Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [English]
- Effects of a multi-component program based on partially hydrolyzed guar gum (Sunfiber®) on glycemic control in South Korea: a single-arm, pre-post comparison pilot clinical trial
- Hyoung Su Park, A-Hyun Jeong, Hyejung Hong, Hana Jang, Hye-Jin Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):40-52. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00276
- Correction in: Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):173
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The aim of this study was to assess the impact of a multi-component program, including partially hydrolyzed guar gum (PHGG, Sunfiber®) supplementation, on glycemic control, gut health, and nutritional status to support diabetes prevention and management among Korean adults.
Methods
A single-arm trial was conducted with 29 adults (aged 20-55 years) with fasting plasma glucose (FPG) ≥ 100 mg/dL. Over a six-week period, participants engaged in a multi-component program that incorporated the supplementation of PHGG (Sunfiber®, 12.5 g/day), weekly nutritional coaching, and the use of continuous glucose monitoring devices. The program’s effectiveness was evaluated by measuring FPG and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels through blood tests conducted before and after the intervention. Improvements in gut health were gauged using the Korean Gut Quotient Measurement Scales, while enhancements in nutritional status were assessed using the Nutrition Quotient (NQ) and surveys that evaluated improvements in gut health and nutritional status.
Results
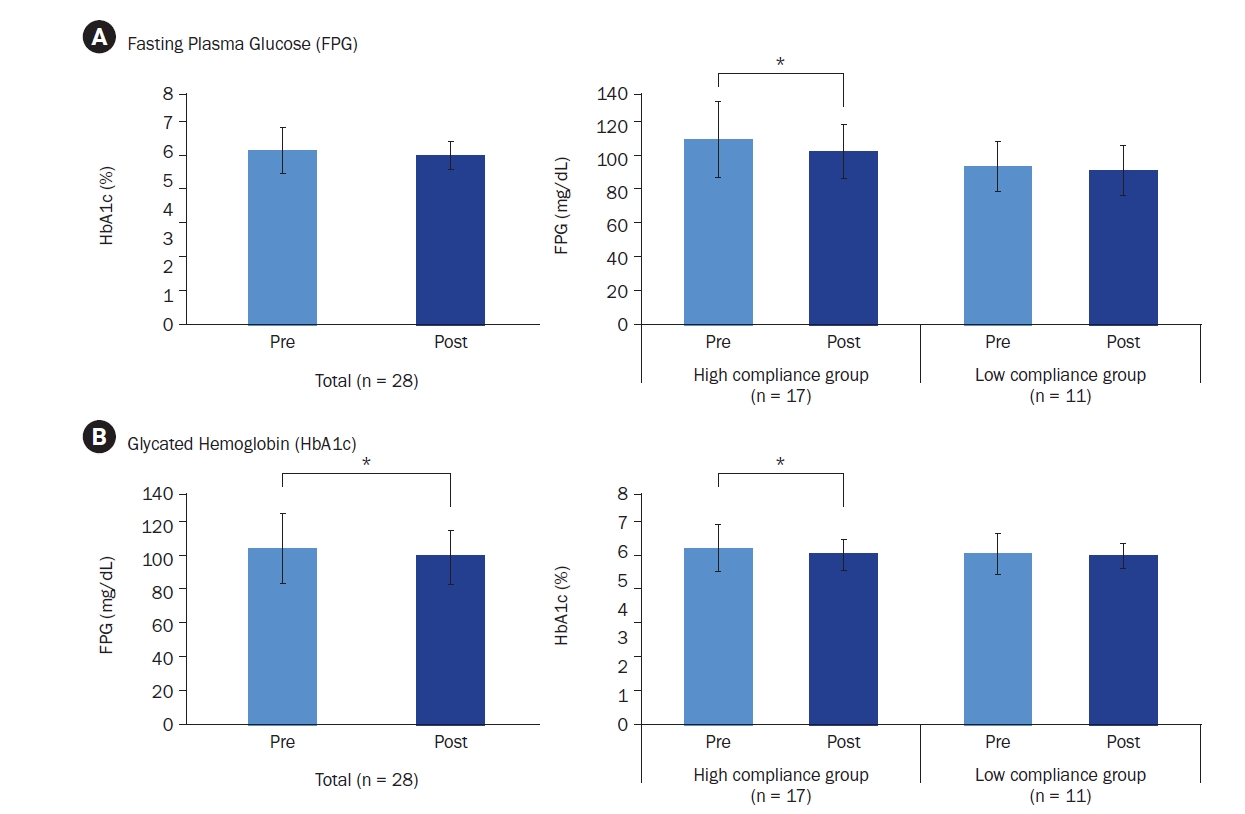
Participants’ average age was 43.89 years, with approximately 80% being male. Most participants (about 75%) were classified as overweight or obese. After six-weeks, 17 participants who adhered closely to the program (meeting certification criteria) exhibited significant reductions in key blood glucose markers. FPG levels decreased from 113.06 ± 23.16 mg/dL to 106.24 ± 16.33 mg/dL (P < 0.05), and HbA1c levels decreased from 6.08% ± 0.81% to 5.87% ± 0.53% (P < 0.05). The NQ evaluation revealed significant increases in comprehensive nutrition scores, and in the balance and practice domain scores for all participants (P < 0.05). Furthermore, in the gut health survey, approximately 82.1% of all participants reported experiencing positive changes.
Conclusion
Among adults with elevated FPG levels, a multi-component intervention program that included PHGG (Sunfiber®) supplementation, structured dietary management, and the use of health-monitoring devices showed significant benefits in improving glycemic control, overall nutritional status, and gut health. Trial Registration: Clinical Research Information Service Identifier: KCT0010049. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative analysis of dietary and lifestyle habits according to the prediabetic status in young adults
Joungyoon Seo, SeongHee Shin, Yuri Kim, Yoo Kyoung Park
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(5): 468. CrossRef - Partially Hydrolyzed Guar Gum Combined with a Low-Fat Diet Ameliorates Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus via Modulating Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolites
Zhiqiang Cao, Hongxia Li, Quantao Cai, Li Chen, Liangzhong Liu, Yuhan Tang, Zhe Zhu, Ping Yao
Nutrients.2025; 17(23): 3746. CrossRef
- Comparative analysis of dietary and lifestyle habits according to the prediabetic status in young adults
- 7,585 View
- 45 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Impact of a public health center nutrition education program on patients with type 2 diabetes in a primary care-based chronic disease management project: a pilot intervention study
- Haerim Yang, Yoo Kyoung Park, Ji-hyun Lee, Hee-Sook Lim, Heejoon Baek, Hyejin Lee, Haeran Park, Pyunghwa Lee, Jooyoun Chung, Won Gyoung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(6):492-503. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00018
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
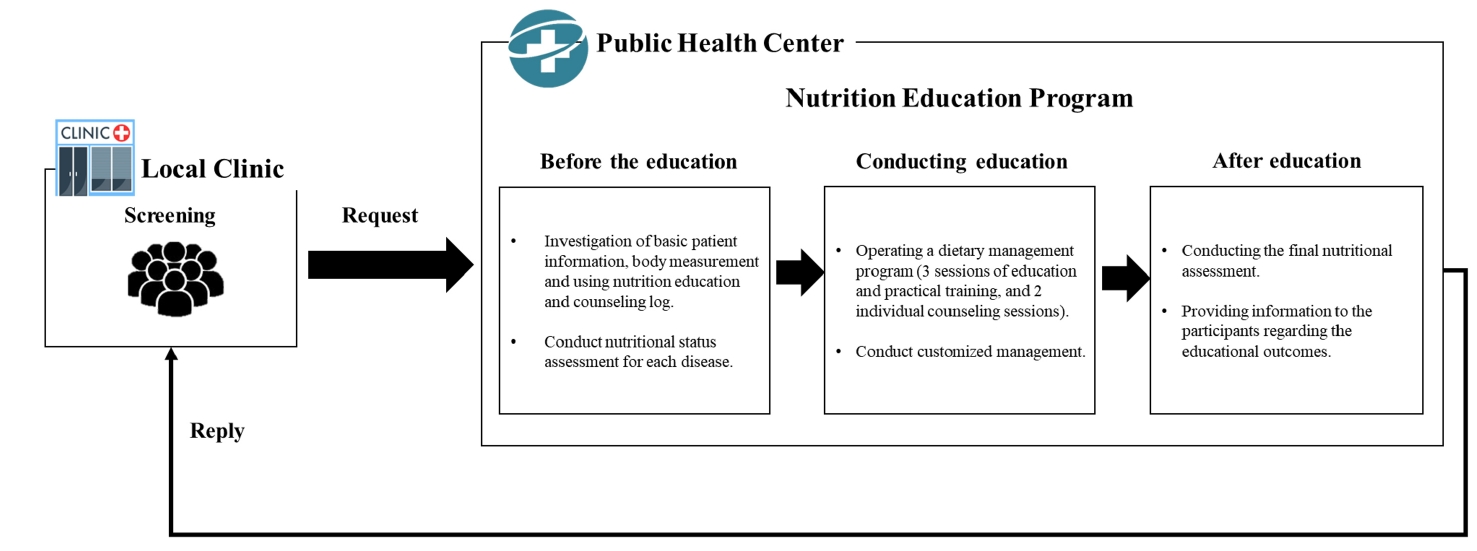
We investigated the impact of an advanced “Nutrition Education Program” on patients with Diabetes mellitus, type 2 from public health centers enrolled in a primary health care-based chronic disease management project. This 12-week dietary management program was developed by the Korea Health Promotion and Development Institute. We assessed if this program improved glycemic control and other health indicators through dietary and nutritional improvements.
Methods
Seventeen patients with Diabetes mellitus type 2 were enrolled in the “Nutrition Education Program.” These patients were referred to public health centers for lifestyle management based on physician assessments at local clinics that were participating in a pilot project on primary health care-based chronic disease management. The participants attended the program comprising face-to-face basic, in-depth, and practical training sessions at the health center during the third, fifth, and seventh weeks, respectively. Anthropometric measurements, body composition analysis, blood biochemical characteristics, nutritional knowledge, and self-efficacy evaluation were performed before and after the program. Data were analyzed using SPSS ver. 28.0.
Results
The mean age of the participants was 62 years, and most participants were female (14, 82.4%). No significant changes in patients’ anthropometric measurements or body composition were observed after the training. However, significant reductions were observed in the blood biochemical characteristics, including glycated hemoglobin, total cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein levels. Additionally, patients’ nutritional knowledge and self-efficacy scores increased significantly.
Conclusions
The “Nutrition Education Program” helped in improving glycemic control and other health indicators in patients with Diabetes mellitus type 2. Further research is required to objectively confirm the long-term and sustained effects of the program in a controlled study. Trial Registration Clinical Research Information Service Identifier: KCT0010010
- 2,434 View
- 87 Download

- [English]
- Effect of Nutrition Counseling by Nutrition Care Process on Diet Therapy Practice and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
- Tae-Jeong Bae, Na-Eun Jeon, Soo-Kyong Choi, Jung-Sook Seo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(3):214-225. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.3.214
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the effects of nutrition counseling by the nutrition care process (NCP) on diet therapy practice and glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods
The survey was conducted on 49 patients whose hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level ranged from 6.5% to below 10% among patients aged 30∼60s with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutrition counseling by the NCP process was carried out twice: first nutrition counseling and follow up counseling. The questionnaires were composed of 54 questions in five fields (general characteristics, health-related behaviors, diet therapyrelated items, dietary life, diet therapy-related knowledge, diet therapy-related barriers). Nutrition intervention in nutrition counseling was performed based on the individualized diagnosis of NCP.
Results
All the subjects practiced self-monitoring of their blood glucose levels, regular exercise, and diet therapy after NCP-based nutrition counseling. Diet therapy-related knowledge and practice by the subjects were improved after nutrition counseling. While the intake of boiled white rice decreased, the intake of boiled brown rice and barley rice in the subjects increased significantly. After nutrition counseling, the weight and HbA1c of the subjects decreased.
Conclusions
These results suggest that personalized nutrition counseling by NCP process is effective for diet therapy compliance and glycemic control of type 2 diabetic patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A study on the development of nutrition counseling manual and curriculum for the disabled in Korea: a mixed-methods study
Kyoung-Min Lee, Woo-jeong Kim, So-young Kim, Young-mi Park, Hwa-young Yoon, Min-Sun Jeon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(5): 376. CrossRef - Nutrition education programs necessary for social welfare facilities for persons with disabilities: a cross-sectional study
Jinkyung Kim, Min-Sun Jeon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(1): 1. CrossRef - Effect of Health educational intervention in the form of counseling on changes in anthropometric and biochemical parameters of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Dijana Stantić-Romić, Hajnalka Požar, Sanja Šumonja
Sestrinska rec.2023; 26(86): 17. CrossRef - The association between nutrition label utilization and disease management education among hypertension or diabetes diagnosed in Korea using 2018 Community Health Survey: a cross-sectional study
Miran Jin, Jayeun Kim, Kyuhyun Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(1): 38. CrossRef
- A study on the development of nutrition counseling manual and curriculum for the disabled in Korea: a mixed-methods study
- 1,595 View
- 58 Download
- 4 Crossref


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



