Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Korean J Community Nutr > Volume 17(5); 2012 > Article
-
Original Article
- Dietary Behaviors Related to Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adults
- Jinkyung Park, Sanghui Kweon, Yangha Kim, Myoung-Jin Jang, Kyungwon Oh
-
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition 2012;17(5):664-675.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.5.664
Published online: October 31, 2012
Division of Health and Nutrition Survey, Center for Disease Prevention, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Osong, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Kyungwon Oh, Division of Health and Nutrition Survey, Center for Disease Prevention, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Osong Health Technology/Administration Complex, 187, Osong-sengmyung-2-ro, Osong-eup, Cheongwon-gun, Chungcheongbuk-do 363-951, Korea. Tel: (043) 719-7460, Fax: (043) 719-7527, kwoh27@korea.kr
Copyright © 2012 The Korean Society of Community Nutrition
- 1,828 Views
- 11 Download
- 23 Crossref
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Higher Animal-Based Protein Intake Levels Show a Greater Likelihood of Having Metabolic Syndrome in Single-Person Households Among Korean Adults
Yeongin Lee, Hyojee Joung
Nutrients.2024; 16(23): 4239. CrossRef - Comparison of health indicators and lifestyle according to atherogenic index of plasma in Korean adults in their 20s and 30s
Bora Hwang, Yoon Jung Yang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(2): 168. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Diet Quality between Meal Frequency and Cardiometabolic Risk among Korean Adults: Data from the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHNES)
Yoo Mi Cho, Kyoung Suk Lee
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2023; 16(2): 67. CrossRef - Association of Seaweed Consumption with Metabolic Syndrome and Its Components: Findings from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Haeun Park, Kyung Won Lee, Dayeon Shin
Foods.2022; 11(11): 1635. CrossRef - Effect of Household Type on the Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Korea: Using Propensity Score Matching
Jisu Park, Ilsu Park
Healthcare.2022; 10(10): 1894. CrossRef - Association between breakfast skipping and metabolic outcomes by sex, age, and work status stratification
Jun Heo, Won-Jun Choi, Seunghon Ham, Seong-Kyu Kang, Wanhyung Lee
Nutrition & Metabolism.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Coexistence of metabolic syndrome and osteopenia associated with social inequalities and unhealthy lifestyle among postmenopausal women in South Korea: the 2008 to 2011 Korea National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey (KNHANES)
Hansongyi Lee, Jieun Kim, Hyunjung Lim
Menopause.2020; 27(6): 668. CrossRef - Effects of BeHaS Program on Health Behavior, Physiologic Index and Self-Esteem of the Elderly Living Alone with Metabolic Syndrome Based on Community Based Participatory Research
Jong Im Kim, Sun Ae Kim, Keumok Park, Jiyoung Kim, Lina Lee, Si Wan Choi, Bon Jeong Ku
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(4): 571. CrossRef - A Study on the Relationship between Metabolic Syndrome and Sodium among the Clients of the General Medical Examination Center
Mi-Jung Yun, Young-Mi Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2018; 28(6): 404. CrossRef - Field Application and Evaluation of Health Status Assessment Tool based on Dietary Patterns for Middle-Aged Women
Hye-Jin Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(4): 277. CrossRef - Motivation Factors for Stages of Behavioral Change among Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome
Rhayun Song, Moonkyoung Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(1): 60. CrossRef - Comparative study on prevalence and components of metabolic syndrome and nutritional status by occupation and gender: Based on the 2013 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ga Ram Kim, Hae Ryun Park, Young Mi Lee, Young Suk Lim, Kyung Hee Song
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(1): 74. CrossRef - Alcohol Consumption and Diabetes Mellitus
Hye-Kyung Chung
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2016; 17(1): 41. CrossRef - Analysis of Dietary Inflammatory Index of Metabolic Syndrome in Korean : Data from the Health Examinee Cohort (2012-2014)
Mi-Sung Kim, Cheong-Min Sohn
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2016; 25(6): 823. CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome Risk by Dietary Fat Energy Ratio in Middle-aged Men - Using the 2012~2013 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data -
Eun-Sil Her
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(6): 1030. CrossRef - Relationship between metabolic syndrome and metabolic syndrome score and beta cell function by gender in Korean populations with obesity
Hyun Yoon, Dae Keun Jeong, Kyu Su Lee, Han Soo Kim, Ae Eun Moon, Jong Park
Endocrine Journal.2016; 63(9): 785. CrossRef - Effect of a Worksite-based Dietary Intervention Program for the Management of Metabolic Syndrome
Hye Jin Kim, Injoo Choi, Won Gyoung Kim, Kana Asano, Jeongmin Hong, Young Min Cho, Jihyun Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(3): 237. CrossRef - An Evaluation of Chronic Disease Risk Based on the Percentage of Energy from Carbohydrates and the Frequency of Vegetable Intake in the Korean Elderly: Using the 2007-2009 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yoon Suk Suh, Min Seon Park, Young-Jin Chung
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(1): 41. CrossRef - Antioxidative activities of various solvent extracts from haw (Crataegus pinnatifida Bunge)
Yishan Duan, Min-A Kim, Jong-Hwan Seong, Hun-Sik Chung, Han-Soo Kim
Korean Journal of Food Preservation.2014; 21(2): 246. CrossRef - Antioxidative Activity of Feral Haw (Crataegus pinnatifida BUNGE) Seed Extracts Using Various Solvents
Min-A Kim, Yishan Duan, Jong-Hwan Seong, Hun-Sik Chung, Han-Soo Kim
Korean journal of food and cookery science.2014; 30(1): 33. CrossRef - Development and Effect of a Metabolic Syndrome Prevention Program for University Students using Mobile Application.
Han Kyu Kang, Tae Bin Kim, Kyu Hyung Kim, Min Jin Kim, Jin Hyun Kim, Hyun Yong Kim, Kyung Hoon Yeom, Ka Hyun Lee, Eun Young Choi, Kyung Ah Kang
Child Health Nursing Research.2014; 20(3): 205. CrossRef - Relation between Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity Pattern Identification Questionnaire in Middle-aged Health Check-up Examinees
Jeong-Eun Yoo, Young-Hye Cho, Hyun-Gyung Gu, Bo-Young Kim, Young-Ju Yun
Journal of Korean Medicine.2014; 35(1): 124. CrossRef - The study of metabolic risk factors and dietary intake in adolescent children by the status of mothers' metabolic syndrome: Using the data from 2007-2010 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
SoYeon Kwon, Mijung Park, YoonJu Song
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2013; 46(6): 531. CrossRef
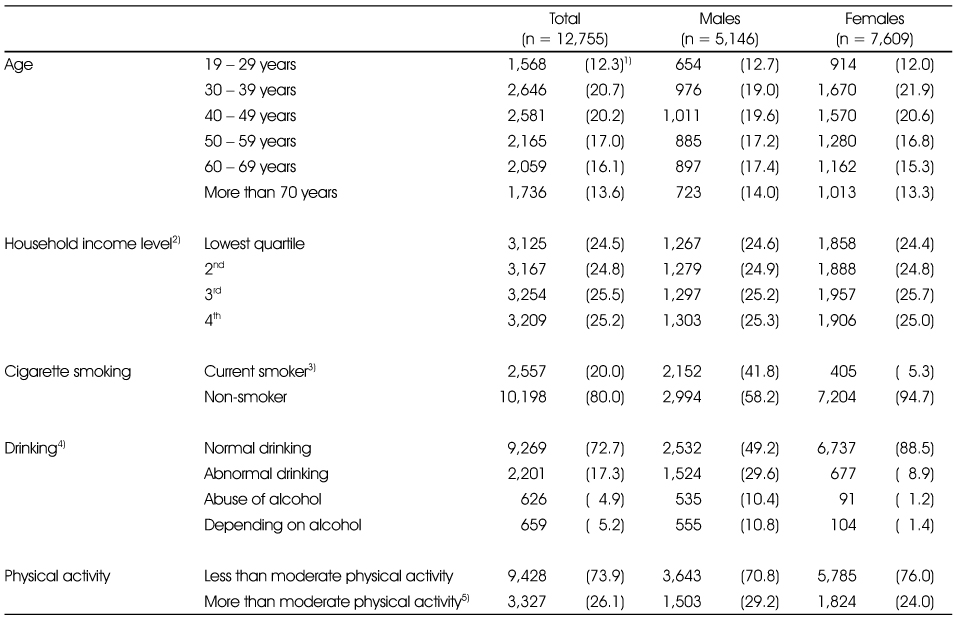
Socio-demographic and lifestyle-related characteristics of Korean adults
1) N (%)
2) Household income level: household equivalent income, monthly household income divided by square root of the number of household member, was categorized to quartile groups within sex and 5-year age group
3) Current smoker: proportion of people who have smoked at least 100 cigarettes in their lifetime and are still smoking
4) Drinking: subjects divided by alcohol use disorders identification test score; normal drinking (≤ 7), abnormal drinking (8 - 15), abuse alcohol (16 - 19), depending on alcohol (≥ 20)
5) More than moderate physical activity: proportion of people who engaged in 'vigorous intensity' activity for at least 20 minutes a day on at least 3 days in the past 7 days or 'moderate intensity' activity for at least 30 minutes a day on at least 5 days in the past 7 days
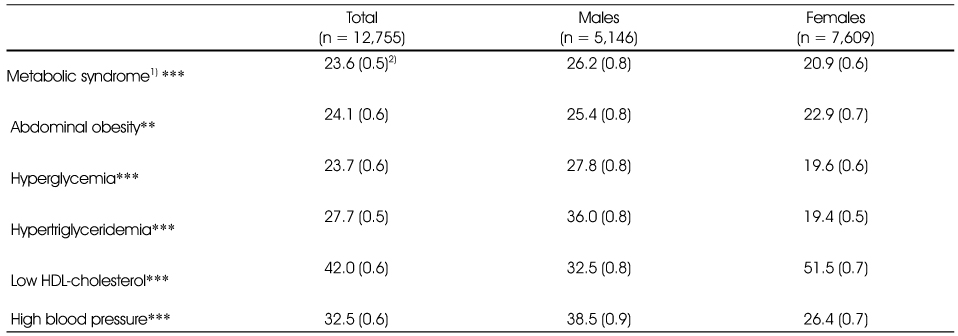
Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome and its components in Korean adults
1) Metabolic syndrome was defined by meeting ≥ 3 of the listed criteria
1. Abdominal obesity: waist circumference ≥ 90 cm in men, ≥ 85 cm in women
2. Hyperglycemia: fasting plasma glucose ≥ 100 mg/dl or drug treatment(the use of oral antihyperglycemic agents or insulin
3. Hypertriglyceridemia: Blood triglyceride ≥ 150 mg/dl
4. Low HDL-cholesterol: Blood HDL-cholesterol < 40 mg/dl in men, < 50 mg/dl in women
5. High blood pressure: Blood pressure systolic ≥ 130 mmHg or diastolic ≥ 85 mmHg or drug treatment(the use of antihypertensive agents
2) % (SE)
**: p < 0.001, ***: p < 0.0001 show the sex difference in the logistic regression model adjusting for age groups
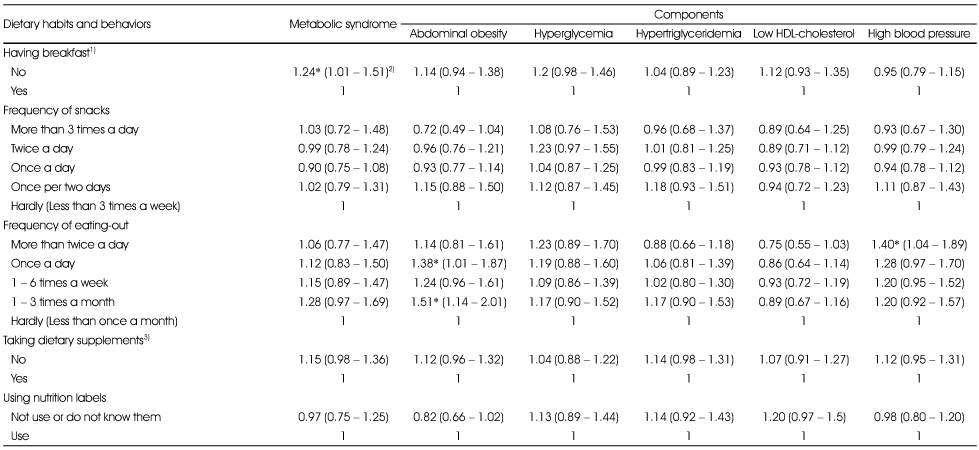
Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for the metabolic syndrome and its components by dietary behaviors in Korean males
1) Subjects having skipped breakfast (having breakfast 'No'): subjects who had skipped breakfast before 1 day or 2 days
2) Values are ORs (95% CI), adjusted for age, income level, smoking and drinking status, and physical activity
3) Subjects having taken dietary supplement: subjects who responded had taken dietary supplement continuously more than 2 weeks within the recent one year
*: p < 0.05 shows significant ORs
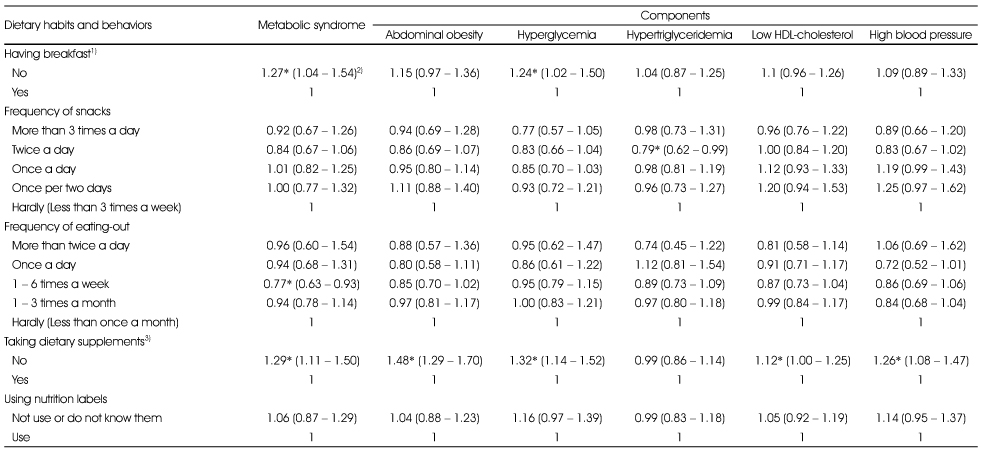
Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for the metabolic syndrome and its components by dietary behaviors in Korean females (continued)
1) Subjects having skipped breakfast (having breakfast 'No'): subjects who had skipped breakfast before 1 day or 2 days
2) Values are ORs (95% CI), adjusted for age, income level, smoking and drinking status, and physical activity
3) Subjects having taken dietary supplement: subjects who responded had taken dietary supplement continuously more than 2 weeks within the recent one year
*: p < 0.05 shows significant ORs
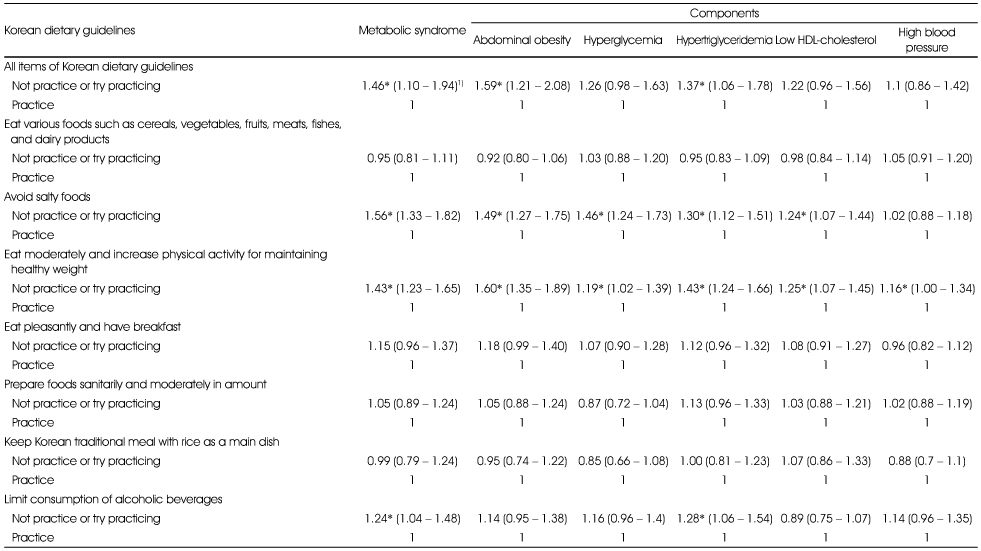
Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for the metabolic syndrome and its components by the practice of Korean Dietary Guidelines in Korean males
1) Values are ORs (95% CI), adjusted for age, income level, smoking and drinking status, physical activity
*: p < 0.05 shows significant ORs
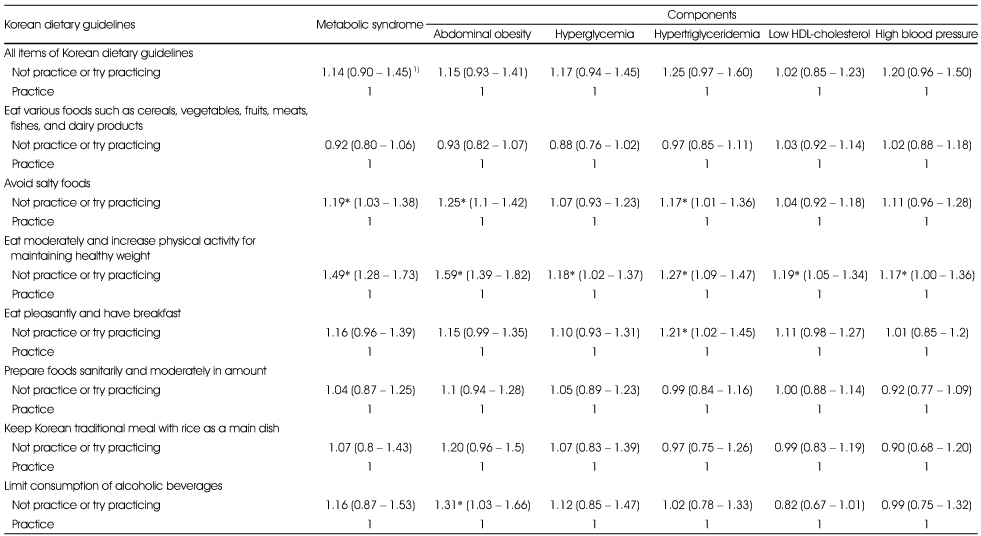
Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for the metabolic syndrome and its components by the practice of Korean Dietary Guidelines in Korean females (continued)
1) Values are ORs (95% CI), adjusted for age, income level, smoking and drinking status, physical activity
*: p < 0.05 shows significant ORs
1) N (%) 2) Household income level: household equivalent income, monthly household income divided by square root of the number of household member, was categorized to quartile groups within sex and 5-year age group 3) Current smoker: proportion of people who have smoked at least 100 cigarettes in their lifetime and are still smoking 4) Drinking: subjects divided by alcohol use disorders identification test score; normal drinking (≤ 7), abnormal drinking (8 - 15), abuse alcohol (16 - 19), depending on alcohol (≥ 20) 5) More than moderate physical activity: proportion of people who engaged in 'vigorous intensity' activity for at least 20 minutes a day on at least 3 days in the past 7 days or 'moderate intensity' activity for at least 30 minutes a day on at least 5 days in the past 7 days
1) Metabolic syndrome was defined by meeting ≥ 3 of the listed criteria 1. Abdominal obesity: waist circumference ≥ 90 cm in men, ≥ 85 cm in women 2. Hyperglycemia: fasting plasma glucose ≥ 100 mg/dl or drug treatment(the use of oral antihyperglycemic agents or insulin 3. Hypertriglyceridemia: Blood triglyceride ≥ 150 mg/dl 4. Low HDL-cholesterol: Blood HDL-cholesterol < 40 mg/dl in men, < 50 mg/dl in women 5. High blood pressure: Blood pressure systolic ≥ 130 mmHg or diastolic ≥ 85 mmHg or drug treatment(the use of antihypertensive agents 2) % (SE) **: p < 0.001, ***: p < 0.0001 show the sex difference in the logistic regression model adjusting for age groups
1) Subjects having skipped breakfast (having breakfast 'No'): subjects who had skipped breakfast before 1 day or 2 days 2) Values are ORs (95% CI), adjusted for age, income level, smoking and drinking status, and physical activity 3) Subjects having taken dietary supplement: subjects who responded had taken dietary supplement continuously more than 2 weeks within the recent one year *: p < 0.05 shows significant ORs
1) Subjects having skipped breakfast (having breakfast 'No'): subjects who had skipped breakfast before 1 day or 2 days 2) Values are ORs (95% CI), adjusted for age, income level, smoking and drinking status, and physical activity 3) Subjects having taken dietary supplement: subjects who responded had taken dietary supplement continuously more than 2 weeks within the recent one year *: p < 0.05 shows significant ORs
1) Values are ORs (95% CI), adjusted for age, income level, smoking and drinking status, physical activity *: p < 0.05 shows significant ORs
1) Values are ORs (95% CI), adjusted for age, income level, smoking and drinking status, physical activity *: p < 0.05 shows significant ORs

 KSCN
KSCN
 Cite
Cite


