Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Article
- [English]
- The dietary factors associated with sleep duration in postmenopausal middle-aged women: a cross-sectional study using 2019–2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
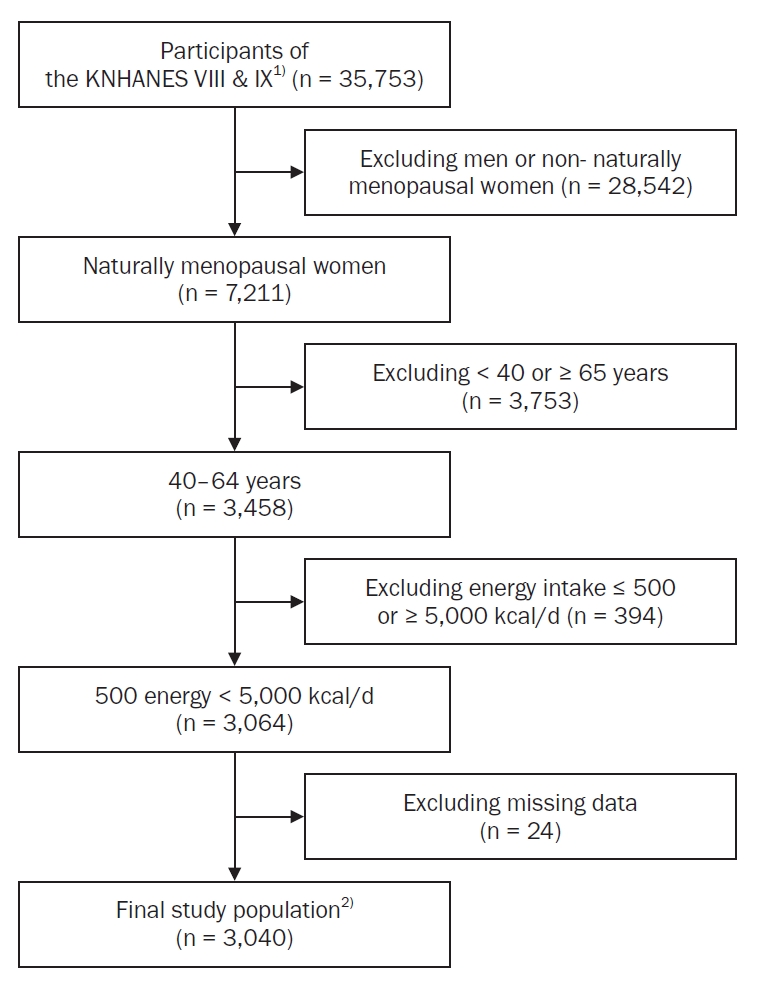
- Eugene Shim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(3):197-213. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00052
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to analyze dietary factors associated with sleep duration in postmenopausal middle-aged women using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), with particular emphasis on the postmenopausal period.
Methods
A total of 3,040 postmenopausal women aged 40–64 years from the 2019–2023 KNHANES were included. Sleep duration was classified into four categories: “appropriate sleep duration” (ASD; 7–9 hours), “short sleep duration” (6–7 hours), “very short sleep duration” (VSSD; < 6 hours), and “long sleep duration” (LSD; > 9 hours). Nutrient and food intake were compared among groups using analysis of covariance. Multinomial logistic and polynomial regression models assessed associations, adjusting for demographic and health covariates.
Results
The VSSD group had higher body mass index and waist circumference than the ASD group, despite lower total energy intake, and also consumed more snack energy and skipped breakfast and dinner more often. This group also had lower intakes of monounsaturated fatty acids and nuts and seeds. In the late menopausal group, greater consumption of cereal grains, fish and shellfish, and beverages was associated with elevated LSD risk. Conversely, higher folate intake in the early menopausal group was inversely associated with VSSD risk. Cholesterol intake was positively associated with LSD risk in both groups. A negative nonlinear association between sleep duration and dietary intake was observed in the early menopausal group when polyunsaturated fatty acid intake exceeded 19.86 g/day and riboflavin intake exceeded 1.76 mg/day. In the late menopausal group, riboflavin intake was strongly correlated with increased LSD risk (odds ratio = 4.776, P = 0.004). Sugar and beverage intake showed a positive linear relationship with sleep duration at average intake levels.
Conclusion
Dietary factors associated with sleep duration differed by postmenopausal period, with specific nutrients and food groups exhibiting variable associations with sleep duration above mean intake levels.meS
- 4,041 View
- 52 Download

Original Articles
- [English]
- Sleep Quality and Its Association with the Dietary Behavior and Lifestyle of University Students in Cheongju
- Sewhan Jin, Munkyong Pae
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(5):395-407. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.5.395
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study examined the association of the sleep quality and patterns with the dietary behavior, including snack and beverage consumption, taste preferences, as well as lifestyle of university students.
METHODS
The subjects were 406 university students in Cheongju, Korea, and the data were collected using a self-administered questionnaire. They were divided into two groups according to the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI): good-quality sleepers (PSQI score ≤ 5) and poor-quality sleepers (PSQI score > 5). The data were analyzed using a χ2-test, independent t-test, and analysis of covariance using the SPSS 25.0 program.
RESULTS
Fifty-two percent of university students were categorized as poor-quality sleepers by the PSQI. Students classified as poor-quality sleepers had delayed bedtimes, and a shorter duration in bed and total sleep hours than the good-quality sleepers did. Poor-quality sleepers were more prevalent among those who were female, having irregular mealtimes, or frequent late night meals. They also consumed fast food frequently, such as fried chicken and hamburgers, and noodles when adjusted for gender. In addition, drinks with caffeine over milk were dominant among poor-quality sleepers. Furthermore, the preferences for spicy and salty tastes and longer smartphone usage were more prevalent in those with poor-sleep quality.
CONCLUSIONS
These results showed that more than 50% of university students reported disturbed sleep and poor quality sleep was associated with less desirable snack consumption and taste preference, more smartphone usage, and others. Therefore, nutrition education program along with lifestyle changes promoting sufficient sleep are encouraged to provide for university students, particularly those who have poor sleep quality. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship of sleep quality, BMI, Dietary, and socioeconomic attributes among young adults: A systematic review
Seohyun Ahn, Wan Safwani Binti Wan Kamarul Zaman, Sim-Kuan Goh, Chow-Khuen Chan
Journal of Health Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Health Behaviors and Dietary Habits according to Sleep Duration in Korean Adults Based on the 2013–2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jin-A Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2019; 19(4): 237. CrossRef
- Relationship of sleep quality, BMI, Dietary, and socioeconomic attributes among young adults: A systematic review
- 2,259 View
- 22 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- The association between Coffee Consumption and All-cause Mortality According to Sleep-related Disorders
- Sunghee Lee, Wookyoun Cho, Namhan Cho, Chol Shin
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(4):301-309. Published online August 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.4.301
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
While recent studies showed that coffee consumption reduced the risk of all-cause mortality, no study has examined the effect of coffee consumption on all-cause mortality related to sleep disorders. We aimed to examine whether sleep-related disorders would differently affect the association between coffee consumption and the risk of all-cause mortality among 8,075 adults aged 40 to 69 years.
METHODS
In a prospective cohort study, the study participants were biennially followed up for 12 years from 2001 to 2012. On each follow-up visit, the participants underwent comprehensive tests including anthropometric examinations, interviewer-administered questionnaires, and biochemical tests. Coffee consumption frequency and the amount were measured using a semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire. Using death certificate data from Korean National Statistical Office, the vital status of each study participant was identified. Sleep-related disorders were examined with interviewer-administered questionnaires. We estimated Hazard ratios and the corresponding 95% confidence intervals from Cox Proportional Hazard models. Multivariable models were established after adjusting for center, total caloric intake, age, gender, body mass index, physical activity, education, smoking, drinking, hypertension, diabetes, total cholesterol, c-reactive protein, energy-adjusted food groups of refined grains, vegetables, fruits, meat, fish, and dairy.
RESULTS
Compared with those who had no coffee consumption, participants who had about three cups of coffee per day showed a reduced risk of all-cause mortality, after adjusting for covariates. Those who had a sleep-related disorder showed no significant effect of coffee consumption on the risk of all-cause mortality, whereas those who had no sleep-related disorders showed significantly reduced risk of all-cause mortality.
CONCLUSIONS
Our findings suggested that approximately three cups of coffee per day would be beneficial to reduce the risk of all-cause mortality only among adults with no sleep-related disorders. Coffee consumption should be prudent for those with sleep-related symptoms. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association with obesity and abdominal obesity according to the kind and amount of coffee intake in Korean adults: 2013 ~ 2016 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyoung-seop Park, Jung-Sug Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(4): 369. CrossRef
- Association with obesity and abdominal obesity according to the kind and amount of coffee intake in Korean adults: 2013 ~ 2016 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,534 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Comparisons of Body Image Perception, Health Related Lifestyle and Dietary Behavior Based on the Self-Rated Health of University Students in Seoul
- Ho Kyung Kwak, Mi Young Lee, Mi Joung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(6):672-682. Published online December 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.6.672
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to examine the differences in perceived body weight and image and various lifestyles based on the self-rated health of university students when gender was adjusted. Five hundred fifty-five participants were asked their perceived health condition, and 58, 289, 160 and 48 students answered themselves as "very healthy", "healthy", "normal", and "unhealthy", respectively. As compared to the other 3 groups, "unhealthy" group showed higher proportions in dissatisfaction of body weight and negative perception of body image (P < 0.01). As health related lifestyles, "very healthy" group reported longer sleeping time than "unhealthy" group (P < 0.05), and had a higher proportion of people with regular exercise. Among the dietary behaviors, the frequencies of followings significantly different among the groups: "Regularity of meal time" (P < 0.01), "Eat protein foods more than twice a day" (P < 0.001), "Eat vegetables" (P < 0.01), "Eat fruit and fruit juice" (P < 0.01), "Eat vegetable oil added foods" (P < 0.01), "Eat seaweed" (P < 0.01), "Eat breakfast" (P < 0.01), "Modulation in animal fat and high in cholesterol intake" (P < 0.01). Particularly, higher proportion of subjects answered "very healthy" had higher frequencies (6-7 times/week) of these dietary behaviors. Overall results suggest that healthy lifestyle including adequate sleeping time, regular exercise, and good dietary behaviors might be potential factors affecting positive perception of health. In addition, positive perception of body weight and image were related with positive perception of health.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Individual Characteristics Associated with Fears and Prevention Behaviors Related to Respiratory Infectious Disease among South Korean Adults Using Complex Sample Design
Gunsoo Han, Jae-Ahm Park
Healthcare.2024; 12(19): 1924. CrossRef - A pilot investigation of a combined food literacy and exercise program for college students: a one-group pre-post intervention study
Minjeong Jeong, Jinhyun Kim, Dahye Han, Eunjin Jang, Kyoungho Choi, Sohyun Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 455. CrossRef - Dietary Behaviors Associated with Health Perception of Korean Adolescents from Multicultural Families: based on data from the 2017 ~ 2019 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Surveys
YueRong Hu, SuJin Song
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(3): 192. CrossRef - A Study on Associations between the Exercise Habits and Subjective Health Perceptions of Adolescents in Area of Seoul: Focusing on Middle School Students
Yoon-Ji Lee, Ha-Young Kim
Exercise Science.2022; 31(2): 238. CrossRef - Self-rated health may be a predictor for metabolic syndrome and high hs-CRP prevalences in healthy adults in South Korea: Based on the 2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Mi Joung Kim, In Woo Kim
Nutrition Research.2022; 102: 71. CrossRef - Comparison of Nutrient Intake and Diet Assessment according to the Subjective Health Perception and Disease Existence : The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data(2013~2017) Analysis
Yi-Na Yoon, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2021; 32(3): 395. CrossRef - Clustering of Healthy Behaviors and Related Factors among 19-64 Aged Korean Adults
Hyae Min Gu, So Yeon Ryu, Jong Park, Seong-Woo Choi, Mi Ah Han, Jun Ho Shin
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2021; 46(3): 267. CrossRef - The Effect of Frequent Use of Convenience Food from Convenience Stores on the Diet Quality of Women’s University Students: Using the Nutrition Quotient for Korean Adults
Sun Hee Lee, Seung-Lim Lee
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2021; 32(4): 581. CrossRef - Development of a Web Application Based on Human Body Obesity Index and Self-Obesity Diagnosis Model Using the Data Mining Methodology
Changgyun Kim, Sekyoung Youm
Sustainability.2020; 12(9): 3702. CrossRef - The Associations between Individual Factors, eHealth Literacy, and Health Behaviors among College Students
Chiao Ling Huang, Shu-Ching Yang, Chia-Hsun Chiang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(6): 2108. CrossRef - Association between Dietary Habits and Self-rated Health According to Sasang Constitution
Kyoungsik Jeong, Hoseok Kim, Siwoo Lee, Younghwa Baek
Journal of Physiology & Pathology in Korean Medicine.2020; 34(1): 53. CrossRef - Comparison of factors affecting weight control experiences by perception types of body shape
Yeo Jeong Gu, Jae Yeon Jeong, Ji Yun Jeong, Hae Jong Lee
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2019; 36(4): 77. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Body Image Discordance Amongst Korean Adults Aged 19–39 Years
Hye-Young Jang, Jung-Won Ahn, Mi-Kyeong Jeon
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2018; 9(4): 197. CrossRef - Body Image Perception and Eating Behaviors among Male Middle and High School Students according to Weight Status in Seoul
Bo-Mi Kim, Kyung-Hee Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2018; 28(2): 123. CrossRef - Body Weight Perception, Mental Health, and Weight Control Behavior in Normal Weight Adolescents: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013-2015
Eun Jee Lee
Child Health Nursing Research.2017; 23(2): 249. CrossRef - Comparison of Dietary Habits and Learning Flow According to Alcohol Drinking Status Among Male University Students in Jeonbuk Province
Sol Yoon, Mi Sung Kim, Cheong Min Sohn
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2016; 25(3): 387. CrossRef - Effects of life style on psychosomatic a subjective a symptoms of the dental technology students
Soon-Suk Kwon, Hye-Eun Lee
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2016; 38(1): 37. CrossRef - Dietary Habits, Dietary Behaviors, Depression and Stress according to Self-Rated Health of University Students in Kyungnam Province
Kyung-Ae Park
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2016; 22(4): 272. CrossRef - Performance of Weight Control Program on University Students in Daejeon
Joon Ho Lee, Hai Yuan Hou
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2016; 27(3): 477. CrossRef - Survey on Health Status and Food Habits of Male College Students in Wonju Area According to Drinking Behavior
Seung-Lim Lee
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2016; 22(1): 41. CrossRef - A study on blood lipid profiles, aluminum and mercury levels in college students
Eunim Jung, Whajin Hyun, Yoona Ro, Hongmie Lee, Kyunghee Song
Nutrition Research and Practice.2016; 10(4): 442. CrossRef - Combined effect of body mass index and body size perception on metabolic syndrome in South Korea: results of the fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (2010-2012)
Sook Hee Yoon, Kyu-Tae Han, Sun Jung Kim, Tae Yong Sohn, Byungyool Jeon, Woorim Kim, Eun-Cheol Park
BMC Public Health.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Night Eating and Nutrient Intake Status according to Residence Type in University Students
Ye-Sook Jun, Mi-Kyeong Choi, Yun-Jung Bae
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2015; 44(2): 216. CrossRef - Survey on Health-related Factors, Nutrition Knowledge and Food Habits of College Students in Wonju Area
Seung Lim Lee, Sun Hee Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(2): 96. CrossRef - A Study on Food Habits and Nutrient Intakes according to BMI in Food and Nutrition Major and Non-major Female Students in Kyungnam University
Eun-Hee Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(4): 297. CrossRef - The Associations between Discordance of Body Image and Physical Activities among Adults Aged 19 to 64 Years: Based on the Data from 2010 Community Health Survey
In Ae Chun, So Yeon Ryu, Jong Park, Mi Ah Han, Seong Woo Choi, Dae Sik Ko
The Korean Journal of Obesity.2014; 23(4): 274. CrossRef - Relations of Body Perception, Anxiety, Psychological Flexibility and Abnormal Eating Attitudes of College Students
Hae Ok Jeon
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(6): 3675. CrossRef - Evaluation of Diet Quality according to Self-Rated Health Status of Korean Middle-Aged Women -Based on 2008~2009 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey-
Hye-Jin Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2013; 42(9): 1395. CrossRef - A Study on the Eating Habits and Healthy Eating Behaviors of the University Students in Jeonbuk Area
Kye-Hong Min
Korean journal of food and cookery science.2013; 29(4): 399. CrossRef - An Analysis of Factors Affecting Energy Drink Consumption in College Students
Haesun Yun, Su Hee Kim, Chung Yul Lee
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2013; 30(3): 1. CrossRef - Comparisons of dietary behavior, food intake, and satisfaction with food-related life between the elderly living in urban and rural areas
Yuri Kim, Sunhee Seo, Oran Kwon, Mi Sook Cho
Korean Journal of Nutrition.2012; 45(3): 252. CrossRef
- Individual Characteristics Associated with Fears and Prevention Behaviors Related to Respiratory Infectious Disease among South Korean Adults Using Complex Sample Design
- 1,508 View
- 8 Download
- 31 Crossref

- [English]
- Association of Daily Sleep Duration with Obesity, Macronutrient Intake, and Physical Activity
- Inkyung Baik, Chol Shin
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(3):315-323. Published online June 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.3.315
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - There are a few studies that reported the association of sleep duration with calorie intake and energy expenditure. Using cross-sectional data from a population-based prospective study, we evaluated the association of sleep duration with indicators of obesity including body mass index and waist circumference, calorie intake and its proportion of macronutrients, and physical activity. The study subjects were 4,226 male and female adults, who were aged 40 to 69 years and were free of diagnosed cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and dyslipidemia at baseline. Robust regression analysis was used to analyze associations. The study found that sleep duration is inversely associated with waist circumference, calorie intake, and percent of calories from fat intake and is positively associated with percent of calories from carbohydrate intake and physical activity. The inverse association between sleep duration and waist circumference was stronger among men than among women. The inverse association between sleep duration and calorie intake was stronger among women than among men and such association was also stronger among obese persons than those with a normal body mass index. The positive association between sleep duration and physical activity was strongly demonstrated regardless of sex or obesity. Physical activity is positively associated with sleep duration independent of potential confounding factors including age, sex, income, occupation, marital status, education, smoking status, waist circumference, calorie and macronutrient intake, and alcohol intake.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Anti-Stress and Sleep-Inducing Effects of a Zizyphus jujuba Mill.-Hypericum perforatum L. Mixture and Its Bioactive Compounds
June-Seok Lim, Yeon-Seok Seong, Geon Oh, Ji-Hyun Im, Xiaolu Fu, Min-Hye Kim, Jin-Ho Roh, Ok-Hwan Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2025; 54(6): 489. CrossRef - A comparative study on eating habits and mental health of Korean middle school students according to their bedtime across regions: using data from the 2020–2022 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Sarim Kim, Jiyoung Jeong, Juyeon Kang, Jihye Kim, Yoon Jung Yang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(2): 269. CrossRef - Grit in Community‐Dwelling Older Adults with Low Back Pain Is Related to Self‐Physical Training Habits
Tsubasa Kawasaki, Ryosuke Tozawa
PM&R.2020; 12(10): 984. CrossRef - Health Behaviors and Dietary Habits according to Sleep Duration in Korean Adults Based on the 2013–2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jin-A Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2019; 19(4): 237. CrossRef - The longitudinal influence of child maltreatment on child obesity in South Korea: The mediating effects of low self-esteem and depressive symptoms
Aely Park, Youngmi Kim
Children and Youth Services Review.2018; 87: 34. CrossRef - Dietary behavior status and its association with study-related factors in middle school students in Gyeonggi area
Myoung Sook Lee, Wha Jin Hyun, Kyung Hee Song
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(5): 455. CrossRef - Relationship between Bone Mineral Density and Bone Metabolic Biochemical Markers and Diet Quality Index-International(DQI-I) in Postmenopausal Obese Women
Yeonah Jeong, Misung Kim, Saeron Shin, Ahreum Han, Geomsuk Seo, Cheongmin Sohn
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(3): 284. CrossRef - Difference in Sleep Circadian Rhythm and Sleep Quality between Normal-weight and Obese Group
Hyun Jin Suk, Yeon Kyung Na, Hae Sook Hong
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2014; 16(4): 309. CrossRef - Experiences of Health Related Lifestyles in High Body Fat but Non-obese Female College Students in Korea
Jeongsoo Kim
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2014; 5(1): 68. CrossRef - Predictors of Poor Sleep Quality among Nursing Students
Young Ran Chae, Dong Hee Choi, Su Jeong Yu
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2014; 16(2): 98. CrossRef - Correlation between Sleep Quality and Snack Intake in Third Year Middle and High School Students in the Gwangju Area
Hyo Bok Kim, Yang Won Park
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2013; 42(2): 212. CrossRef - A Study on the Correlation of the accompanying symptoms, Heart Rate Variability and Body Component Analysis in 350 Insomnia Patients
Ji-Won Ha, Bo-Kyung Kim, Jin-Hyeong Jung
Journal of Oriental Neuropsychiatry.2012; 23(3): 47. CrossRef - Physical activity level, total daily energy expenditure, and estimated energy expenditure in normal weight and overweight or obese children and adolescents
Myung Hee Kim, Eun Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Nutrition.2012; 45(6): 511. CrossRef
- Analysis of Anti-Stress and Sleep-Inducing Effects of a Zizyphus jujuba Mill.-Hypericum perforatum L. Mixture and Its Bioactive Compounds
- 1,430 View
- 0 Download
- 13 Crossref


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



