Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Korean J Community Nutr > Volume 25(1); 2020 > Article
-
Research Article
-
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition 2020;25(1):1-12.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.1.1
Published online: January 20, 2020
1)Department of Food Science and Nutrition, Pusan National University, Busan, Korea, Graduate Student
2)Department of Food Science and Nutrition, Pusan National University, Research Institute of Ecology, Busan, Korea, Professor
- †Corresponding author Ho Kyung Ryu Department of Food Science and Nutrition, Pusan National University, 2, Busandaehak-ro 63beon-gil, Geumjeong-gu, Busan 46241, Korea Tel: (051) 510-7397 Fax: (051) 583-3648 E-mail: hokryu@pusan.ac.kr
Copyright © 2020 Journal of the Korean Society of Community Nutrition
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 2,429 Views
- 47 Download
- 4 Crossref
Abstract
-
Objectives
- This study investigates the current state of consuming breakfast among elementary school students residing in Malang, East Java, Indonesia, and to identify factors that influence breakfast behavior.
-
Methods
- The research model was set up as per the health belief model, and slightly modified by adding the subjective normative factors of the theory of planned behavior. The survey was conducted from July 17 to August 15, 2017 using a questionnaire, after receiving the permission PNU IRB (2017_60_HR).
-
Results
- The subjects were 77 boys (49.4%) and 79 girls (50.6%) suffering from malnutrition with anemia (21.2%) and stunting ratio of Height for Age Z Score (HAZ) (11.5%). Furthermore, moderate weakness (14.8%) and overweight and obesity (12.3%) by Body Mass Index for Age Z Score (BMIZ) were coexistent. According to the results obtained for breakfast, 21.8% did not eat breakfast before school, with 18.8% of the reasons for skipping breakfast being attributed to lack of food. Even for subjects partaking breakfast, only about 10% had a good balanced diet. The average score of behavioral intention on eating breakfast was 2.60 ± 0.58. The perceived sensitivity, perceived severity, perceived benefits, and self-efficacy of the health belief model correlated with breakfast behavior. Of these, self-efficacy (β=0.447, R2=0.200) and perceived sensitivity (β=0.373, R2=0.139) had the greatest effect on breakfast behavior. Mother was the largest impact person among children.
-
Conclusions
- In order to increase the level of breakfast behavior intention among children surveyed in Indonesia, we determined the effectiveness by focus on education which helps the children recognize to be more likely to get sick when they don't have breakfast, and increase their confidence in ability to have breakfast on their own. We believe there is a necessity to seek ways to provide indirect intervention through mothers, as well as impart direct nutrition education to children.
| Variables | Boys | Girls | Total | t or χ2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anthtropometric status | |||||
| Height (cm) | 136.8 ± 7.5 | 141.5 ± 6.5 | 139.1 ± 7.0 | 0.003∗∗ | |
| Weight (kg) | 931.8 ± 7.2 | 933.2 ± 6.9 | 932.5 ± 7.0 | 0.366 | |
| Growth and development status | |||||
| HAZ1) | Severe stunting | 0 (880.0) | 0 (880.0) | 0 (880.0) | 6.574∗ |
| Moderate stunting | 14 (818.2) | 4 (885.1) | 18 (811.5) | ||
| Normal | 63 (881.8) | 75 (894.9) | 138 (888.5) | ||
| BMIZ2) | Severe weakness | 2 (882.6) | 3 (883.8) | 5 (883.2) | 0.844 |
| Moderate weakness | 9 (811.7) | 9 (811.4) | 18 (811.5) | ||
| Normal | 55 (871.4) | 59 (874.7) | 114 (873.1) | ||
| Overweight | 10 (813.0) | 7 (888.9) | 17 (810.9) | ||
| Obesity | 1 (881.3) | 1 (881.3) | 2 (881.3) | ||
| Anemia | |||||
| Anemia | 18 (823.4) | 15 (819.0) | 33 (821.2) | 0.883 | |
| Normal | 59 (876.6) | 64 (881.0) | 123 (878.8) | ||
| Total | 77 (100.0) | 79 (100.0) | 156 (100.0) | ||
∗P<0.05, ∗∗ P<0.01, ∗∗∗ P<0.001 1) Correlation coefficient between independent variable and dependent variable 2) Coefficient of determination, indicating how many percent of the total variability can be explained by independent variables 3) Test statistic of significance of the regression model 4) Regression coefficient, influence of independent variables on dependent variables, the closer to 1, the higher the influence 5) Test statistic of regression coefficient
- 1. Stefani M, Harfika A, Anwar K, Humayah W, Pujilestari S, Azni IN, et al. An integrated healthy breakfast education for teachers, school children, and parents in West Java. ICCD 2018; 1(1): 165-170.ArticleLink
- 2. Hong JK. A study on the professional guidance and counseling for children in elementary schools. J Elementary Educ 2002; 15(1): 1-20.
- 3. Susanto F. Breakfast skipper and breakfast eater: which is better. Int J Nutr Food Sci 2015; 4(5): 565-573.Article
- 4. Brown JL, Beardslee WH, Prothrow-Stith D. Impact of school breakfast on children's health and learning: An analysis of the scientific research [Internet]. Sodexo Foundation; 2008. [cited 2019 Jul 1]. Available from:. http://us.stop-hunger.org/files/live/sites/stophunger-us/files/HungerPdf/Impact. %20of%20School %20Breakfast%20Study_tcm150–212606.pdf..
- 5. Huang CJ, Hu HT, Fan YC, Liao YM, Tsai PS. Association of breakfast skipping with obesity and health-related quality of life: evidence from a national survey in Taiwan. Int J Obes 2010; 34(4): 720-725.ArticlePDF
- 6. The national institute of health research and development, Ministry of health, Republic of Indonesia. Report on result of national basic health research (RISKESDAS) [Internet]. Jakarta, Indonesia: Ministry of health, Republic of Indonesia; 2007. [cited 2019 Jul 1]. Available from:. http://biofarmaka.ipb.ac.id/biofarmaka/2014/Riskesdas2007. %20-%20Report%20on%20Result%20of% 20National%20Basic%20Health%20Research.pdf..
- 7. Trihono, MSc. Riset Kesehatan Dasar: Riskesdas 2013. Badan Penelitian dan Pengemb A Nagan Kesehatan Kementerian Kesehatan RI;. 2013; [cited 2019 Jul 1]. Available from:. http://www.depkes.go.id/resources/download/general/Hasil. %20Riskesdas%202013.pdf..
- 8. Yang RJ, Wang EK, Hsieh YS, Chen MY. Irregular breakfast eating and health status among adolescents in Taiwan. BMC Public Health 2006; 6(1): 295.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 9. Nurul Fadhilah A, Teo PS, Huybrechts I, Foo LH. Infrequent breakfast consumption is associated with higher body adiposity and abdominal obesity in Malaysian school aged children. PLoS One 2013; 8(3): e59297.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. WHO Working Group. Use and interpretation of anthropometric indicators of nutritional status. Bull World Health Organ 1986; 64(6): 929-941.PubMedPMC
- 11. Mei Z, Grummer-Strawn LM. Standard deviation of anthropometric Z-scores as a data quality assessment tool using the 2006 WHO growth standards: a cross country analysis. Bull World Health Organ 2007; 85(6): 441-448.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Kuczmarski RJ, Ogden CL, Guo SS, Grummer-Strawn LM, Flegal KM, Mei Z, et al. 2000 CDC growth charts for the United States: Methods and development [Internet]. National Center for Health Statistics, USA;. 2002; [cited 2019 Jul 1]. Available from:. https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/6451.
- 13. Hardinsyah H, Aries M. Jenis pangan sarapan dan perannya dalam asupan gizi harian anak usia 6–12 tahun di Indonesia. Jurnal Gizi dan Pangan 2012; 7(2): 89-96.ArticleLink
- 14. Sekiyama M, Roosita K, Othsuka R. Snack foods consumption contributes to poor nutrition of rural children in West Java, Indonesia. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2012; 21(4): 558-567.PubMed
- 15. Februhartanty J. Nutrition education: It has never been an easy case for Indonesia. Food Nutr Bull 2005; 26(2): S267-274.ArticlePubMedLink
- 16. Lee KA. Elementary school children's perceptions of traditional Korean foods, based on the health belief model. Korean J Nutr 2013; 46(1): 86-97.Article
- 17. Shin KO, Yoon JA, Je H, Hwang HJ, Lee Y, Choi JH. The effect of nutrition education based on health belief model for male college students in Seoul. Korean J Hum Ecol 2018; 27(4): 305-319.Article
- 18. Fathi A, Sharifirad G, Gharlipour Z, Hakimelahi J, Mohebi S. Effects of a nutrition education intervention designed based on the health belief model (HBM) on reducing the consumption of unhealthy snacks in the sixth grade primary school girls. Int J Pediatr 2017; 5(2): 4361-4370.
- 19. UNICEF. Child poverty and disparities in Indonesia: challenges for inclusive growth [Internet]. Jakarta UNICEF; 2013. [cited 2019 Jul 1]. Available from:. https://www.unicef.org/indonesia/Child_Poverty_Indonesia.pdf.
- 20. Lee CH. The effect of locus of control and health belief model on handwashing: expanding health belief model [master's thesis]. Hanyang University;. 2015.
- 21. Kim JE. Study on predicting behavioral intention of breastfeeding among primigravida [Master's thesis]. Dongguk University;. 2000.
- 22. Kim JE. Microbiological analysis of hands and education of handwashing among preschool children in a day care center [master's thesis]. Hanyang University;. 2010.
- 23. WHO. Iron deficiency anaemia: assessment, prevention and control. A guide for programme managers [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2001. [cited 2019 Jul 1]. Available from:. http://www.who.int/nutrition/publications/micronutrients/anaemia_iron_deficiency/WHO_NHD_01.3/en/index.html.
- 24. Insani PN, Rimbawan R, Palupi E. Dietary habits and nutritional status among school children in rural and urban area: a comparative study from Bogor, Indonesia. Future Food J Food Agric Soc 2018; 6(2): 55-66.
- 25. OECD/World Health Organization. Health at a glance: Asia/Pacific 2012 [Internet]. OECD; 2013. [cited 2019 Jul 3]. Available from:. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/87269/9789264183902_kor.pdf?sequence=3&isAllowed=y.
- 26. WHO. The world health report 2002: Reducing risks, promoting healthy life [Internet]. World Health Organization, Geneva; 2002. [cited 2019 Jul 1]. Available from:. https://www.who.int/whr/2002/en/.
- 27. Hardinsyah MS. Sarapan sehat salah satu pilar gizi seimbang [Internet]. Ketua umum pergizi pangan; 2013. [cited 2019 Jul 1]. Available from:. https://pergizi.org/images/stories/downloads/materi_PESAN/materi3.pdf.
- 28. Rampersaud GC, Pereira MA, Girard BL, Adams J, Metzl JD. Breakfast habits, nutritional status, body weight, and academic performance in children and adolescents. J Am Diet Assoc 2005; 105(5): 743-760.ArticlePubMed
- 29. Evers S, Taylor J, Manske S, Midgett C. Eating and smoking behaviours of school children in southwestern Ontario and Charlottetown, PEI. Can J Public Health 2001; 92(6): 433-436.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 30. Ming MF, Ying GC, Kassim M. Eating patterns of school children and adolescents in Kuala Lumpur. Malays J Nutr 2006; 12(1): 1-10.
- 31. So HK, Nelson EA, Li AM, Guldan GS, Yin J, Ng PC, et al. Breakfast frequency inversely associated with BMI and body fatness in Hong Kong Chinese children aged 9–18 years. Br J Nutr 2011; 106(5): 742-751.ArticlePubMed
- 32. Barker M, Robinson S, Wilman C, Barker DJ. Behaviour, body composition and diet in adolescent girls. Appetite 2000; 35(2): 161-170.ArticlePubMed
- 33. Kosti RI, Panagiotakos DB, Zampelas A, Mihas C, Alevizos A, Leonard C, et al. The association between consumption of breakfast cereals and BMI in schoolchildren aged 12–17 years: the VYRONAS study. Public Health Nutr 2008; 11(10): 1015-1021.ArticlePubMed
- 34. Kovarova M, Vignerova J, Blaha P, Osancova K. Bodily characteristics and lifestyle of Czech children aged 7.00 to 10.99 years, incidence of childhood obesity. Cent Eur J Public Health 2002; 10(4): 169-173.PubMed
- 35. Sjoberg A, Hallberg L, Hoglund D, Hulthen L. Meal pattern, food choice, nutrient intake and lifestyle factors in The Goteborg Adolescence Study. Eur J Clin Nutr 2003; 57(12): 1569-1578.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 36. Keski-Rahkonen A, Kaprio J, Rissanen A, Virkkunen M, Rose RJ. Breakfast skipping and health-compromising behaviors in adolescents and adults. Eur J Clin Nutr 2003; 57(7): 842-853.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 37. O'Neil CE, Nicklas TA. A review of the relationship between 100% fruit juice consumption and weight in children and adolescents. Am J Lifestyle Med 2008; 2(4): 315-354.ArticleLink
- 38. Cotton PA, Subar AF, Friday JE, Cook A. Dietary sources of nutrients among US adults, 1994 to 1996. J Am Diet Assoc 2004; 104(6): 921-930.ArticlePubMed
- 39. Whittaker P, Paul R. Tufaro PR, Rader JI. Iron and folate in fortified cereals. J Am Coll Nutr 2001; 20(3): 247-254.PubMed
- 40. Rampersaud GC. Benefits of breakfast for children and adolescents: Update and recommendations for practitioners. Am J Lifestyle Med 2008; 3(2): 86-103.ArticleLink
- 41. Menteri Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. Peraturan menteri kesehatan republik Indonesia nomor 41 tahun 2014 [Internet]. Jakarta, Indonesia;. 2014; [cited 2019 Jul 1]. Available from:. http://hukor.depkes.go.id/uploads/produk_hukum/PMK. %20No.%2041%20ttg%20Pedoman%20Gizi%20Seimbang.pdf..
- 42. Imanningsih N, Jahari AB, Permaesih ID, Chan P, Amarra S. Consumption and sources of added sugar in Indonesia: a review. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2018; 27(1): 47-64.PubMed
- 43. Lee SJ, Ryu HK. Relationship between dietary intakes and the double burden of malnutrition in adults of Malang, Indonesia: An exploratory study. Nutr Res Pract 2018; 12(5): 426-435.ArticlePubMedPMCLink
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- The School Food Environment in Ghana is Associated With Dietary Diversity and Anemia: Findings From the 2022 National Nutrition and Health Survey of In-School Adolescents
Mica Jenkins, Esi Foriwa Amoaful, Mutala Abdulai, Veronica Quartey, Porbilla Ofosu-Apea, Jevaise Aballo, Maku E. Demuyakor, Maria Elena D. Jefferds, Nancy J. Aburto, Usha Ramakrishnan, Reynaldo Martorell, O. Yaw Addo
Food and Nutrition Bulletin.2025; 46(2-3): 78. CrossRef - Analysis of the factors that influence preschool children eating behavior by applying the health belief model: Seoul and Gyeonggi Province
Sung-Mi Cha, Soo-Youn Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(3): 541. CrossRef - Evaluation of dietary behavior and investigation of the affecting factors among preschoolers in Busan and Gyeongnam area using nutrition quotient for preschoolers (NQ-P)
Soo-Youn Kim, Sung-Mi Cha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(6): 596. CrossRef - Psychoactive substance use among Chinese non-engaged youth: The application of the Health Belief Model
Phoenix Kit-han Mo, Joseph Tak Fai Lau
Children and Youth Services Review.2020; 113: 105008. CrossRef
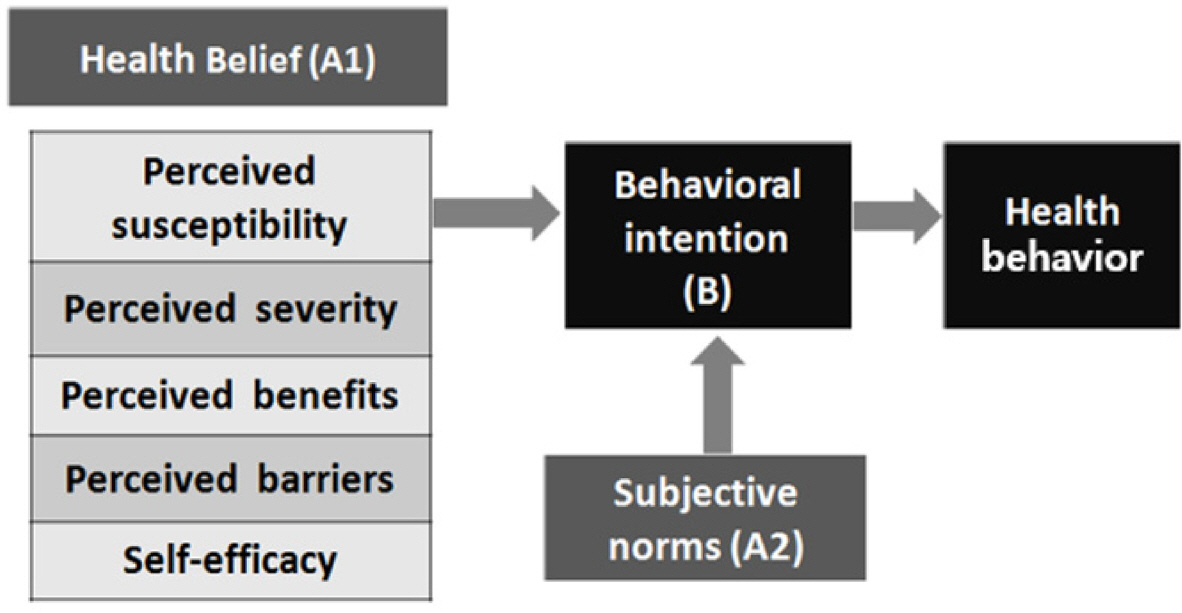
Fig. 1.
General characteristics of subjects
| Variables | Frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | Boys | 77 (849.4) |
| Girls | 79 (850.6) | |
| Age | 99 | 14 (889.0) |
| 10 | 51 (832.7) | |
| 11 | 57 (836.5) | |
| 12 | 30 (819.2) | |
| 13 or over | 4 (882.6) | |
| Tribe | Java | 150 (896.2) |
| The Others | 6 (883.8) | |
| Main meal preparation | Grandfather | 2 (881.3) |
| Grandmother | 21 (813.5) | |
| Father | 6 (883.8) | |
| Mother | 138 (888.5) | |
| Brothers and sisters | 1 (886.0) | |
| Father's education level | College | 14 (889.0) |
| High school | 44 (828.2) | |
| Middle school | 24 (815.4) | |
| Elementary school | 31 (819.9) | |
| No school | 2 (881.3) | |
| Non-response | 38 (824.4) | |
| Mother's education level | College | 7 (884.5) |
| High school | 36 (823.1) | |
| Middle school | 42 (826.9) | |
| Elementary school | 28 (817.9) | |
| No school | 1 (880.6) | |
| Non-response | 39 (825.0) | |
| Economic status | High | 2 (881.3) |
| Medium | 135 (886.5) | |
| Low | 2 (881.3) | |
| Non-response | 17 (810.9) | |
| Total | 156 (100.0) | |
n (%)
Growth and development status and anemia of the subjects
| Variables | Boys | Girls | Total | t or χ |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anthtropometric status | |||||
| Height (cm) | 136.8 ± 7.5 | 141.5 ± 6.5 | 139.1 ± 7.0 | 0.003∗∗ | |
| Weight (kg) | 931.8 ± 7.2 | 933.2 ± 6.9 | 932.5 ± 7.0 | 0.366 | |
| Growth and development status | |||||
| HAZ1) | Severe stunting | 0 (880.0) | 0 (880.0) | 0 (880.0) | 6.574∗ |
| Moderate stunting | 14 (818.2) | 4 (885.1) | 18 (811.5) | ||
| Normal | 63 (881.8) | 75 (894.9) | 138 (888.5) | ||
| BMIZ2) | Severe weakness | 2 (882.6) | 3 (883.8) | 5 (883.2) | 0.844 |
| Moderate weakness | 9 (811.7) | 9 (811.4) | 18 (811.5) | ||
| Normal | 55 (871.4) | 59 (874.7) | 114 (873.1) | ||
| Overweight | 10 (813.0) | 7 (888.9) | 17 (810.9) | ||
| Obesity | 1 (881.3) | 1 (881.3) | 2 (881.3) | ||
| Anemia | |||||
| Anemia | 18 (823.4) | 15 (819.0) | 33 (821.2) | 0.883 | |
| Normal | 59 (876.6) | 64 (881.0) | 123 (878.8) | ||
| Total | 77 (100.0) | 79 (100.0) | 156 (100.0) | ||
n (%) or Mean ± SD ∗ P<0.05, ∗∗ P<0.01 by student's t-test or χ
2test 1) Height for Age Z score 2) BMI for Age Z score
Breakfast eating status of subjects
| Eating status | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Frequency | |
| Everyday | 98 (862.8) |
| About once every two days | 24 (815.4) |
| Hardly eat | 34 (821.8) |
| Total | 156 (100.0) |
| Reasons for skipping1) | |
| Nothing to eat | 12 (818.8) |
| No one to prepares meals | 2 (883.1) |
| No time to eat | 18 (828.1) |
| Poor appetite | 17 (826.6) |
| Do not want to eat | 15 (823.4) |
| Total | 64 (100.0) |
| How to manage hunger1) | |
| Home-made lunch box | 33 (845.8) |
| Buy a meal around school | 21 (829.2) |
| Snack | 6 (888.3) |
| The others | 12 (816.7) |
| Total | 72 (100.0) |
n (%) 1) Multiple response was allowed
Types of foods for breakfast
| Types of foods | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Carbohydrates1) | 39 (825.6) |
| Meat and fish | 4 (882.6) |
| Vegetables | 29 (818.6) |
| Fruits | 2 (881.3) |
| Beverage | 2 (881.3) |
| Carbohydrates + meat and fish | 11 (887.1) |
| Carbohydrates + meat and fish + beverage | 3 (881.9) |
| Carbohydrates + meat and fish + vegetables | 3 (881.9) |
| Carbohydrates + meat and fish + vegetables + beverage | 7 (884.5) |
| Carbohydrates + meat and fish + vegetables + fruits + beverage | 6 (883.8) |
| Carbohydrates + vegetables | 11 (887.1) |
| Carbohydrates + vegetables + fruits | 3 (881.9) |
| Carbohydrates + vegetables + beverage | 9 (885.8) |
| Carbohydrates + vegetables + fruits + beverage | 1 (880.6) |
| Carbohydrates + fruits | 4 (882.6) |
| Carbohydrates + beverage | 14 (889.0) |
| Meat and fish + beverage | 7 (884.5) |
| Ratio of single-food meal | 49.4% |
| Ratio of balanced meal | 10.2% |
| Ratio of intakes of meat and fish | 26.3% |
| Total | 156 (100.0) |
| n (%) | |
1)Carbohydrates included rice, bread, noddles, casava, potatoes, etc.
Behavioral intention on eating breakfast
| Construct | Measurement questions | Scores | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Behavioral intention | I will wake up earlier in the morning to eat breakfast for my health and go to school. | 2.47 ± 0.66 | 2.60 ± 0.581) |
| I will make it a habit to eat breakfast. | 2.60 ± 0.60 | ||
| I will eat breakfast evenly for the sake of nutrition. | 2.73 ± 0.50 | ||
Mean ± SD Scoring criteria: ‘I don't think so' 1 point, ‘I think it's normal' 2 point, ‘I think so' 3 point 1) Average of 3 questions
Health beliefs on eating breakfast
| Health beliefs | Measurement questions | Scores | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Perceived susceptibility | If you skip breakfast, you will not feel cheerful and dizzy | 2.46 ± 0.71 | 2.50 ± 0.701) |
| If you are hungry for a long time, you can be sick. | 2.53 ± 0.70 | ||
| If you do not eat breakfast, you may lose concentration. | 2.51 ± 0.70 | ||
| Perceived severity | I think that obesity caused by snacking can be life-threatening. | 2.33 ± 0.74 | 2.43 ± 0.70 |
| I think severe anemia prevents proper growth. | 2.42 ± 0.71 | ||
| Chronic malnutrition is thought to reduce cognitive ability and brain function. | 2.56 ± 0.67 | ||
| Perceived benefits | When you eat breakfast, you feel better. | 2.67 ± 0.52 | 2.78 ± 0.43 |
| If you eat breakfast, you can study well. | 2.83 ± 0.42 | ||
| If you eat breakfast consistently, it will help you grow. | 2.85 ± 0.35 | ||
| Perceived barriers | I usually do not have enough food to eat breakfast at home. | 2.18 ± 0.75 | 2.31 ± 0.72 |
| There is no one to prepare breakfast, nor does it prepare. | 2.48 ± 0.70 | ||
| There is not enough time to get breakfast before school. | 2.20 ± 0.70 | ||
| I am afraid that eating breakfast every day will make me fat. | 2.41 ± 0.74 | ||
| Self-efficacy | I can practice breakfast for my studies. | 2.55 ± 0.60 | 2.44 ± 0.63 |
| I can prepare my own meal without anyone preparing it. | 2.34 ± 0.67 | ||
Mean ± SD Scoring criteria: ‘I don't think so' 1 point, ‘I think it's normal' 2 point, ‘I think so' 3 point 1) Average of questions
Subjective norms on eating breakfast

 KSCN
KSCN
 Cite
Cite


