Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [English]
- Total sugar intake and its contributed foods by age groups in Koreans using the 8th (2019–2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey: a cross-sectional study
- Hyejin Yu, Sang-Jin Chung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(3):222-233. Published online June 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.3.222
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to investigate the status of total sugar intake and contributing foods in Korea according to age groups.
Methods
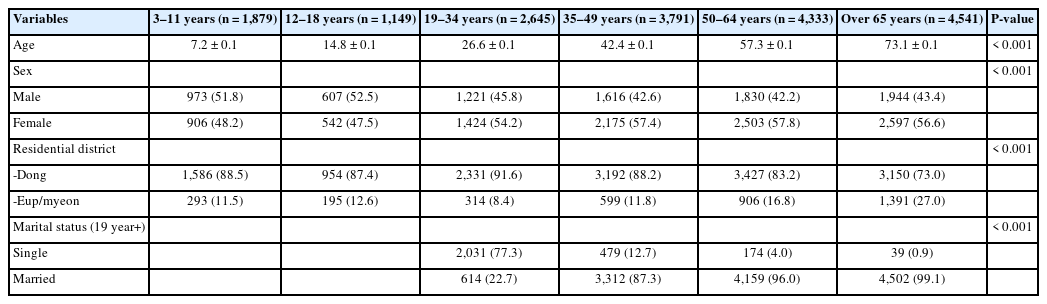
This study used 24-hour dietary recall data from the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2021) to investigate the nutritional and total sugar intake status among Koreans. A total of 18,338 research participants (≥3 years old) were included in this study. To analyze the types of foods contributing to total sugar intake, these foods were categorized into 15 types. Moreover, we examined the total sugar intake and ranked the most consumed foods by age groups (3–11 years, 12–18 years, 19–34 years, 35–49 years, 50–64 years, over 65 years). A survey procedure was employed for statistical analysis.
Results
The energy intake ratio from total sugars was approximately 12%–15%, which was within the recommended range. However, the proportion of individuals consuming total sugar exceeding 20% of their total caloric intake is nearly 20%, raising concerns about excessive sugar consumption. Furthermore, the percentage of participants whose intake of sugar from processed foods exceeded 10% of their total calories was highest in the 12–18 age group at 37.1%, followed by the 3–11 age group at 35.2%, and the 19–34 age group at 34.0%. Carbonated drinks, cola, and cider were the primary foods consumed by children and adolescents (3–18 years old) and young adults (19–34 years old). For middle-aged and older adults, mixed coffee with sugar and cream was a prominent contributor to sugar intake.
Conclusions
This study investigated sugar consumption patterns among Koreans, finding the principal foods contributing to this intake. Identifying these contributors is pivotal, given their potential impact on public health.
- 11,584 View
- 141 Download

- [Korean]
- Association of ultra-processed food with diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in elderly populations (urban and rural): a cross-sectional study
- Seung Jae Lee, Mi Sook Cho
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(1):51-64. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.1.51
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the association between ultra-processed food (UPF) consumption and chronic diseases in elderly Koreans.
Methods
Data from the 2019–2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey were analyzed. Dietary intake and UPF consumption were assessed using the NOVA food classification based on 24-hour recall data from 3,790 participants (aged 65+ years). Participants were divided into 4 groups based on the quartile of energy intake from UPFs. Regions were classified as urban or rural. Multivariable logistic regression was employed to estimate the adjusted odds ratios (AORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) after controlling for potential confounders.
Results
Among the participants, 71.3% resided in urban and 28.7% in rural areas. Compared to the urban elderly, rural participants tended to be older, have lower education and income levels, be more likely to live in single-person households, and have a higher smoking rate (P < 0.05). Urban elderly consumed more UPFs daily (146.1 g) compared to rural residents (126.6 g; P < 0.05). “Sugar-sweetened beverages” were the most consumed category in both regions. “Sweetened milk and its products” and “traditional sauces” were prominent in urban areas, while rural elderly consumed more “traditional sauces” and “distilled alcoholic beverages.” Rural areas also had a higher carbohydrate-to-calorie ratio than urban areas. Compared to the lowest quartile of UPF intake, the highest quartile was significantly associated with impaired fasting glucose only in rural areas (AOR, 1.48; 95% CI, 1.00–2.19; P for trend = 0.0014). No significant associations were observed for diabetes in either urban or rural areas.
Conclusions
This study suggests that high intake of UPFs is associated with increased odds of impaired fasting glucose in rural elderly. Further research is needed to elucidate the specific negative health effects of UPFs in different populations, and targeted efforts should promote healthy diets in both urban and rural areas. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ultra-Processed Foods and Cardiometabolic Health: A Review of Current Evidence
Nazlıcan Erdoğan Gövez, Eda Köksal
Current Nutrition Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Study of the Chemosensory Properties of Commercial Processed Foods Using Electronic Sensors
Hyeonjin Park, Younglan Ban, Sojeong Yoon, Hyangyeon Jeong, Seong Jun Hong, Hee Sung Moon, Se Young Yu, Hyun-Wook Kim, Kyeong Soo Kim, Eun Ju Jeong, Eui-Cheol Shin
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 53(8): 805. CrossRef - Analysis of Flavor and Taste Patterns of Various Processed Animal Foods: Using the Electronic Tongue and Nose
Hee Sung Moon, Se Young Yu, Younglan Ban, Hyeonjin Park, Sojeong Yoon, Na Eun Yang, Seong Jun Hong, Hyun-Wook Kim, Kyeong Soo Kim, Eun Ju Jeong, Eui-Cheol Shin
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 53(12): 1267. CrossRef
- Ultra-Processed Foods and Cardiometabolic Health: A Review of Current Evidence
- 2,036 View
- 68 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Development of Korean NOVA Food Classification and Estimation of Ultra-Processed Food Intake Among Adults: Using 2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Hae Jin Park, Sohyun Park, Jee Young Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(6):455-467. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.6.455
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
In this study, we suggest a Korean NOVA food classification that can be applied to food consumption among Korean. Based on this suggestion, the nutritional intake of Korean adults from ultra-processed foods (UPFs) was estimated.
Methods
Korean commercial food was categorized based on the NOVA food classification criteria through the Korea Food Code and expert meetings. Then, the nutrient intake status of 6,991 participants in the 2018 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey was analyzed according to the food processing level. Then, 4,152 adult participants (age 19-65) were divided into quartiles on the basis of their intake of UPFs, and the nutrient intakes from UPFs were compared.
Results
Korean NOVA Food Classification defines with priority Group I (Unprocessed/ Minimally processed foods) and Group II (Processed culinary ingredients) foods based on the food cooking or consumption. Then, Group III (Processed foods) and Group IV (UPFs) are classified according to whether the characteristics of the raw materials used are maintained or whether the food was consumed before the 1970s. Our analysis results showed that most of the calories in the diet were consumed by Group I (52.7%), followed by Group IV (29.3%). After categorization of the adult participants into four groups according to their energy consumption from UPFs, we found that the highest consumption group (Q4) was younger and had higher percentage of men than women. The comparative analysis of the consumption of ultra-processed foods by Korean adults revealed that participants of a younger age and men consumed higher energy from UPFs than older participants and women, respectively (P < 0.01). Furthermore, the larger intake of UPFs was associated with an increasing trend for a higher intake of energy, sugar, saturated fat (P for trend < 0.001), total fat (P for trend = 0.021), and sodium (P for trend = 0.005), whereas the intake of carbohydrate, protein, and dietary fiber had a decreasing trend (P for trend < 0.001).
Conclusions
With the current increase in the consumption of processed and ultra-processed foods, it is important to carefully consider not only nutrient intake but also the level of food processing. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Consumption of ultra-processed foods and major contributing foods according to the age group in Korean adults and older adults: using data from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016–2019)
Seulgi Lee, Jee Young Kim, Kirang Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2025; 58(1): 59. CrossRef - Potential misclassification of ultra-processed foods across studies and the need for a unified classification system: a scoping review
Sukyoung Jung, Jee Young Kim, Sohyun Park, Jung Eun Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(3): 331. CrossRef - Gender Differences in Ultra-Processed Food Consumption and Its Association with Obesity Among Korean Adults
Seung Jae Lee, Kyung Won Lee
Nutrients.2025; 17(12): 2027. CrossRef - Interaction between chronotype and ultra-processed food intake on triglyceride-glucose index in Korean adults
Sarang Jeong, Eunjin Jang, Sukyoung Jung, Jinhyun Kim, Minjeong Jeong, Dahye Han, Sohyun Park
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(4): 591. CrossRef - Ultra-processed food intake and risk of type 2 diabetes: a pooled analysis of three prospective cohorts of Korean adults and an updated meta-analysis
Yujin Kim, Yoonkyoung Cho, Bonjae Koo, Zhangling Chen, Qi Sun, Hannah Oh
European Journal of Epidemiology.2025; 40(11): 1293. CrossRef - Sex Differences in the Association Between Ultra-Processed Food Consumption and NAFLD: An Analysis of KNHANES 2013–2021 Data
Byung Soo Kwan, Nak Gyeong Ko, Ji Eun Park
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(22): 7930. CrossRef - Associations of Ultra-Processed Food Intake with Body Fat and Skeletal Muscle Mass by Sociodemographic Factors
Sukyoung Jung, Jaehee Seo, Jee Young Kim, Sohyun Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(4): 780. CrossRef - Navigating Ultra-Processed Foods with Insight
Ji A Seo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(4): 713. CrossRef - Association of ultra-processed food with diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in elderly populations (urban and rural): a cross-sectional study
Seung Jae Lee, Mi Sook Cho
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(1): 51. CrossRef - Sustainable diets: a scoping review and descriptive study of concept, measurement, and suggested methods for the development of Korean version
Sukyoung Jung
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(1): 34. CrossRef - Eating patterns in Korean adults, 1998–2018: increased energy contribution of ultra-processed foods in main meals and snacks
Sukyoung Jung, Jee Young Kim, Sohyun Park
European Journal of Nutrition.2024; 63(1): 279. CrossRef - Association Between Ultraprocessed Food Consumption and Metabolic Disorders in Children and Adolescents with Obesity
Gyeong-yoon Lee, Joo Hyun Lim, Hyojee Joung, Dankyu Yoon
Nutrients.2024; 16(20): 3524. CrossRef - Changes in Ultra-Processed Food Consumption among Adolescents before and after the COVID-19 Pandemic : Using Data from the 7th (2018~2019) and 8th (2020~2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyun-Jin Hwang, Yoo Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2024; 33(6): 981. CrossRef - Higher consumption of ultra-processed food is associated with cardiovascular risk in Korean adults: KNHANES 2016–2018
Sukyoung Jung, Eunjin Jang, Hyeongyeong Lee, Jee Young Kim, Sohyun Park
Frontiers in Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Consumption of ultra-processed foods and major contributing foods according to the age group in Korean adults and older adults: using data from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016–2019)
- 3,678 View
- 131 Download
- 14 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Study of the Coverage of Nutrition Labeling System on the Nutrient Intake of Koreans - using the 2013 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) Data
- Ji Eun Park, Haeng Shin Lee, Yoonna Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(2):116-127. Published online April 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.2.116
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to examine the coverage of the current mandatory nutrition labeling system on the nutrient intake of Koreans.
METHODS
KNHANES dietary intake data (2013) of 7,242 subjects were used in the analysis. KNHANES dietary intake data were collected by a 24-hour recall method by trained dietitians. For analysis, all food items consumed by the subjects were classified into two groups (foods with mandatory labeling and other foods). In the next step, all food items were reclassified into four groups according to the food type and nutrition labeling regulations: raw material food, processed food of raw material characteristics, processed foods without mandatory labeling, and processed foods with mandatory labeling. The intake of energy and five nutrients (carbohydrate, protein, fat, saturated fat, and sodium) of subjects from each food group were analyzed to determine the coverage of the mandatory nutrition labeling system among the total nutrient intake of Koreans.
RESULTS
The average intake of foods with mandatory labeling were 384g/day, which was approximately one quarter of the total daily food intake (1,544 g/day). The proportion of energy and five nutrients intake from foods with mandatory labeling was 18.1%~47.4%. The average food intake from the 4 food groups were 745 g/day (48.3%) for the raw food materials, 54 g/day (3.5%) for the processed food of raw material characteristics, 391 g/day (25.3%) for the processed foods without mandatory labeling, and 354 g/day (22.9%) for the processed foods with mandatory labeling.
CONCLUSIONS
Although nutrition labeling is a useful tool for providing nutritional information to consumers, the coverage of current mandatory nutrition labeling system on daily nutrient intake of the Korean population is not high. To encourage informed choices and improve healthy eating habits of the Korean population, the nutrition labeling system should be expanded to include more food items and foodservice menus.
- 1,075 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- High School Students' Sugar Intake Behaviors and Consumption of Sugary Processed Food Based on the Level of Sugar-related Nutrition Knowledge in Seoul Area
- Nami Joo, Shin Kyum Kim, Ji young Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(1):1-12. Published online February 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The present study aimed to investigate high school students' sugar intake behaviors, the status of consuming sugary processed foods, the awareness of sugar, and the experience and interest in sugar-related education based on the level of sugar-related nutrition knowledge.
METHODS
In this study, five high schools were selected in Seoul, Korea, and a survey was conducted in 400 students on the level of sugar-related nutrition knowledge and sugar intake status. A total of 349 questionnaires were used for the final analysis. For statistical analysis, descriptive statistics was performed; a t-test, χ2 test, and Friedman test were used for comparative analysis.
RESULTS
The study results showed a positive association between the knowledge level of sugar and the appropriate sugar intake behavior and sugary food choices. The group with more nutrition knowledge on sugar was found to have good eating habits and to eat less sugary food. The main sources of sugar were beverages, confectionary, and bakery goods in the corresponding order, irrespective of the level of nutrition knowledge related to sugar. A significant difference was found in the groups' awareness of the sugar content of the drinks with 89.4% for the higher-knowledge group, and only 81.5% for the lower-knowledge group (p < 0.05). Results also showed that 43.9% of the higher-knowledge group and 36.4% of the lower knowledge group were interested in participating in education on sugar.
CONCLUSIONS
This study result indicated the need to help adolescents to avoid excessive sugar intake from only certain favorite foods. Therefore, it is necessary to seek a systematic foundation for participatory education in order for them to maintain a low sugar intake in daily life and lead healthy eating habits by increasing their level of sugar-related information and knowledge. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Socioecological factors influencing sugar-sweetened beverage consumption among adolescents in South Korea: a cross-sectional study
Jin Suk Ra, Sun Hwa Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2025; 31(1): 28. CrossRef - Factors affecting sugar intake in adults based on the social cognitive theory
Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(1): 120. CrossRef - Sex-Based Differences in Factors Associated With Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Consumption Among Korean High School Students
Jin Suk Ra, Moonkyoung Park
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Mobile application-based dietary sugar intake reduction intervention study according to the stages of behavior change in female college students
Yunjung Choi, Hyun-Sook Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(5): 488. CrossRef - Study on Sugar Consumption of Adult Workers According to Smoking Status
Jung-Yeon Yun, Boram Kim, Hee Sun Jeong, Nami Joo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(3): 228. CrossRef
- Socioecological factors influencing sugar-sweetened beverage consumption among adolescents in South Korea: a cross-sectional study
- 1,513 View
- 8 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Preference and the Frequency of Processed Food Intake according to the Type of Residence of College Students in Korea
- Su Jin Kim, So Young Bu, Mi Kyeong Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(3):188-196. Published online June 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.3.188
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to investigate the eating behavior toward processed foods among college students who live in different types of residence.
METHODS
This is a cross-sectional study targeting a total of 476 college students living at home with their family, living in a rental house with self-boarding, living in a lodging house, and living in a dormitory. Eating behaviors, including preference and the frequency of processed food intake were surveyed and compared according to the type of residence.
RESULTS
The rate of skipping a meal was significantly higher among students who reported self-boarding than those living in other types of residences. The main reason for skipping meals was that they got up late. In the entire study population, the main reason for consuming processed food was easy-to-cook (33.8%) and the primary consideration for choosing processed food was the price (54.0%). The processed food the most favored by college students was the processed noodles; those living at home with their family or living in a dormitory preferred milk products; those living in a rental house with self-boarding or in a lodging house preferred confectionery, retort pouch, convenience food, and canned/bottled food. The frequency of processed food intake was significantly higher in the students who reported self-boarding than those living in other types of residences (p < 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
Students' preference toward processed foods differed according to their type of residence. The frequency of processed food intake was significantly higher in students who reported self-boarding indicating that the type of residence of student is associated with their choices and consumption of processed foods. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Trajectories of Nutritional Quality, Diet-Related Environmental Impact, and Diet Cost in China: How Much Does Ultra-Processed Food and Drink Consumption Matter?
Zhiyao Chang, Elise F. Talsma, Hongyi Cai, Shenggen Fan, Yuanying Ni, Xin Wen, Pieter van ‘t Veer, Sander Biesbroek
Nutrients.2025; 17(2): 334. CrossRef - Differences in Nutritional Status According to the Residence Types among University Students in Gwangju
Geum-Bi Ryu, Young-Ran Heo
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 53(2): 207. CrossRef - Effects of Korean Versus Western Diets on Reproductive Function in Young Korean Men: A 12-Week Randomized Parallel Clinical Trial
Su-Jin Jung, Young-Gon Kim, Seung-Ok Lee, Soo-Wan Chae
Journal of Lifestyle Medicine.2024; 14(1): 20. CrossRef - Usage and Quality Satisfaction of Convenience Food at Convenience Stores according to the Eating Behavior of University Students in Southern Gyeonggi Province
Se-In Oh, Ok-Sun Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2023; 33(6): 492. CrossRef - Dietary guidelines adherence and changes in eating habits among college students in the post-COVID-19 period: a cross-sectional study
Eunyoung Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(3): 220. CrossRef - Lifestyle and dietary changes related to weight gain in college students during the COVID-19 pandemic
Jihyun Kim, Seunghee Kye
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(3): 288. CrossRef - Development of Keyword Trend Prediction Models for Obesity Before and After the COVID-19 Pandemic Using RNN and LSTM: Analyzing the News Big Data of South Korea
Gayeong Eom, Haewon Byeon
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Actual Status of Mukbang Viewing and Food Habits of University Students in Wonju Area
Seung-Lim Lee, Sun Hee Lee
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2022; 33(4): 631. CrossRef - The Effect of Frequent Use of Convenience Food from Convenience Stores on the Diet Quality of Women’s University Students: Using the Nutrition Quotient for Korean Adults
Sun Hee Lee, Seung-Lim Lee
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2021; 32(4): 581. CrossRef - Comparison of consumption behaviors and development needs for the home meal replacement among Chinese college students studying abroad in Korea, Chinese college students in China, and Korean college students in Korea
Mi Ae Bae, So Hyun Park, Siyao Cheng, Kyung Ja Chang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2021; 15(6): 747. CrossRef - Change of dietary habits and the use of home meal replacement and delivered foods due to COVID-19 among college students in Chungcheong province, Korea
Mi-Hyun Kim, Jee-Young Yeon
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(4): 383. CrossRef - Predictive Growth Modeling of Listeria monocytogenes in Rice Balls and Its Risk Assessment
Seoungsoon Yeo, Misook Kim
Journal of Food Quality.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Analysis of Dietary Behaviors, Food Consumption Frequency and Blood Clinical Indices by Residence Types of Female College Students in Seoul
Ru Zi Lee, Jung Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(3): 183. CrossRef - Short-Term Effect of Convenience Meal Intake on Glycemic Response and Satiety among Healthy College Students in South Korea
Eunji Jang, Jeunghyun Lee, Sukyeong Lee, Mi-Hyun Kim
Clinical Nutrition Research.2017; 6(3): 215. CrossRef - Nutritional Evaluation of Convenience Meals in Convenience Stores near the Universities
Go-Na Shin, Yu-Ri Kim, Mi-Hyun Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(5): 375. CrossRef - Recognition and Consumption of Meal Alone and Processed Food according to Major of College Students
Byung Bum Choi
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(6): 911. CrossRef - Eating Habit and Stress Status according to Exercising Habits of Middle-Aged Adults in Chungnam
Se-Yune Kim, Yeon-Ja Seo, Mi-Hyun Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(1): 43. CrossRef - Dietary Habits and Perception Toward Food Additives according to the Frequency of Consumption of Convenience Food at Convenience Stores among University Students in Cheongju
Munkyong Pae
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(2): 140. CrossRef - Comparison of Processed Food Intake by Allowance Level in College Students in Chungnam
Yi-Yeong Kim, Su-Jin Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2015; 21(4): 280. CrossRef
- Trajectories of Nutritional Quality, Diet-Related Environmental Impact, and Diet Cost in China: How Much Does Ultra-Processed Food and Drink Consumption Matter?
- 1,915 View
- 9 Download
- 19 Crossref

- [English]
- Food Habits and Dietary Behavior Related to Using Processed Food among Male College Students Residing in Dormitory and Self-boarding in Gangwon
- Mi Hyun Kim, Hyun Kim, Woo Keun Lee, Soon Joo Kim, Jee Young Yeon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(4):372-385. Published online August 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.4.372
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to examine food habits and dietary behavior related to using processed food among male college students residing in dormitory and self-boarding in Gangwon. A total of 344 students (dormitory group: 227, self-boarding group: 117) were surveyed from May to June of 2012. The results are summarized as follows: self-boarding group had a significantly higher frequency of skipping breakfast and lunch and frequency of out meal compared with the dormitory group (p < 0.05, p < 0.05, p < 0.05 respectively). The self-boarding group had a significantly lower the score of 'eat vegetables and Kimchi at every meal' (p < 0.001) and 'eat a variety of food everyday' (p < 0.001) compared with the dormitory group. The self-boarding group had a significantly higher the preference for meat products (p < 0.05) and canned food (p < 0.01) for selecting processed food compared with the dormitory group. The consideration for selecting processed food was ranked by 'taste', 'price', 'expiration', 'appearance' and 'nutrition' in both dormitory and the self-boarding group. In the dormitory group, nutrition labels were identified certainly 2.6%, sometimes 12.8%, and rarely 17.2%. In the self-boarding group, nutrition labels were identified certainly 1.7%, sometimes 18.0%, and rarely 24.8%. The necessity of nutrition education was high in both dormitory group (51.6%) and the self-boarding group (62.4%). Therefore, development of an educational program and application of the information from nutrition labels for male college students, especially self-boarding students will be effective in improving dietary life in order to maintain healthy dietary habits.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differences in Nutritional Status According to the Residence Types among University Students in Gwangju
Geum-Bi Ryu, Young-Ran Heo
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 53(2): 207. CrossRef - Usage and Quality Satisfaction of Convenience Food at Convenience Stores according to the Eating Behavior of University Students in Southern Gyeonggi Province
Se-In Oh, Ok-Sun Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2023; 33(6): 492. CrossRef - Sugar Intake and Perception of Sugar Reduction among University Students in Gwangju
Yeon-Ok Park
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(11): 1170. CrossRef - Application and effectiveness of a nutrition education program based on the 2020 Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans for undergraduates in Gyeongsangnam-do and Gyeonggi-do
Mijoo Choi, Hyein Jung, Nayoung Kim, Sangah Shin, Taejung Woo, Eunju Park
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(6): 730. CrossRef - Development of a campus-based intervention program to strengthen food literacy among university students: A qualitative formative study
Eunji Ko, Eunjin Jang, Jiwon Sim, Minjeong Jeong, Sohyun Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(6): 495. CrossRef - Effect of Type of Nutrition Labeling on the Healthfulness Evaluation and Purchase Intentions of Home Meal Replacements (HMR) in South Korea
Mee-Young Joe
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(5): 387. CrossRef - Actual Status of Mukbang Viewing and Food Habits of University Students in Wonju Area
Seung-Lim Lee, Sun Hee Lee
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2022; 33(4): 631. CrossRef - Association Between Health Literacy and Health Promoting Behavior (Eating Habits, Physical Activity, and Stress) of University Students
Yoon-Sun Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(2): 94. CrossRef - Analysis of Usage, Preference, and Satisfaction for Convenience
Store Dessert among University Students in Chungbuk Area
Go Eun Lee, Hye-In Yang, Yun-Jung Bae
Journal of Biotechnology and Bioindustry.2021; 9: 63. CrossRef - The Effect of Frequent Use of Convenience Food from Convenience Stores on the Diet Quality of Women’s University Students: Using the Nutrition Quotient for Korean Adults
Sun Hee Lee, Seung-Lim Lee
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2021; 32(4): 581. CrossRef - Change of dietary habits and the use of home meal replacement and delivered foods due to COVID-19 among college students in Chungcheong province, Korea
Mi-Hyun Kim, Jee-Young Yeon
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(4): 383. CrossRef - Analysis of Dietary Behaviors, Food Consumption Frequency and Blood Clinical Indices by Residence Types of Female College Students in Seoul
Ru Zi Lee, Jung Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(3): 183. CrossRef - Comparison of Dietary Behavior of Eating Alone in Single Households by Status of Workers and Age
Pil Kyoo Jo, Yu Jin Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(5): 408. CrossRef - Analysis of the Difference in Nutrients Intake, Dietary Behaviors and Food Intake Frequency of Single- and Non Single-Person Households: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), 2014–2016
Na-Yeon Kang, Bok-Mi Jung
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(1): 1. CrossRef - Sleep Quality and Its Association with the Dietary Behavior and Lifestyle of University Students in Cheongju
Sewhan Jin, Munkyong Pae
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(5): 395. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Nutrition Status and Metabolic Syndrome Prevalence of the Members according to the Number of Household Members based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013–2014)
Jin-Young Lee, Soo-Kyong Choi, Jung-Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(3): 232. CrossRef - Nutritional Evaluation of Convenience Meals in Convenience Stores near the Universities
Go-Na Shin, Yu-Ri Kim, Mi-Hyun Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(5): 375. CrossRef - Studies on Dietary Habits and Residence Students’ Satisfaction with University Dormitory Foodservice in Jeollabuk-do Iksan Area
Kyung-Jin Min, Il-Sook Choi
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2016; 31(5): 442. CrossRef - Comparison of Dietary Habits and Learning Flow According to Alcohol Drinking Status Among Male University Students in Jeonbuk Province
Sol Yoon, Mi Sung Kim, Cheong Min Sohn
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2016; 25(3): 387. CrossRef - Relationship between thresholds and self-assessed preference for saltiness and sodium intake in young women
Eugene Shim, Yoon Jung Yang, Yoon Kyoun Yang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2016; 49(2): 88. CrossRef - Dietary Habits and Perception Toward Food Additives according to the Frequency of Consumption of Convenience Food at Convenience Stores among University Students in Cheongju
Munkyong Pae
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(2): 140. CrossRef - Lunch Eating Patterns and Dietary Habits of University Students according to Major Lunch Place
Hyunji Kim, Hongmie Lee
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2016; 22(4): 261. CrossRef - Eating Habit and Stress Status according to Exercising Habits of Middle-Aged Adults in Chungnam
Se-Yune Kim, Yeon-Ja Seo, Mi-Hyun Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(1): 43. CrossRef - Night Eating and Nutrient Intake Status according to Residence Type in University Students
Ye-Sook Jun, Mi-Kyeong Choi, Yun-Jung Bae
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2015; 44(2): 216. CrossRef - Preference and the Frequency of Processed Food Intake according to the Type of Residence of College Students in Korea
Su-Jin Kim, So Young Bu, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(3): 188. CrossRef - Use and Awareness of Nutrition Labeling of Snacks based on One Serving Size among University Students in Chungbuk
Mi-Hyun Kim, Yeon Woo Lee, Hyewon Jung
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2015; 28(5): 858. CrossRef - Differences in Solo Eating Perceptions and Dietary Behaviors of University Students by Gender
Youngmee Lee, Yu Jin Oh, Wookyoun Cho, Pil Kyoo Jo
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2015; 21(1): 57. CrossRef - Comparison of Processed Food Intake by Allowance Level in College Students in Chungnam
Yi-Yeong Kim, Su-Jin Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2015; 21(4): 280. CrossRef - A Study on Sodium-related Dietary Attitude and Behaviors According to Sodium-related Nutrition Knowledge of University Students
Mi-Hyun Kim, Jee-Young Yeon, Jong Wook Kim, Jae-Eon Byun, So-Young Bu, Mi-Kyeong Choi, Yun-Jung Bae
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(5): 327. CrossRef - Study on Sodium-related Dietary Attitude, Behaviors according to Practice of Dietary Guidelines of University Students
Yun-Jung Bae, Seung-Eun No, Jeong-Hwa Seo, Joo-Hee Son, Mi-Jin Lee, Da-Woon Jung
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2015; 28(3): 376. CrossRef - Energy Content Estimation by Collegians for Portion Standardized Foods Frequently Consumed in Korea
Jin Kim, Hee Jung Lee, Hyun Jung Lee, Sun Ha Lee, Jee-Young Yun, Mi-Kyeong Choi, Mi-Hyun Kim
Clinical Nutrition Research.2014; 3(1): 24. CrossRef - The Dietary and Late-night eating Behavior according to Residence Type of University Students in Daejeon
Huck Soon Joung, Nan Sook Koo
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2014; 23(4): 721. CrossRef
- Differences in Nutritional Status According to the Residence Types among University Students in Gwangju
- 1,359 View
- 10 Download
- 32 Crossref

- [English]
- Prevalence of Nutrition Labeling and Claims on Processed, and Packaged Foods
- Kwang Il Kwon, So Hyun Park, Jun Hyung Lee, Jee Young Kim, Kwang Soo Yoo, Jee Sun Lee, Seo Young Kim, Hyuni Sung, Hye Seon Nam, Jong Wook Kim, Hye Young Lee, Hye Kyung Park, Myung Chul Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2007;12(2):206-213. Published online April 30, 2007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated the prevalence of nutrition labeling and claims on processed and packaged foods. The final database consists of 1,287 foods, which were collected in two supermarkets in the Seoul area from September to November, 2006. An estimated 78% of KFDA-regulated processed, and packaged foods have nutrition labels. Nutrient content claims on food labels were identified in 21% of the foods which have nutrition labels. The prevalence of nutrition labels in this study is much higher than in previous studies due to the current expansion of the mandatory labeling regulation. However, false labeling and misleading contents claims were also identified. The food label is an important tool for enhancing the public's understanding of healthy choices of processed foods. Therefore, to maximize the benefits of the nutrition labeling regulation, industries, government agencies and health professionals should work together to help consumers make healthy dietary choices and improve their health.
- 303 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- A Study on the Current Nutrition Labelling Practices for Processed Foods
- Hyun Jung Lee, Hae Rang Chung, Young Ai Jang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2002;7(4):585-594. Published online August 31, 2002
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study examined the status of current nutrition labelling and claims for the processed foods that were purchased in the supermarket. They were assessed in the aspects of frequency and content of nutrition labelling and claims. The results are summarized as follows; The percentage of products contain the nutrition labelling or claims of processed foods of investigation were 18.7% and 18.8% respectively. In the nutrition labelling method, the format separated by expression contents with 'only liability indication nutrient' or 'liability indication nutrients plus discretion indication nutrients' were 44.7% and 43.4% respectively. In the case of type and title, 'table' and 'nutrition composition' were used most frequently, 83.9% and 83.2% respectively. And in the case of expression unit, 'per 100 g or 100 ml' was higher (56.8%) than others. Nutrition claims were divided into 'nutrition content claim' and 'comparative claim', in the former the most claim was 'containing' and in the other 'more or plus' used most frequently. 'Nutrient function claim' was 13.4% and 'Implied nutrient claim' was 7.3% of all the claims. Results of the evaluation of current nutrition labeling system, nutrition labelling was less advanced and variable in content and format and also the information was not easy for consumers to understand and use them. To support achievement of the nutrition label, there must be program and initiatives for better understanding and communication and guidances on food labelling and nutrition for food manufactures.
- 303 View
- 1 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



