Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Korean J Community Nutr > Volume 17(3); 2012 > Article
-
Original Article
- Comparison of Eating Behavior between Commensality and Solo-eating of University Students by BMI
- Youngmee Lee, Wookyoun Cho, Yujin Oh
-
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition 2012;17(3):280-289.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.3.280
Published online: June 30, 2012
Department of Food and Nutrition, Kyungwon Campus at Gacheon University, Seongnam, Korea.
1Nutrition and Health Service Team, Korea Health Promotion Foundation, Seoul, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Yujin Oh, Nutrition and Health service team, Korea Health Promotion Foundation, 11-13, Yeouido-dong, Youngdeungpo-gu, Seoul 150-868, Korea. Tel: (02) 3781-3541, Fax: (02) 3781-3579, oyujin@khealth.or.kr
Copyright © 2012 The Korean Society of Community Nutrition
- 1,249 Views
- 9 Download
- 18 Crossref
Abstract
- The objective of this research was to explore the influences of 'having a meal with someone' on individuals' eating pattern. Eating is not a simple matter of energy intake but also serves to anchor daily routines being cultivated by people and society. This study was conducted using a cross-sectional eating behavior survey of university students (N = 893, 380 men, 513 women) aged 20 to 24 years. Results were analyzed and presented as frequencies, means and χ2-test with SPSS 14.0. Differences in dietary habits by commensality and solo-eating were observed; Students who ate alone, spent 15 min for a meal and ate convenience food items when they didn't feel hungry. Compared to students who ate alone, those who ate together with someone spent 30 min for a meal and ate more amount of food. Eighty percent of respondents ate more various menus in commensality than solo-eating. They felt lonely when they ate alone and preferred to eat together. In conclusion, university students start to decide and select their own meals by themselves after junior and high school food services which are fixed with regard to menu and the amount. Dietary habits of Koreans rapidly changed concomitant with social changes over the past half century. Governments and health experts recognize that unbalanced meals cause lifestyle-related diseases, in particular obesity. Our research findings will contribute to more comprehensive efficient nutrition education programs in order to prevent obesity and other lifestyle-related diseases in early stages of adulthood.
-
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant (NRF-2011-B00003).
NOTES
- 1. Brownell KD, Wadden TA. Etiology and treatment of obesity: understanding a serious, prevalent, and refractory disorder. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1992; 60(4): 505-517.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Chang HB, Lee HY, Han YH, Kim KN, Hyn TS. Changes in food and nutrient intakes of college students between 1999 and 2009. Korean J Community Nutr. 2011; 16(3): 324-336.Article
- 3. Cho SH, Jang JH, Ha TY, Lee KS, Kim MK, Seo JS. A survey on breakfast of workers in Daegu area. Korean J Community Nutr. 2004; 9(6): 673-682.
- 4. Cho YT. Promotion of aging science and technology research. 2007; cited 2012 March 1. Available from http://www.pharmstoday.com/news/articleView.html?idxno=32998.
- 5. Daviglus ML, Liu K, Yan LL, Pirzada A, Garside DB, Schiffer L. Body mass index in middle age and health-related quality of life in order age: the Chicago heart association detection project in industry study. Arch Intern Med. 2003; 163(20): 2448-2455.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Ha KH. Stress and dietary life of college students in Daejeon area. 2011; cited 2012 March 1. Available from http://dx.doi.org/10.5392/JKCA.2011.11.11.329.
- 7. Heini AF, Weinsier RL. Divergent trends on obesity and fat intake patterns: the American paradox. Am J Med. 1997; 102(3): 259-264.PubMed
- 8. Hermans R, Lichtwarck-Aschoff A, Bevelander KE, Herman CP, Larsen JK, Engels R. Mimicry of food intake: the dynamic interplay between eating companions. PLoS One. 2012; 7(2): e31027.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Jin EH. A study on the body mass index and health behavior in college students. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 2005; 11(2): 200-205.
- 10. Kang MJ, Joung HJ, Lim JH, Lee YS, Song YJ. Secular trend in dietary patterns in a Korean adult population, using the 1998, 2001, and 2005 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Korean J Nutr. 2011; 44(2): 152-161.Article
- 11. Kelly RM. The associative group analysis method and evaluation research. Eval Rev. 1985; 9(1): 35-50.ArticlePDF
- 12. Kim HS. A study on the university students' obesity status and acknowledgement. Korea Sport Res. 2003; 14(6): 1417-1434.
- 13. Kim SH. A study on the relationship between time spent on lunch and degree of obesity, eating habits in culinary college male students. Korean J Community Nutr. 2006; 11(6): 695-706.
- 14. Kim SH, Joung KH, Chae BS. Dietary life and eating-out style related to breakfast frequency of male students in culinary college. Korean J Community Nutr. 2007; 12(1): 13-24.
- 15. Kim SH, Kim JY, Ryu KA, Sohn CM. Evaluation of the dietary diversity and nutrient intakes in obese adults. Korean J Community Nutr. 2007; 12(5): 583-591.
- 16. Kim BS, Lee YE. College student's dietary behavior related to their Myers-Briggs type indicator personality preferences. Korean J Community Nutr. 2002; 7(1): 32-44.
- 17. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and Korea Institute for Health and Social Affaire. In-Depth analysis on the 3rd (2005) Korea Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). 2007.
- 18. Korea Statistics. Statistics of the cause of death. 2008.
- 19. Lee JS. A study of female college students' behavior and ideal breakfast types -2. dining-out behavior of breakfast and preference on breakfast menu-. Korean J Food Cult. 2003; 18(5): 466-474.
- 20. Lee KA, Jeong BY, Moon SK, Kim IS, Soichiro N. Comparisons of Korean adults' eating habits, food preferences, and nutrient intake by generation. Korean J Nutr. 2006; 39(5): 433-504.
- 21. Lim YS, Park HR, Han QJ. Comparison of preference for convenience and dietary attitude in college students by sex in Seoul and Kyunggi-do area. J Korean Diet Assoc. 2005; 11(1): 11-20.
- 22. Ministry of Health and Welfare. National Health and Nutrition Survey 1998. 1998.
- 23. Ministry of Health and Welfare. National Health and Nutrition Survey 2001. 2001.
- 24. Ministry of Health and Welfare. National Health and Nutrition Survey 2005. 2005.
- 25. Ministry of Health and Welfare. National Health and Nutrition Survey 2007. 2007.
- 26. Ministry of Health amd Welfare. The National Health Plan 2020. 2011.
- 27. Oh HS. Alcohol consumption rates and the perception of drinking cultures among college students in the Wonju area. Korean J Food Cult. 2011; 26(2): 101-112.
- 28. Park KA. Food preferences and dietary habits of university students in Kyungbuk province. J East Asian Soc Diet Life. 2003; 13(6): 527-541.
- 29. Rhee MK. The development of a healthy diet program for weigh control in the obese. Korean J Health Psychol. 2007; 12(1): 59-75.Article
- 30. Seymour M, Hoerr SL, Hunag YL. Inappropriate dieting behaviors and related lifestyle factors in young adults: Are college students different? J Nutr Educ. 1997; 29(1): 21-26.Article
- 31. Song YJ, Paik HY, Joung HJ. A comparison of cluster and factor analysis to derive dietary patterns in Korean adults using data from the 2005 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Korean J Community Nutr. 2009; 14(6): 722-733.
- 32. You JS, Chin JH, Kim MJ, Chang KJ. College students' dietary benavior, health-related lifestyles and nutrient intake status by physical activity levels using International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) in Incheon area. Korean J Nutr. 2008; 41(8): 818-831.
- 33. Yu HH, Nam JE, Kim IS. A study of the nutritional intake and health condition of female college students as related to their frequency of eating breakfast. Korean J Community Nutr. 2003; 8(6): 964-976.
- 34. Winkleby MA, Cubbin C. Changing patterns in health behaviors and risk factor related to chronic diseases, 1990-2000. Am J Health Promot. 2004; 19(1): 19-27.ArticlePubMedPDF
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Risk factors of overweight/obesity-related lifestyles in university students: Results from the EHU12/24 study
Nerea Telleria-Aramburu, Marta Arroyo-Izaga
British Journal of Nutrition.2022; 127(6): 914. CrossRef - Rice vs. Wheat: Does staple food consumption pattern affect food waste in Chinese university canteens?
Long Qian, Feng Li, Hongbo Liu, Lingen Wang, Breda McCarthy, Shaosheng Jin
Resources, Conservation and Recycling.2022; 176: 105902. CrossRef - Are the Slimmer More Wasteful? The Correlation between Body Mass Index and Food Wastage among Chinese Youth
Long Qian, Feng Li, Hongbo Liu, Lingen Wang
Sustainability.2022; 14(3): 1411. CrossRef - Determinants of food waste generation in Chinese university canteens: Evidence from 9192 university students
Long Qian, Feng Li, Baoming Cao, Lingen Wang, Shaosheng Jin
Resources, Conservation and Recycling.2021; 167: 105410. CrossRef - Lonely or alone? Solitary dining in Japan and Taiwan
Yevvon Yi-Chi Chang
International Journal of Culture, Tourism and Hospitality Research.2021; 15(1): 10. CrossRef - Gender and age group differences in nutrition intake and dietary quality of Korean adults eating alone: based on Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data, 2013–2016
Yoonjin Ahn, Youngmi Lee, Haeryun Park, Kyunghee Song
Nutrition Research and Practice.2021; 15(1): 66. CrossRef - Analysis of differences in eating alone attitude of Koreans by dietary habits and age
Eun Jung Lee, Kyung-Ran Lee, Ju-Yeon Kim
Appetite.2020; 152: 104695. CrossRef - Solitary eating, an inferior alternative? An examination of time-use data in South Korea
Sangmoon Kim
International Sociology.2020; 35(4): 415. CrossRef - Comparison of Dietary Behavior of Eating Alone in Single Households by Status of Workers and Age
Pil Kyoo Jo, Yu Jin Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(5): 408. CrossRef - Analysis of the Difference in Nutrients Intake, Dietary Behaviors and Food Intake Frequency of Single- and Non Single-Person Households: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), 2014–2016
Na-Yeon Kang, Bok-Mi Jung
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(1): 1. CrossRef - Association between family dinner and BMI in adults: data from the 2013 to 2015 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Woongchan Rah, Jaewon So, Eun-Cheol Park, Sang Ah Lee, Sung-In Jang
Public Health Nutrition.2019; 22(4): 681. CrossRef - Eating Alone is Differentially Associated with the Risk of Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Men and Women
Chul-Kyoo Kim, Hyun-jin Kim, Hae-Kyung Chung, Dayeon Shin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2018; 15(5): 1020. CrossRef - Recognition and Consumption of Meal Alone and Processed Food according to Major of College Students
Byung Bum Choi
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(6): 911. CrossRef - Differences in Solo Eating Perceptions and Dietary Behaviors of University Students by Gender
Youngmee Lee, Yu Jin Oh, Wookyoun Cho, Pil Kyoo Jo
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2015; 21(1): 57. CrossRef - Survey on Health-related Factors, Nutrition Knowledge and Food Habits of College Students in Wonju Area
Seung Lim Lee, Sun Hee Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(2): 96. CrossRef - Health-related Factors, Nutrition Knowledge and Dietary Habits among Nursing and Allied Health College Students
Su Ol Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of School Health.2015; 28(3): 158. CrossRef - The Relationship between Obesity Degree and Psychological Factors, Dietary Behaviors and Health-Related Quality of Life in Adult Women in their Twenties in Seoul and Kyungin Area
Sang-Yeon Kim
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2013; 26(3): 535. CrossRef - The study of Perception in Body Somatotype and Dietary Behaviors - The Comparative Study between Korean and Chinese College Students -
Youngmee Lee, Lin Sun
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(1): 25. CrossRef
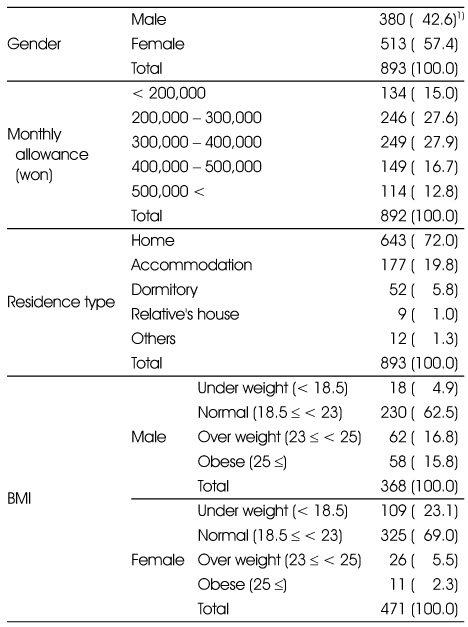
General characteristics of subjects
1) N (%)
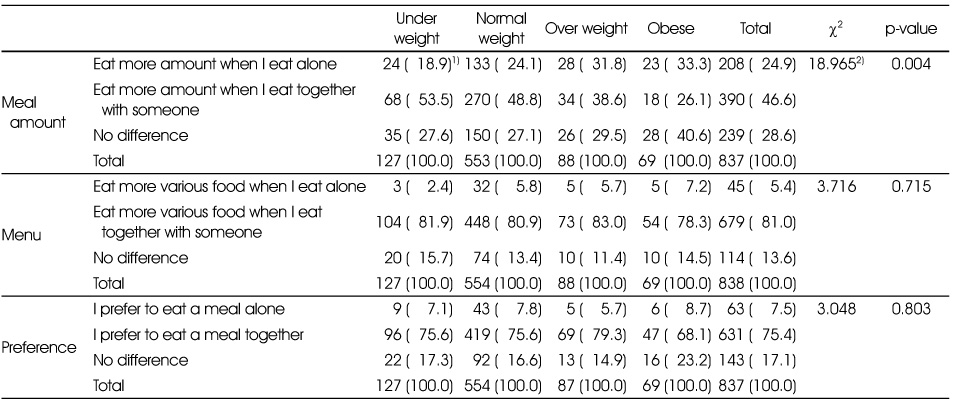
Comparison of food behavior of commensality and sole eating by BMI
1) N (%)
2) Measured by χ2-test
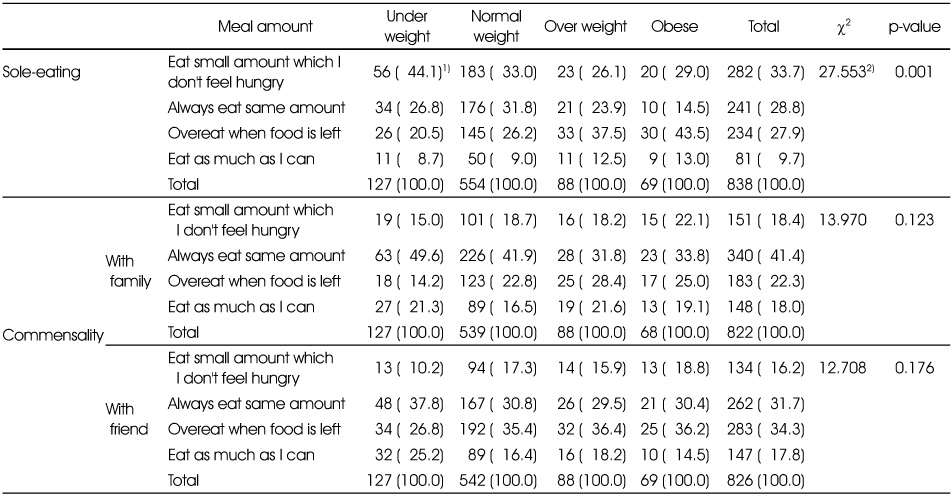
Meal amount of commensality and sole eating by BMI
1) N (%)
2) Measured by χ2-test
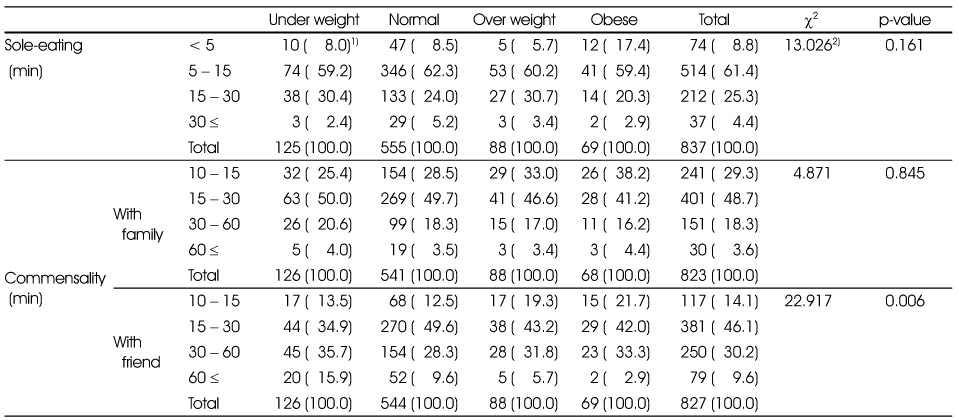
Duration meal time of commensality and sole eating by BMI
1) N (%)
2) Measured by χ2-test
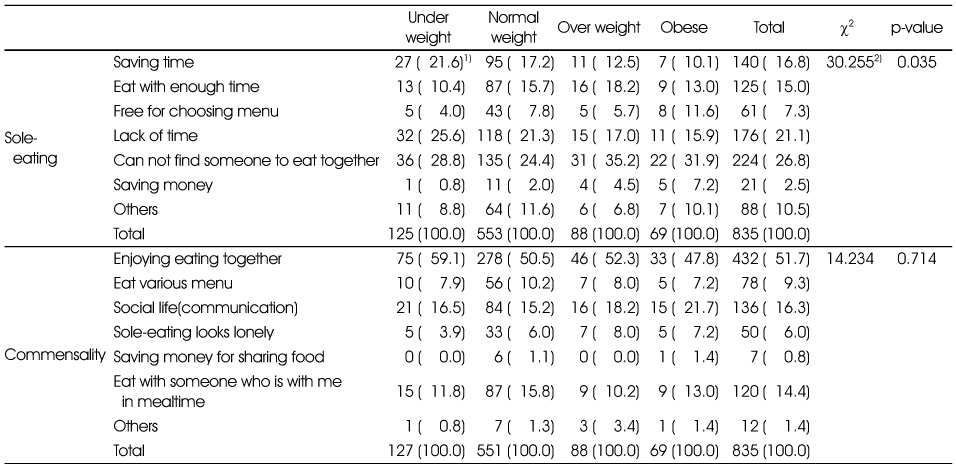
The reasons of commensality and sole eating by BMI
1) N (%)
2) Measured by χ2-test
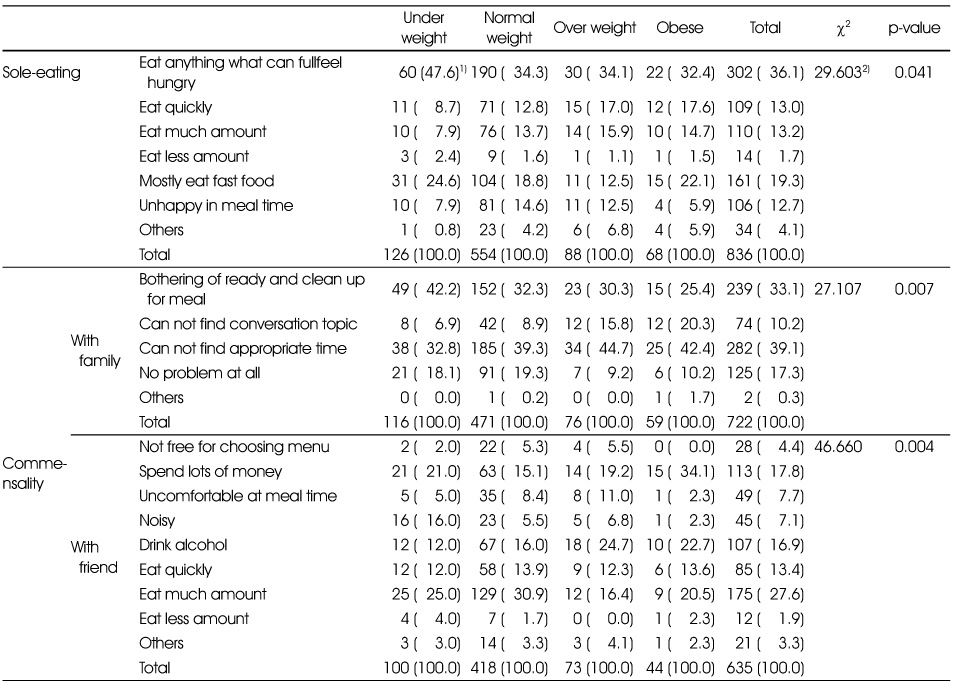
Self-recognized problems of commensality and sole eating by BMI
1) N (%)
2) Measured by χ2-test
1) N (%)
1) N (%) 2) Measured by χ2-test
1) N (%) 2) Measured by χ2-test
1) N (%) 2) Measured by χ2-test
1) N (%) 2) Measured by χ2-test
1) N (%) 2) Measured by χ2-test

 KSCN
KSCN
 Cite
Cite


