Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Korean J Community Nutr > Volume 16(3); 2011 > Article
-
Original Article
- Association of Whole Grain Consumption with Socio-Demographic and Eating Behavior Factors in a Korean Population: Based on 2007-2008 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Seungmin Lee
-
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition 2011;16(3):353-363.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.3.353
Published online: June 30, 2011
Department of Food & Nutrition, Sungshin Women's University, Seoul, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Seungmin Lee, Department of Food & Nutrition, Sungshin Women's University, 147 Mia-dong, Kangbuk-gu, Seoul 142-100, Korea. Tel: (02) 920-7671, Fax: (02) 920-2076, smlee@sungshin.ac.kr
Copyright © 2011 The Korean Society of Community Nutrition
- 1,400 Views
- 9 Download
- 18 Crossref
Abstract
- The objective of the current study was to examine associations of whole grain consumption with socio-demographic (i.e.: sex, age, household income, education, marriage status) and certain eating behavior factors (i.e.: dish source, eating place, meal type) among a generally healthy Korean population. Using twenty-four hour recall data from the 2007-2008 National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, whole grain intake (g/day) was calculated for a total of 8,836 generally healthy Koreans aged 6 years and higher. The study subjects had very low whole grain intake. Specifically approximately 60% of the subjects reported no whole grain consumption on the survey day, and mean daily intake ranged from 8.0 g to 15.1 g in different gender and age groups. Living with a spouse was found to be a positive environment factor for whole grain consumption, especially among men. As household income levels increased, whole grain consumption status also improved. The proportion of non-consumer was lowest in a 6-19 year group, and mean intake amount was highest in middle-aged adults. Major dish sources for whole grain consumption included boiled rice with mixed grains, corn, boiled rice with brown rice, cereal products, and other types of boiled rice. It was found that whole grain consumption was highly affected by eating places rather than meal types. The best contributing eating place was home in each age and gender group. The study findings may be useful in planning nutrition education strategy and formulating dietary behavior guidelines for whole grain consumption improvement.
-
This research was conducted by the generous financial support of the Youlchon Foundation (Nongshim Corporation and its affiliated companies) in Korea.
NOTES
- 1. Anderson JW, Hanna TJ, Peng X, Kryscio RJ. Whole grain foods and heart disease risk. J Am Coll Nutr. 2000; 19: 3 Suppl. 291S-299S.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Albertson AM, Tobelmann RC. Consumption of grain and whole grain foods by an American population during the years 1990-92. J Am Diet Assoc. 1995; 95(6): 703-704.PubMed
- 3. Bakke A, Vickers Z. Consumer liking of refined and whole wheat breads. J Food Sci. 2007; 72(7): S473-S480.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Burgess-Champoux TL, Rosen R, Marguart L, Reicks M. The development of psychosocial measures for whole-grain intakeamong children and their parents. J Am Diet Assoc. 2008; 108(4): 714-717.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Chase K, Reicks M, Jones JM. Applying the theory of planned behavior to promotion of whole-grain foods by dietitians. J Am Diet Assoc. 2003; 103(12): 1639-1642.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Chase K, Reicks M, Smith C, Henry H, Reimer K. Use of the think-aloud method to identify factors influencing purchase of bread and cereals by low-income African American women and implications for whole-grain education. J Am Diet Assoc. 2003; 103(4): 501-504.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Cleveland LE, Moshfegh AJ, Albertson AM, Goldman JD. Dietary intake of whole grains. J Am Coll Nutr. 2000; 19: 3 Suppl. 331S-338S.ArticlePubMed
- 8. de Munter JS, Hu FB, Spiegelman D, Franz M, van Dam RM. Whole grain, bran, and germ intake and risk of type 2 diabetes: a prospective cohort study and systematic review. PLoS Med. 2007; 4(8): e261.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Flint AJ, Hu FB, Glynn RJ, Jensen MK, Franz M, Sampson L, Rimm EB. Whole grains and incident hypertension in men. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009; 90(3): 493-498.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. Fung TT, Hu FB, Pereira MA, Liu S, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Willett WC. Whole-grain intake and the risk of type 2diabetes: a prospective study in men. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002; 76(3): 535-540.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Gellar L, Rovner AJ, Nansel TR. Whole grain and legume acceptability among youths with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Educ. 2009; 35(3): 422-427.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 12. Jacobs DR Jr, Marquart L, Slavin J, Kushi LH. Whole-grain intake and cancer: an expanded review and meta analysis. Nutr Cancer. 1998; 30(2): 85-96.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Jones JM, Reicks M, Adams J, Fulcher G, Weaver G, Kanter M, Marquart L. The importance of promoting a whole grain food message. J Am Coll Nutr. 2002; 21(4): 293-297.PubMed
- 14. Lacey JM. Enhancing students' understanding of whole cereal grains in a university experimental foods course. J Nutr Educ Behav. 2007; 39(4): 235-236.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Liu S, Stampfer MJ, Hu FB, Giovannucci E, Rimm E, Manson JE, Hennekens CH, Willett WC. Whole-grain consumption and risk of coronary heart disease: result from the Nurses Health Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 1999; 70(3): 412-429.PubMed
- 16. Marquart L, Pham AT, Lautenschlager L, Croy M, Sobal J. Beliefs about whole-grain foods by food and nutrition professionals, health club members, and special supplemental nutrition program for women, infants, and children participants/state fair attendees. J Am Diet Assoc. 2006; 106(11): 1856-1860.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Meyer KA, Kushi LH, Jacobs DR Jr, Slavin J, Sellers TA, Folsom AR. Carbohydrates, dietary fiber, and incident type 2 diabetes in older women. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000; 71(4): 921-930.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Content of Korea National Health & Nutrition Examination Survey. Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs & Center for Disease Control and Prevention. 2011; cited 2011 April 20. Available from http://knhanes.cdc.go.kr/.
- 19. Montonen J, Knekt P, järvinen R, Aromaa A, Reunanen A. Whole grain and fiber intake and the incidence of type 2 diabetes. Am J Clin Nutr. 2003; 77(3): 622-629.ArticlePubMed
- 20. O'Neil CE, Nicklas TA, Zänovec M, Cho S. Whole-grain consumption is associated with diet quality and nutrient intake in adults: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999-2004. J Am Diet Assoc. 2010; 110(10): 1461-1468.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Eating well with Canada's food guide. The Minister of Health Canada. 2007; cited 2009 September 25. Available from http://www.hc-sc.gc.ca/fn-an/food-guide-aliment/index-eng.php.
- 22. The eatwell plate. U.K. Food Standards Agency. 2007; cited 2009 September 25. Available from http://www.eatwell.gov.uk/healthydiet/eatwellplate.
- 23. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services & U.S. Department of Agriculture. Dietary guidelines for American. 2005; 6th ed. Washington, DC: Government Printing Office; 52-55.
REFERENCES
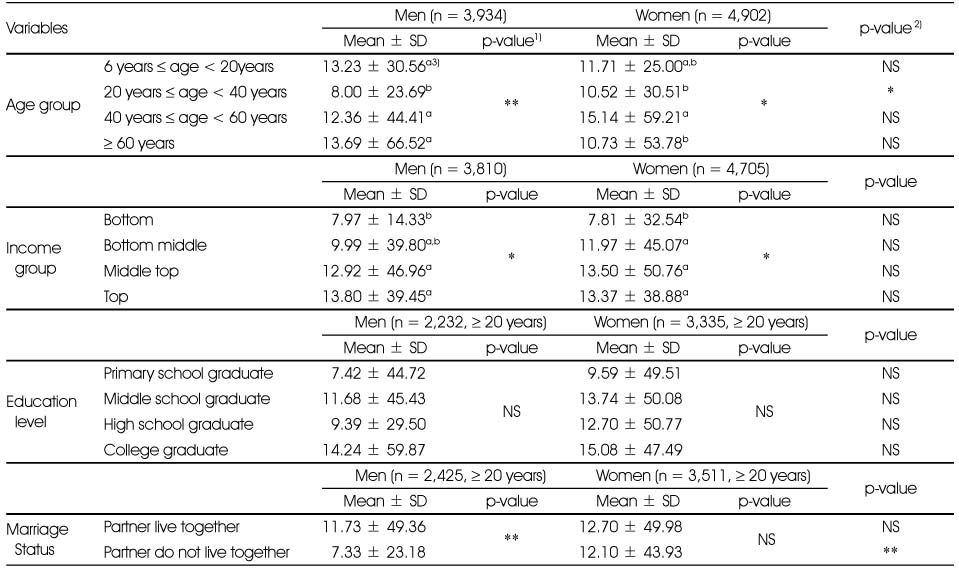
1) NS: not significant, *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01 by ANOVA or t test for difference between socio-demographic status within gender
2) NS: not significant, *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01 by t test for difference between gender within a row
3) Different letters represent statistical difference by Duncanís multiple comparison test
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Whole grain metabolite 3,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid is a beneficial nutritional molecule with the feature of a double-edged sword in human health: a critical review and dietary considerations
Waldemar Wagner, Katarzyna Sobierajska, Łukasz Pułaski, Anna Stasiak, Wojciech M. Ciszewski
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 64(24): 8786. CrossRef - Association between quality and quantity of dietary carbohydrate and pregnancy-induced hypertension: A case–control study
Fereshteh Sanjarimoghaddam, Fatemeh Bahadori, Farnush Bakhshimoghaddam, Mohammad Alizadeh
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN.2019; 33: 158. CrossRef - Three types of a high-carbohydrate diet are differently associated with cardiometabolic risk factors in Korean adults
SuJin Song, YoonJu Song
European Journal of Nutrition.2019; 58(8): 3279. CrossRef - Associations between Low-Carbohydrate Diets from Animal and Plant Sources and Dyslipidemia among Korean Adults
Seong-Ah Kim, Kyungjoon Lim, Sangah Shin
Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics.2019; 119(12): 2041. CrossRef - High-Carbohydrate Diets and Food Patterns and Their Associations with Metabolic Disease in the Korean Population
Yun Jung Lee, SuJin Song, YoonJu Song
Yonsei Medical Journal.2018; 59(7): 834. CrossRef - Association between dietary carbohydrate quality and the prevalence of obesity and hypertension
D.‐Y. Kim, S. H. Kim, H. Lim
Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics.2018; 31(5): 587. CrossRef - Analysis of Kimchi, vegetable and fruit consumption trends among Korean adults: data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (1998-2012)
Eun-Kyung Kim, Ae-Wha Ha, Eun-Ok Choi, Se-Young Ju
Nutrition Research and Practice.2016; 10(2): 188. CrossRef - Evaluation of Obesity and Nutritional Status by Age among Low-income Women aged over 20 -Using Data from the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey-
Hee-Kyung Jang
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(2): 246. CrossRef - A Study on the Kimchi Consumption of Korean Adults:Using Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2010~2012)
Eun-Kyung Kim, Yoo-Kyung Park, Se-Young Ju, Eun-Ok Choi
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2015; 30(4): 406. CrossRef - Associations between food insecurity and healthy behaviors among Korean adults
In-Ae Chun, So-Yeon Ryu, Jong Park, Hee-Kyung Ro, Mi-Ah Han
Nutrition Research and Practice.2015; 9(4): 425. CrossRef - An Evaluation of Dietary Habit and Nutritional Status by Household Income in Female Adults over the Age of 20 - Using Data from the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey -
Hee-Kyung Jang
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(4): 660. CrossRef - Relations of Whole Grain Consumption with Predisposing, Reinforcing, and Enabling Factors among Korean Adults
Da-Hae Chae, Jin-Hee Yum, Seung Min Lee
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2014; 20(2): 133. CrossRef - Effects of Green Whole Grain Mixed Diet on Body Weight and Waist Circumference in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Bo Kyung Han, Young Mi Kang, Sang Hyeon Ju, Min Young Shin, Ji Min Kim, So Young Rha, Kyong-Hye Joung, Ju Hee Lee, Koon Soon Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Bon Jeong Ku
The Korean Journal of Obesity.2014; 23(1): 41. CrossRef - Association of Whole Grain Consumption with Nutrient Intakes and Metabolic Risk Factors in Generally Healthy Korean Middle-Aged Women
Ye Jin Kim, Jin Hee Yum, Seungmin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(2): 176. CrossRef - Quality Characteristics of Bakery Products with Whole Green Wheat Powder
Jin-Young Kim, Ki-Teak Lee, Jeung-Hee Lee
Korean journal of food and cookery science.2013; 29(2): 137. CrossRef - Nutritional Evaluation and Its Relation to the Risk of Metabolic Syndrome according to the Consumption of Cooked Rice and Cooked Rice with Multi-grains in Korean Adults: Based on 2007-2008 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Soo-Hyun Son, Hwa-Jung Lee, Kyong Park, Tae-Youl Ha, Jung-Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(1): 77. CrossRef - Study on Food Culture of Koreans over 80-Years-Old Living in Goorye and Gokseong
Hae-Kyung Chung, Mi-Hye Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Culture.2012; 27(2): 142. CrossRef - Diet Quality and Food Patterns of Obese Adult Women from Low Income Classes -Based on 2005 KNHANES-
Jin-Sook Yoon, Heekyung Jang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2011; 16(6): 706. CrossRef
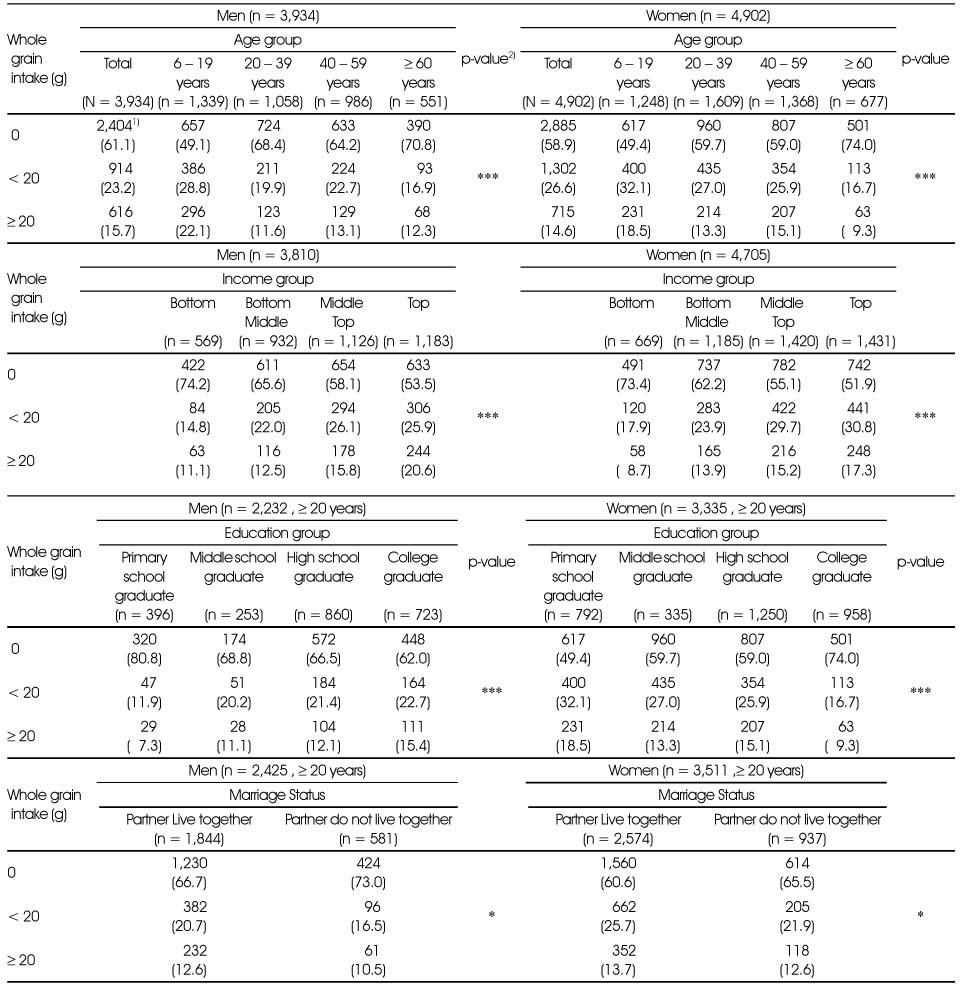
Distribution of whole grain intake levels by socio-demographic factors
1) N (%)
*: p < 0.05, ***: p < 0.001 by chi-square test for difference between socio-demographic status within gender
Mean whole grain intake (g/day) by socio-demographic factors
1) NS: not significant, *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01 by ANOVA or t test for difference between socio-demographic status within gender
2) NS: not significant, *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01 by t test for difference between gender within a row
3) Different letters represent statistical difference by Duncanís multiple comparison test
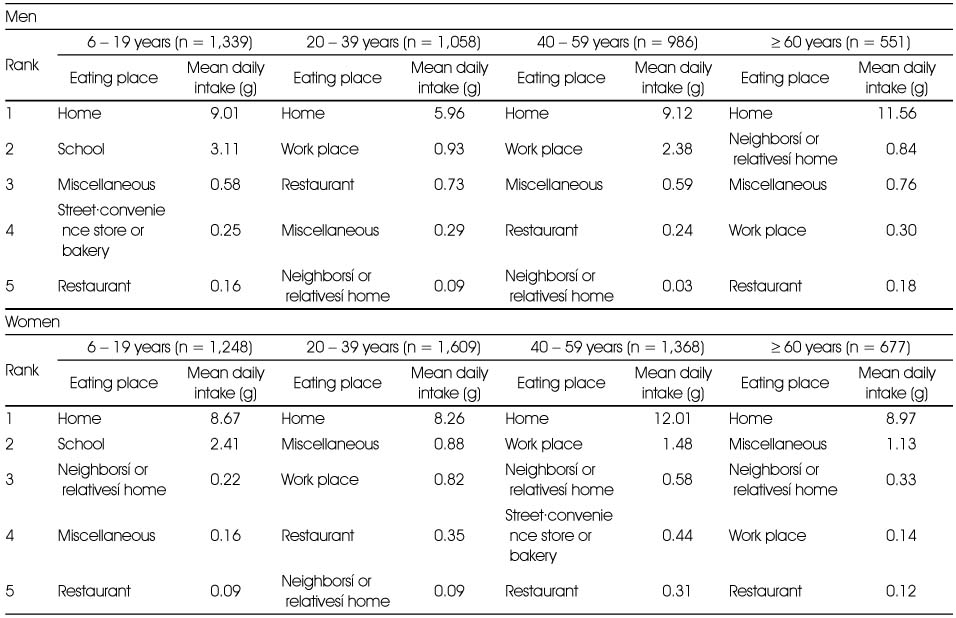
Top 5 dish items for whole grain intake by gender and age group
Eating places for whole grain intake by gender and age group
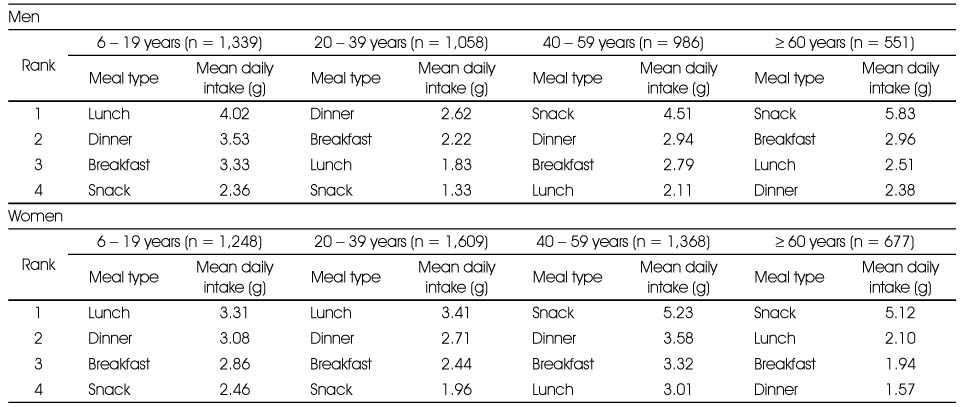
Meal type for whole grain intake by gender and age group
1) N (%) *: p < 0.05, ***: p < 0.001 by chi-square test for difference between socio-demographic status within gender
1) NS: not significant, *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01 by ANOVA or t test for difference between socio-demographic status within gender 2) NS: not significant, *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01 by t test for difference between gender within a row 3) Different letters represent statistical difference by Duncanís multiple comparison test

 KSCN
KSCN

 Cite
Cite


