Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Article
- [Korean]
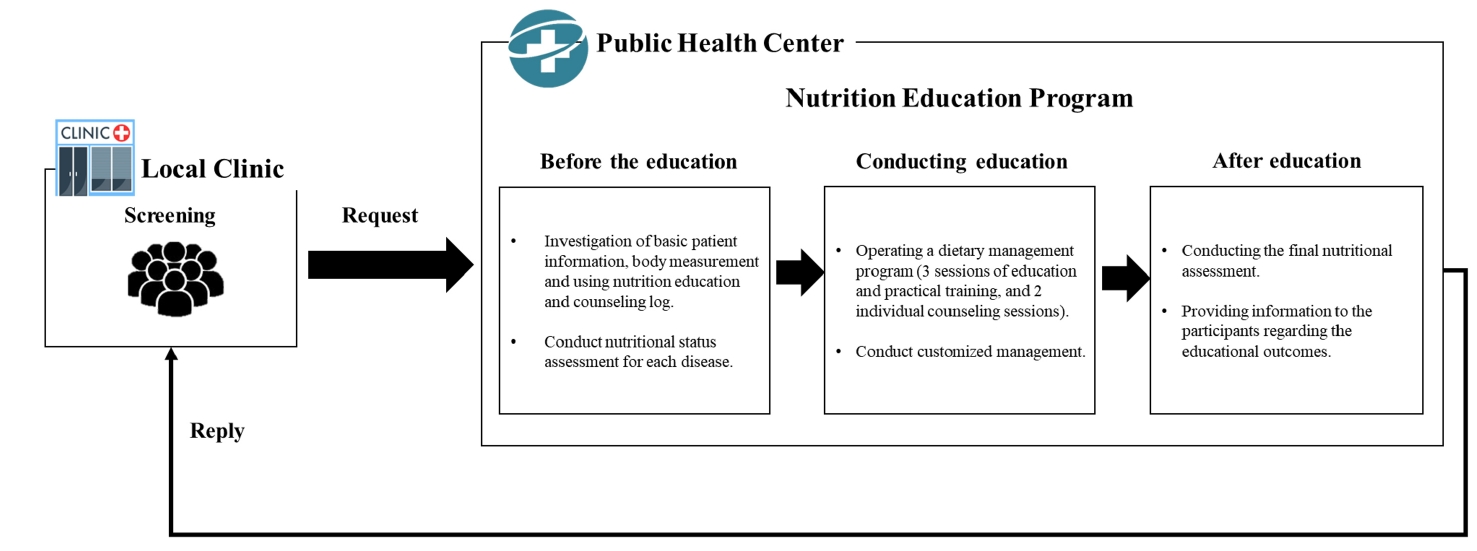
- Impact of a public health center nutrition education program on patients with type 2 diabetes in a primary care-based chronic disease management project: a pilot intervention study
- Haerim Yang, Yoo Kyoung Park, Ji-hyun Lee, Hee-Sook Lim, Heejoon Baek, Hyejin Lee, Haeran Park, Pyunghwa Lee, Jooyoun Chung, Won Gyoung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(6):492-503. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00018
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
We investigated the impact of an advanced “Nutrition Education Program” on patients with Diabetes mellitus, type 2 from public health centers enrolled in a primary health care-based chronic disease management project. This 12-week dietary management program was developed by the Korea Health Promotion and Development Institute. We assessed if this program improved glycemic control and other health indicators through dietary and nutritional improvements.
Methods
Seventeen patients with Diabetes mellitus type 2 were enrolled in the “Nutrition Education Program.” These patients were referred to public health centers for lifestyle management based on physician assessments at local clinics that were participating in a pilot project on primary health care-based chronic disease management. The participants attended the program comprising face-to-face basic, in-depth, and practical training sessions at the health center during the third, fifth, and seventh weeks, respectively. Anthropometric measurements, body composition analysis, blood biochemical characteristics, nutritional knowledge, and self-efficacy evaluation were performed before and after the program. Data were analyzed using SPSS ver. 28.0.
Results
The mean age of the participants was 62 years, and most participants were female (14, 82.4%). No significant changes in patients’ anthropometric measurements or body composition were observed after the training. However, significant reductions were observed in the blood biochemical characteristics, including glycated hemoglobin, total cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein levels. Additionally, patients’ nutritional knowledge and self-efficacy scores increased significantly.
Conclusions
The “Nutrition Education Program” helped in improving glycemic control and other health indicators in patients with Diabetes mellitus type 2. Further research is required to objectively confirm the long-term and sustained effects of the program in a controlled study. Trial Registration Clinical Research Information Service Identifier: KCT0010010
- 2,647 View
- 92 Download

Original Article
- [English]
- The Related Factors Influencing on Self-rated Health Level of Middle-aged Women
- Hyejin Lee, Kyung Hea Lee, Eunkyung Kim, Mi Jung Kim, Suk Man Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(3):290-301. Published online June 30, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.3.290
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This survey of 836 midlife women (51.0 +/- 4.0 yrs) was undertaken by exclusively a face to face interview by well-trained interviewers guarantying data collection of higher quality. This survey data was analyzed using the SPSS program. The main purpose of this study was to describe the factors affecting self-rated health status, including dietary habits and physical . mental . social factors. In the self-rated health status of a 'good' group, age was lower (p < 0.05), monthly income was higher (p < 0.01), dietary habits score (p < 0.001) and appetite (p < 0.001) and the degree of movement (p < 0.001) and life satisfaction (p < 0.001), marital intimacy (p < 0.001) and relationship satisfaction with their children (p < 0.001) were significantly higher than the 'bad' group. The level of depression (p < 0.001) and severe feeling of menopausal symptoms (p < 0.001) were significantly higher in the 'poor' group. The results of correlation analysis demonstrated that educational level (r = 0.069, p < 0.05),income (r = 0.157, p < 0.001), eating habits (r = 0.235, p < 0.001), appetite (r = 0.263, p < 0.001), life satisfaction (r = 0.197, p < 0.001), marital intimacy (r = 0.167, p < 0.001), child relationship satisfaction (r = 0.149, p < 0.001), positive attitude toward menopause (r = 0.070, p < 0.05) showed a positive correlation, but depression (r = -0.122, p < 0.001) and menopausal symptoms (r = -0.292, p < 0.001) showed a negative association with self-rated health status. The predictable factors affecting the self-rated health status of middle-aged women were examined by multiple regression analysis. The 'menopausal symptoms - physical discomfort' was the most important variables followed by the 'appetite', 'eating habits', 'menopause symptoms - sensory problems', 'BMI', 'positive attitude toward menopause' and 'high marital intimacy'. These results showed that the 'appetite' and 'eating habits' are important factors affecting the self-rated health status. Therefore, a program of dietary education must be considered for the effective health education and counseling of middle-aged women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of the health and dietary characteristics of postmenopausal middle-aged women according to subjective health perception: Based on the 8th (2019–2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Taegyeong Yeo, Chong-Su Kim, Yoon Jung Yang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(2): 200. CrossRef - Dietary Patterns and the Risk of Composite-Defined Osteoporosis in Pre- and Postmenopausal Women: A Prospective Cohort Study
Yejung Choi, Kyong Park
Nutrients.2025; 17(18): 2947. CrossRef - Self-rated health according to change of lifestyle after COVID-19: Differences between age groups
Dan Bi Lee, Jung Hyun Ahn, Jin Young Nam
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2022; 39(2): 1. CrossRef - Role Stress and Sense of Control Predict Using Food to Cope With Stress in Midlife Women
Dana R. Riedy, Ashley MacPherson, Natalie D. Dautovich
Journal of Aging and Health.2021; 33(9): 732. CrossRef - Food consumption frequency of Korean adults based on whether or not having chewing difficulty using 2013–2016 KNHANES by sex-stratified comparative analysis
Mi Jeong Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2020; 14(6): 637. CrossRef - Influence of Midlife Health Condition and Awareness of Successful Aging on Preparation for Old Age
Eun Ho Ha, Young Mi Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(5): 472. CrossRef - Analysis of Convergent Factors on Subjective Health Status of Patients with Depression
Myoung-Jin Kwon, Young-Ju Kim
Journal of Digital Convergence.2016; 14(6): 309. CrossRef - Health Status Assessment Tool Development based on Dietary Patterns in Middle-Aged Women
Hye-Jin Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(1): 37. CrossRef - Acculturation, Food Intake and Dietary Behaviors of Chinese College Students in Busan by Residential Period
Fangfang Song, Mi Jeong Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(4): 594. CrossRef - The Impacts of Dietary Habits on Self-perceived Health-related Physical Fitness in Middle-aged Women -Focused on Changwon Province-
Hye-Jin Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2014; 43(6): 916. CrossRef - Effects of Cultural Facilities and City Parks on the Regional Suicide Rates in Korea
Soo-Mi Cho, Hyung-Deok Shin
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(8): 4874. CrossRef - A Study on Dietary Behaviors, Health-Related Lifestyle of Adult Visitors at Public Health Centers in Gyeonggi Urban Area
Jong-Sook Kwon, Kyungmin Kim, Hyun-Chang Seo, Yoonna Lee, Seunggeon Lim, Young-Sug Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(6): 611. CrossRef - A Study on the Knowledge, Attitudes, Cancer Preventive Dietary Behavior, and Lifestyles of Adults in the Jeonbuk Area
Jeongok Rho, Suyoun Choi
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2013; 22(1): 201. CrossRef - Evaluation of Diet Quality according to Self-Rated Health Status of Korean Middle-Aged Women -Based on 2008~2009 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey-
Hye-Jin Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2013; 42(9): 1395. CrossRef - Anthropometric Index, Dietary Habits and Nutrient Intake of the Oldest-old Population Aged 95 and Over Living in Seoul
Chung Shil Kwak, Ji Hyun Cho, Miyong Yon, Sang Chul Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(5): 603. CrossRef - Health-Related Factors Influencing the Quality of Life of Rural Elderly Subjects - Activities of Daily Living, Cognitive Functions, Prevalence of Chronic Diseases and Nutritional Assessment
Mee Sook Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(6): 772. CrossRef - Characteristics of the Health Factors in 45~60 Year Old Korean Women related to Menopausal Stages - Based on 2008~2009 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey -
Hye-Jin Lee, Kwang-Hyun Cho, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(4): 450. CrossRef
- Comparison of the health and dietary characteristics of postmenopausal middle-aged women according to subjective health perception: Based on the 8th (2019–2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,337 View
- 0 Download
- 17 Crossref


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



