Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Article
- [English]
- Comparison of clinical characteristics and dietary intakes according to phenotypes of type 2 diabetes mellitus in South Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Mi-Jin Kim, Ji-Sook Park, Sung-Rae Cho, Daeung Yu, Jung-Eun Yim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):127-139. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00059
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Clinical nutrition treatment is the central part of diabetes management, such as prevention, treatment, and self-management of diabetes, and personalized clinical nutrition treatment, which enables improvement in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Our study aimed to contribute to the improvement of appropriate nutrition management in personalized treatment for obese and non-obese diabetes patients.
Methods
T2DM patients were recruited as participants, and 36 final participants were assigned to the lean diabetes mellitus group (LDM; body mass index [BMI] < 25 kg/m2) and the obese diabetes mellitus group (ODM; BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2). We assessed the dietary intakes, body composition, dietary habits, the Korean version of obesity-related quality of life, and biochemical indices.
Results
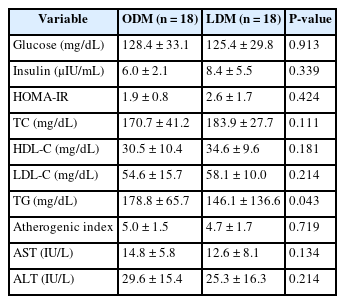
According to the phenotype’s comparison, the ODM group had a high prevalence of T2DM complications and hypertension, had a dietary habit of less than 10 minutes of mealtime duration and preferred fast food intake, and had a low obesity-related quality of life. However, the LDM group had a high choice of Korean dishes at the time of eating out and a high intake of vitamin C, and iodine because of the intake of vegetables and seaweeds.
Conclusion
We observed differences in diet, nutrient intake, and clinical characteristics according to the phenotype of T2DM patients. In particular, obese diabetes patients have an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, bad dietary habits, and low obesity-related quality of life. Therefore, personalized nutrition treatment is needed in consideration of the risk of cardiovascular disease and dietary habits for patients in the ODM group, as well as determining the energy requirements of Korean patients with T2DM.
- 2,286 View
- 33 Download

Original Articles
- [English]
- Food and Nutrient Intake Level by the Risk of Osteoporosis and Cardiovascular Disease in Postmenopausal Women: The use of the 5th Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (2010–2011)
- Hyobin Kim, Heysook Kim, Oran Kwon, Heejung Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(2):152-162. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.2.152
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to investigate the food, nutrient intake, and diet quality of postmenopausal women at high risk of osteoporosis (OP) and cardiovascular disease (CVD) compared with those of control subjects.
METHODS
A total of 1,131 post-menopausal women aged over 45 years, who took the 2010–2011 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), were included for analysis. These participants were classified into the following groups: the OP group, with a risk of OP (n=135); the CVD group, with a risk of CVD (n=373); the OP+CVD group, with a risk of OP and CVD concurrently (n=218); and the control group (n=405) according to bone mineral density (BMD) and CVD risk. Anthropometric measurements, blood profiles, dietary intake, and dietary quality indices were measured and compared among the four groups.
RESULTS
Waist circumference, total body fat percentage, blood pressure, fasting plasma glucose, total cholesterol, triglyceride, and LDL-cholesterol were higher, and HDL-cholesterol and BMD were lower in the OP+CVD group than in the control group. In the food frequency questionnaire, the OP+CVD group had significantly higher frequencies of grain (except for multi-grain) and lower frequencies of fruit and dairy product. The frequency of consumption of red meat, processed meat, and carbonated beverages was higher in OP+CVD group. In nutrient density analysis, proteins and vitamin B2 levels were significantly lower in the OP+CVD group than in the control group. The nutritional quality index (INQ) values of calcium were in the order of 0.63, 0.58, 0.56, and 0.55 in each group, and it was urgent to improve the dietary intake for calcium in postmenopausal women. In addition, vitamin B2 was inadequately consumed by all groups.
CONCLUSIONS
These results suggest that it is necessary to increase the intake of vitamin B2 and calcium and decrease the frequency of intake of red meat, processed meat, and carbonated beverages in postmenopausal women with the risk of OP and CVD. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Arterial stiffness index, physical activity and food and nutrient intake: cross-sectional study in adults aged 40 years and older
Eun-A Kim, Yun-Mi Kim, Eun-Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 81. CrossRef - Comparison of the Nutrient Intake and Health Status of Elderly Koreans According to their BMI Status: Focus on the Underweight Elderly Population
You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(5): 422. CrossRef - Association between frailty and dietary intake amongst the Korean elderly: based on the 2018 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Suhyeon Yang, Won Jang, Yangha Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(6): 631. CrossRef - Cardiorespiratory Fitness is Inversely Associated with Risk of Low Bone Mineral Density in Older Korean Men
Inhwan Lee, Jeonghyeon Kim, Hyunsik Kang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(21): 7907. CrossRef - Research Trend of Nutrition through Analysis of Articles Published in 'Korean Journal of Community Nutrition'
Jin Suk Jo, Kyoung Sin Lee, Ki Nam Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2011; 16(2): 278. CrossRef
- Arterial stiffness index, physical activity and food and nutrient intake: cross-sectional study in adults aged 40 years and older
- 1,247 View
- 4 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity and Their Association with Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Postmenopausal Women: Results for the 2008-2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Misung Kim, Cheongmin Sohn
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(4):378-385. Published online August 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.4.378
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to investigate the association between sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity and cardiovascular disease risk in Korean postmenopausal women.
METHODS
We analyzed data of 2,019 postmenopausal women aged 50-64 years who participated in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey in 2008-2011 and were free of cardiovascular disease history. Blood pressure, height, and weight were measured. We analyzed the serum concentrations of glucose, total cholesterol, high density lipoprotein cholesterol, low density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Waist circumference was used to measure obesity. Appendicular skeletal muscle mass was measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Sarcopenia was defined as the appendicular skeletal muscle mass/body weight<1 standard deviation below the gender-specific means for healthy young adults. The estimated 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease risk was calculated by Pooled Cohort Equation. Subjects were classified as non-sarcopenia, sarcopenia, or sarcopenic obesity based on status of waist circumference and appendicular skeletal muscle mass.
RESULTS
The prevalence of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity was 16.3% (n=317) and 18.3% (n=369), respectively. The 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease risk in the sarcopenic obesity group was higher (3.82 ± 0.22%) than the normal group (2.73 ± 0.09%) and sarcopenia group (3.17 ± 0.22%) (p < 0.000). The odd ratios (ORs) for the ≥7.5% 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease risk were significantly higher in the sarcopenic obesity group (OR 3.609, 95% CI: 2.030-6.417) compared to the sarcopenia group (OR 2.799, 95% CI: 1.463-5.352) (p for trend < 0.000) after adjusting for independent variables (i.e., exercise, period of menopausal, alcohol use disorders identification test (AUDIT) score, income, education level, calorie intake, %fat intake and hormonal replacement therapy).
CONCLUSIONS
Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity appear to be associated with higher risk factors predicting the 10-year risks of cardiovascular disease risk in postmenopausal women. These findings imply that maintaining normal weight and muscle mass may be important for cardiovascular disease risk prevention in postmenopausal women. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Health Behavior Factors According to the Presence of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Middle-Aged Men: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016-2018)
Junya Kang, In-Kyung Jung
Journal of Korean Association of Physical Education and Sport for Girls and Women.2024; 38(4): 201. CrossRef - The Impact of Possible Sarcopenia and Obesity on the Risk of Falls in Hospitalized Older Patients
Kahyun Kim, Dukyoo Jung
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2023; 26(1): 18. CrossRef - Association of Sarcopenia with Heart Rate Variability
Jeong-Min Ji, Hyun-Min Koh, Ji-Yong Jang, Jin-Sook Moon, Hye-Rang Bak, Hye-Jin Jang, An-Na Lee, Nak-Gyeong Ko
Korean Journal of Family Practice.2022; 12(5): 311. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Sarcopenia, Sarcopenic Obesity, and Sarcopenia Without Obesity in Older Adults
Seo-hyun Kim, Chung-hwi Yi, Jin-seok Lim
Physical Therapy Korea.2021; 28(3): 177. CrossRef - Association among the Prevalence of Sarcopenia without Obesity, Nonsarcopenic Obesity, Sarcopenic Obesity, and Metabolic Syndrome in Cancer Survivors: Based on Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yoon J Park, Young M Lee
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2021; 8(6): 679. CrossRef
- Comparison of Health Behavior Factors According to the Presence of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Middle-Aged Men: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016-2018)
- 1,494 View
- 7 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Milk Intake is Associated with Metabolic Syndrome: Using Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007~2010
- Chang Jin Lee, Hyojee Joung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(6):795-804. Published online December 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.6.795
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study aimed to examine associations between milk intake and metabolic syndrome. The subjects included 1,928 males and 3,103 females, aged 19 to 64 years, from the data of 'The Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey 2007-2010'. Daily intake of milk and dairy products was obtained by a 24 hour dietary recall method and divided into two categories by equivalent weight of one serving. The average individual intakes of milk and dairy products were 59.4 g and 74.1 g per day respectively. Milk intake was inversely associated with metabolic syndrome (OR: 0.69, 95% CI: 0.54~0.89), central obesity (OR: 0.75, 95% CI: 0.62~0.91), and hypertriglyceridemia (OR: 0.73, 95% CI: 0.59~0.90). The total intake of dairy products was also inversely associated with metabolic syndrome (OR: 0.74, 95% CI 0.60~0.92), central obesity (OR: 0.73, 95% CI: 0.62~0.86), hypertension (OR: 0.80, 95% CI: 0.65~0.99). The association between intakes of milk and dairy products and metabolic syndrome was significant in women, but not in men. These results indicate that increased consumption of milk and its products is associated with a reduced likelihood of metabolic syndrome and metabolic syndrome risk factors. Further research on causal relationship and dose-response association between milk intake and metabolic syndrome risk is necessary prior to applying the observed results in nutrition policies and programs to prevent the metabolic syndrome.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a nutrition education program on metabolic syndrome risk factors in middleaged Korean adults: an intervention study
Minji Kang, Young-Hee Park, Subeen Kim, Eunyoung Tak, Hyun Wook Baik, Hee Young Paik, Hyojee Joung
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(4): 265. CrossRef - Intakes of Dairy and Soy Products and 10-Year Coronary Heart Disease Risk in Korean Adults
Sinwoo Hwang, Ae Wha Ha
Nutrients.2024; 16(17): 2959. CrossRef - Evaluation of Dietary Nutrient Intake and Food Variety by Milk Consumption in Postmenopausal Korean Women: Data Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013~2015
Ae Wha Ha, Woo Kyung Kim, Sun Hyo Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2022; 51(9): 912. CrossRef - Inverse association of improved adherence to dietary guidelines with metabolic syndrome: the Seoul Metabolic Syndrome Management program
Dongwoo Ham, YoungYun Cho, Mi-Suk Park, Yun-Sug Park, Sun-Young Kim, Hye-Min Seol, Yoo Mi Park, Sunok Woo, Hyojee Joung, Do-Sun Lim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2020; 14(6): 621. CrossRef - Association between dairy product intake and hypertriglyceridemia in Korean adults
Seon-Joo Park, Junghyun Park, Hong Ji Song, Chang-Ho Lee, Hae-Jeung Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2020; 14(2): 152. CrossRef - Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to the Frequency of Milk Consumption in Korean Adolescents: Data from the 2010~2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ji Hyun Kim, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(6): 485. CrossRef - Association of total dietary antioxidant capacity with oxidative stress and metabolic markers among patients with metabolic syndrome
Dongwoo Ham, Shinyoung Jun, Minji Kang, Sangah Shin, Gyung-Ah Wie, Hyun Wook Baik, Hyojee Joung
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(3): 246. CrossRef - Study on relationship between milk intake and prevalence rates of chronic diseases in adults based on 5thand 6thKorea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Sehyug Kwon, Jung-Sug Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(2): 158. CrossRef - Association of Metabolic Syndrome with Whole Milk and Low Fat Milk: Using Data from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013–2015
Hyun-Chul Moon, Da-Hye Choi, Tae-Young Lee, Taek-Young Kim, Young-In An, Seong-Jee Park, Myung-Chul Jung
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2017; 17(4): 234. CrossRef - Serum Lipid Levels in Relation to Consumption of Yogurt: The 2012 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Bong-Kyung Seo, Nam-Eun Kim, Kyong-Min Park, Kye-Yeung Park, Hoon-Ki Park, Hwan-Sik Hwang
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2017; 38(5): 249. CrossRef - Comparison of Diet Quality and Diversity according to Obesity Type among 19-64 year old Korean Adults
Hyae Min Gu, So Yeon Ryu, Jong Park, Mi Ah Han, Yeong Eun Son
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(6): 545. CrossRef - Dyslipidemia patterns are differentially associated with dietary factors
SuJin Song, Hee Young Paik, Minseon Park, YoonJu Song
Clinical Nutrition.2016; 35(4): 885. CrossRef - Meat and milk intake in the rice-based Korean diet: impact on cancer and metabolic syndrome
Shinyoung Jun, Kyungho Ha, Sangwon Chung, Hyojee Joung
Proceedings of the Nutrition Society.2016; 75(3): 374. CrossRef - Evaluation of Obesity and Nutritional Status by Age among Low-income Women aged over 20 -Using Data from the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey-
Hee-Kyung Jang
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(2): 246. CrossRef - Low consumption of fruits and dairy foods is associated with metabolic syndrome in Korean adults from outpatient clinics in and near Seoul
SuJin Song, Eun-Kyung Kim, Soyoung Hong, Sangah Shin, YoonJu Song, Hyun Wook Baik, Hyojee Joung, Hee Young Paik
Nutrition Research and Practice.2015; 9(5): 554. CrossRef - Assessment on Dietary Diversity According to Korean Dietary Pattern Score of Korean Adolescents and Children: Using 2007~2013 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) Data
Yong-Suk Kwon, Yangsuk Kim
Korean journal of food and cookery science.2015; 31(5): 660. CrossRef - The Association between Dietary Fiber Intake and Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Middle-aged Adults in Gyeonggi Province
You-Sin Lee, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2015; 15(2): 75. CrossRef - Food Insecurity and Related Risk Factors in the Elderly: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013 Data
Hye-Sang Lee
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2015; 21(4): 308. CrossRef - Prevalence of Osteoarthritis and Related Risk Factors in the Elderly: Data from the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V), 2010~2012
Hye-Sang Lee
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2014; 20(2): 99. CrossRef - Development of Han-sik Database Utilizing an Expert Focus Group and Assessment of Han-sik Effects on Diet Quality
Minji Kang, Hyun Ju Jung, Hyojee Joung, Jae Eun Shim, Sang Eun Lee, Young-Hee Park, Hee Young Paik
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Culture.2014; 29(1): 9. CrossRef - The Factors Influencing Health-Related Quality of Life in the Elderly: Focused on the General Characteristics, Health Habits, Mental Health, Chronic Diseases, and Nutrient Intake Status: Data from the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination
Hye-Sang Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(5): 479. CrossRef - The effect of high-carbohydrate diet and low-fat diet for the risk factors of metabolic syndrome in Korean adolescents: Using the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (KNHANES) 1998-2009
Mi-Rhan Han, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2014; 47(3): 186. CrossRef - Utilization of Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Database: Estimation of Tomato Consumption and the Risk of Metabolic Syndrome
Eunha Youn, Jean Kyung Paik, Bumsik Kim
Food Engineering Progress.2014; 18(2): 109. CrossRef - An Evaluation of Dietary Habit and Nutritional Status by Household Income in Female Adults over the Age of 20 - Using Data from the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey -
Hee-Kyung Jang
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(4): 660. CrossRef - The Specific Food Consumption Pattern and Blood Lipid Profiles of Korean Adults
Youngok Kim
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2013; 19(2): 124. CrossRef
- Effects of a nutrition education program on metabolic syndrome risk factors in middleaged Korean adults: an intervention study
- 1,519 View
- 0 Download
- 25 Crossref

- [English]
- Association of Plasma Osteoprotegerin with Adiponectin and Difference according to Obesity in Men with Metabolic Syndrome
- Woori Na, Cheongmin Sohn
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(6):762-770. Published online December 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.6.762
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Osteoprotegerin (OPG) plays a core role in bone reformation by antagonizing the effect of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand (RANKL), and mediates vascular calcification in cardiovascular disease patients. Thus, we aimed to examine the relationship between serum OPG levels and cardiovascular factors and inflammatory markers in metabolic syndrome patients (MS). This cross-sectional study included 96 men who visited the diet clinic between May and July 2011. Patients were classified into 2 groups based on NCEP-ATP guidelines: normal and with MS (n = 50 and 46, respectively). Physical measurements, biochemical assay were measured. Serum OPG and IL-6, diponectin and hs-CRP were assessed. MS were aged 50.02 +/- 10.85 years, and normal patients 52.07 +/- 9.56 years, with no significant differences. Significant differences were not observed in BMI between the 2 groups. Moreover, significant differences were not observed in serum OPG, however, the serum OPG level (4.41 +/- 1.86 pmol/L) differed significantly between an overweight MS (BMI > 25) and normal patients. OPG was correlated to age (r = 0.410, p = 0.000), HDL-cholesterol (r = 0.209, p = 0.015), and log adiponectin (r = 0.175, p = 0.042). Multiple regression analyses using the enter method showed that age (beta = 0.412, p = 0.000) and BMI (beta = 0.265, p = 0.000) considerably affected OPG. In conclusion, out study showed that serum OPG levels are correlated with cardiovascular risk factors, such as BMI, HDL-cholesterol and adiponectin in MS and adiponectin, suggesting that serum OPG has potential as a cardiovascular disease indicator and predictor.
- 1,014 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Optimal Waist Circumference for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease
- Inkyung Baik, Chol Shin
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(2):275-283. Published online April 30, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - There are few studies reporting optimal waist circumference that can be utilized to prevent the incidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD). We evaluated the association of waist circumference and waist and hip circumference ratio (WHR) with incident cases of CVD developed over 6 years in a population-based prospective study including Korean adults. Analyses for receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve were performed with data for 1,733 men and 1,579 women who were aged 40 to 69 years and were free of a physician-diagnosis of CVD at baseline. Information on the diagnosis of CVD was periodically reported using interviewer-administered questionnaires and anthropometric measures were obtained by biennial health examinations. We newly identified 77 cases of CVD during a follow-up period between 2003 and 2008. On the basis of measures of diagnostic accuracy including minimum distance to ROC curve and Youden index, waist circumference of 85 cm for men, in particular for male nonsmokers, and of 80 cm for women and WHR of 0.88 to 0.90 for men and of 0.83 for women were found to be optimal cutoff points to identify individuals at CVD risks. The study also found that the use of the suggested optimal values for waist circumference show higher sensitivity and lower specificity compared with 90 cm for men and 85 cm for women, which are waist cutoff points given by the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity to define abdominal obesity for Korean adults. Although lower cutoff points of waist circumference (83 cm) and WHR (0.87) were observed to be optimal for male smokers compared with male nonsmokers, whether suggesting waist cutoff points specific to smokers is needed warrants further studies. After taking into account other cardiovascular risk factors including smoking, men with waist circumference of 85 cm or greater and women with 80 cm or greater were at an increased risk of CVD. Thus, these cutoff points of waist circumference may be able to capture more individuals at CVD risks contributing to the prevention of future development of CVD.
- 395 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Changes of Plasma Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors according to the Health Practice and Dietary Habits in Healthy Male University Studnets
- Kyeong Sook yim
- Korean J Community Nutr 1998;3(5):685-694. Published online November 30, 1998
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This cross-sectional study was conducted to describe the changes of plasma cardiovascular disease(CVD) risk factors in Korea. Overnight fasting plasma levels of total cholesterol, high density lipoprotein(HDL)-cholesterol, triacylglycerol and glucose were analyzed. Blood pressure and anthropometric data were also measured. Health practice factors such as smoking status, alcohol consumption and frequency fo exercise were evaluated by a self-administered questionnaire. Questions regarding dietary habits and food preferences were also asked. Seventy eight percent of the subjects had more than one CVD risk factor. Plasma total cholesterol, triacylglycerol, and fasting blood glucose were significantly increased according to the subjects body mass index(kg/m2, BMI), whereas HDL-cholesterol, low density lipoprotein(LDL)-cholesterol and blood pressure showed no significant differences with BMI. Current smokers had significantly high plasma total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol and triacylglycerol levels. Alcohol consumption significantly increased plasma total cholesterol and fasting blood sugar, but regular exercise had no effects on the plasma CVD risk factors. Overeating and frequency of fast food consumption were positively correlated with the CVD risk score, whereas intake of grains, meats and vegetables were negatively correlated with that score. A stepwise multiple regression analysis was performed to examine the effects of specific dietary factors on plasma lipid levels. For plasma total cholesterol level, the frequency of fast food intake explained 8% of the variance, followed by habitual overeating, frequency of grain intake and high cholesterol food intake(Model R2=22.4%). For plasma triacylglycerol level, preference of oily foods accounted for 7.5% of the variance, followed by eating breakfast, preference of fruit and frequency of grain intake(Model R2=22.0%). The findings suggest that intervention programs to reduce the risk of CVD should focus on health practice through reducing BMI, smoking cessation and moderate or no alcohol drinking. Moreover, desirable dietary habits such as eating breakfast, not overeating and reduced intake of fast food may improve CVD risk.
- 366 View
- 2 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



