Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Adult consumers’ perception of plant-based meat substitutes and related factors in Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Yun-A Lee, Mi-Kyeong Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(3):237-248. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00115
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
We aimed to examine differences in experience, consumption, and perception of plant-based meat substitutes according to consumer characteristics, and to identify associated factors.
Methods
In this cross-sectional study, 410 adult consumers were surveyed regarding their eating habits, experience with and consumption of plant-based meat substitutes, and their intentions and perceptions of these products. Statistical analyses were conducted.
Results
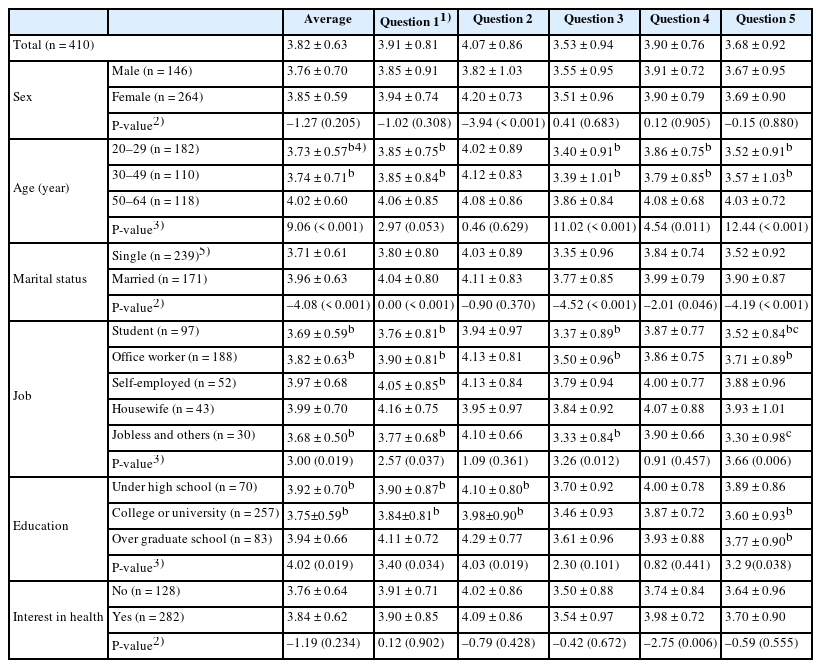
Approximately 84% of participants had heard of plant-based meat substitutes, most commonly through mass media and social media. Overall, 65.12% reported having consumed plant-based substitutes, with higher consumption observed among older and more health-conscious individuals. The most common reason for consumption was curiosity about new foods (36.33%), whereas the primary reason for non-consumption was lack of opportunity (61.54%). Additionally, 77.32% of respondents indicated willingness to try plant-based substitutes, with taste identified as the most influential factor in purchasing decisions. Perception of plant-based meat substitutes was rated 3.82 out of 5, with significantly higher awareness among individuals aged 50–64, married individuals, housewives, graduate students or graduates, and those with irregular meal times or infrequent dining out.
Conclusion
Older, married, more educated, and health-conscious individuals who dine out less frequently tend to have higher perception scores for plant-based meat substitutes, along with greater experience and stronger future use intention.
- 1,515 View
- 63 Download

- [English]
- Association between dietary intake, body measurements, and urinary bone resorption markers in young adults with osteopenia and osteoporosis: a cross-sectional study
- Mi-Hyun Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(4):282-292. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.4.282
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Bone health in early adulthood, as individuals approach peak bone mass, plays a critical role in preventing osteoporosis later in life. This study aimed to investigate the associations between lifestyle and dietary factors, anthropometric measurements, and urinary bone resorption markers in young adults.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted with 100 healthy Korean adults (50 men and 50 women) in their 20s and early 30s. Bone mineral density (BMD), anthropometric measurements, dietary intake (24-hour recall), and urinary bone resorption indicators (deoxypyridinoline and N-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen) were analyzed. Variables were compared between the osteopenia and osteoporosis groups (OSTEO group: 30% men and 60% women) and the healthy control group.
Results
Men in the OSTEO group were significantly taller than those in the control group (P < 0.05). Women in the OSTEO group had significantly lower body weight and body composition (muscle and body fat) than those in the normal group (P < 0.01). Men in the OSTEO group had a significantly higher intake of animal calcium (Ca) than those in the normal group (P < 0.05). Women in the OSTEO group had significantly higher dietary fiber, vitamin A, Ca, plant Ca, and potassium intake than did those in the normal group (P < 0.05). There were no significant differences in caffeinated beverage consumption, eating habits, or urinary bone resorption indicators between the OSTEO and control groups of either sex.
Conclusions
In our study of young South Korean adults, we observed low bone density levels, with particularly low BMD in taller men and underweight women. We found a higher nutrient intake in the OSTEO group, indicating the possibility of reverse causality, a phenomenon often found in cross-sectional studies. Therefore, there is a need to further elucidate dietary factors related to osteoporosis in young adults through prospective cohort studies involving a larger population.
- 1,333 View
- 19 Download

- [English]
- Sugar Reduction Perception and Sugary Food Intake among High School Students in Incheon
- Gyeong-Ja Bae, Mi-Kyeong Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(2):111-121. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.2.111
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined ways to promote desirable eating habits by choosing foods with low sugar contents and provide nutrition education in adolescents. Methods: This study was a cross-sectional survey. The sugar reduction perception and knowledge, sugary food preference, and intake frequency of 487 male and female high school students in Incheon were analyzed comparatively. Results: Approximately 94.9% and 94.5% of the subjects were unaware of the promotion of a sugar reduction policy and the sugar reduction in the basic guidelines for school meals, respectively. Approximately 95% of them had not received any sugar reduction nutrition education, and 90% were not interested in sugar reduction. The perception for sugar reduction was significantly higher in girls (3.43 out of 5 points) than in boys (3.16 out of 5 points) (P < 0.001). Knowledge about sugar was 3.65 out of 6 points in girls and 3.04 points in boys (P < 0.001). The preference and intake frequency for fruits of the total students were 4.24 out of 5 points and 2.56, respectively. For beverages, the preference was significantly higher in boys (3.97 points) than in girls (3.70 points) (P < 0.001), and the intake frequency was significantly higher in boys (2.26 points) than in girls (2.08 points) (P < 0.001). The preference for snacks was significantly higher for girls (4.19 points) than boys (4.02 points) (P < 0.01), and the intake frequency was 2.22 points in boys and 2.17 in girls, showing no significant difference. Sugar reduction perception and knowledge about sugar showed significant negative correlations with the snack intake frequency (r = -0.11, P < 0.05; -0.13, P < 0.05) after adjusting for gender, grade, and body mass index. Conclusions: The high school students' perception of sugar reduction was very low, and there was a significant correlation with sugary food intake, suggesting that the sugary food intake will decrease as the sugar reduction perception and knowledge about sugar increase. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Status of Sugar-Reduced Beverage Consumption according to Sex, among Adults in Their 20s and 30s in Gwangju
Na-In Kim, Bok-Mi Jung
Human Ecology Research.2025; 63(1): 1. CrossRef - Analysis of Health-Related Factors according to the Frequency of Consumption of Sugar-Reduced Beverages among Adults in Their 20s and 30s in Gwangju Area
Na-In Kim, Bok-Mi Jung
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(6): 459. CrossRef - Sugar Intake and Perception of Sugar Reduction among University Students in Gwangju
Yeon-Ok Park
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(11): 1170. CrossRef - 충북지역 중등학생의 건강식생활 관련 식행동과 영양관리 정책에 대한 인식
은서 고, 영은 이
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(3): 197. CrossRef
- Status of Sugar-Reduced Beverage Consumption according to Sex, among Adults in Their 20s and 30s in Gwangju
- 1,188 View
- 16 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- E-commerce Food Purchases by Adult Women according to their Household Types
- Yu-Jin Park, Yu-Mi Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(6):464-473. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.6.464
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to compare and analyze e-commerce food purchase behavior and the perceptions of adult women according to their household types. Methods: The e-commerce food purchases of 318 adult women were surveyed and analyzed according to their household types (one-person or couple household (OCH); a household with children (HC); a household with parents (HP)). Results: The total amount of food purchases over 6 months through e-commerce according to household types was in the descending order of OCH (60.3%), HC (57%), and HP (55.1%) thus showing a significant difference (P < 0.05) in behavior between household types. The reasons for purchasing food through e-commerce included: a lower price than offline (30.8%), convenient delivery and transportation (30.2%), and food diversity (21.1%). When purchasing food online, the most important factor was price and quality, followed by quick and accurate delivery for OCH, exact information given about the product for HC, and recommendation from other consumers for HP (P < 0.01). The main foods purchased through e-commerce were coffee, tea (42.1%), instant and frozen foods (39.9%), water, beverages, dairy products (37.7%), snacks, bread, rice cakes (31.5%), and functional foods (27.4%). The percentage of respondents who were very satisfied or satisfied with their ecommerce food purchases was HP (84.1%), OCH (69.9%), and HC (65.6%) in that order (P < 0.05), and 96.5% of all subjects stated that they would be willing to purchase food through e-commerce in the future. The advantages of purchasing food through e-commerce were seen to be the highest in order and payment convenience with 4.1 points out of 5, followed by low price (4.0), variety of products (3.9), and ease of food purchase (3.9).Among the disadvantages listed, concerns about product damage and deterioration during delivery and differences between the displayed product and the delivered product were the highest with 3.7 points. Conclusions: The characteristics and perceptions of female consumers according to household types are important factors in enhancing the reach of e-commerce, and in preparing guidelines for food selection through e-commerce. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of the Perceived Quality and Attitude on Satisfaction in Online Fresh Food Shopping
Jin-Yi Jeong, Yoon-Ji Choi, Hye-Sung Chae, Jung Shin Choi, Joo-Lee Son
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2022; 32(3): 202. CrossRef - Examination the Factors that Influence Online Food Purchase Intention : An Empirical Study Based on the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM)
Jin-Yi Jeong, Yoon-Ji Choi, Hye-Sung Chae, Jung Shin Choi, Joo-Lee Son
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2021; 31(5): 320. CrossRef
- Effects of the Perceived Quality and Attitude on Satisfaction in Online Fresh Food Shopping
- 1,063 View
- 7 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Association between Stress and Nutritional status of High School Students in Chungbuk using Nutrition Quotient for Korean Adolescents
- In Young Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(5):361-373. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.5.361
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between stress levels and eating habits in adolescents. Methods A total of 453 male and female high school students were surveyed to ascertain their stress levels, Nutrition Quotients for Korean Adolescents (NQ-A), and stress-related eating behavior. Results The average age of the subjects was 18 and they were mostly from nuclear families. Their average daily conversation time with their parents was between 10 to 30 minutes. The average sleep time for female students was observed to be less than that of male students. The satisfaction level of academic achievement of female students was significantly lower than that of the male students (P < 0.001). The average stress level score for female students was 2.7 out of 5, which was significantly higher than the male student's score of 2.4 (P < 0.001). The eating speed of male students was related to stress levels. Both male and female students ate more and craved spicy food when under stress. All male and female students had significantly ascending NQ-A scores rising in the order of stress from ‘low level’ to ‘medium level’, to ‘high level’ (P< 0.001). There was a significant negative correlation between the stress score and the NQ-A score adjusted for general characteristics (r = −0.29, P < 0.001). Conclusions Since stress and NQ-A were negatively correlated in high school students, higher stress levels can be associated with irregular eating habits and negative eating behavior. Therefore, stress management and nutrition education focusing on stress status are needed for adolescents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on the relationship between dietary habits and the quality of life of some high school students in Seoul based on the nutrition quotient for adolescents (NQ-A)
Ho-Jung Kim, Jung-Sug Lee, Yookyung Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(3): 320. CrossRef - Development of evaluation items for adolescents’ dietary habits and nutritional practices reflecting eating behaviors and food environment
Jimin Lim, Hye Ji Seo, Jieun Oh
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(1): 136. CrossRef - 충북지역 중등학생의 건강식생활 관련 식행동과 영양관리 정책에 대한 인식
은서 고, 영은 이
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(3): 197. CrossRef - Revision of Nutrition Quotient for Korean adolescents 2021 (NQ-A 2021)
Ki Nam Kim, Hyo-Jeong Hwang, Young-Suk Lim, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sehyug Kwon, Jung-Sug Lee, Hye-Young Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(3): 247. CrossRef - The Relationship between Lifestyle and Nutrition Quotient in Middle School Students
Ha Jin Park, Ho Kyung Ryu
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2021; 32(2): 243. CrossRef
- Study on the relationship between dietary habits and the quality of life of some high school students in Seoul based on the nutrition quotient for adolescents (NQ-A)
- 1,620 View
- 32 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Eating Out Status according to Skipping and Type of Breakfast among Male High School Students in Incheon
- Eun-Jin Choi, Mi-Kyeong Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(2):102-111. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.2.102
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The frequency of eating out among adolescents seems to be connected to a high rate of skipping breakfast and be interrelated to various nutritional problems. The purpose of this study was to assess the dietary habits of breakfast and eating out and investigate their relationships in male adolescents.
Methods
This study conducted a cross-sectional survey. Dietary habits and eating out status were surveyed among 510 male students at a high school in Incheon and compared according to their breakfast skipping and breakfast type.
Results
The percentages of subjects in the breakfast skipping group and breakfast group were 41.0% and 59.0%, respectively, and the breakfast group comprised a Korean meal group (74%) and a convenience meal group (26%). In the breakfast skipping group, the percentage of subjects buying and eating snacks due to hunger was 39.7%. Reasons for eating breakfast among subjects who ate breakfast were because parents prepared breakfast (41.9%) and out of habit (31.5%) in the Korean meal group, in contrast to because parents prepared breakfast (36.7%) and due to hunger (29.1%) in the convenience meal group (P < 0.001). Breakfast preparer was mother (91.4%) in the Korean meal group, in contrast to mother (67.1%) and self (20.3%) in the convenience meal group (P < 0.001). A high proportion of the breakfast group woke up at 07~07:30 or 06:30-07, whereas a high proportion of the breakfast skipping group woke up at 07~07:30 or after 07:30, showing a significant difference according to breakfast skipping (P < 0.001). A high proportion of the breakfast group spent 10,000 won (32.5%) a week eating out while a high proportion of the breakfast skipping group spent 20,000 won or more (28.2%), showing a significant difference (P < 0.01).
Conclusions
About 40% of male high school students skipped breakfast and consumed snacks as a solution after breakfast skipping. The students who skipped breakfast spent more money on eating out. These results show that breakfast status may be related to eating out. Therefore, practical education on food choice and meal preparation along with regular breakfast instruction is needed in male adolescents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analytic Hierarchy Process approach to estimate weights of menu management in the school foodservice
Hyo Bin Im, Seo Ha Lee, Hojin Lee, Lana Chung, Min A Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(3): 349. CrossRef - Study on the Eating Out Behavior and the Status of Meal Delivery and Take-Out Consumption according to the Food-related Lifestyles of Adolescents : Using the Consumption Behavior Survey for Food in 2020
Eun Jung Lee, Hyeon Min Yang, Yeong Ju Lee, Sun A Choi, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(4): 284. CrossRef - A prediction model for adolescents’ skipping breakfast using the CART algorithm for decision trees: 7th (2016–2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Sun A Choi, Sung Suk Chung, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(3): 300. CrossRef - Trends in Prevalence and the Differentials of Unhealthy Dietary Habits by Maternal Education Level among Korean Adolescents
Yunseo Chung, Kyunghee Jung-Choi, Bo Young Kim, Kyoung Ae Kong
The Ewha Medical Journal.2021; 44(4): 133. CrossRef
- Analytic Hierarchy Process approach to estimate weights of menu management in the school foodservice
- 1,750 View
- 12 Download
- 4 Crossref


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



