, Hasan AS, Scott DA. Mechanisms of action of environmental factors-tobacco smoking. J Clin Periodontol 2005; 32: Suppl 6. 180-195.PubMed
- 50. Palmer R, Scott D, Meekin T, Poston R, Odell E, Wilson R. Potential mechanisms of susceptibility to periodontitis in tobacco smokers. J Periodont Res 1999; 34(7): 363-369.
- 51. Parvez S, Malik K, Ah Kang S, Kim H. Probiotics and their fermented food products are beneficial for health. J Appl Microbiol 2006; 100(6): 1171-1185.PubMed
- 52. Pihlstrom BL, Michalowicz BS, Johnson NW. Periodontal diseases. Lancet 2005; 366(9499): 1809-1820.PubMed
- 53. Preshaw P, Alba A, Herrera D, Jepsen S, Konstantinidis A, Makrilakis K, Taylor R. Periodontitis and diabetes: A two-way relationship. Diabetologia 2012; 55(1): 21-31.ArticlePubMed
- 54. Rech RL, Nurkin N, Cruz Id, Sostizzo F, Baião C, Perrone JA, Wainstein R, Pretto D, Manenti ERF, Bodanese LC. Association between periodontal disease and acute coronary syndrome. Arq Bras Cardiol 2007; 88(2): 185-190.PubMed
- 55. Sakanaka S, Okada Y. Inhibitory effects of green tea polyphenols on the production of a virulence factor of the periodontal-disease-causing anaerobic bacterium porphyromonas gingivalis. J Agric Food Chem 2004; 52(6): 1688-1692.PubMed
- 56. Salvi GE, Yalda B, Collins JG, Jones BH, Smith FW, Arnold RR, Offenbacher S. Inflammatory mediator response as a potential risk marker for periodontal diseases in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients. J Periodontol 1997; 68(2): 127-135.PubMed
- 57. Saremi A, Nelson RG, Tulloch-Reid M, Hanson RL, Sievers ML, Taylor GW, Shlossman M, Bennett PH, Genco R, Knowler WC. Periodontal disease and mortality in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2005; 28(1): 27-32.PubMed
- 58. Schifferle RE. Periodontal disease and nutrition: Separating the evidence from current fads. Periodontol 2000 2009; 50: 78-89.PubMed
- 59. Schwartz N, Kaye EK, Nunn ME, Spiro A 3rd, Garcia RI. High-fiber foods reduce periodontal disease progression in men aged 65 and older: The veterans affairs normative aging study/dental longitudinal study. J Am Geriatr Soc 2012; 60(4): 676-683.PubMed
- 60. Scott D, Palmer R. The influence of tobacco smoking on adhesion molecule profiles. Tob Induc Dis 2002; 1(1): 7-25.PubMed
- 61. Seto H, Toba Y, Takada Y, Kawakami H, Ohba H, Hama H, Horibe M, Nagata T. Milk basic protein increases alveolar bone formation in rat experimental periodontitis. J Periodont Res 2007; 42(1): 85-89.
- 62. Shimazaki Y, Shirota T, Uchida K, Yonemoto K, Kiyohara Y, Iida M, Saito T, Yamashita Y. Intake of dairy products and periodontal disease: The hisayama study. J Periodontol 2008; 79(1): 131-137.PubMed
- 63. Signoretto C, Bianchi F, Burlacchini G, Sivieri F, Spratt D, Canepari P. Drinking habits are associated with changes in the dental plaque microbial community. J Clin Microbiol 2010; 48(2): 347-356.PubMed
- 64. Song KH, Cho SJ. A study on the relationship among peridontal diseases, obesity and health risk factors. J Korean Soc Dent Hyg 2011; 13(1): 47-60.
- 65. Taylor GW, Burt BA, Becker MP, Genco RJ, Shlossman M, Knowler WC, Pettitt DJ. Severe periodontitis and risk for poor glycemic control in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Periodontol 1996; 67: 10 Suppl. 1085-1093.
- 66. Willett WC. Nutritional epidemiology. 2nd ed. New York: Oxford University Press; 1998. p. 288-291.
- 67. van Winkelhoff AJ, Bosch-Tijhof CJ, Winkel EG, van der Reijden WA. Smoking affects the subgingival microflora in periodontitis. J Periodontol 2001; 72(5): 666-671.PubMed
- 68. Yoon JW, Paik DI, Moon HS. The effects of camomile, rhatany, myrrh, glcyrrhetic acid and their combinations against the periodontal pathogens. J Korean Acad Oral Health 1997; 21(2): 323-330.
- 69. Yun J, Pang E, Kim C, Yoo Y, Cho K, Chai J, Kim C, Choi S. Inhibitory effects of green tea polyphenol (-)- epigallocatechin gallate on the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and on the formation of osteoclasts. J Periodont Res 2004; 39(5): 300-307.
- 70. Zhu Y, Xiao L, Shen D, Hao Y. Competition between yogurt probiotics and periodontal pathogens in vitro. Acta Odontol Scand 2010; 68(5): 261-268.PubMed
REFERENCES

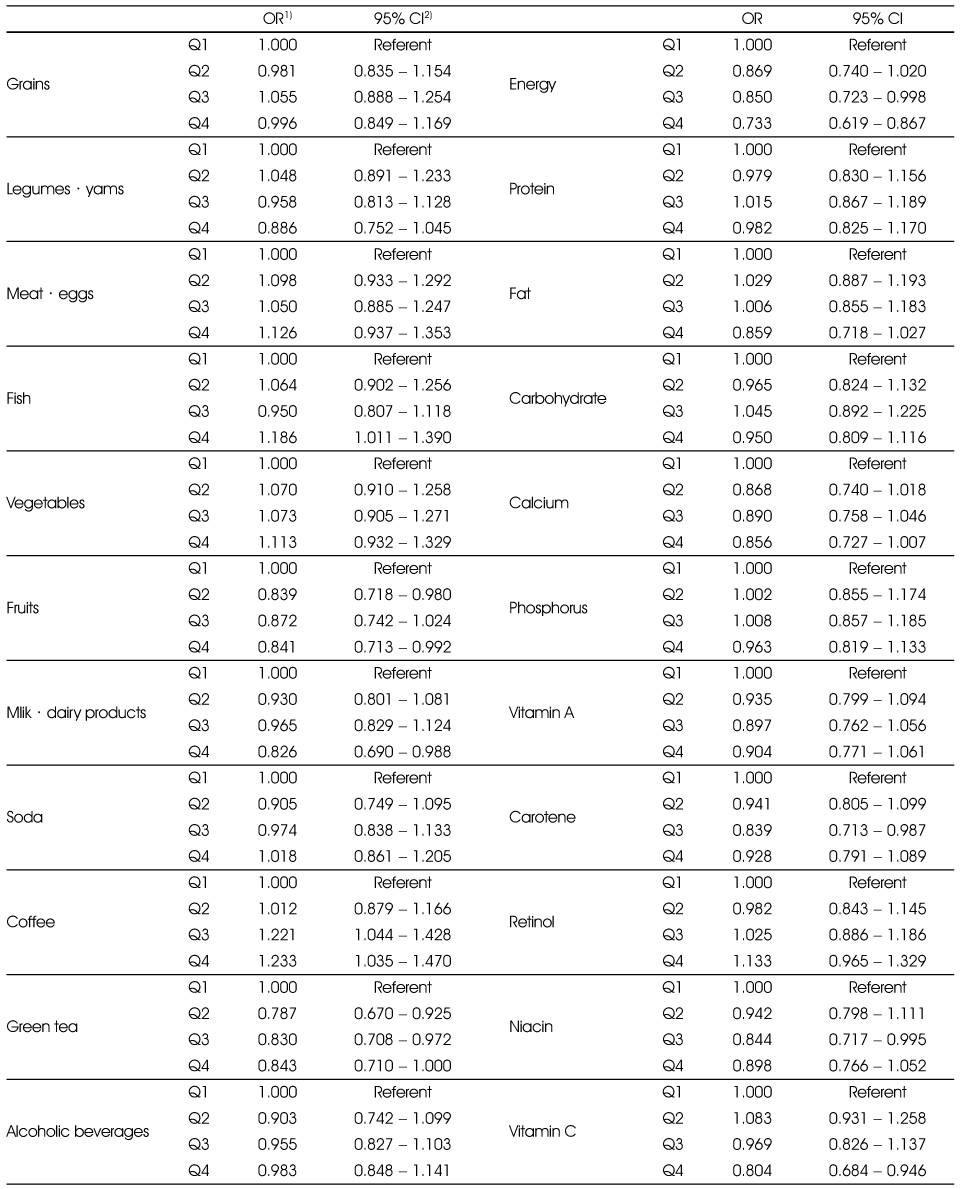
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Association between consumption of milk and dairy products, calcium and riboflavin, and periodontitis in Korean adults: Using the 2007-2010 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
Sang Mi Koo, Deog-Gyu Seo, Yoon Jung Park, Ji-Yun Hwang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2014; 47(4): 258. CrossRef

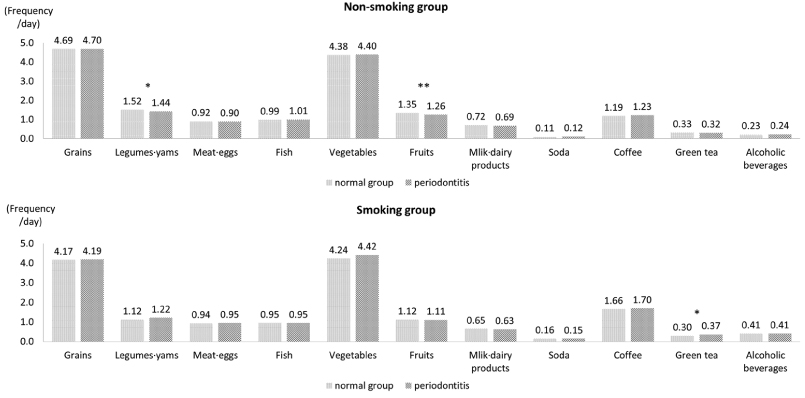
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
General characteristics of the study subjects and by the periodontitis by smoking status
1) t-test for continuous variables and χ2-test for categorical variables
2) Mean ± SD
3) N (%)
4) Chronic diseases were defined as including one of more of diabetes, dyslipidemia, hypertension, angina or myocardial infarction
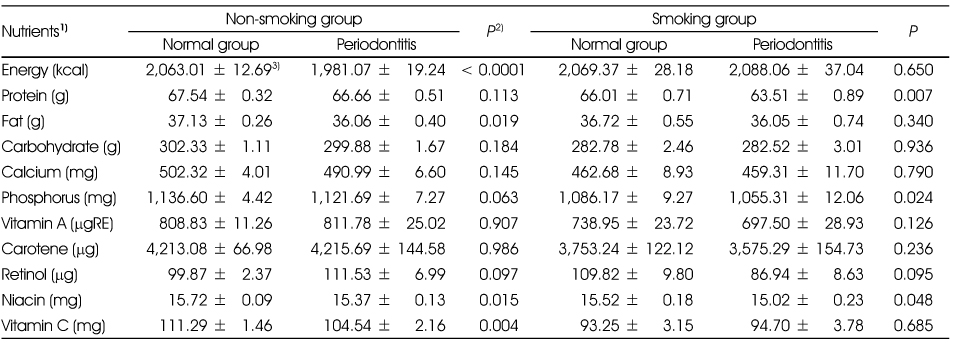
Nutrient intakes of the subjects according to periodontitis by the smoking status
1) All nutrients except energy were total energy adjusted by residual method after log transformation.
2) t-test
3) Mean ± SD
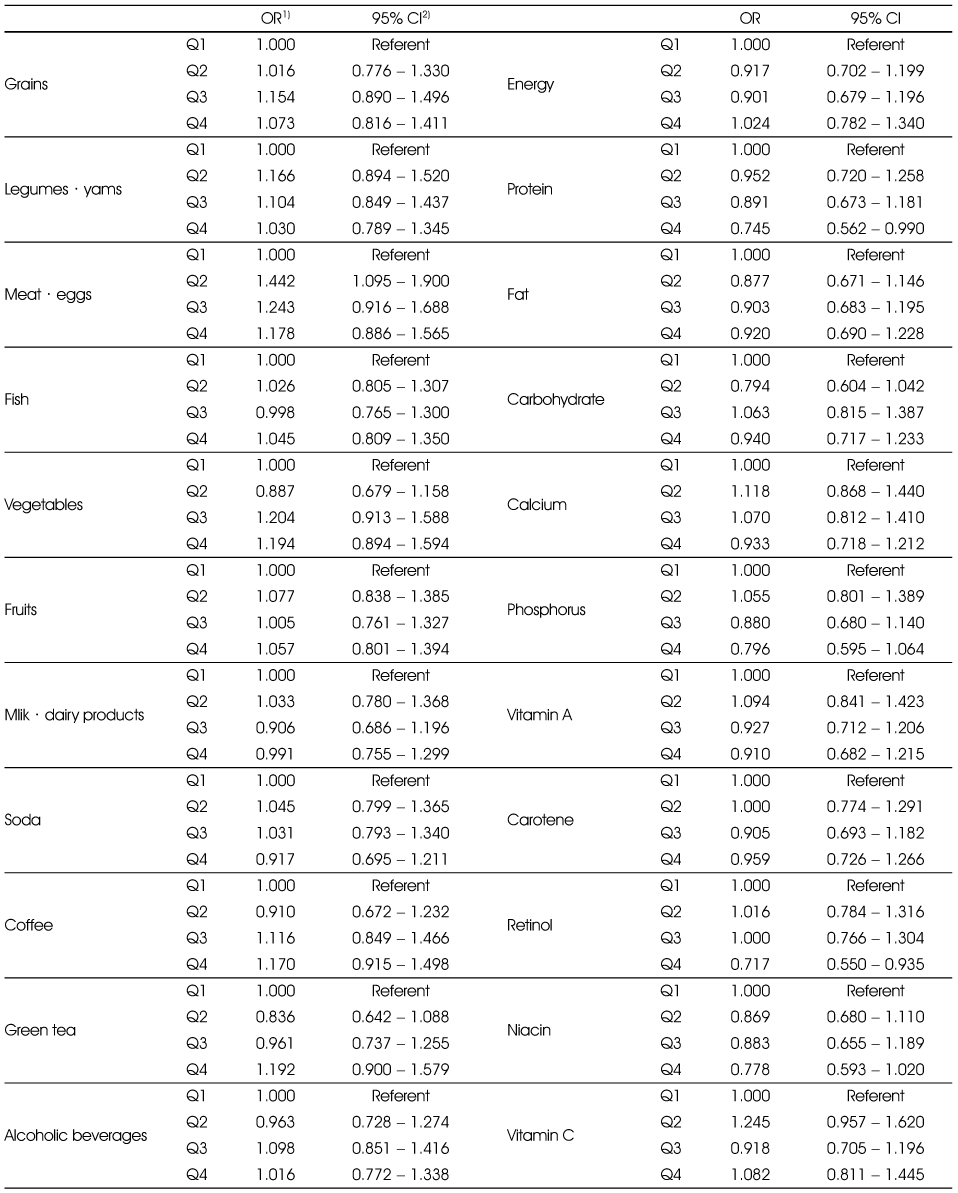
Adjusted ORs and 95% CIs between the prevalence of periodontitis and food and nutrient intakes in the non-smoking group
Multiple logistic regression analysis after adjusting for age, sex education (elementary, middle, high, college), tooth brushing after lunch (yes, no), and chronic diseases (yes, no).
1) Odds Ratio
2) 95% confidence interval
Adjusted ORs and 95% CIs between the prevalence of periodontitis and food and nutrient intakes in the smoking group
Multiple logistic regression analysis after adjusting for age, sex education (elementary, middle, high, college), tooth brushing after lunch (yes, no), and chronic disease (yes, no).
1) Odds Ratio
2) 95% confidence interval
1) t-test for continuous variables and χ2-test for categorical variables 2) Mean ± SD 3) N (%) 4) Chronic diseases were defined as including one of more of diabetes, dyslipidemia, hypertension, angina or myocardial infarction
1) All nutrients except energy were total energy adjusted by residual method after log transformation. 2) t-test 3) Mean ± SD
Multiple logistic regression analysis after adjusting for age, sex education (elementary, middle, high, college), tooth brushing after lunch (yes, no), and chronic diseases (yes, no). 1) Odds Ratio 2) 95% confidence interval
Multiple logistic regression analysis after adjusting for age, sex education (elementary, middle, high, college), tooth brushing after lunch (yes, no), and chronic disease (yes, no). 1) Odds Ratio 2) 95% confidence interval

 KSCN
KSCN
 Cite
Cite


