Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Factors associated with nutritional risk among disabled persons in the Republic of Korea: a cross-sectional study using 2020 Disability and Life Dynamics Panel
- Seong-Ah Kim, Seul Ki Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(5):364-375. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00262
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Persons with disabilities face heightened nutritional risks due to barriers in dietary management, yet research remains limited. This study examined the nutritional health status and associated risk factors among disabled adults in Korea.
Methods
Data were drawn from the 2020 Disability and Life Dynamics Panel, a nationally representative survey of registered disabled Koreans aged ≥ 20 years. Nutritional health was assessed using the Nutrition Screening Initiative checklist and categorized as low, moderate, or high risk. Multivariate multinomial logistic regression was applied to identify predictors of nutritional risk.
Results
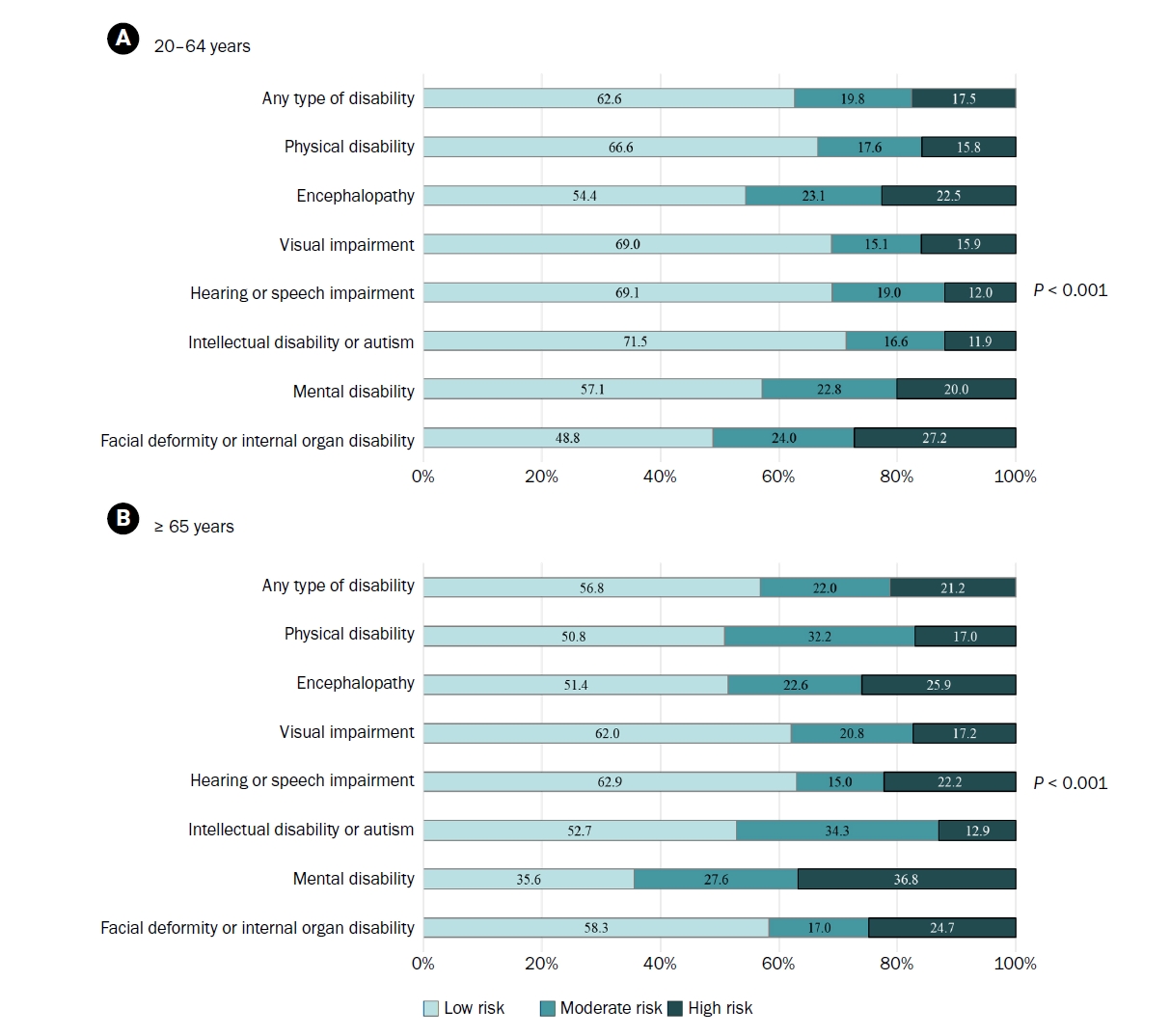
Among adults with disabilities aged 20–64 years, the prevalence of low, moderate, and high nutritional risk was 62.6%, 19.8%, and 17.5%, respectively. In the ≥ 65 years group, the distribution was 56.8% (low), 22.0% (moderate), and 21.2% (high). Moderate to high nutritional risk was most prevalent among individuals with facial deformity or internal organ disability (51.2%) in the 20–64 years group, and those with mental disabilities (61.7%) in the ≥ 65 years group. Significant predictors of high nutritional risk included living alone, lowest income quartile, chronic disease, depressive symptoms, and perceived underweight for both age groups. Compared with visual or speech impairments, facial deformity or internal organ disability (in the 20–64 years group) and physical disability (in the ≥ 65 years group) were significantly associated with moderate or high nutritional risk.
Conclusion
Nearly 40% of disabled Koreans are at nutritional risk. Tailored dietary interventions that address disability type, socioeconomic status, and health conditions are required to reduce disparities in nutritional health.
- 494 View
- 29 Download

- [Korean]
- A study on the development of nutrition counseling manual and curriculum for the disabled in Korea: a mixed-methods study
- Kyoung-Min Lee, Woo-jeong Kim, So-young Kim, Young-mi Park, Hwa-young Yoon, Min-Sun Jeon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(5):376-388. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00192
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Individuals with disabilities require targeted interventions to ameliorate disability-related conditions and improve overall health status. Nutritional challenges and counseling needs vary according to the type of disability, necessitating comprehensive assessments of dietary habits, physical activity, and food intake. Compared to traditional education, nutrition counseling offers a more sustainable and environmentally adaptable approach that effectively addresses individualized nutritional issues. Therefore, this study aimed to develop and evaluate a practical nutrition counseling manual and meal guidelines for people with disabilities in Korea, addressing their diverse dietary needs and improving nutritional care in social welfare facilities.
Methods
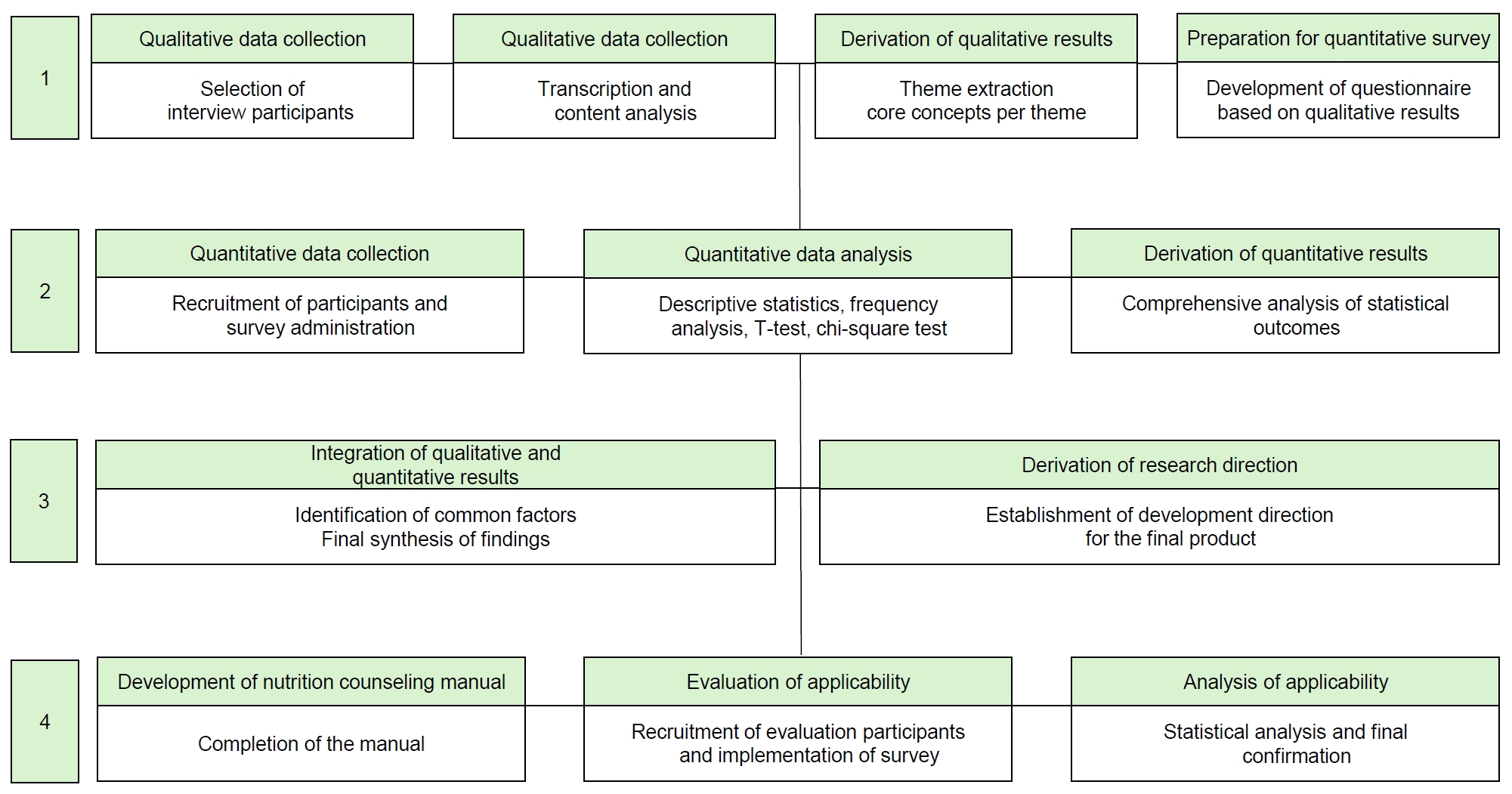
A four-stage integrated research design was employed. Stage 1 involved qualitative research through in-depth interviews with 11 facility staff. In Stage 2, a nationwide survey (n = 249) was conducted based on the results of the interviews. Stage 3 integrated both qualitative and quantitative findings. Stage 4 focused on developing and evaluating a nutrition counseling manual and five types of meal guidelines through feedback from 26 nutritionists at 24 Korean Centers for Social Welfare Foodservice Management.
Results
Six major nutrition counseling topics were identified: healthy eating, managing salt and sugar intake, dysphagia diet, appropriate intake, and hygiene. The manual and guidelines demonstrated high field usability, with average satisfaction scores of 3.98 and 3.99, respectively.
Conclusion
The integrated study resulted in the development of a specialized nutrition counseling manual and handbook for individuals with disabilities in Korean social welfare facilities. The materials were revised and improved based on practical evaluations by dietitians, enhancing their field applicability. These tools are expected to contribute to better dietary management and health promotion among facility residents. The developed materials reflect the real-world needs of people with disabilities and offer practical tools for effective nutrition counseling and dietary management in institutional settings.
- 429 View
- 19 Download


 KSCN
KSCN
 First
First Prev
Prev



