Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Korean J Community Nutr > Volume 17(6); 2012 > Article
-
Original Article
- Adaptability and Preference to Korean Food with Foreigners Who Reside in Seoul, Korea
- Soojin Park, Dong-Ju Kim, Weon-Sun Shin
-
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition 2012;17(6):782-794.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.6.782
Published online: December 31, 2012
Department of Oriental medical Food and Nutrition, Semyung University, Jecheon, Korea.
1Graduate School of Education, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea.
2Department of Food and Nutrition, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Weon-Sun Shin, Food & Nutrition Dept, Hanyang University, 222 Wangsimni-ro, Seongdong-gu, Seoul 133-791, Korea. Tel: (02) 2220-1204, Fax: (02) 2292-1226, hime@hanyang.ac.kr
Copyright © 2012 The Korean Society of Community Nutrition
- 2,512 Views
- 14 Download
- 11 Crossref
Abstract
- The purpose of this study was to investigate the Korea-resident foreigners's adaptability and preference to Korean foods. The survey was carried out among 144 foreigners living in Seoul, Korea (male 57, female 87; from the East 109, from the West 35). Based on the first impression of Korean food, 'spicy', 'strong taste of seasoning', 'salty' were most common. About 90 percent of the foreigners adapted to Korean food in six months. It took more time to adapt to Korean food for Western people, compared to people from the East. Factors that influenced their adaption to Korean food were shown to be 'efforts by myself' and 'from friends'. Foreigners posited positive attitude toward Korean food according to their answers like 'nutritionally great food' and 'food with interesting ways of eating'. Westerners appeared to be more satisfied with Korean food. 'Too strong seasoning taste' and 'too sweet' were pointed out for further improvements. Beef Bulgogi, (Korean) fruit, Beef Ribs, Pork Ribs, and Grilled Pork Belly in order were foreigners' favorite foods, but Soju, Korean Sausage, Sliced Rice Cake Soup, Radish Kimchi and Vegetable Side Dishes were not. Taken together, the adaptability and preference to Korean foods to foreigners were different according to the gender and cultural background. Target marketing strategy of Korean Foods should be considered for foreign customers.
- 1. Brich LL. Effect of peer model' food choices and eating behaviors on preschool' food preferences. Child Dev. 1980; 51(2): 489-496.
- 2. Fugita S, O'Brien D. Structural assimilation, ethnic group membership, and political participation among Japanese Americans. Soc Forces. 1985; 63(4): 986-995.
- 3. Han YH. Influential factor on Korean dietary life and eating behaviour of female marriage immigrants. 2010; Hanyang University; MS thesis.
- 4. Jang MJ, Cho MS. Recognition and preference to Korean traditional food of foreign visitors in Korea. Korean J Diet Cult. 2000; 15(3): 215-223.
- 5. Jang JH. Influence of acculturation and uncertainty avoidance on the dining out behavior of foreigners living in Korea. 2008; Ewha University; MS thesis.
- 6. Jang BS. A study on dietary life of female marriage immigrants. 2009; Kyung Hee University; MS thesis.
- 7. Kim DJ. A study on adaptability and preference of Korean food for foreigners in Korea. 2010; Hanyang University; MS thesis.
- 8. Kim MY. The perception of quick service restaurants and Korean foods by Los Angeles residents. 2007; Sejong University; MS thesis.
- 9. Kim MH. Foreign students staying in Korea who prefer Korean food. 2008; Sookmyung Women's University; MS thesis.
- 10. Kim JS. Universalizing Korean food. Korean J Food Cult. 2005; 20(5): 499-505.
- 11. Statistical Yearbook of Seoul (2007): Foreign population. cited 2012 June 10. available from http://stat.seoul.go.kr/jsp/WWS8/WWSDS8123.jsp.
- 12. Kwak DW. Research to ingestion of food and an attitude from food and drink of multicultural family. 2009; Woosong University; MS thesis.
- 13. Kweon SY, Yoon SJ. Recognition and preference to Korean traditional food of Chinese at Seoul residence. Korean J Food Cult. 2006; 21(1): 17-30.
- 14. Lee KJ, Cho MS, Lee JM. Content analysis of the New York Times on Korean food from 1980 to 2005. Korean J Food Cult. 2007; 22(2): 289-298.
- 15. Lee KR, Lee JM, Cho MS. A research on swedish university students' perceptions of asian food; focused on Thai, Chinese,Japanese and Korean food. Korean J Food Cult. 2008; 23(3): 348-355.
- 16. Lee YJ. A study on the preference of Korean food and revisiting intention of Japanese tourists. J East Asian Soc Diet Life. 2005; 15(3): 247-256.
- 17. Seo KH, Lee SB, Shin MJ. Research on Korean food preference and the improvement of Korean restaurants for Japanese and Chinese students in Korea. Korean J Food Cookery Sci. 2003; 19(6): 715-722.
- 18. Skinner JD, Carruth BR, Bounds W, Ziegler PJ. Children's food preferences: A longitudinal analysis. J Am Diet Assoc. 2002; 102(1): 1638-1647.PubMed
- 19. Yoon HR. A study on recognition and preference of Korean foods for foreigners in different nationality. Korean J Food Cult. 2005; 20(3): 367-373.
REFERENCES
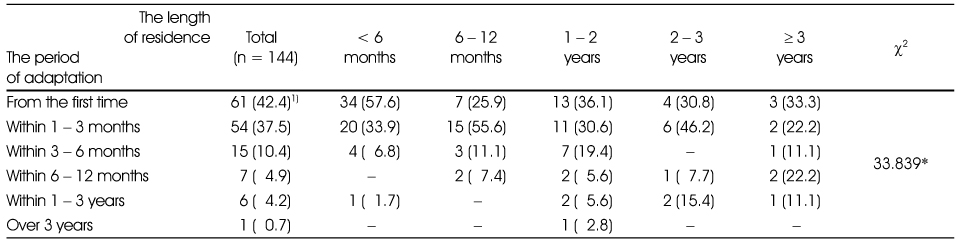
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Domestic Muslims Consumer Preference on HMR Product of Halal Base Freeze-Dried Sauces and its Sensory Characteristics
Ji-Na Kim, Eugene Choi, Hyeon Min Lee, Hyun-Ji Park, Weon-Sun Shin
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2018; 34(2): 163. CrossRef - Survey on the Status and Needs of Korean Food Consumption for the Development of Home Meal Replacement for Chinese and Japanese
Gyusang Han, Jiyu Choi, Sooyoun Kwon
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2017; 27(4): 420. CrossRef - A Study on Recognition, Preference and Popularization of Temple Food - Among Local and Foreign Restaurant Visitors
Yang-Su Moon, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(1): 53. CrossRef - Female Marriage Immigrants’ Information Awareness, Perception and Familiarity on Korean Food Culture by Personal Characteristics and Food Neophobia Degree
Hee-sun Jeong, Ji-young Yoon
Korean Journal of Food & Cookery Science.2016; 32(2): 233. CrossRef - A Comparative Analysis of the Relationship between Food Neophobia Scale and Korean Food Perception of Southeast Asian Workers Living in South Korea
Kyung-Ran Lee, Eun Jung Lee
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2016; 31(2): 131. CrossRef - Preparation and Stability of Capsaicin-loaded Nanoemulsions by Microfluidazion
Min-Ji Kim, Soo-Jeong Lee, Chong-Tai Kim
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(6): 985. CrossRef - Nutrition knowledge, eating attitudes, nutrition behavior, self-efficacy of childcare center foodservice employees by stages of behavioral change in reducing sodium intake
Yun Ahn, Kyung Won Kim, Kyungmin Kim, Jinwon Pyun, Ikhyun Yeo, Kisun Nam
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(5): 429. CrossRef - Sensory characteristics and cross-cultural acceptability of Chinese and Korean consumers for ready-to-heat (RTH) type bulgogi (Korean traditional barbecued beef)
Su-Gyeong Jo, Soh Min Lee, Kyung-Hyun Sohn, Kwang-Ok Kim
Food Science and Biotechnology.2015; 24(3): 921. CrossRef - Cross-cultural Investigation on Chinese and Korean Consumers’ Reasons for Liking and Disliking for Bulgogi Using Check-all-that-apply Questionnaire
Nam-E Kang, Su-Kyung Jo, Soh Min Lee, Kwang-Ok Kim
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2014; 29(6): 567. CrossRef - A Survey on the Recognition and the Preference of Bibimbab with Students in Bayreuther, Germany
Joo-Eun Song
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Culture.2014; 29(4): 307. CrossRef - Establishment of the standard recipe according to preference of Korean, residents foreigner in Korea and American
Eun-Mi Kim, Sang-Hee Seo, Chang-Keun Kwock, Eun-Jung Lee, Seug-Hee Wie
Korean journal of food and cookery science.2013; 29(5): 463. CrossRef
General characteristics of the subjects
Anthropometric data of the subjects
1) Means ± SD, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001, NS: Not Significant
The adaptability to Korean food with foreigners who reside in Korea
1) Result by t-test (continuous data of 5-point scale), 2) Mean ± SD, 3) Result by χ2-test, 4) n (%), 5) χ2-value, *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
Correlation with length of residence in Korea and period of adaptation on Korean food. Correlation between the length of residence and the period of adaptation to Korean food
1) n (%)
*: p < 0.05
Contributing factors for adaptation to Korean food with foreigners who reside in Korea
1) n (%)
Eating habits of foreigners who reside in Korea in post-adaptation to Korean food
1) n (%)
*: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
Preference of Korean food with foreigners who reside in Korea
1) Mean ± SD (Score- 1: very much, 3: average, 5: dislike)
2) Korean fruit: Charmoi (oriental melon), Gam (persimmon), Gyul (tangerine) and so on
*: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
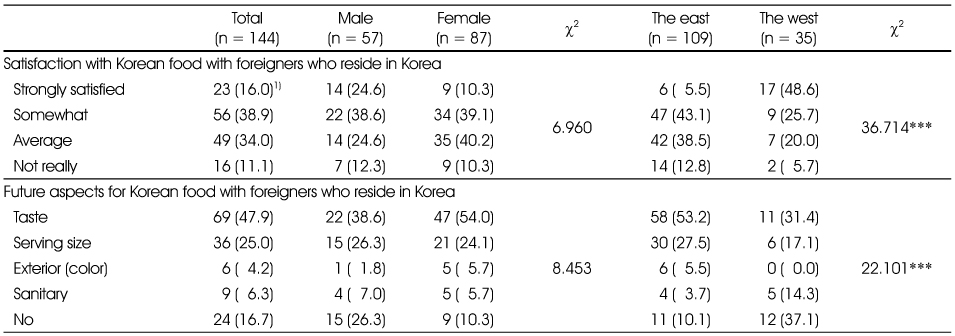
Satisfaction with Korean food and Future aspects for Korean food
1) n (%)
***: p < 0.001
Reason for liking and disliking to Korean food
1) n (%)
2) p-value calculated by χ2 test (categorical data)
Advises on taste and serving size improvement of Korean food
1) p-value calculated by χ2 test (categorical data) *: p < 0.05 **: p < 0.01
2) n (%)
1) Means ± SD, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001, NS: Not Significant
1) Result by t-test (continuous data of 5-point scale), 2) Mean ± SD, 3) Result by χ2-test, 4) n (%), 5) χ2-value, *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
1) n (%) *: p < 0.05
1) n (%)
1) n (%) *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
1) Mean ± SD (Score- 1: very much, 3: average, 5: dislike) 2) Korean fruit: *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
1) n (%) ***: p < 0.001
1) n (%) 2) p-value calculated by χ2 test (categorical data)
1) p-value calculated by χ2 test (categorical data) *: p < 0.05 **: p < 0.01 2) n (%)

 KSCN
KSCN








 Cite
Cite


