Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Korean J Community Nutr > Volume 19(5); 2014 > Article
-
Research Article
- A Comparison between Asia-Pacific Region Criteria and Entropy Model Criteria about Body Mass Index of Elderly Females Using Morbidity of Chronic Disease
- Gu-Beom Jeong, Jin-Yong Park, Se-Young Kwon, Kyung-Ok Park, Pil-Sook Park, Mi-Yeon Park
-
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition 2014;19(5):490-498.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.5.490
Published online: October 31, 2014
1School of Computer Information, Kyungpook National University, Sangju, Korea.
2Department of Microbiology, Gyeongsang National University Medical School, Jinju, Korea.
3Department of Biomedical Laboratory Science, Daegu Health College, Daegu, Korea.
4Department of Statistics and Actuarial Science, Soongsil University, Seoul, Korea.
5Department of Food Science & Nutrition, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
6Department of Food & Nutrition, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Mi-Yeon Park. Department of Food & Nutrition, Gyeongsang National University, 501, Jinju-daero, Jinju, Gyeongnam 660-701, Korea. Tel: (055) 772-1438, Fax: (055) 772-1439, mypark@gnu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2014 The Korean Society of Community Nutrition
This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 1,046 Views
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Factors related to cancer screening behaviors
Boyoung Choi, Tae Rim Um, Kwang-Soo Lee
Epidemiology and Health.2018; 40: e2018011. CrossRef - Nutrition States and Related Factors of Female Elderly according to Residence
Mi-Yeon Park
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2015; 25(1): 39. CrossRef
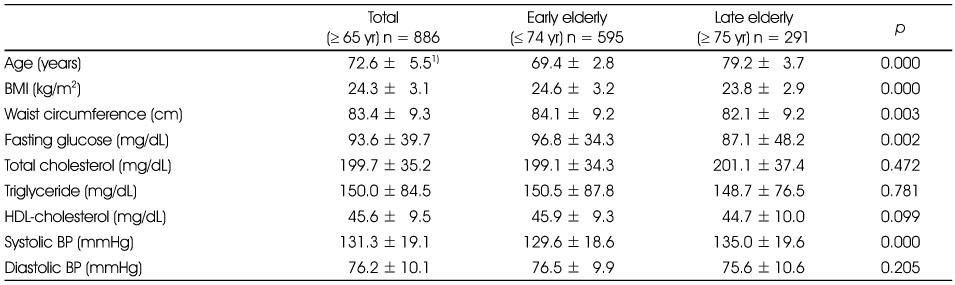
The distribution of general characteristics of subjects
1) Mean ± SD
Partial correlation coefficient between body mass index and biochemical results and blood pressure in subjects1)
1) Results after controlling for ages of the subjects
2) BMI: Body mass index
3) correlation coefficient (p value)
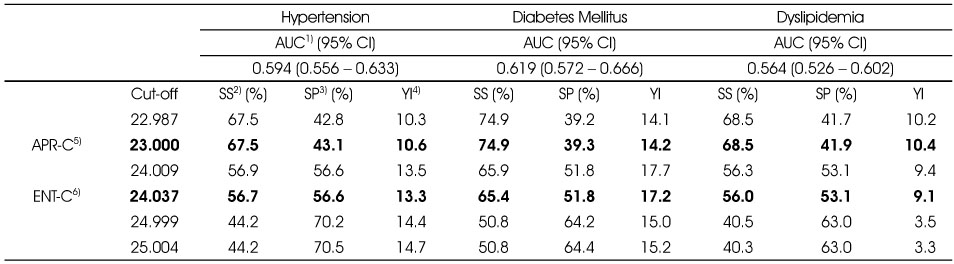
The sensitivity, specificities and Youden's index for the morbidity of hypertension, diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia according to cut-off points of BMI
1) AUC: Area under the ROC curve
2) SS: Sensitivity
3) SP: Specificity
4) YI: Youden's index
5) Asia-Pacific Region Criteria
6) Entropy Model Criteria
The sensitivity, specificities and Youden's index by the number of diseases among hypertension, diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia according to cut-off points of BMI
1) AUC: Area under the ROC curve
2) SS: Sensitivity
3) SP: Specificity
4) YI: Youden's index
5) Asia-Pacific Region Criteria
6) Entropy Model Criteria
The adjusted odds ratio and 95% confidence interval for overweight or obesity of Asia-Pacific region criteria and entropy model criteria by the stage of hypertension
1) Asia-Pacific Region Criteria
2) Entropy Model Criteria
The adjusted odds ratio and 95% confidence interval for overweight or obesity of Asia-Pacific Region Criteria and Entropy Model Criteria by the stage of diabetes mellitus
1) Asia-Pacific Region Criteria
2) Entropy Model Criteria
The adjusted odds ratio and 95% confidence interval for overweight or obesity of Asia-Pacific Region Criteria and Entropy Model Criteria by the stage of dyslipidemia
1) Asia-Pacific Region Criteria
2) Entropy Model Criteria
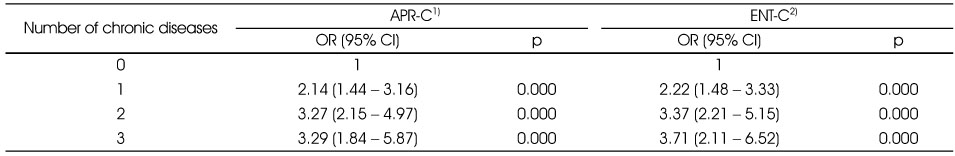
The adjusted odds ratio and 95% confidence interval for overweight or obesity of Asia-Pacific Region Criteria and Entropy Model Criteria by the number of chronic diseases
1) Asia-Pacific Region Criteria
2) Entropy Model Criteria
1) Mean ± SD
1) Results after controlling for ages of the subjects 2) BMI: Body mass index 3) correlation coefficient (p value)
1) AUC: Area under the ROC curve 2) SS: Sensitivity 3) SP: Specificity 4) YI: Youden's index 5) Asia-Pacific Region Criteria 6) Entropy Model Criteria
1) AUC: Area under the ROC curve 2) SS: Sensitivity 3) SP: Specificity 4) YI: Youden's index 5) Asia-Pacific Region Criteria 6) Entropy Model Criteria
1) Asia-Pacific Region Criteria 2) Entropy Model Criteria
1) Asia-Pacific Region Criteria 2) Entropy Model Criteria
1) Asia-Pacific Region Criteria 2) Entropy Model Criteria
1) Asia-Pacific Region Criteria 2) Entropy Model Criteria

 KSCN
KSCN





 Cite
Cite


