Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Korean J Community Nutr > Volume 16(1); 2011 > Article
-
Original Article
- Comparison of the Dietary Factors between Normal and Constipation Groups by Self-reported Constipation in Female College Students
- Chae Rin Lee, Soon Kyung Kim
-
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition 2011;16(1):23-36.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.1.23
Published online: February 28, 2011
Department of Food Science and Nutrition, College of Natural Science, Soonchunhyang University, Asan, Chungnam, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Soon Kyung Kim, Department of Food Science and Nutrition, College of Natural Science, Soonchunhyang University, Asan, Chungnam 336-745, Korea. Tel: (041) 530-1261, Fax: (041) 530-1264, soon56@sch.ac.kr
Copyright © 2011 The Korean Society of Community Nutrition
- 822 Views
- 1 Download
- 6 Crossref
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- The Effects of Life Style Modification on Constipation of the Older Adults at a Geriatric Hospital
Ho-Suk Kang, Inja Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2017; 20(1): 52. CrossRef - Perception on Optimal Diet, Diet Problems and Factors Related to Optimal Diet Among Young Adult Women Using Focus Group Interviews: Based on Social Cognitive Theory
Hye Jin Kim, A Reum Lee, Kyung Won Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(4): 332. CrossRef - A Study on Life Style and Eating Habits Correlated with Constipation of Working Women in Kangwon Provicne
Jeong-Sill Lee
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(4): 581. CrossRef - Actual Status of Constipation and Life Factors Affecting Constipation by Diagnosis of Rome in Female University Students in Korea
Su-Jin Jung, Soo-Wan Chae, Hee-Sook Sohn, Sook-Bae Kim, Jeong-Ok Rho, Sang-Ho Baik, Myung-Hee Kang, Gun-Hee Kim, Mi-Hyun Kim, Hyun-Sook Kim, Eun-Ju Park, Young-Ran Heo, Youn-Soo Cha
The Korean Journal of Nutrition.2011; 44(5): 428. CrossRef - Iron Status in Female College Students in the Gyeongnam Area
Mi-Young Park, Sung-Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Nutrition.2011; 44(3): 222. CrossRef - A Survey on Dietary Behaviors and Liquid Consumptions of University Students in Kongju of Chungnam Province in Korea
Sun Hyo Kim
The Korean Journal of Nutrition.2009; 42(4): 327. CrossRef
Anthropometric parameters of the subjects
1) Mean ± SD, 2) Body Fat Mass, 3) Fat Free Mass, 4) Body Mass Index, 5) Percent of Body Fat, 6) Waist-Hip Ratio, 7) Visceral Fat Area, 8) Abdominal Circumference, 9) Hip Circumference, 10) Systolic Pressure, 11) Diastolic Pressure, 12) N.S. : not significant
Bowel habits of the subjects
1) N (%)
2) Significantly different between normal and constipation by chi-square test
*: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
General characteristics & Life styles of the subjects
1) N (%)
2) Significantly different between normal and constipation by chi-square test
*: p < 0.05, ***: p < 0.001
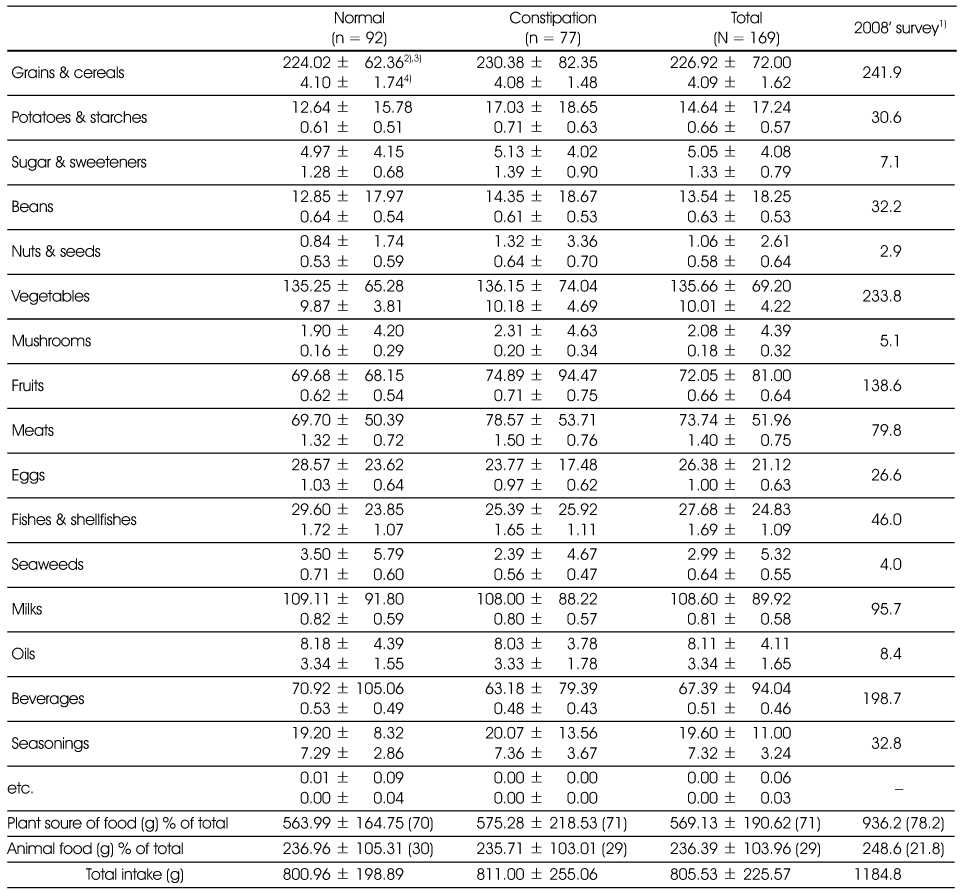
Daily food intakes of the subjects
1) 2008 survey (19~29yr, women), National Health Statics, The Korea Centers for Disease Control & Prevention 2009
2) Daily food intakes of the subjects (g), 3) Mean ± SD
4) The foods intake frequency of the subjects (times/day)
Daily nutrients intakes of the subjects
1) Estimated energy requirement, Values are expressed as EER amount (%EER of intake)
2) Recommended intake based on dietary reference for koreans (2010). Values are expressed as RI amount (% RI of intake)
3) Adequate intake based on dietary reference intakes for koreans (2010). Values are expressed as AI amount (% AI of intake)
4) Significance as determined by student's t-test
*: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01
Daily nutrients intake of the subject per kg of body weight
1) Mean ± SD, 2) N.S. : not significant
Intake frequency of foods (concern with fiber) and water
1) N (%)
Correlation coefficient between bowel habits and factors that influence in constipation
Significance as determined by Pearson's correlation coefficient
*: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01
1) Mean ± SD, 2) Body Fat Mass, 3) Fat Free Mass, 4) Body Mass Index, 5) Percent of Body Fat, 6) Waist-Hip Ratio, 7) Visceral Fat Area, 8) Abdominal Circumference, 9) Hip Circumference, 10) Systolic Pressure, 11) Diastolic Pressure, 12) N.S. : not significant
1) N (%) 2) Significantly different between normal and constipation by chi-square test *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
1) N (%) 2) Significantly different between normal and constipation by chi-square test *: p < 0.05, ***: p < 0.001
1) 2008 survey (19~29yr, women), National Health Statics, The Korea Centers for Disease Control & Prevention 2009 2) Daily food intakes of the subjects (g), 3) Mean ± SD 4) The foods intake frequency of the subjects (times/day)
1) Estimated energy requirement, Values are expressed as EER amount (%EER of intake) 2) Recommended intake based on dietary reference for koreans (2010). Values are expressed as RI amount (% RI of intake) 3) Adequate intake based on dietary reference intakes for koreans (2010). Values are expressed as AI amount (% AI of intake) 4) Significance as determined by student's t-test *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01
1) Mean ± SD, 2) N.S. : not significant
1) N (%)
Significance as determined by Pearson's correlation coefficient *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01

 KSCN
KSCN







 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite


