Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [English]
- The dietary factors associated with sleep duration in postmenopausal middle-aged women: a cross-sectional study using 2019–2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
- Eugene Shim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(3):197-213. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00052
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
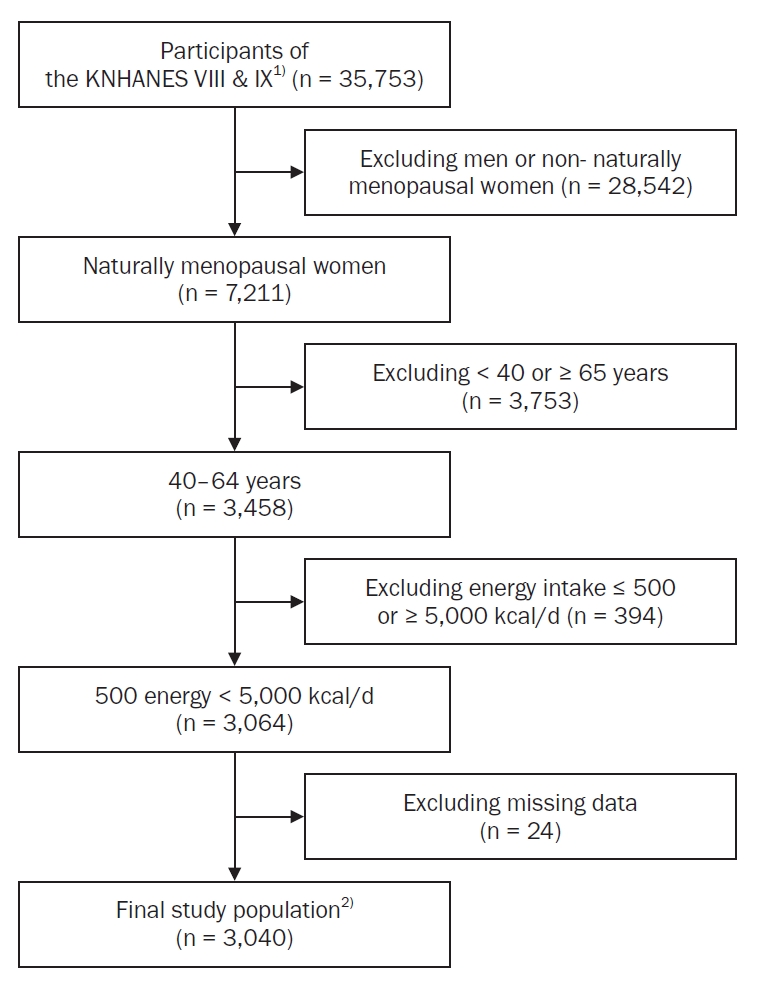
This study aimed to analyze dietary factors associated with sleep duration in postmenopausal middle-aged women using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), with particular emphasis on the postmenopausal period.
Methods
A total of 3,040 postmenopausal women aged 40–64 years from the 2019–2023 KNHANES were included. Sleep duration was classified into four categories: “appropriate sleep duration” (ASD; 7–9 hours), “short sleep duration” (6–7 hours), “very short sleep duration” (VSSD; < 6 hours), and “long sleep duration” (LSD; > 9 hours). Nutrient and food intake were compared among groups using analysis of covariance. Multinomial logistic and polynomial regression models assessed associations, adjusting for demographic and health covariates.
Results
The VSSD group had higher body mass index and waist circumference than the ASD group, despite lower total energy intake, and also consumed more snack energy and skipped breakfast and dinner more often. This group also had lower intakes of monounsaturated fatty acids and nuts and seeds. In the late menopausal group, greater consumption of cereal grains, fish and shellfish, and beverages was associated with elevated LSD risk. Conversely, higher folate intake in the early menopausal group was inversely associated with VSSD risk. Cholesterol intake was positively associated with LSD risk in both groups. A negative nonlinear association between sleep duration and dietary intake was observed in the early menopausal group when polyunsaturated fatty acid intake exceeded 19.86 g/day and riboflavin intake exceeded 1.76 mg/day. In the late menopausal group, riboflavin intake was strongly correlated with increased LSD risk (odds ratio = 4.776, P = 0.004). Sugar and beverage intake showed a positive linear relationship with sleep duration at average intake levels.
Conclusion
Dietary factors associated with sleep duration differed by postmenopausal period, with specific nutrients and food groups exhibiting variable associations with sleep duration above mean intake levels.meS
- 4,002 View
- 51 Download

- [Korean]
- Application of a living lab model to an evidence-based reduced-sodium healthy eating practice program in Korea: a pre-post study
- Jung-Hyun Kim, Eugene Shim, Min Sook Kyung, Sooyoun Kwon, Hyoung Su Park, Jae-Heon Kang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):53-63. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00346
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
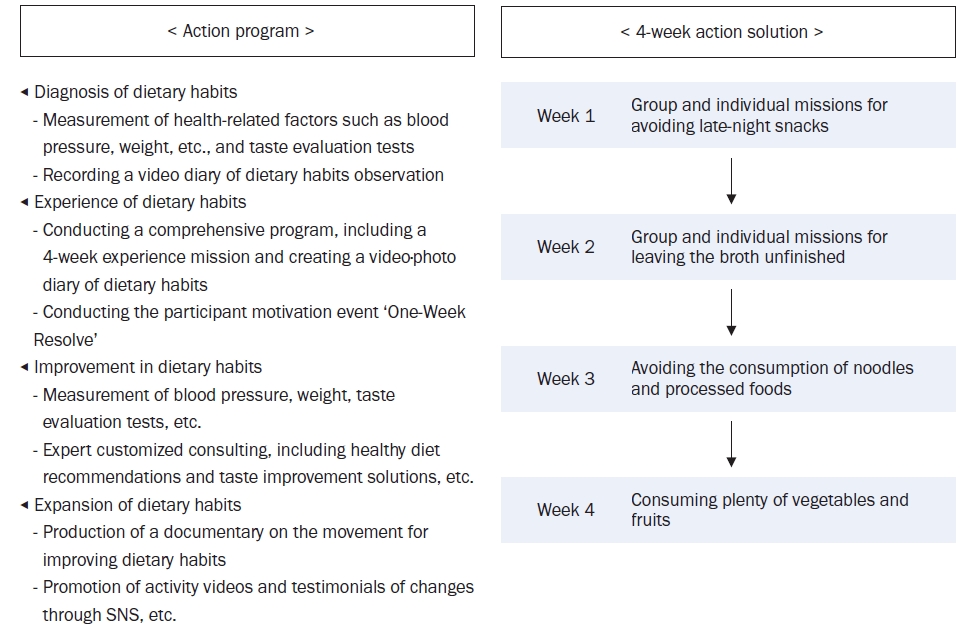
To apply a healthy dietary program with reduced sodium intake, developed using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), focusing on the sodium intake level and eating patterns.
Methods
The program was implemented using a living lab model, an open innovation ecosystem for user-centered problem-solving. Analysis of the KNHANES data revealed that older age groups had a low energy intake but a high sodium intake, particularly among those who frequently dined out. The program was designed to improve sodium-reduction literacy and enhance practical competency. Over four weeks, 40 participants tracked their dietary intake and worked with a clinical nutritionist through a process of diagnosis, experience, improvement, and expansion. A self-administered survey was conducted before and after the program to assess effectiveness.
Results
Participants were four teenagers (10%), 26 in their twenties (65%), and 10 aged ≥ 30 years (25%), with eight males (20%) and 32 females (80%). Post-program analysis showed significant improvements in sodium-related nutrition knowledge (P < 0.01), with increased agreement on adopting low-sodium intake practices (e.g., interest in sodium content, choosing lower-sodium foods). Nutrient intake analysis showed a decrease in energy, carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins (P < 0.001), with sodium intake decreasing from 3,382.37 mg/d to 2,119.05 mg/d (P < 0.001).
Conclusion
The community-based, living lab model for the sodium-reduction program effectively improved participant sodium-reduction literacy and practical competency, suggesting that step-by-step, autonomous learning, can reduce sodium intake and promote healthier eating habits. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of food literacy on short- and long-term healthy eating intentions among adolescent and adult convenience store users: An application of the extended theory of planned behavior
Wonyeong Park, Hae Jin Park, Suah Moon, Jieun Oh
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(6): 917. CrossRef
- Influence of food literacy on short- and long-term healthy eating intentions among adolescent and adult convenience store users: An application of the extended theory of planned behavior
- 1,934 View
- 62 Download
- 1 Crossref

Educational Materials
- [Korean]
- Systematization of food and nutrition education content based on national kindergarten curriculum: a qualitative formative study
- Jung-Hyun Kim, Eugene Shim, Eunyoung Baik
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(6):509-522. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.6.509
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study is intended to develop a curriculum for kindergarten food and nutrition education aimed at preschool children, reflecting government policy and meeting the demands of preschool settings.
Methods
Existing educational materials were analyzed, and key elements of the 2019 Revised Nuri Curriculum (“Nuri Curriculum”) and Guidelines for Nutrition and Food Education in Kindergartens, Elementary, Middle, and High Schools (“Guidelines”) were examined as foundational information for developing the curriculum for food and nutrition education.
Results
Basing ourselves on the five domains of the Nuri Curriculum, “Physical Activity and Health,” “Communication,” “Social Relationships,” “Art Experience,” and “Natural Science Inquiry,” we integrated three areas from the Guidelines, namely “Dietary Habits and Health,” “Dietary Habits and Safety,” and “Dietary Habits and Culture,” to structure the curriculum for kindergarten food and nutrition education. Three specific domains, “Nutrition and Health,” “Food and Culture,” and “Safe Dietary Practices,” were tailored for preschool children, each comprising core concepts, content elements, and educational materials. In the “Nutrition and Health” domain, core concepts such as “nutrition” were addressed through content elements such as “balanced eating” and “vegetables and fruit,” while “health” included elements such as “eating regularly” and “nutrients for disease prevention,” each with two educational content components. The “Food and Culture” domain focused on “food” with content on “local foods (vegetable-garden experience)” and “food culture” with content on “our dining table (rice and side dishes),” “our agricultural products,” “global cuisine (multiculture),” and “considerate dietary practices,” each with four educational content components. The “Safe Dietary Practices” domain included core concepts such as “hygiene” with content on “hand-washing habits” and “food poisoning management,” and “safety” with content on “food labeling.”
Conclusions
The systematized curriculum for kindergarten food and nutrition education aligns with the Nuri Curriculum and is interconnected with the Guidelines. This curriculum can be used as foundational material for developing educational resources tailored to the characteristics of preschoolers, contributing to effective implementation in early childhood education. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Parents' needs and perceptions of dietary and nutrition education in early childhood education institutions in South Korea: a mixed methods study
Jounghee Lee, Sookyung Choi, Minseo Kim, Seonghyun Lim, Jeong-Weon Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(6): 441. CrossRef
- Parents' needs and perceptions of dietary and nutrition education in early childhood education institutions in South Korea: a mixed methods study
- 1,160 View
- 50 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Article
- [English]
- Levels of Serum Antioxidant Minerals and Enzyme Capacities of Korean Male Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
- Eugene Shim, Soo Yeon Kim, Eun Jung Chung, Seung Yun Cho, Yang Cha Lee-Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2007;12(4):396-404. Published online August 31, 2007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Increased oxidative stress contributes to the progression of atherosclerosis. We measured serum antioxidant mineral concentrations, capacities of serum antioxidant enzymes and fasting lipid profile in 97 male patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) and 21 male controls. Nutrient intake was assessed by the semi-quantitative food frequency method. CAD patients were divided into single-vessel disease (SVD, n = 66) and multi-vessel disease (MVD, n = 31) groups on the coronary angiography. The ratio of serum LDL- to HDL-cholesterol elevated with an increasing number of diseased vessels compared to the control (control < SVD
- 280 View
- 0 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



