Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Korean J Community Nutr > Volume 19(4); 2014 > Article
-
Research Article
- Chinese Female Marriage Immigrants' Dietary Life after Immigration to Korea : Comparison between Han-Chinese and Korean-Chinese
- Kana Asano, Jihyun Yoon, Si-Hyun Ryu
-
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition 2014;19(4):317-327.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.4.317
Published online: August 31, 2014
1Department of Food and Nutrition, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
2Department of Nutrition and Foodswervice Management, Paichai University, Daejeon, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Si-Hyun Ryu. Department of Nutrition and Foodservice Management, Paichai University, 155-40 Baejae-ro, Seo-gu, Daejeon 302-735, Korea. Tel: (042) 520-5907, Fax: (070) 4369-1778, ryush@pcu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2014 The Korean Society of Community Nutrition
This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 1,633 Views
- 1 Download
- 17 Crossref
Abstract
-
Objectives
- This study was conducted to investigate Chinese female marriage immigrants' dietary life after immigration to Korea, focusing on comparison between Han-Chinese (traditional Chinese) and Korean-Chinese (Chinese of Korean descent).
-
Methods
- An in-person survey was conducted with women married to Korean men, having one child or more aged 1-6 years old, and having resided in Korea for at least one year before the survey. The data were collected from the 309 respondents comprising 151 Han-Chinese and 158 Korean-Chinese in the summer of 2013.
-
Results
- Overall, there was no significant difference in dietary practice, dietary acculturation, dietary behavior, dietary habits, and food intake between the Han-Chinese and the Korean-Chinese respondents. Over 50% of the respondents ate Korean food every day. The overall level of dietary acculturation was about 3.5 out of 5 points. The average score of healthy dietary behavior was a little bit higher than 3 out of 5 points. Approximately 3/4 of the respondents showed increasing frequency of eating out. The respondents reporting increase food diversity were over 70%. Decreased frequency of skipping meal was about 60% of the respondents. Over 50% of the respondents showed increasing consumption of Kimchi, vegetables, fruit, and meat.
-
Conclusions
- Dietary life of Korean-Chinese female marriage immigrants was similar to that of Han-Chinese female marriage immigrants after immigration to Korea. The results from this study suggest that not only Han-Chinese but also Korean-Chinese should be targeted in various diet-related acculturation support programs as important multicultural populations in Korea.
-
This research was supported by Multicultural Human Ecology Center, Research Institute of Human Ecology, Seoul National University.
NOTES
- 1. Cha SM, Bu SY, Kim EJ, Kim MH, Choi MK. Study of dietary attitudes and diet management of married immigrant women in Korea according to residence period. J Korean Diet Assoc 2012; 18(4): 297-307.Article
- 2. Gray VB, Cossman JS, Dodson WL, Byrd SH. Dietary acculturation of Hispanic immigrants in Mississippi. Salud Pblica Mex 2005; 47(5): 351-360.Article
- 3. Han YH. Influential factor on Korean dietary life and eating behaviour of female marriage immigrants. Hanyang University; 2010; 56-57 MS thesis.
- 4. Han YH, Shin WS, Kim JN. Special theme:multicultural society and the identity of migrants; influential factor on Korean dietary life and eating behaviour of female marriage migrants. Comp Korean Stud 2011; 19(1): 115-159.
- 5. Hyun KJ, Kim YS. Development of a Korean life adaptation measure for female marriage immigrants. Health Soc Welf Rev 2011; 31(4): 63-100.Article
- 6. Jeong MJ, Jung EK, Kim AJ, Joo N. Nutrition knowledge and need for a dietary education program among marriage immigrant women in Gyeongbuk region. J Korean Diet Assoc 2012; 18(1): 30-42.Article
- 7. Kim HR, Paik SH, Jung HW, Lee AR, Kim E. Survey on dietary behaviors and needs for nutrition services, and development contents of nutrition education for female immigrants in multicultural families in Korea. Seoul: Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs; 2011.
- 8. Kim JM, Lee HS, Kim MH. Food adaptation and nutrient intake of female immigrants into Korea through marriage. Korean J Nutr 2012; 45(2): 159-169.Article
- 9. Kim JM, Lee NH. Analysis of the dietary life of immigrant women from multicultural families in the Daegu area. J Korean Diet Assoc 2009; 15(4): 405-418.
- 10. Kim SH. Characteristics and implications of Chinese multicultural families. Incheon: Incheon Development Institute; 2013. p. 1-16.
- 11. Kim SH, Kim WY, Lyu JE, Chung HW, Hwang JY. Dietary intakes and eating behaviors of Vietnamese female immigrants to Korea through marriage and Korean spouses and correlations of their diets. Korean J Community Nutr 2009; 14(1): 22-30.
- 12. Statistics Korea. 2013 Marriage divorce statistics. 2014; cited May 2, 2013]. Available from http://www.kostat.go.kr.
- 13. Lee JS. The factors for Korean dietary life adaptation of female immigrants in multi-cultural families in Busan. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr 2012; 41(6): 807-815.Article
- 14. Li SJ, Paik HY, Kim JS, Wen Y, Joung HJ. Comparative study on dietary patterns of Korean,-Chinese and Koreans. Korean J Diet Cult 2001; 16(4): 341-353.
- 15. Park HM, Moon ST. Analysis on the actual condition of female immigrants in rural area for social adjustment education. J Agric Edu Hum Resour Dev 2008; 40(2): 69-91.Article
- 16. Rosenmller DL, Gasevic D, Seidell J, Lear SA. Determinants of changes in dietary patterns among Chinese immigrants: a cross-sectional analysis. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 2011; 8: 42.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 17. Shin BG, Kwon YJ. Research articles: difference analysis on the cognition, image, attitude, and globalization of Korean foods among American, Chinese, and Japanese groups. J Foodserv Manage 2010; 13(3): 311-332.
- 18. So J, Han SN. Diet-related behaviors, perception and food preferences of multicultural families with Vietnamese wives. Korean J Community Nutr 2012; 17(5): 589-602.Article
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Dietary acculturation and changes of Central Asian immigrant workers in South Korea by health perception
EunJung Lee, Juyeon Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(3): 305. CrossRef - Flavor principle as an implicit frame: Its effect on the acceptance of instant noodles in a cross-cultural context
Meng Li, Seo-Jin Chung
Food Quality and Preference.2021; 93: 104293. CrossRef - Development and evaluation of semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire for marriage migrant women in multicultural families
Jung-Hyun Kim, Oh Yoen Kim, Min June Lee, Eunju Park
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(1): 76. CrossRef - Consumption of Han-sik and its Association with Socioeconomic Status among Filipino Immigrant Women: the Filipino Women's Diet and Health Study (FiLWHEL)
Nayeon Kim, Minji Kang, Grace Abris, Sherlyn Mae P. Provido, Hyojee Joung, Sangmo Hong, Sung Hoon Yu, Chang Beom Lee, Jung Eun Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(6): 475. CrossRef - Analysis of Korean Dietary Life Adaptation of Married Female Immigrants
Jeong-Sook Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(2): 103. CrossRef - Study on the change and acculturation of dietary pattern of Southeast Asian workers living in South Korea
Eun Jung Lee, Kyung-Ran Lee, Seung-Joo Lee
Appetite.2017; 117: 203. CrossRef - Development of a Korean Food Culture Education Textbook for Married Female Immigrants
Jeong-Sook Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(5): 415. CrossRef - Dietary behaviors of female marriage immigrants residing in Gwangju, Korea
Eun Ju Yang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2016; 49(3): 179. CrossRef - Female Marriage Immigrants’ Information Awareness, Perception and Familiarity on Korean Food Culture by Personal Characteristics and Food Neophobia Degree
Hee-sun Jeong, Ji-young Yoon
Korean Journal of Food & Cookery Science.2016; 32(2): 233. CrossRef - Food intake and nutritional status of female marriage immigrants residing in Gwangju, Korea
Eun Ju Yang, Jin Mo Khil
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2016; 49(5): 358. CrossRef - Acculturation and changes in dietary behavior and anthropometric measures among Chinese international students in South Korea
Jounghee Lee, Ran-Ran Gao, Jung-Hee Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2015; 9(3): 304. CrossRef - Factors related to Korean Dietary Adaptation in Chinese Female Marriage Immigrants living in the Seoul Metropolitan Area
Kana Asano, Jihyun Yoon, Si-Hyun Ryu
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(2): 234. CrossRef - Comparison of Eating Habits and Food Preference of Elementary School Children between Multi-cultural Families and Ordinary Families in Gyeongnam Province
Joo Hee Lee, Seon Ok Jeong, Changim Kim
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2015; 28(6): 973. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Dietary and Weight Control Behavior of Female College Students in Korea and China
Li Song, Na Young An, Ho Kyung Ryu
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2015; 26(4): 761. CrossRef - Comparative Study on Dietary Life of Southeast Asian Workers Living in South Korea
Eun Jung Lee, Kyung-Ran Lee
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2015; 30(4): 422. CrossRef - Korean Food Acculturation Phenomena of Married Immigrant Women and Their Children’s Eating Habits
Jisun Lee, Solji Lee, Bokyung Ryu, Lana Chung
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2015; 30(5): 545. CrossRef - Japanese Female Marriage Immigrants' Dietary Life and Health-related Characteristics by Level of Dietary Adaptation after Immigration to Korea
kana Asano, Jihyun Yoon, Si-Hyun Ryu
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(5): 765. CrossRef
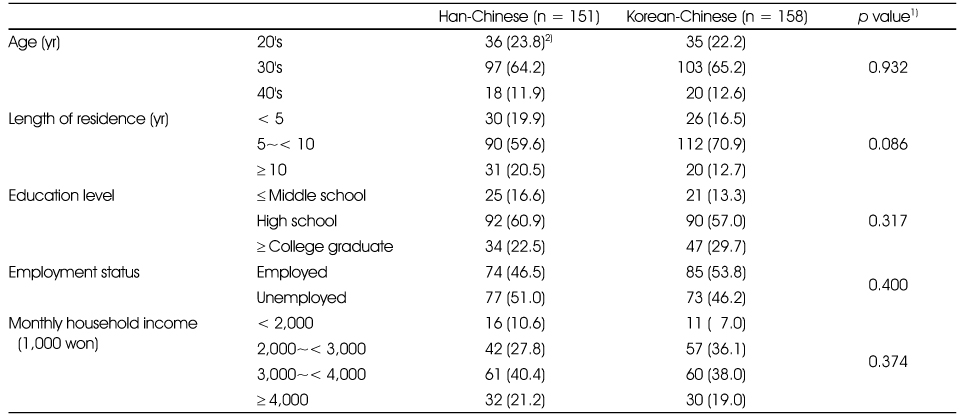
The general characteristics of the respondents
1) p-value by chi-square test
2) N (%)
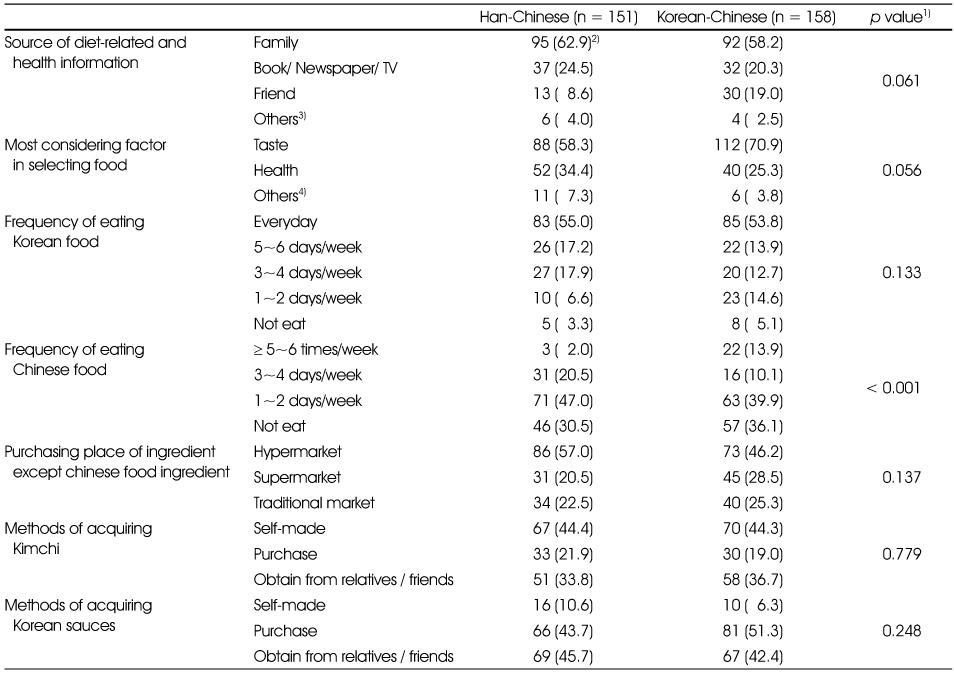
The dietary practice of Chinese female marriage immigrants in Korea
1) p-value by chi-square test
2) N (%)
3) Community / Internet
4) Price / Korean-style
The dietary acculturation level of Chinese female marriage immigrants in Korea
1) p-value by chi-square test
2) 5 point scale: 1 = strongly disagree, 2 = disagree, 3 = neutral, 4 = agree, 5 = strongly agree
3) Mean ± SD
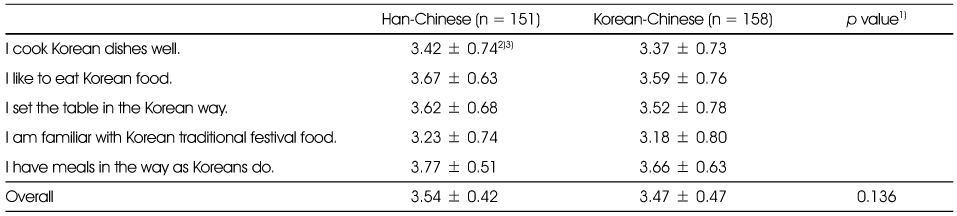
The perception on Korean food of Chinese female marriage immigrants in Korea
1) p-value by chi-square test
2) 5 point scale: 1 = strongly disagree, 2 = disagree, 3 = neutral, 4 = agree, 5 = strongly agree
3) Mean ± SD
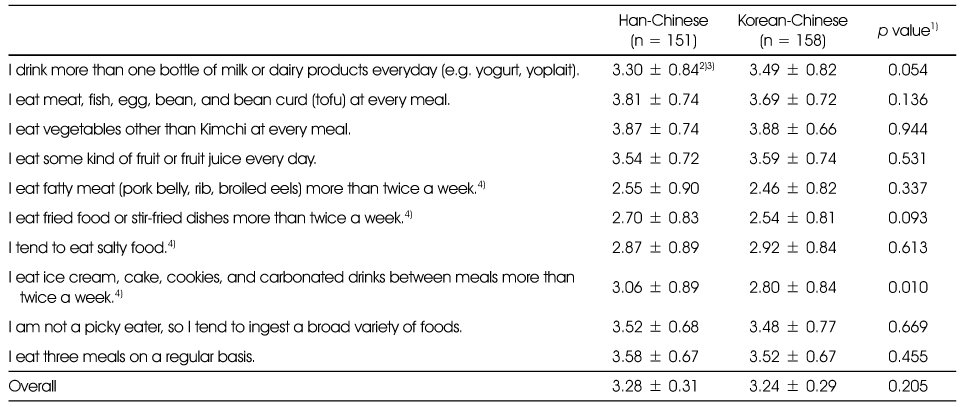
The healthy dietary behavior of Chinese female marriage immigrants in Korea
1) p-value by chi-square test
2) 5 point scale: 1 = strongly disagree, 2 = disagree, 3 = neutral, 4 = agree, 5 = strongly agree
3) Mean ± SD
4) Reverse coding
Chinese female marriage immigrants' changes in dietary habits after immigration to Korea
1) p-value by chi-square test
2) N (%)
3) 33% of the cells had expected counts of less than 5. Therefore "no change" and "decrease" response categories were combined into a single category for chi-square test.
Chinese female marriage immigrants' change in food intake after immigration to Korea
1) 2) N (%)
1) 2) N (%) 3) Community / Internet 4) Price / Korean-style
1) 2) 5 point scale: 1 = strongly disagree, 2 = disagree, 3 = neutral, 4 = agree, 5 = strongly agree 3) Mean ± SD
1) 2) 5 point scale: 1 = strongly disagree, 2 = disagree, 3 = neutral, 4 = agree, 5 = strongly agree 3) Mean ± SD
1) 2) 5 point scale: 1 = strongly disagree, 2 = disagree, 3 = neutral, 4 = agree, 5 = strongly agree 3) Mean ± SD 4) Reverse coding
1) 2) N (%) 3) 33% of the cells had expected counts of less than 5. Therefore "no change" and "decrease" response categories were combined into a single category for chi-square test.

 KSCN
KSCN



 Cite
Cite


