Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [English]
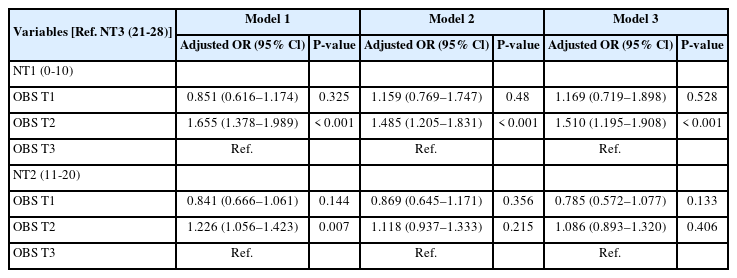
- Association between number of teeth and oxidative balance score in Korean adults: a population-based study
- Jung-Eun Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2026;31(1):64-74. Published online February 28, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00325
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between oxidative balance score (OBS), a metric indicating an individual’s oxidative balance status, and the number of teeth in a sample of Korean adults.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 13,199 adults aged 19 and older who participated in a health survey and oral examination. Subsequent to the adjustment for confounding factors, a logistic regression analysis was employed to evaluate the probability of a subject belonging to a number of teeth category based on OBS level.
Results
In the group with OBS level T2, the likelihood of having NT1 (0–10 teeth) was found to be significant adjusted for all variables (odds ratios: 1.51, 95% confidence intervals: 1.195–1.908). In the multinomial model, a significant association was observed for the NT1 category, whereas no significant association was found for the NT2 (11–20 teeth) category after adjustment.
Conclusion
In the group with OBS level T2, the likelihood of having NT1 (0–10 teeth) was found to be significant. As this study examines cross-sectional associations, the necessity of conducting longitudinal research as subsequent studies is evident to ascertain the existence of causality.
- 28 View
- 2 Download

- [Korean]
- Effects of night eating on oral health characteristics and symptoms of poor oral health in adolescents: a cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- Seung–Hee Hong
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):150-162. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00038

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
To determine the association between night eating habits and oral health in adolescents.
Methods
Data from the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey conducted in 2022 were analyzed. The study included 51,850 middle and high school students and assessed the frequency of night eating per week, dietary habits, oral health characteristics, and factors affecting the presence of symptoms of poor oral health.
Results
Almost thirty-seven percent (36.6%) of Korean adolescents have eaten at night one to two times per week and 23.0% more than three times per week. An increased frequency of night eating was associated with poor dietary habits. Adolescents who consumed more at night were less likely to have breakfast, drink water, and eat fruit, while their consumption of fast food, sweet drinks, and high-caffeine drinks increased (P < 0.001). An increased frequency of night eating was also associated with poor oral health. In a logistic regression analysis, more frequent night eaters were significantly less likely to brush their teeth at least three times per day (odds ratio [OR], 0.78; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.75–0.82; P for trend < 0.001), and brush their teeth before going to sleep (OR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.65–0.75; P for trend < 0.001), while they were more likely to experience sealant (OR, 1.19; 95% CI, 1.13–1.26). More frequent night eaters were significantly more likely to have tooth fracture (OR, 1.41; 95% CI, 1.30–1.53; P for trend < 0.001), tooth pain when eating (OR, 1.59; 95% CI, 1.50–1.67; P for trend < 0.001), toothache (OR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.52–1.70), and bad breath (OR, 1.51; 95% CI, 1.43–1.60).
Conclusion
Our findings suggest that frequent night eating is linked to symptomatically poor oral health in adolescents. Therefore, oral health education programs related to dietary habits are necessary to reduce the potential of night eating to negatively influence dietary habits and oral health. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between Sleep Quality and Perceived Oral Health among Adolescents: Analysis of the 2024 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Bo Young Park, Eun Bi Sim
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2025; 25(4): 370. CrossRef
- Association between Sleep Quality and Perceived Oral Health among Adolescents: Analysis of the 2024 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- 2,672 View
- 62 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Article
- [English]
- Relationship between Snack Intake and Oral Health Behavior of Middle School Students in Gyeonggi Area
- Hyunsook Kang, Kyunghee Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(4):336-346. Published online August 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.4.336
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The study was performed to investigate the relationship between snack intake and oral health behavior in middle school students in Gyeonggi-do area.
METHODS
The survey questionnaire was recorded by middle school students from July 6 to August 24, 2011. The questionnaire included items on general characteristics, snack intake status, and oral health behavior. Among collected survey questionnaire, a total of 620 questionnaires (320 males and 300 females) were analyzed using SPSS 15.0 program.
RESULTS
Frequencies of snack and beverage intakes were significantly higher in males than in females (p < 0.001). Oral health behavior was significantly higher in students with lower snack intake compared to those with higher or average snack intake (p < 0.05). Oral health behavior for tooth brushing and toothbrush care were significantly higher in females than in males (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
Oral health behavior score that reflected better oral health of the subjects were higher as the snack intake was lower. Oral health behavior score was higher in females than in males. We conclude that the contents for oral health and nutrition education focused on snack intake need to be developed to induce changes in oral health behavior in middle school students. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of night eating on oral health characteristics and symptoms of poor oral health in adolescents: a cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Seung–Hee Hong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(2): 150. CrossRef - Evaluation of frequency of consumption of cariogenic snacks by freshmen versus the senior dental students in Tehran and the related factors: a cross-sectional study
Mahdia Gholami, Simin Z Mohebbi, Milad Mafakheri, Houra Shahhosseini
BMJ Open.2024; 14(9): e086041. CrossRef
- Effects of night eating on oral health characteristics and symptoms of poor oral health in adolescents: a cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- 1,712 View
- 9 Download
- 2 Crossref


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



