Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Korean J Community Nutr > Volume 18(5); 2013 > Article
-
Original Article
- A Survey on the Salt Content of Kindergarten Lunch Meals and Meal Providers' Dietary Attitude to Sodium Intake in Gyeonggi-do Area
- Jin Nam Kim, Seoyun Park, Sohyun Ahn, Hye-Kyeong Kim
-
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition 2013;18(5):478-490.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.5.478
Published online: October 31, 2013
Department of Food Science & Nutrition, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Hye-Kyeong Kim, Department of Food Science & Nutrition, The Catholic University of Korea, 43-1 Yeokgok 2-dong, Wonmi-gu, Bucheon, Gyeonggi-do 420-743, Korea. Tel: (02) 2164-4314, Fax: (02) 2164-4314, hkyeong@catholic.ac.kr
Copyright © 2013 The Korean Society of Community Nutrition
This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 1,451 Views
- 3 Download
- 18 Crossref
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Changes in the importance and performance of low-sodium management among childcare center cooks in Yongin, South Korea, after salinometer support programs: a descriptive study
Jiwoo Min, Youngmi Lee, Yunhee Chang, Yujin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(4): 304. CrossRef - Sodium Reduction Practice and Importance-Performance Analysis of Sodium Reduction Methods in School Foodservice in Daegu
Su-Hyeon Kim, Eun-Kyung Shin, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(5): 386. CrossRef - Dietary status of young children in Korea based on the data of 2013 ~ 2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Eun-kyung Kim, Byengchun Song, Se-Young Ju
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(4): 330. CrossRef - Effects of a Practice Program for Low-Salt Meals on Infant Foodservices : Focusing on Infant Foodservices registered in Center for Children's Foodservice Management in Busan Metropolitan City
Chae-Young Jo, Jin-Suk Han
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2018; 28(1): 66. CrossRef - Comparison of nutrients and food intakes of young children according to lunch places: based on the fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Young-Sun Choi
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(3): 254. CrossRef - Status of Recognition, Effort, and Satisfaction of Customers on Low-Sodium Diet in Industry Foodservice
Sang Jin Yoon, Kun Og Kang
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2017; 27(2): 168. CrossRef - Salinity Monitoring of Soups of The Institutions Enrolled at Center for Children’s Foodservice Management
Hyun Nae Park, Soon Mi Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2016; 26(6): 507. CrossRef - School Dietitian Awareness, Practice, and Sodium Reduction Plan in School Meal Service
Eun Kyung Kim, Hae Young Kim
Korean Journal of Food & Cookery Science.2016; 32(2): 222. CrossRef - Survey on Actual Situation and Importance of Use of Snacks according to Young Children Mother’s Nutrition Knowledge
Sun-Hyun Kim, Geum-Soon Park
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2016; 26(2): 141. CrossRef - Study on the Salt and Sodium Content of Middle School Lunch Meals in Gyeongsangbuk-do Area - Focus on Application of 'SamSam Foodservice' -
So-Young Park, Kyung-A Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2016; 45(5): 757. CrossRef - The awareness level and needs for education on reducing sugar consumption among mothers with preschool children
Younhee Lee, Nami Joo
Nutrition Research and Practice.2016; 10(2): 229. CrossRef - Study on Sodium Contents of Kindergarten Lunch Meals in Gyeoungsangbuk-do Area
Dan-Bi Song, Kyung-A Lee
Korean Journal of Food & Cookery Science.2016; 32(5): 648. CrossRef - An Evaluation of the Foodservice Quality and Management of Preschool Foodservice Establishments by IPA - Focusing on Parents of Preschoolers in Metropolitan Area of Korea, China and Japan -
Sanghyun Park, Nami Joo
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2015; 28(1): 160. CrossRef - Sodium-related Eating Behaviors of Parents and Its Relationship to Eating Behaviors of Their Preschool Children
Ye Seul Kim, Hong Mie Lee, Jung Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(1): 11. CrossRef - Nutrition knowledge, eating attitudes, nutrition behavior, self-efficacy of childcare center foodservice employees by stages of behavioral change in reducing sodium intake
Yun Ahn, Kyung Won Kim, Kyungmin Kim, Jinwon Pyun, Ikhyun Yeo, Kisun Nam
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(5): 429. CrossRef - A Study on Eating Out Behavior and Recognition of Salinity in Restaurant Food in Jecheon Area
Soojin Park, Sung Hee Min
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2015; 30(1): 20. CrossRef - Assessment of Nutritional Status of Children in Community Child Center by Nutrition Quotient(NQ) - Gyeongiu -
Na-Hyung Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(1): 73. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Na Reduction Program for Cook in Child-care Center: Focus on Self-reevaluation and Strengthen Consciousness
Hyewon Shin, Youngmee Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(5): 425. CrossRef
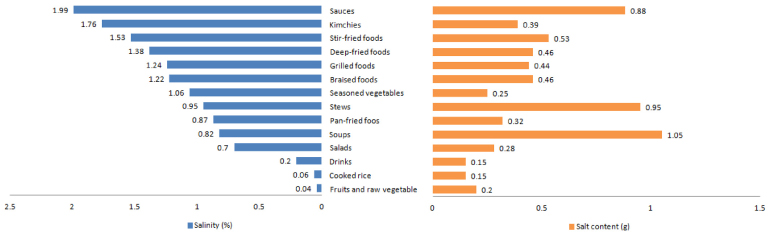
Fig. 1
Salt content and salinity of menu groups from kindergarten meals
1) Weight of food supplied supplied for each meal (g)
2) Measured by salimeter (%)
3) Amount of food multiplied by salinity × 0.01 (g)
4) Salt content of each dish group divided by total salt content of the meal × 100 (%)
5) Mean±SD
abcd: Means with different superscripts are significantly different among groups by Duncan's multiple range test
***: p < 0.001
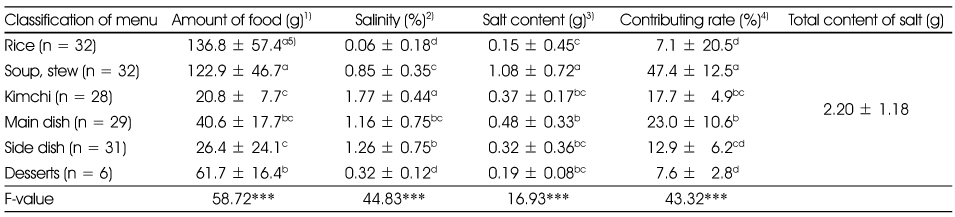
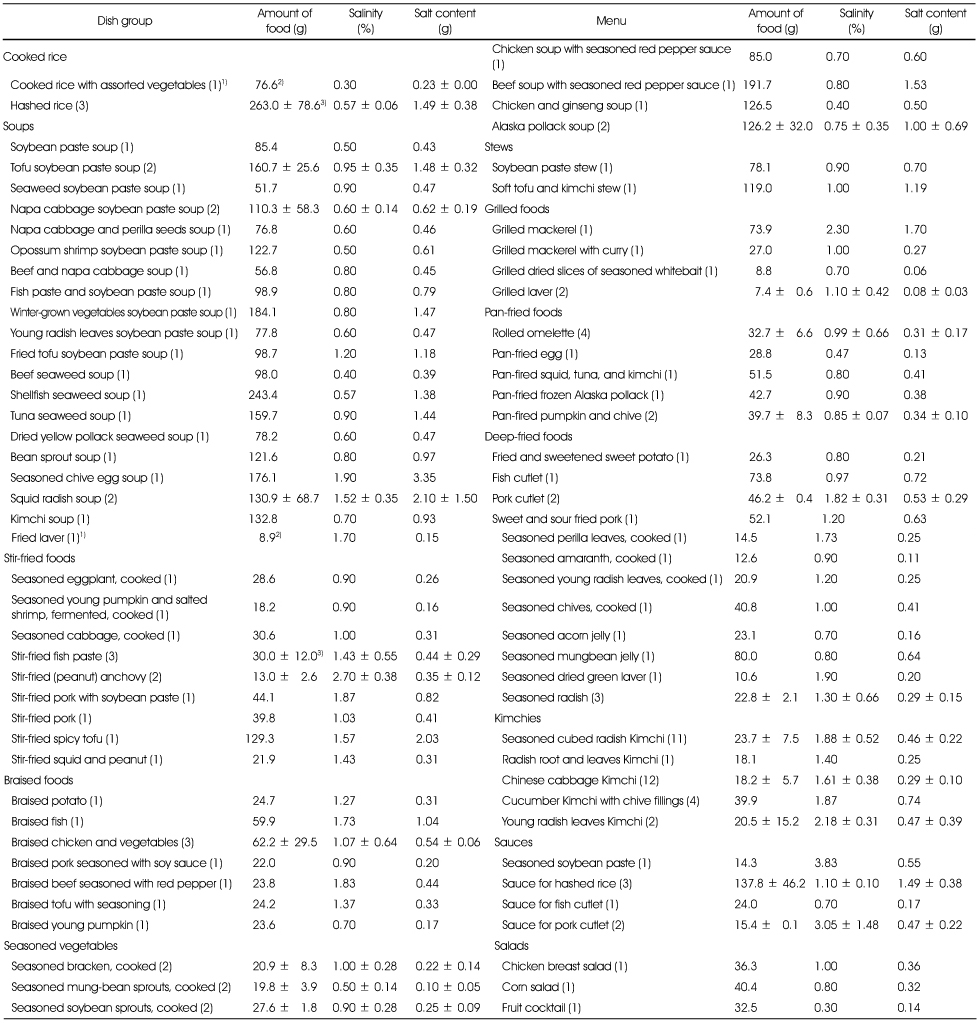
The salinity and salt content of dish groups served in kindergartens
1) Weight of food supplied for each meal (g)
2) Measured by salimeter (%)
3) Amount of food multiplied by salinity × 0.01 (g)
4) Sum of salt content of food in each dish group divided by total salt content × 100 (%)
5) N
6) Mean ± SD
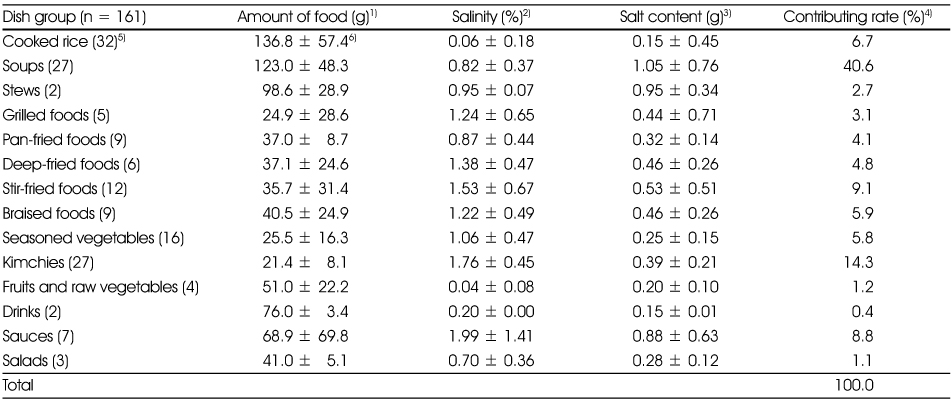
The salinity and salt content of foods per serving
1) N
2) Mean
3) Mean ± SD
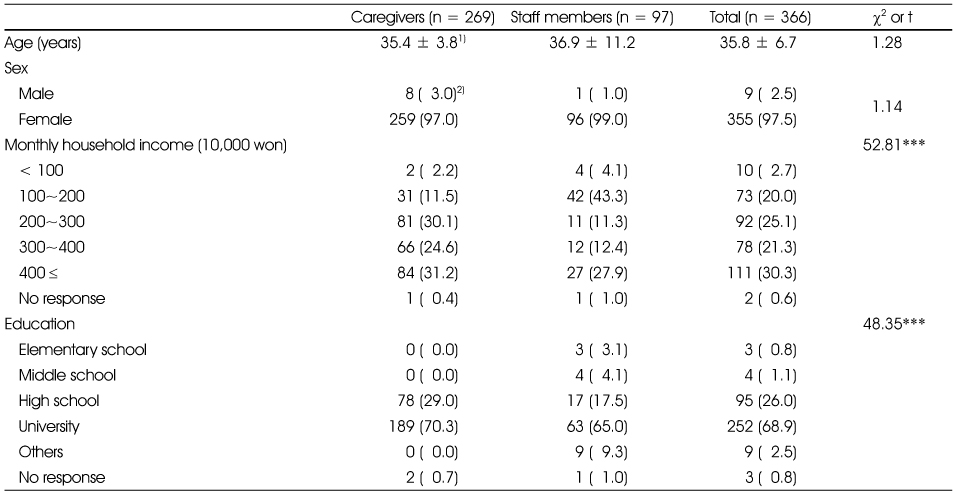
General characteristics of study subjects
1) Mean ± SD
2) N (%)
***: p < 0.001
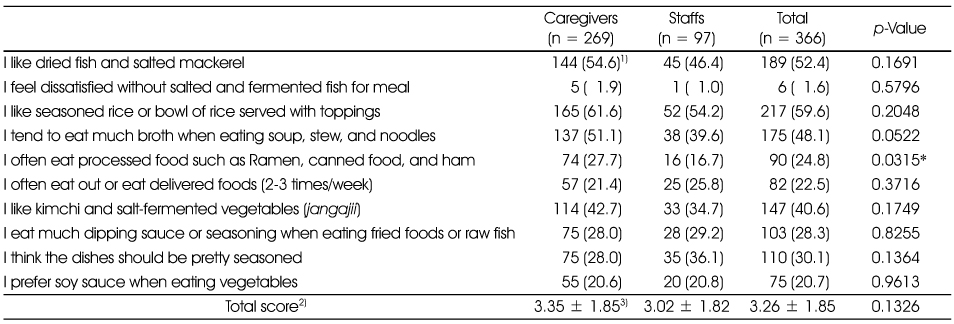
Dietary attitude related to salt intake
1) N (%): Response rate of "Yes" in each item
2) Total number of 'yes' response in each subject
3) Mean ± SD
*: p < 0.05, significantly different between the groups by χ2-test
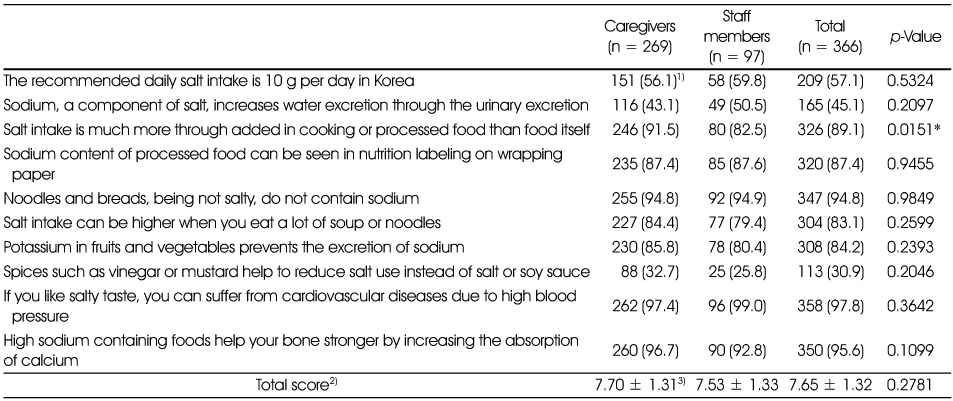
Nutrition knowledge related to salt intake
1) N (%): Response rate of "Yes" in each item
2) Total number of correct answer in each subject
3) Mean ± SD
*: p < 0.05, significantly different between the groups by χ2-test
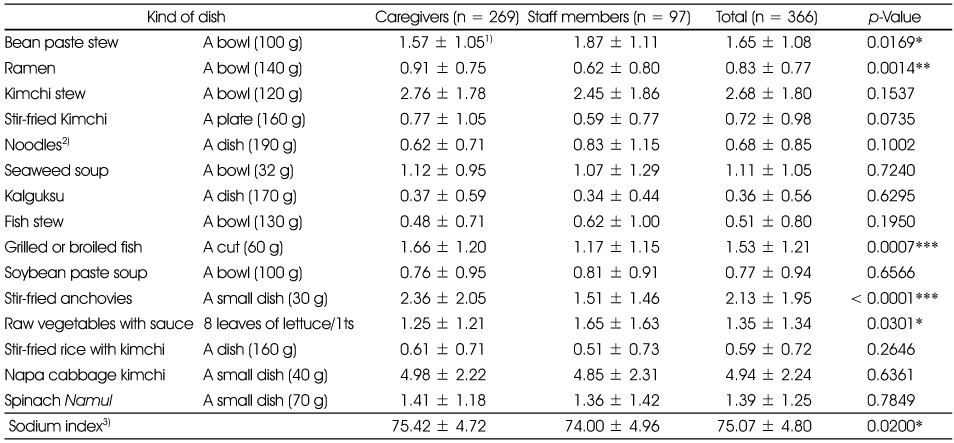
Dish frequency questionnaire (DFQ)
1) Mean ± SD, Standard score is 'Once per week = 1'.
2) Except bibimguksu, noodles mixed with vegetables and red pepper sauce
3) Sum of values calculated by multiplying weighed score according to the sodium content of serving size and consumption frequency (adopted from Son et al 2005)
*: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01 ***: p < 0.001 significantly different between the groups by t-test
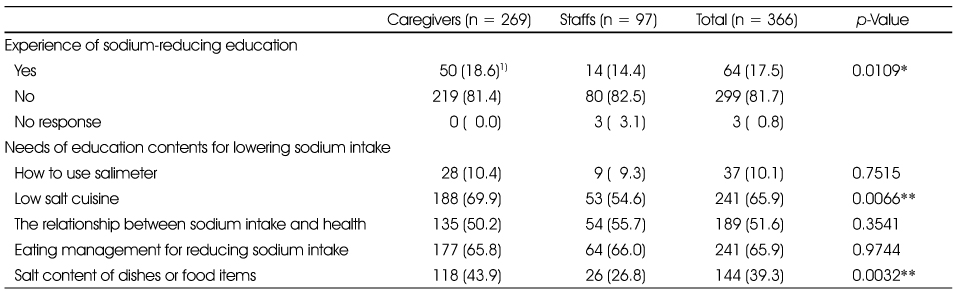
Experience of nutrition education and needs of education contents for lowering sodium intake
1) N (%): The frequency of answer in each item
*: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01 significantly different between the groups by χ2-test
1) Weight of food supplied supplied for each meal (g) 2) Measured by salimeter (%) 3) Amount of food multiplied by salinity × 0.01 (g) 4) Salt content of each dish group divided by total salt content of the meal × 100 (%) 5) Mean±SD abcd: Means with different superscripts are significantly different among groups by Duncan's multiple range test ***: p < 0.001
1) Weight of food supplied for each meal (g) 2) Measured by salimeter (%) 3) Amount of food multiplied by salinity × 0.01 (g) 4) Sum of salt content of food in each dish group divided by total salt content × 100 (%) 5) N 6) Mean ± SD
1) N 2) Mean 3) Mean ± SD
1) Mean ± SD 2) N (%) ***: p < 0.001
1) N (%): Response rate of "Yes" in each item 2) Total number of 'yes' response in each subject 3) Mean ± SD *: p < 0.05, significantly different between the groups by χ2-test
1) N (%): Response rate of "Yes" in each item 2) Total number of correct answer in each subject 3) Mean ± SD *: p < 0.05, significantly different between the groups by χ2-test
1) Mean ± SD, Standard score is 'Once per week = 1'. 2) Except bibimguksu, noodles mixed with vegetables and red pepper sauce 3) Sum of values calculated by multiplying weighed score according to the sodium content of serving size and consumption frequency (adopted from Son et al 2005) *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01 ***: p < 0.001 significantly different between the groups by t-test
1) N (%): The frequency of answer in each item *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01 significantly different between the groups by χ2-test

 KSCN
KSCN
 Cite
Cite


