Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Adult consumers’ perception of plant-based meat substitutes and related factors in Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Yun-A Lee, Mi-Kyeong Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(3):237-248. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00115
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
We aimed to examine differences in experience, consumption, and perception of plant-based meat substitutes according to consumer characteristics, and to identify associated factors.
Methods
In this cross-sectional study, 410 adult consumers were surveyed regarding their eating habits, experience with and consumption of plant-based meat substitutes, and their intentions and perceptions of these products. Statistical analyses were conducted.
Results
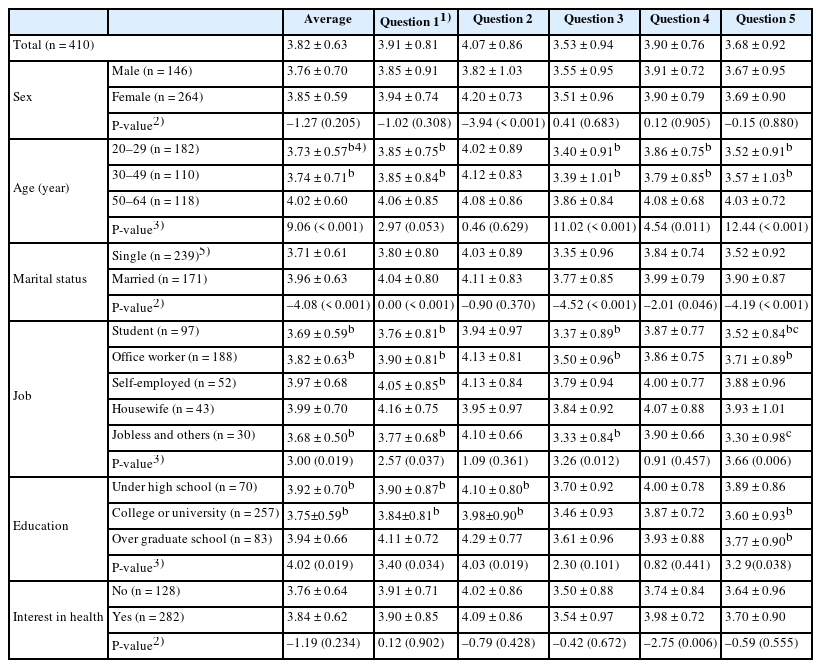
Approximately 84% of participants had heard of plant-based meat substitutes, most commonly through mass media and social media. Overall, 65.12% reported having consumed plant-based substitutes, with higher consumption observed among older and more health-conscious individuals. The most common reason for consumption was curiosity about new foods (36.33%), whereas the primary reason for non-consumption was lack of opportunity (61.54%). Additionally, 77.32% of respondents indicated willingness to try plant-based substitutes, with taste identified as the most influential factor in purchasing decisions. Perception of plant-based meat substitutes was rated 3.82 out of 5, with significantly higher awareness among individuals aged 50–64, married individuals, housewives, graduate students or graduates, and those with irregular meal times or infrequent dining out.
Conclusion
Older, married, more educated, and health-conscious individuals who dine out less frequently tend to have higher perception scores for plant-based meat substitutes, along with greater experience and stronger future use intention.
- 1,449 View
- 61 Download

- [Korean]
- Analysis of pork consumption attribute factors by consumer lifestyle in Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Jounghee Lee, Juhyun Lee, Wookyoung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(1):75-88. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00332
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aims to identify and analyze how different South Korean lifestyles impact attitudes towards pork consumption.
Methods
We implemented a cross-sectional survey targeting 705 adult consumers in South Korea using hierarchical and K-means cluster analyses. Respondents were classified into three relevant lifestyles: (1) domestic preference, (2) price-sensitive, and (3) quality-experience-oriented. The importance-performance analysis was employed to evaluate discrepancies between how they rated pork consumption using factors of “importance” and “satisfaction”. We employed Borich’s needs assessment and the Locus for Focus model to prioritize management areas.
Results
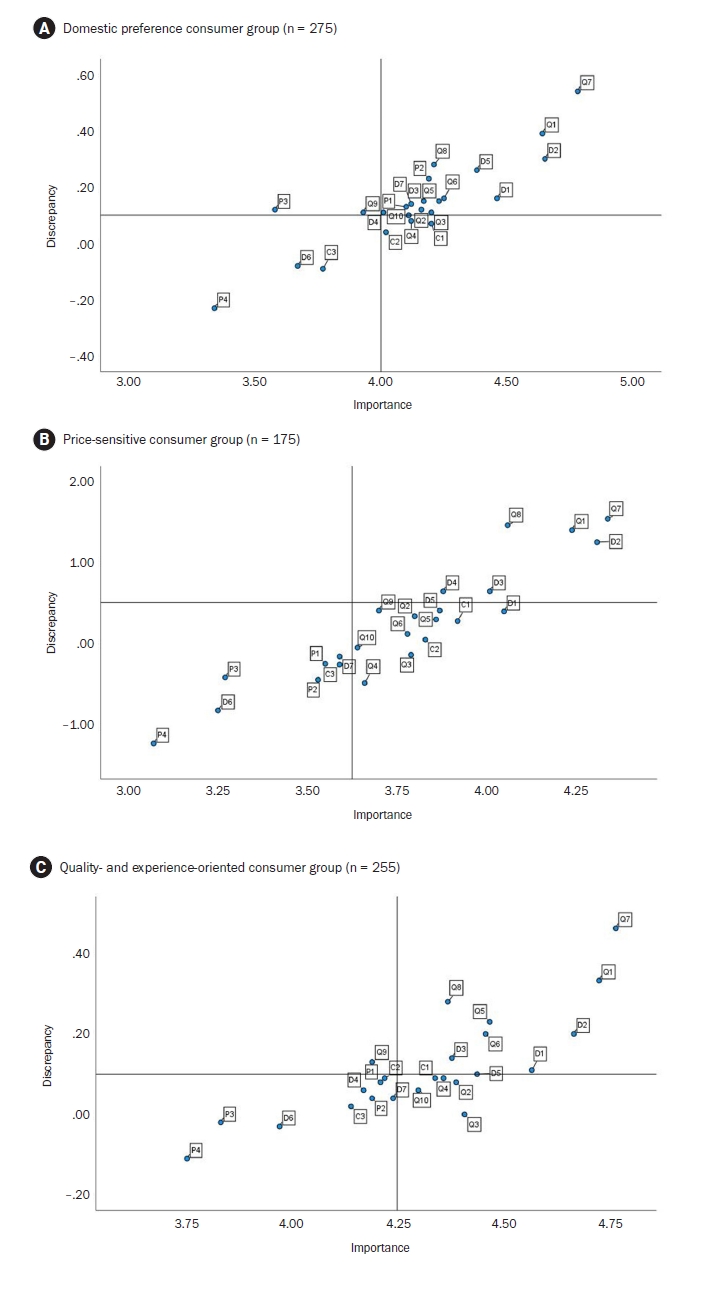
The research findings highlight that unpleasant odor/smell (Q7) and hygiene (Q1) were common key areas for management across all consumer groups, emphasizing their importance in enhancing pork consumption satisfaction. Among the groups, the domestic preference group showed high importance-performance discrepancies in attributes like expiry date (D2), suggesting a need for strengthened trust in domestic pork distribution and information transparency. The price-sensitive group prioritized economic factors, with fat thickness (Q8) identified as an essential management area. The quality-experience-oriented group emphasized sensory qualities such as juiciness (Q6) and meat color (Q5), with off-flavors (Q7) displaying the largest discrepancy. These results show the significant role of sensory attributes in consumer satisfaction.
Conclusion
This study demonstrated the multidimensional nature of pork consumption behavior, emphasizing the need for tailored strategies across consumer groups. Managing hygiene (Q1) and reducing off-flavors (Q7) are critical for all segments, while group-specific strategies include managing sensory quality for the quality-experience-oriented group, providing product information (D2) to increase trust for the domestic preference group, and emphasizing value for money for the price-sensitive group.
- 1,994 View
- 43 Download

- [Korean]
- Association between Relative Preference for Vegetables and Meat and Cancer Incidence in Korean Adults: A Nationwide Population-based Retrospective Cohort Study
- Ga-Eun Yie, An Na Kim, Hyun Jeong Cho, Minji Kang, Sungji Moon, Inah Kim, Kwang-Pil Ko, Jung Eun Lee, Sue K. Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(3):211-227. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.3.211
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
We aimed to examine the association between the relative preference for vegetables and meat and cancer incidence, in a population-based retrospective cohort in Korea.
Methods
We included 10,148,131 participants (5,794,124 men; 4,354,007 women) who underwent national health screening between 2004 and 2005 from the National Health Information Database of the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS-NHID). Participants were asked whether they preferred consuming 1) vegetables more often, 2) both vegetables and meat or 3) meat more often. Participants were followed up to Dec. 31, 2017. All cancer and eighteen common cancer cases were identified through the code from the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision. We estimated sexspecific relative risks and 95% confidence intervals, adjusting for age, body mass index, alcohol consumption, smoking, physical activity, and income level.
Results
During an average follow-up of 12.4 years, 714,170 cancer cases were documented. In men, consuming meat more often was associated with lower risk of esophageal, liver, and stomach cancers, but higher risk of lung and kidney cancers. Consuming both vegetables and meat was associated with higher risk of prostate cancer, but with lower risk of esophageal, liver, and stomach cancers in men. In women, consuming meat more often was associated with a higher risk of colorectal cancer and breast, endometrial, and cervical cancers diagnosed before the age of 50. Consuming both vegetables and meat was associated with lower risk of liver cancer in women.
Conclusions
Our study suggests a potential link between vegetable and meat intake and cancer incidence in the Korean population. Further investigation on the association between the intake of specific types of vegetables and meat and cancer risk in Korean prospective cohort studies is needed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Consumer Preferences for Conventional Meat and Meat
Alternatives
Jae Bong Chang
Food Science of Animal Resources.2025; 45(4): 1191. CrossRef
- Consumer Preferences for Conventional Meat and Meat
Alternatives
- 1,566 View
- 29 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Estimation of Usual Meat Intake Distribution Considering Meat Content in Processed Foods: Based on the KNHANES 2009
- Yun-Jung Shin, Ae-Jung Kim, Dong Woo Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(2):150-158. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.2.150
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to estimate usual meat intake distribution, which may have been over/underestimated when estimations were made using only the third food codes of the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES).
Methods
For this purpose, 24-hour recall data from the 2009 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, which conducted a partial 2-day survey of food intake, were used. The Multiple Source Method (MSM) was used to estimate the distribution of the usual intake of red and processed meats.
Results
The results of this study show that the mean intake of red meat was 45.07 g while that of processed meat was 4.33 g. These results are slightly higher than the consumption calculated using only tertiary food code, and the difference was statistically significant. Furthermore, characteristics of the estimated usual intake distribution were a smaller standard deviation, increased lower percentiles, and decreased upper percentiles compared to the 2- day mean intake distribution for both red and processed meats. The proportion of individuals not consuming red meat decreased substantially from approximately 37% to 0.7%. The proportion of consumption that exceeded 90 g, which is the upper limit of red meat intake recommended by the National Health Service (NHS), was only approximately 10% in the distribution of usual intake.
Conclusions
As the consumption of processed foods is expected to continuously increase, caution is needed regarding the processes used to calculate food (group) intake to avoid over/underestimation. Moreover, use of KNHANES data to calculate the proportion of the population at risk of insufficiency or excess intake of certain nutrients or food (group), based on one day intake that does not address within-individual variation, may lead to biased estimates. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Red meat and processed meat consumption and the risk of dyslipidemia in Korean adults: A prospective cohort study based on the Health Examinees (HEXA) study
Seong-Ah Kim, Sangah Shin
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2021; 31(6): 1714. CrossRef
- Red meat and processed meat consumption and the risk of dyslipidemia in Korean adults: A prospective cohort study based on the Health Examinees (HEXA) study
- 1,262 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Article
- [English]
- Studies on Fatty Acid Intake Patterns, Serum Lipids and Serum Fatty Acid Compositions of High School Students in Seoul
- Eun Jung Chung, Hong Seok Ahn, Young Sook Um, Yang Cha Lee-Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2004;9(3):263-273. Published online June 30, 2004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate the pattern of individual fatty acid intake and to compare serum lipid levels and total serum fatty acid composition of high school students in Seoul (total:234;male:91;female:143). In serum lipid levels, total cholesterol (Chol.), HDL -Chol. and LDL-Chol. levels of female students were significantly higher than those of male students and there was no significant difference between High Fish & Low Meat intake (HFLM) and Low Fish & High Meat intake (LFHM) groups. The average fat intake was 22 - 25 energy % of total subjects and especially, that of LFHM group was 29%, which were over the recommendation level. Although the average P/M/S ratio of dietary fat was 1.1/1.2/1.0, the average range of omega 6/omega 3 fatty acid ratio of dietary fat was found to be 17.9 - 20.7, which was far beyond the suggested range, 4 - 10. The average intake of cholesterol of total subjects was 360mg. LFHM group had more meats and beverages such as carbonated drinks and tended to have less beans, vegetables and mushrooms. In addition, LFHM group had more energy and fat intake than those of HFLM group, the P/S ratio of dietary fat (0.73) was lower than the recommended ratio. Serum C16:0 composition of LFHM group was significantly higher than that of HFLM group, and EPA and DHA composition of HFLM was significantly lower than that of LFHM. Therefore, in HFLM group, the P/S ratio of serum fatty acids was significantly higher and the omega 6/omega 3 ratio was lower. Dietary C18: 0 was negatively correlated with serum EPA and DHA composition. Individual PUFA intake was negatively correlated with serum C16:0 and sum of SFA, and positively correlated with serum C18:2omega 6 (LA), sum of omega 6 and sum of PUFA. Serum C18:1, C18:3omega 3 and C20:4omega 6 (AA) compositions were not correlated with dietary fatty acid. Only serum triglyceride (TG) levels were significantly correlated with serum fatty acid compositions. Sum of SFA, C14:0, C16:0, sum of MUFA and C18:1 compositions were positively correlated with serum TG levels, but LA, AA, sum of PUFA and P/S ratio were negatively correlated with it.
- 338 View
- 0 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



