Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Korean J Community Nutr > Volume 17(1); 2012 > Article
-
Original Article
- A Study of Nutrient Intakes, Blood Lipids and Bone Mineral Density according to Obesity Degree by Percentage of Body Fat and Age between Male and Female Teacher in Jeonbuk Province, Korea
- Hye-Soon Chang
-
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition 2012;17(1):49-68.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.1.49
Published online: February 29, 2012
Department of Food and Nutrition, Gunsan National University, Gunsan, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Department of Food & Nutrition, Gunsan National University, San 68 Miryong-dong, Gunsan 573-701, Korea. Tel: (063) 469-4633, Fax: (063) 468-2085, hschang@kunsan.ac.kr
Copyright © 2012 The Korean Society of Community Nutrition
- 822 Views
- 8 Download
- 4 Crossref
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Machine learning-based obesity classification considering 3D body scanner measurements
Seungjin Jeon, Minji Kim, Jiwun Yoon, Sangyong Lee, Sekyoung Youm
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Current progress of nanomedicine for prostate cancer diagnosis and treatment
Jiang Zhao, Chi Zhang, Weihao Wang, Chen Li, Xupeng Mu, Kebang Hu
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 155: 113714. CrossRef - A Study on Weight Control Behaviour, Eating Habits and Health-related Life Habits According to Obesity Degree of Teacher in Jeonbuk Province, Korea
Hye-Soon Chang
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2015; 30(1): 105. CrossRef - Analysis of Bone Mineral Density, Biochemical Index and Nutrient Intakes of 30-70 Years Old Women: Based on 2011 KNHANES
Jae Ok Koo, Myung Sook Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(4): 328. CrossRef
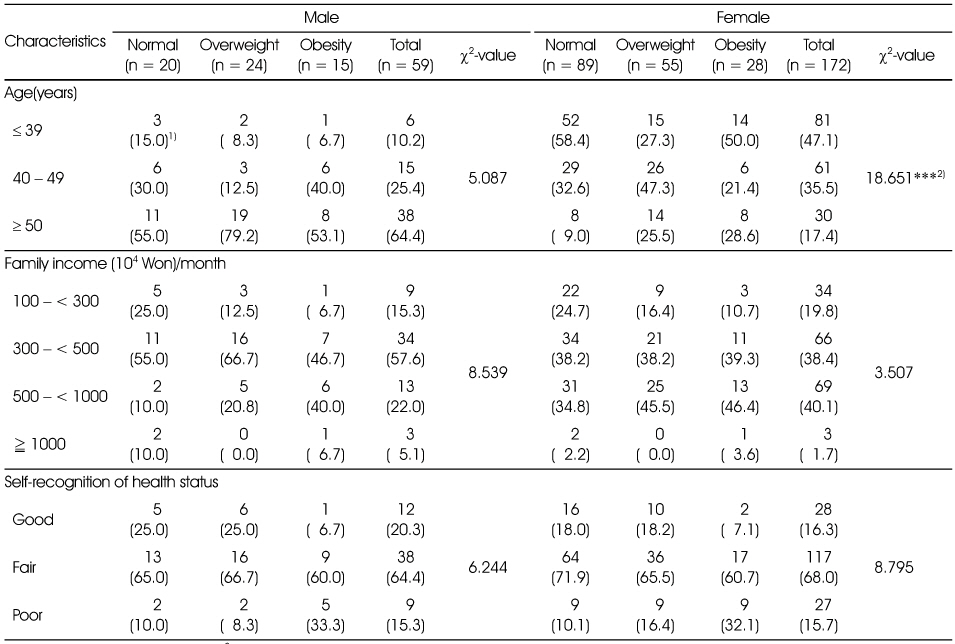
General characteristics of the subjects according to obesity degree by %fat
1) N (%), 2) ***: p < 0.001 by χ2-test
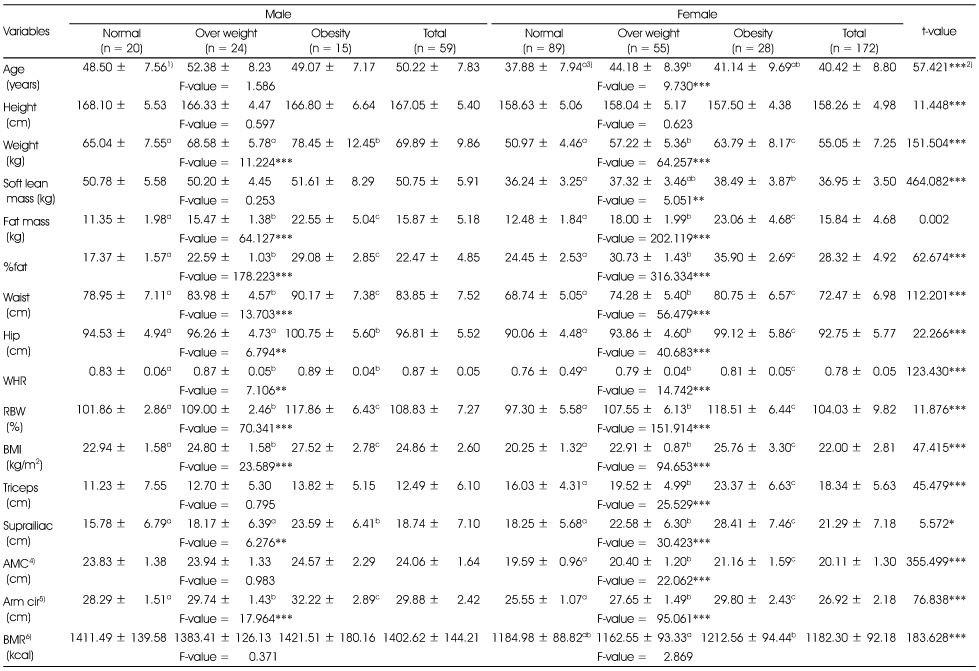
Comparisons of anthropometric measurements and body composition of the subjects according to obesity degree by %fat
1) Mean ± SD, 2) *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by t-test or one-way ANOVA, 3) Different alphabets at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple test (p < 0.05), 4) AMC: Arm muscle circumference, 5) Arm cir: Arm circumference, 6) BMR: Basal Metabolic Rate
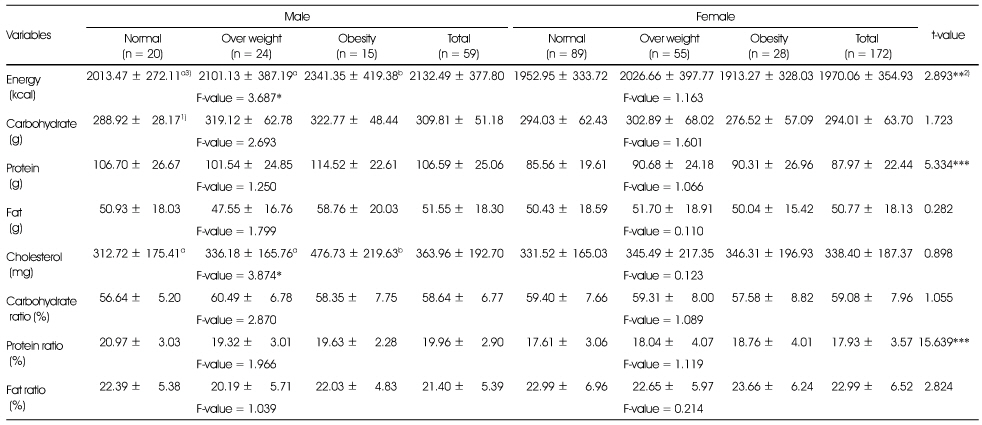
The daily caloric nutrients and cholesterol intakes, and CPF ratio of subjects according to obesity degree by %fat
1) Mean ± SD
2) *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by t-test or one-way ANOVA
3) Different alphabets at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple test (p < 0.05)
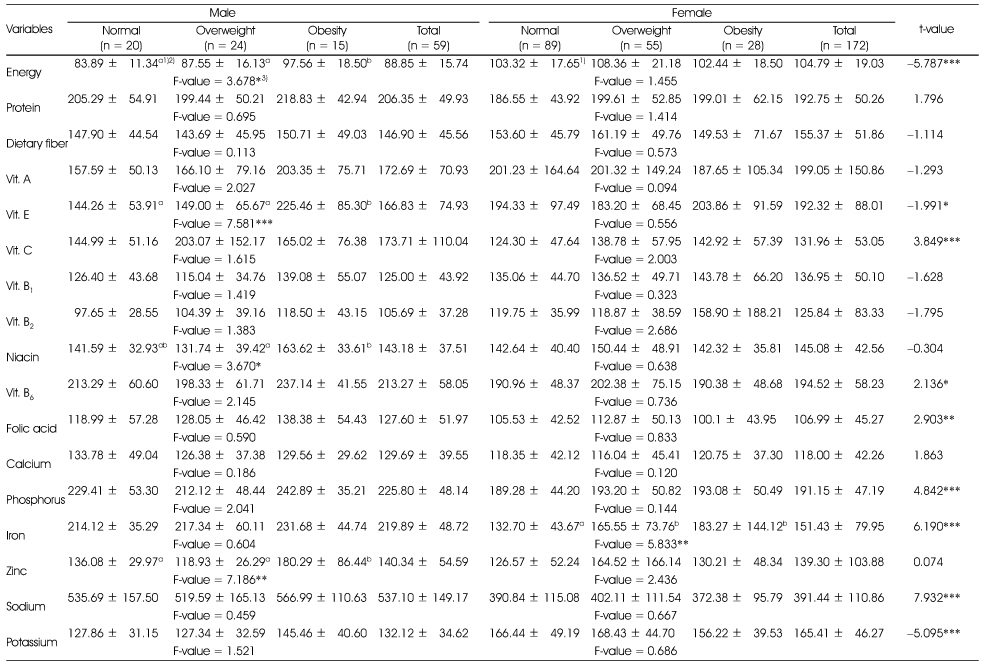
The percentage of nutrients intakes for the dietary reference intakes for Koreans(KDRIs) of subjects according to obesity degree by %fat
1) Mean ± SD, 2) Different alphabets at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple test (p < 0.05), 3) *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by t-test or one-way ANOVA
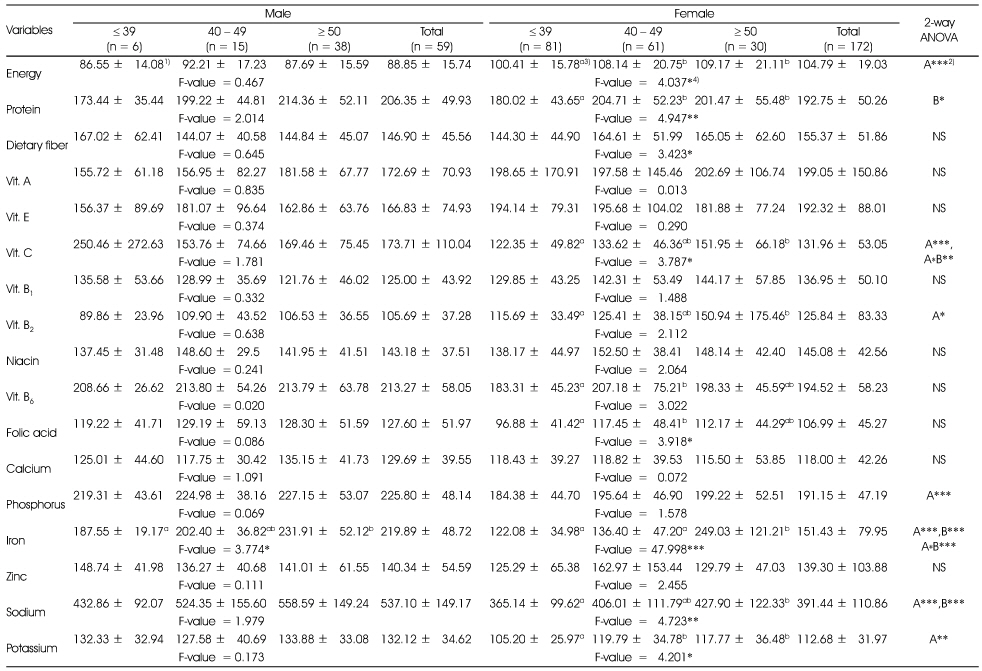
The percentage of nutrients intakes for the dietary reference intakes for Koreans(KDRIs) of subjects according to age
1) Mean ± SD, 2) A: effect of gender; B: effect of age; A*B: interaction of gender and age; NS: not significantly different; *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA, 3) Different alphabets at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple test (p < 0.05), 4) *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA
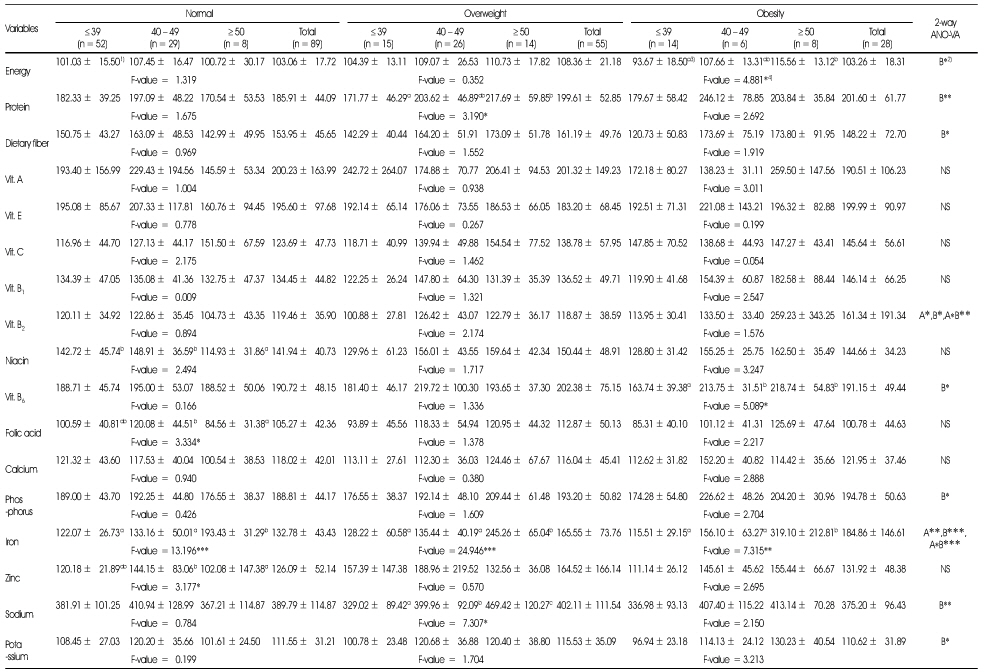
The percentage of nutrients intakes for the dietary reference intakes for Koreans(KDRIs) of female subjects according to age
1) Mean ± SD, 2) A: effect of obese index; B: effect of age; A*B: interaction of obese index and age; NS: not significantly different; *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA, 3) Different alphabets at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple test (p < 0.05), 4) *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA
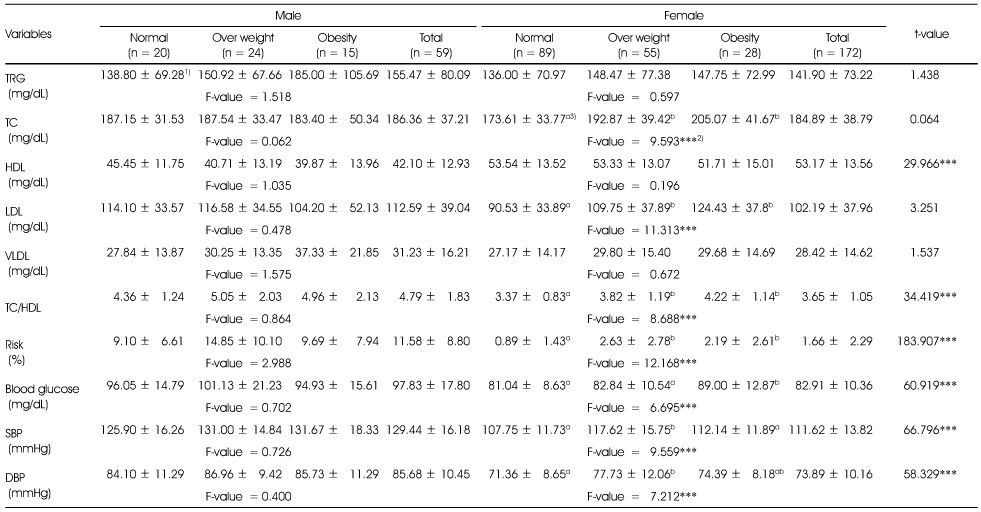
Comparison of blood lipids, blood glucose and blood pressures of subjects according to obesity degree by %fat
1) Mean ± SD
2) **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by t-test or one-way ANOVA
3) Different alphabets at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple test (p < 0.05)
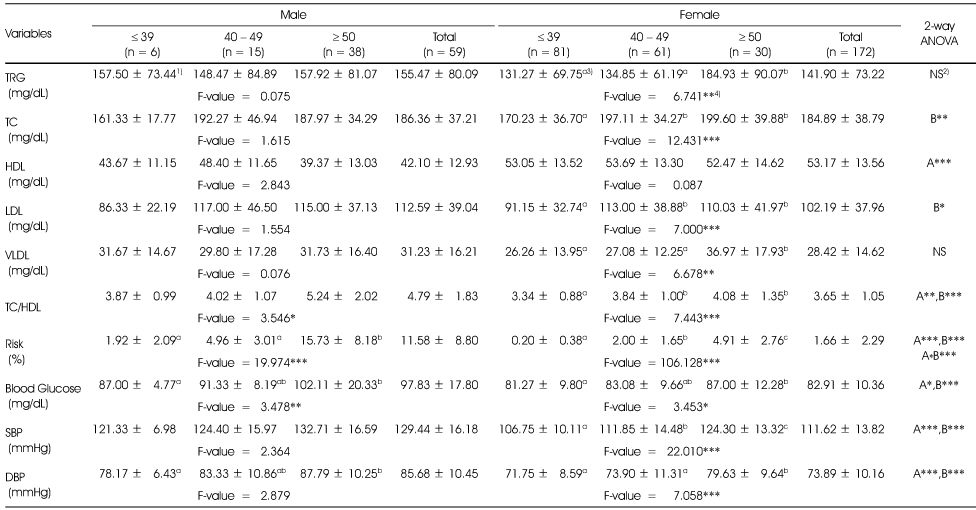
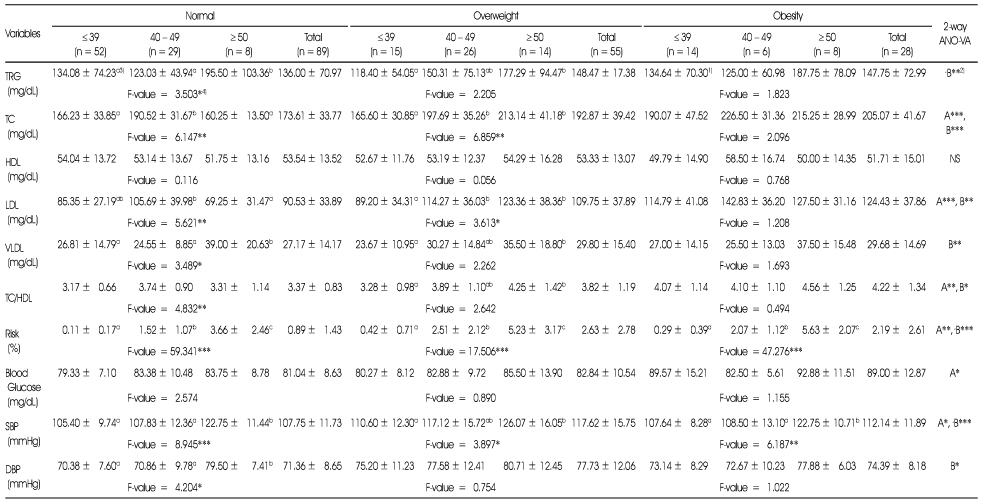
Comparison of blood lipids, blood glucose and blood pressures of subjects according to age
1) Mean ± SD
2) A: effect of gender; B: effect of age; A*B: interaction of gender and age; NS: not significantly different; *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA
3) Different alphabets at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple test (p < 0.05)
4) *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA
Comparison of blood lipids, blood glucose and blood pressures of female subjects according to age
1) Mean ± SD
2) A: effect of obese index; B: effect of age; A*B: interaction of obese index and age; NS: not significantly different; *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA
3) Different alphabets at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple test (p < 0.05)
4) *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA
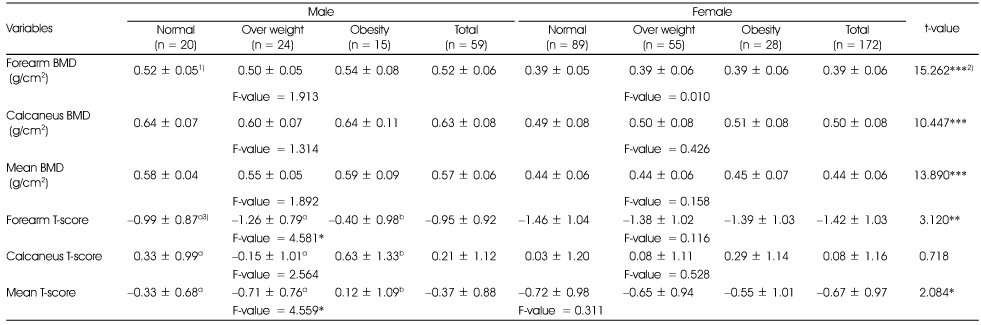
Bone mineral density and T-scores of subjects according to obesity degree by %fat
1) Mean ± SD, 2) *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by t-test or one-way ANOVA
3) Different alphabets at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple test (p < 0.05)
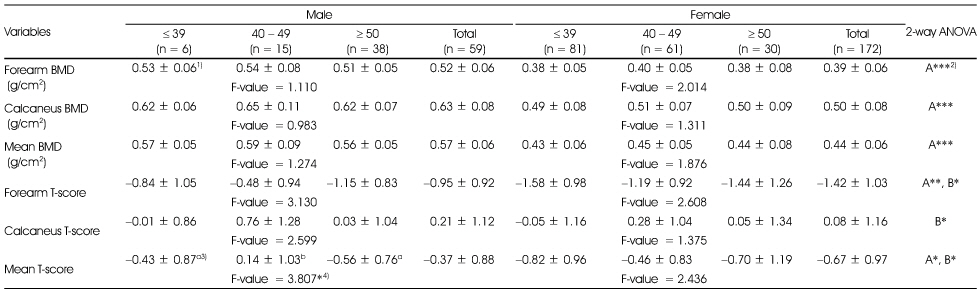
Bone mineral density and T-scores of subjects according to age
1) Mean ± SD, 2) A: effect of gender; B: effect of age; A*B: interaction of gender and age; NS: not significantly different; *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA, 3) Different alphabets at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple test (p < 0.05), 4) *: p < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA
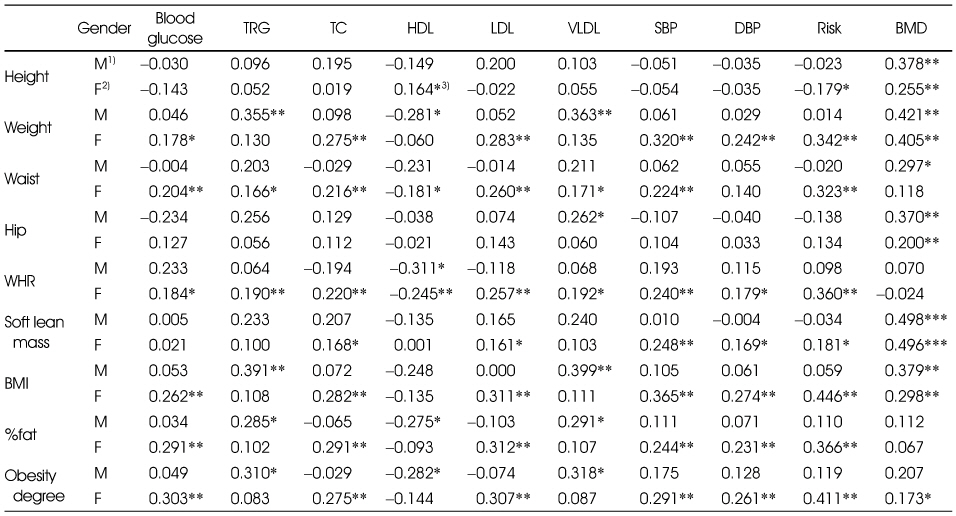
Pearson correlation coefficient in each variable in the study subjects
1) M: Male
2) F: Female
3) *,**,***: Significant at p < 0.05, p < 0.01 and p < 0.001 by Pearson's correlation
1) N (%), 2) ***: p < 0.001 by χ2-test
1) Mean ± SD, 2) *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by t-test or one-way ANOVA, 3) Different alphabets at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple test (p < 0.05), 4) AMC: Arm muscle circumference, 5) Arm cir: Arm circumference, 6) BMR: Basal Metabolic Rate
1) Mean ± SD 2) *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by t-test or one-way ANOVA 3) Different alphabets at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple test (p < 0.05)
1) Mean ± SD, 2) Different alphabets at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple test (p < 0.05), 3) *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by t-test or one-way ANOVA
1) Mean ± SD, 2) A: effect of gender; B: effect of age; A*B: interaction of gender and age; NS: not significantly different; *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA, 3) Different alphabets at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple test (p < 0.05), 4) *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA
1) Mean ± SD, 2) A: effect of obese index; B: effect of age; A*B: interaction of obese index and age; NS: not significantly different; *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA, 3) Different alphabets at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple test (p < 0.05), 4) *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA
1) Mean ± SD 2) **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by t-test or one-way ANOVA 3) Different alphabets at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple test (p < 0.05)
1) Mean ± SD 2) A: effect of gender; B: effect of age; A*B: interaction of gender and age; NS: not significantly different; *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA 3) Different alphabets at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple test (p < 0.05) 4) *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA
1) Mean ± SD 2) A: effect of obese index; B: effect of age; A*B: interaction of obese index and age; NS: not significantly different; *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA 3) Different alphabets at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple test (p < 0.05) 4) *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA
1) Mean ± SD, 2) *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by t-test or one-way ANOVA 3) Different alphabets at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple test (p < 0.05)
1) Mean ± SD, 2) A: effect of gender; B: effect of age; A*B: interaction of gender and age; NS: not significantly different; *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA, 3) Different alphabets at the same row are significantly different by Duncan's multiple test (p < 0.05), 4) *: p < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA
1) M: Male 2) F: Female 3) *,**,***: Significant at p < 0.05, p < 0.01 and p < 0.001 by Pearson's correlation

 KSCN
KSCN
 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite


