Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Korean J Community Nutr > Volume 29(2); 2024 > Article
-
Research Article
- Developing educational videos to inform rightly about school foodservice from kindergarten to high school: a case study
-
Gyoungok Gang1)
 , Chaewon Park2)
, Chaewon Park2) , Haejin Kang3)
, Haejin Kang3) , Wan Soo Hong4)
, Wan Soo Hong4) , Yoo Kyoung Park5)
, Yoo Kyoung Park5) , Sook Hee Choi6)
, Sook Hee Choi6) , Seung Hye Kim7)
, Seung Hye Kim7) , Jieun Choi8)
, Jieun Choi8) , Jihyun Park8)
, Jihyun Park8) , Hyeja Chang9),†
, Hyeja Chang9),†
-
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition 2024;29(2):97-113.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.2.97
Published online: April 24, 2024
1)Associate Researcher, Department of Food Science and Nutrition, Pukyong National University, Busan, Korea
2)Master Student, Department of Food Science and Nutrition, Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea
3)PhD Student, Department of Medical Nutrition (AgeTech-Service Convergence Major), Graduate School of East-West Medical Science, Kyung Hee University, Yongin, Korea
4)Professor, Department of Foodservice Management and Nutrition, Sangmyung University, Seoul, Korea
5)Professor, Department of Medical Nutrition (AgeTech-Service Convergence Major), Graduate School of East-West Medical Science, Kyung Hee University, Yongin, Korea
6)Nutrition Teacher, Seoul Kongduck Elementary School, Seoul, Korea
7)Nutrition Teacher, Seoul Robotics High School, Seoul, Korea
8)Staff, Eunpyeong Center for Children’s Foodservice Management, Seoul, Korea
9)Professor, Department of Food Science and Nutrition, Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea
- †Corresponding author: Hyeja Chang Department of Food Science and Nutrition, Dankook University, 119 Dandae-ro, Dongnam-gu, Cheonan 31116, Korea. Tel: +82-41-550-3478 Fax: +82-41-559-7567 Email: hjc10@dankook.ac.kr
© 2024 The Korean Society of Community Nutrition
This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 2,809 Views
- 37 Download
Abstract
-
Objectives
- Since the enactment of the School Nutrition Act in 1981, school lunch programs in South Korea have grown quantitatively and qualitatively with a current student participation rate of 99.8%. Nonetheless, educational materials are needed to reduce misunderstanding and ignorance about school lunch programs. This study aimed to develop 3 educational videos that help students of various ages (kindergarteners/lower-grade elementary, upper-grade elementary, and secondary school, respectively), understand the school lunch program.
-
Methods
- A scenario was created, was made, and the opinions on the scenario from experts in foodservice sectors were collected. A survey was conducted to students and parents to determine topics they wanted to know about school foodservice. The final videos were produced using this information and the expert opinions. The data were analyzed using SPSS 27.0 for Mac (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA); a P-value of < 0.05 was considered significant.
-
Results
- Three videos on school foodservice were developed for various age levels of students: kindergarten/lower-grade elementary, upper-grade elementary, and secondary school. Additionally, English subtitles were included for the multicultural student population. These videos, each lasting about 7 minutes, cover topics such as nutrition, hygiene, and the cultural significance of the school lunch program. The survey results showed that parents and students wanted to know the following topics about the school lunch program: “nutritionally balanced diet” (11.9%), “purchasing safe food ingredients” (10.9%), and “healthy eating habits” (9.9%).
-
Conclusions
- The developed videos will serve as valuable educational resources on school foodservice, foster a deeper understanding of the school lunch program in parents and students, and potentially address their inquiries regarding production processes, nutrition, hygiene, cultural heritage, and health.
INTRODUCTION
METHODS
RESULTS
DISCUSSION
CONCLUSIONS
-
Conflict of Interest
There are no financial or other issues that might lead to conflict of interest.
-
Funding
This research was supported by Korea Educational Environments Protection Agency (R202201176).
-
Data Availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as very limited questionnaire items were used in this study.
-
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Supported by Korea Educational Environments Protection Agency.
NOTES

| Category |
School level |
Total (n = 532) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parents of kindergarten/lower-grade elementary students (n = 101) | Upper elementary school students (n = 152) | Middle and high school students (n = 279) | ||
| Age | 40.29 ± 5.56 | 10.66 ± 2.44 | 14.96 ± 2.37 | 17.83 ± 10.58 |
| Father’s highest educational level1) | ||||
| High school graduation | 1 (1.6) | 1 (2.8) | 4 (7.1) | 6 (3.8) |
| College graduation | 42 (65.6) | 23 (63.9) | 44 (78.6) | 109 (69.9) |
| Graduate school graduation | 21 (32.8) | 12 (33.3) | 8 (14.3) | 41 (26.3) |
| No response | 37 | 116 | 223 | 376 |
| Mother’s highest educational level1) | ||||
| Unschooled | 0 (0) | 1 (2.7) | 0 (1) | 1 (0.7) |
| Elementary school graduation | 0 (0) | 1 (2.7) | 0 (0) | 1 (0.7) |
| High school graduation | 2 (3.2) | 2 (5.4) | 6 (11.8) | 10 (6.7) |
| College graduation | 42 (67.7) | 28 (75.7) | 37 (72.5) | 107 (71.3) |
| Graduate school graduation | 18 (29.0) | 5 (13.5) | 8 (15.7) | 31 (20.7) |
| No response | 39 | 115 | 228 | 382 |
| Average monthly household total income1) (unit: 10,000 won) | ||||
| 150–300 less | 2 (3.5) | 1 (4.5) | 0 (0) | 3 (2.7) |
| 300–450 less | 6 (10.5) | 2 (9.1) | 1 (3.2) | 9 (8.2) |
| 450–600 less | 14 (24.6) | 4 (18.2) | 8 (25.8) | 26 (23.6) |
| 600–750 less | 8 (14.0) | 4 (18.2) | 4 (12.9) | 16 (14.5) |
| 750–900 less | 11 (19.3) | 2 (9.1) | 8 (25.8) | 21 (19.1) |
| 900–1,500 less | 15 (26.3) | 4 (18.2) | 8 (25.8) | 27 (24.5) |
| More than 1,500 | 1 (1.8) | 5 (22.7) | 2 (6.5) | 8 (7.3) |
| No response | 44 | 130 | 248 | 422 |
| Category | Parents of kindergarten/lower-grade elementary students (n = 101) | Upper elementary school students (n = 152) | Middle and high school students (n = 279) | Total (n = 532) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The importance of kindergarten and school foodservice | 3 (1.0) | 10 (2.6) | 11 (1.7) | 24 (1.8) |
| Nutritionally balanced diet | 68 (23.5) | 21 (5.5) | 66 (10.4) | 155 (11.9) |
| Reasons for not serving meals with low-simple sugar and low-sodium | 12 (4.2) | 32 (8.4) | 51 (8.0) | 95 (7.3) |
| Purchasing safe food ingredients | 52 (18.0) | 48 (12.6) | 43 (6.8) | 143 (10.9) |
| School meal production process | 21 (7.3) | 33 (8.6) | 70 (11.0) | 124 (9.5) |
| Food hygiene management in accordance with HACCP | 30 (10.4) | 19 (5.0) | 31 (4.9) | 80 (6.1) |
| Purpose of kindergarten and school foodservice | 0 (0.0) | 15 (3.9) | 15 (2.4) | 30 (2.3) |
| Healthiness of school meals | 23 (8.0) | 34 (8.9) | 47 (7.4) | 104 (8.0) |
| Transparent food cost management | 9 (3.1) | 12 (3.1) | 41 (6.4) | 62 (4.7) |
| Dining etiquette | 9 (3.1) | 24 (6.3) | 42 (6.6) | 75 (5.7) |
| Inheriting traditional food culture | 3 (1.0) | 19 (5.0) | 16 (2.5) | 38 (2.9) |
| Meal management using the computerized system (NEIS) | 1 (0.3) | 10 (2.6) | 13 (2.0) | 24 (1.8) |
| Movement to reduce food waste | 10 (3.5) | 22 (5.8) | 46 (7.2) | 78 (6.0) |
| Healthy eating habits | 41 (14.2) | 30 (7.9) | 59 (9.3) | 130 (9.9) |
| History of kindergarten/school foodservice | 3 (1.0) | 26 (6.8) | 28 (4.4) | 57 (4.4) |
| Reasons for not serving fast foods or favorite foods | 4 (1.4) | 27 (7.1) | 57 (9.0) | 88 (6.7) |
| Total1) | 289 (100.0) | 382 (100.0) | 636 (100.0) | 1,307 (100.0) |
| Category | Strongly agree | Agree | Neutral | Disagree | Strongly disagree | Mean score1) | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enjoyment of video | 9.872*** | ||||||
| K/E (n = 19) | 16 (84.2) | 2 (10.5) | 1 (5.3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 4.79 ± 0.54a | |
| UE (n = 62) | 19 (30.6) | 19 (30.6) | 17 (27.4) | 2 (3.2) | 5 (8.1) | 3.73 ± 1.18b | |
| M/H (n = 49) | 21 (42.9) | 18 (36.7) | 10 (20.4) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 4.22 ± 0.77ab | |
| Total (n = 130) | 56 (43.1) | 39 (30.0) | 28 (21.5) | 2 (1.5) | 5 (3.8) | 4.07 ± 1.02 | |
| Helpfulness for understanding school foodservice | 1.465 | ||||||
| K/E (n = 19) | 13 (68.4) | 5 (26.3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (5.3) | 4.53 ± 0.96 | |
| UE (n = 62) | 25 (40.3) | 26 (41.9) | 9 (14.5) | 1 (1.6) | 1 (1.6) | 4.18 ± 0.86 | |
| M/H (n = 49) | 24 (49.0) | 18 (36.7) | 7 (14.3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 4.35 ± 0.72 | |
| Total (n = 130) | 62 (47.7) | 49 (37.7) | 16 (12.3) | 1 (0.8) | 2 (1.5) | 4.29 ± 0.83 | |
| Comprehensibility of video | 3.914* | ||||||
| K/E (n = 19) | 16 (84.2) | 3 (15.8) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 4.84 ± 0.37a | |
| UE (n = 62) | 31 (50.0) | 21 (33.9) | 9 (14.5) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.6) | 4.31 ± 0.84b | |
| M/H (n = 49) | 26 (53.1) | 18 (36.7) | 5 (10.2) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 4.43 ± 0.68ab | |
| Total (n = 130) | 73 (56.2) | 42 (32.3) | 14 (10.8) | 0 (0) | 1 (0.8) | 4.43 ± 0.75 |
n (%) or Mean ± SD.
Different superscript letters mean significantly different groups with a Scheffe test.
K/E, parents of kindergarten/lower-grade elementary students; UE, upper-grade elementary students; M/H, middle and high school students.
1)Five points rating scales: 1-point strongly disagree, 5-point strongly agree.
*P < 0.05,
***P < 0.001.
- 1. Ministry of Education. School meals act [Internet]. Ministry of Education; 2022 [updated 2022 Jun 29; cited 2023 Nov 25]. Available from: https://www.law.go.kr/%EB%B2%95%EB%A0%B9/%ED%95%99%EA%B5%90%EA%B8%89%EC%8B%9D%EB%B2%95
- 2. Lee HY, Yi BS, Cha J, Ham SO, Park MK, Lee MN, et al. Development of model for the survey on school foodservice program. Korean J Community Nutr 2019; 24(1): 60-76.ArticlePDF
- 3. Kwak TK, Lyu ES, Lee HS, Ryu K, Choi SK, Hong WS, et al. Institutional foodservice operations. 5th ed. Seoul: Shinkwang Pub; 2022. p. 15-16.
- 4. Lee O, Cho M, Chang H. The organization commitment and perception of human resource management by employment types of school foodservice employees. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr 2014; 43(1): 162-171.Article
- 5. Cho Y. A study on the current policy issues and ways to improve the publicness of private kindergartens: focused on the kindergarten 3 acts. Law Rev 2021; 21(4): 353-372.
- 6. Park MK, Shin S, Kim H, Lee J, Kim Y. Analysis of operational meal costs and operator perception of optimal price through an application of the price sensitivity measurement (PSM) technique by the size of kindergartens. J Korean Soc Food Cult 2022; 37(4): 335-344.
- 7. Jung R, Kim GH, Oh J, Ham S, Lee S. Foodservice status and perception regarding foodservice management in kindergartens attached to elementary schools in Seoul. Korean J Community Nutr 2022; 27(6): 492-502.ArticlePDF
- 8. Ministry of Education. Kindergarten meal implementation status for the 2022 school year [Internet]. School Meal Information Center; 2022 [updated 2023 Sep 11; cited 2023 Nov 27]. Available from: http://www.sfic.go.kr/board/view.do?boardId=BBS_0000007&menuCd=DOM_000000103003000000&startPage=1&searchType=DATA_TITLE&keyword=%EC%9C%A0%EC%B9%98%EC%9B%90&dataSid=57610
- 9. Ministry of Education. School meal implementation status for the 2022 school year [Internet]. School Meal Information Center; 2022 [updated 2023 Sep 11; cited 2023 Nov 27]. Available from: http://www.sfic.go.kr/board/view.do?boardId=BBS_0000007&menuCd=DOM_000000103003000000&startPage=1&searchType=DATA_TITLE&keyword=%ED%95%99%EA%B5%90%EA%B8%89%EC%8B%9D&dataSid=57609
- 10. Seoul Metropolitan Office of Education. 2023 Basic directions for school meals. Seoul: Seoul Metropolitan Office of Education; 2023.
- 11. Kwak TK, Lee KM, Chang HJ, Kang YJ, Hong WS, Moon HK. Analysis of critical control points through field assessment of sanitation management practices in foodservice establishments. Korean J Food Cook Sci 2005; 21(3): 290-300.
- 12. Kim IN. Lunch meal interest survey by kindergarten parents' employment status in Hwaseong Region [master’s thesis]. Suwon University; 2018.
- 13. Yu JS. A study on the factors of public kindergarten choice among parents, their perception of public kindergarten management and satisfaction level [master’s thesis]. Inha University; 2010.
- 14. Oh BN. A research on hygienic attitude of students about middle school food service in Gyeonggi-do [master’s thesis]. Hanyang University; 2013.
- 15. Go YS, Jeon ER, Jung LH. The dietary habits and perception of vegetable intake of elementary students in Gwangju and Jeonnam. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr 2013; 42(2): 223-233.Article
- 16. Um M, Park S, Kye S. Evaluation of dietary habits and nutrition quotient scores according to leftover food during school meal service among middle school students in Gyeonggi. J Korean Soc Food Cult 2021; 36(2): 198-209.
- 17. Chang H, Go E. The effectiveness of nutrition education provided by dietitians in child care centers. Korean J Community Nutr 2007; 12(3): 299-309.
- 18. Oh N, Kwon S, Kim K, Shon J, Park H, Seo J. Status and need assessment on nutrition & dietary life education among nutrition teachers in elementary, middle and high schools. Korean J Community Nutr 2016; 21(2): 152-164.ArticlePDF
- 19. Park M, Kim S. Effects of nutrition education using dietary guidebook in higher grade elementary students of Jeonbuk area. Korean J Community Nutr 2018; 23(1): 13-27.ArticlePDF
- 20. Lee SH, Lee SS. The effect of a career program using video media on career self-efficacy of elementary students. J Korean Pract Arts Educ 2021; 34(3): 43-65.Article
- 21. Kim KA, Lee YK. The effect of nutrition education using animations on the nutrition knowledge, eating habits and food preferences of elementary school students. Korean J Community Nutr 2010; 15(1): 50-60.
- 22. Ministry of Education; Korea Educational Environments Protection Agency; Korean Society of Food Service Sanitation. Kindergarten foodservice hygiene management education materials: cooking [Internet]. Ministry of Education; 2021 [updated 2022 Mar 15; cited 2023 Nov 27]. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NbSQuhZ7F4I
- 23. Jeju Special Self-Governing Provincial Office of Education. “Liking vegetables” Let's practice proper eating habits together [Internet]. Jeju Special Self-Governing Provincial Office of Education; 2021 [updated 2020 Jan 30; cited 2023 Nov 27]. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2cMl_kW4Zi8&t=5s
- 24. Kim HY, Kim MH, Lee JH. Awareness and satisfaction on the school foodservice by elementary students and parents in Incheon city. J Korean Soc Food Nutr 2018; 31(3): 355-365.
- 25. Kim YR, Kim EJ, Choi MJ. Perception and satisfaction of free foodservice in male middle school students in Chungnam. J Korean Diet Assoc 2014; 20(2): 87-98.Article
- 26. Park SE, Park SM. Study on implementation plan for free kindergarten meals. Daegu: Daegu Future Education Research Institute; 2017. p. 4-16.
- 27. Kim MH, Kim HJ, Choi MK, Kim EY. Study on dietary habits of middle school students and perception of school food services in Chungnam Province. J East Asian Soc Diet Life 2011; 21(5): 756-770.
- 28. Park HJ, Kim H, Kim M. Analysis on perception, knowledge, and practice level for school food hygiene and need for hygiene education of elementary school students in Daegu. Korean J Hum Ecol 2015; 24(3): 371-386.Article
- 29. Park JE, Choi KS. Improving perception and satisfaction on middle and high school foodservice: the role of student participation program in serving school meals. Korean J Community Nutr 2018; 23(3): 243-256.ArticlePDF
- 30. Budd EL, Franz DJ, Kelly NR, Giuliani NR. Oregon parents’ perceptions of the supportiveness of the school environment for their children’s health behaviors. J Nutr Educ Behav 2020; 52(10): 975-981.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

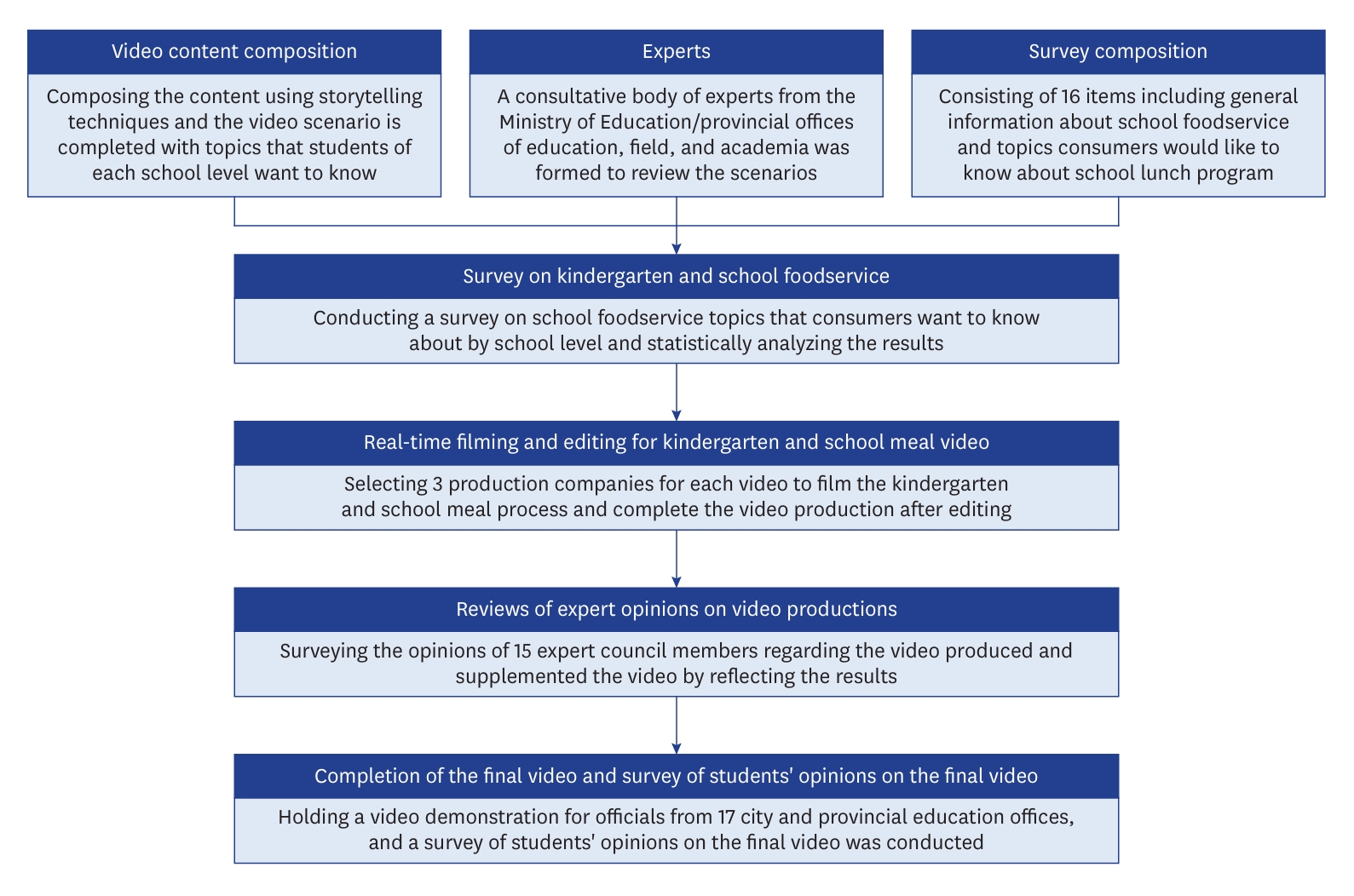

Fig. 1.
Fig. 2.
| School level | Opinions or reflected part |
|---|---|
| Kindergarten/lower grades of elementary school | - Use of characters is appropriate to induce interests for students of kindergarten and lower grades of elementary school. |
| - Contents intended to convey to students (nutritious diets, hygienic meals, etc.) are clear. | |
| - The systematic approach leading to the intro, body 1, body 2, and finish is excellent. | |
| - Now that several adult terms exist in the written scenario, the terms need to be revised as children's language by getting feedback from early childhood educators. | |
| - A dining etiquette education needs to be included in the ending part of the scenario. | |
| - The phrase interfering with the overall flow needs to be deleted, for example, “traditional Korean food such as soybean paste and red pepper paste”. | |
| - The sentence comparing Korean school lunch program and foreign one to highlight the excellence of our school program should be deleted, because it may cause a negative view. | |
| Upper elementary school | - A format of drama and the contents composition are appropriated to the levels and characteristics of the upper elementary school students. |
| - The amount and quality of information to be conveyed to students are excellent, especially the point of connecting the school lunch program with the environment. | |
| - The story's progress is natural and it’s easy to understand the contents. | |
| - According to the opinion that it is difficult to understand the content in some scenes, it was revised by getting feedbacks from the relevant grade teachers and students. | |
| - The phrase inserted for enjoyment (e.g., greeting a friend while hanging a headlock on the way to school) should be deleted because it is somewhat uneducational. | |
| - For the hearing impaired, subtitles need to be inserted on the video screen. | |
| - According to the opinions that applications of photos and subtitles instead of much dialogue are needed to increase the focus of the video, the parts are revised by inserting special effects, images, etc. | |
| Middle and high school | - A quiz format of question-and-answer is excellent to the levels and characteristics of the secondary school students. |
| - Knowing the school lunch program is an excellent historical-level approach. | |
| - To inform the history of school lunch program is an excellent approach for the secondary students. | |
| - The video flow leading to the history of the school lunch program, advantages, objectives, operation standards, hygiene management, and food ingredient purchasing process is excellent, and the quantity and quality of information are excellent. | |
| - It is important to proceed with the question-answer composition to induce interest. | |
| - Some question-answer compositions need to be revised for inducing interests. | |
| - According to the opinion of a facilitator who can lead the question being needed, it is revised as the nutrition teacher playing a role of facilitator. | |
| - The questions of subjective, multiple-choice, and OX forms need to be appropriately allocated. | |
| - NEIS feeding log, HACCP reporting log, various thermometers (inspection, cooking, refrigerator, and freezer), etc., needs to be placed on the video screen to emphasize scientific and systematic foodservice management. |
| Category | School level |
Total (n = 532) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parents of kindergarten/lower-grade elementary students (n = 101) | Upper elementary school students (n = 152) | Middle and high school students (n = 279) | ||
| Age | 40.29 ± 5.56 | 10.66 ± 2.44 | 14.96 ± 2.37 | 17.83 ± 10.58 |
| Father’s highest educational level |
||||
| High school graduation | 1 (1.6) | 1 (2.8) | 4 (7.1) | 6 (3.8) |
| College graduation | 42 (65.6) | 23 (63.9) | 44 (78.6) | 109 (69.9) |
| Graduate school graduation | 21 (32.8) | 12 (33.3) | 8 (14.3) | 41 (26.3) |
| No response | 37 | 116 | 223 | 376 |
| Mother’s highest educational level |
||||
| Unschooled | 0 (0) | 1 (2.7) | 0 (1) | 1 (0.7) |
| Elementary school graduation | 0 (0) | 1 (2.7) | 0 (0) | 1 (0.7) |
| High school graduation | 2 (3.2) | 2 (5.4) | 6 (11.8) | 10 (6.7) |
| College graduation | 42 (67.7) | 28 (75.7) | 37 (72.5) | 107 (71.3) |
| Graduate school graduation | 18 (29.0) | 5 (13.5) | 8 (15.7) | 31 (20.7) |
| No response | 39 | 115 | 228 | 382 |
| Average monthly household total income |
||||
| 150–300 less | 2 (3.5) | 1 (4.5) | 0 (0) | 3 (2.7) |
| 300–450 less | 6 (10.5) | 2 (9.1) | 1 (3.2) | 9 (8.2) |
| 450–600 less | 14 (24.6) | 4 (18.2) | 8 (25.8) | 26 (23.6) |
| 600–750 less | 8 (14.0) | 4 (18.2) | 4 (12.9) | 16 (14.5) |
| 750–900 less | 11 (19.3) | 2 (9.1) | 8 (25.8) | 21 (19.1) |
| 900–1,500 less | 15 (26.3) | 4 (18.2) | 8 (25.8) | 27 (24.5) |
| More than 1,500 | 1 (1.8) | 5 (22.7) | 2 (6.5) | 8 (7.3) |
| No response | 44 | 130 | 248 | 422 |
| Category | Parents of kindergarten/lower-grade elementary students (n = 101) | Upper elementary school students (n = 152) | Middle and high school students (n = 279) | Total (n = 532) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The importance of kindergarten and school foodservice | 3 (1.0) | 10 (2.6) | 11 (1.7) | 24 (1.8) |
| Nutritionally balanced diet | 68 (23.5) | 21 (5.5) | 66 (10.4) | 155 (11.9) |
| Reasons for not serving meals with low-simple sugar and low-sodium | 12 (4.2) | 32 (8.4) | 51 (8.0) | 95 (7.3) |
| Purchasing safe food ingredients | 52 (18.0) | 48 (12.6) | 43 (6.8) | 143 (10.9) |
| School meal production process | 21 (7.3) | 33 (8.6) | 70 (11.0) | 124 (9.5) |
| Food hygiene management in accordance with HACCP | 30 (10.4) | 19 (5.0) | 31 (4.9) | 80 (6.1) |
| Purpose of kindergarten and school foodservice | 0 (0.0) | 15 (3.9) | 15 (2.4) | 30 (2.3) |
| Healthiness of school meals | 23 (8.0) | 34 (8.9) | 47 (7.4) | 104 (8.0) |
| Transparent food cost management | 9 (3.1) | 12 (3.1) | 41 (6.4) | 62 (4.7) |
| Dining etiquette | 9 (3.1) | 24 (6.3) | 42 (6.6) | 75 (5.7) |
| Inheriting traditional food culture | 3 (1.0) | 19 (5.0) | 16 (2.5) | 38 (2.9) |
| Meal management using the computerized system (NEIS) | 1 (0.3) | 10 (2.6) | 13 (2.0) | 24 (1.8) |
| Movement to reduce food waste | 10 (3.5) | 22 (5.8) | 46 (7.2) | 78 (6.0) |
| Healthy eating habits | 41 (14.2) | 30 (7.9) | 59 (9.3) | 130 (9.9) |
| History of kindergarten/school foodservice | 3 (1.0) | 26 (6.8) | 28 (4.4) | 57 (4.4) |
| Reasons for not serving fast foods or favorite foods | 4 (1.4) | 27 (7.1) | 57 (9.0) | 88 (6.7) |
| Total |
289 (100.0) | 382 (100.0) | 636 (100.0) | 1,307 (100.0) |
| Category | Kindergarten/lower grades of elementary school | Upper grades of elementary school | Middle and high school |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subject of school foodservice | Getting to know school foodservice with Fanny correctly | Learn the excellence and meaning of school foodservice from the student's point of view | This material helps promote the perception of school foodservice among teenage students |
| Title | Learn about school foodservice with Fanny | All that school foodservice by three musketeers | Facts about school foodservice |
| Education goals | Understand the process of making kindergarten and school meal, nutrition, and hygienic characteristics | Know the excellence of school foodservice | Understand the history and excellence of school foodservice in Korea |
| Understand the importance of healthy growth through school meals | Understand the purpose and significance of school foodservice and the standards for nutrition and hygiene management | ||
| Understand the importance of meals in consideration of the global environment | Know the food purchasing for school foodservice | ||
| Content composition | Introduction to the importance of school foodservice | Body 1. Meal production process | The history of school foodservice |
| Nutritious diet composition | Process 1: Inspection | The importance of school foodservice | |
| Food ingredient inspection | Process 2: Cooking | - Advantages of school foodservice | |
| Tableware disinfection | Process 3: Food serving | - Aiming of school foodservice: nutrition balance-health and proper eating habits formation | |
| Personal hygiene | Body 2. Diet composition | The process of making school meals | |
| Food serving | Meal composition | - School meal hygiene management | |
| Ending and dining etiquette | No picky eating! | - School meal ingredient quality Ending | |
| Body 3. Earth environment | |||
| To prevent global climate change | |||
| Ending |
| Category | Strongly agree | Agree | Neutral | Disagree | Strongly disagree | Mean score |
F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enjoyment of video | 9.872 |
||||||
| K/E (n = 19) | 16 (84.2) | 2 (10.5) | 1 (5.3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 4.79 ± 0.54a | |
| UE (n = 62) | 19 (30.6) | 19 (30.6) | 17 (27.4) | 2 (3.2) | 5 (8.1) | 3.73 ± 1.18b | |
| M/H (n = 49) | 21 (42.9) | 18 (36.7) | 10 (20.4) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 4.22 ± 0.77ab | |
| Total (n = 130) | 56 (43.1) | 39 (30.0) | 28 (21.5) | 2 (1.5) | 5 (3.8) | 4.07 ± 1.02 | |
| Helpfulness for understanding school foodservice | 1.465 | ||||||
| K/E (n = 19) | 13 (68.4) | 5 (26.3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (5.3) | 4.53 ± 0.96 | |
| UE (n = 62) | 25 (40.3) | 26 (41.9) | 9 (14.5) | 1 (1.6) | 1 (1.6) | 4.18 ± 0.86 | |
| M/H (n = 49) | 24 (49.0) | 18 (36.7) | 7 (14.3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 4.35 ± 0.72 | |
| Total (n = 130) | 62 (47.7) | 49 (37.7) | 16 (12.3) | 1 (0.8) | 2 (1.5) | 4.29 ± 0.83 | |
| Comprehensibility of video | 3.914 |
||||||
| K/E (n = 19) | 16 (84.2) | 3 (15.8) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 4.84 ± 0.37a | |
| UE (n = 62) | 31 (50.0) | 21 (33.9) | 9 (14.5) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.6) | 4.31 ± 0.84b | |
| M/H (n = 49) | 26 (53.1) | 18 (36.7) | 5 (10.2) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 4.43 ± 0.68ab | |
| Total (n = 130) | 73 (56.2) | 42 (32.3) | 14 (10.8) | 0 (0) | 1 (0.8) | 4.43 ± 0.75 |
NEIS, National Education Information System; HACCP, Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point.
Mean ± SD or n (%). Not mandatory to respond.
n (%). HACCP, Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point; NEIS, National Education Information System. Multiple response.
n (%) or Mean ± SD. Different superscript letters mean significantly different groups with a Scheffe test. K/E, parents of kindergarten/lower-grade elementary students; UE, upper-grade elementary students; M/H, middle and high school students. Five points rating scales: 1-point strongly disagree, 5-point strongly agree.

 KSCN
KSCN
 Cite
Cite


