Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Korean J Community Nutr > Volume 17(1); 2012 > Article
-
Original Article
- Nutritional Status, Quality of Diet and Quality of Life in Postmenopausal Women with Mild Climacteric Symptoms Based on Food Group Intake Patterns
- Okhwa Lee, Jinkyung Kim, Hansongyi Lee, Ryowon Choue
-
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition 2012;17(1):69-80.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.1.69
Published online: February 29, 2012
1Department of Medical Nutrition, Graduate School of East-West Medical Science, Kyung Hee University, Yongin, Korea.
2Research Institute of Clinical Nutrition, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Ryowon Choue, Department of Medical Nutrition, Graduate School of East-West Medical Science, Kyung Hee University, Seocheon-dong, Giheung-gu, Yongin-si, Gyeonggi-do 446-701, Korea. Tel: (031) 201-2317, Fax: (031) 204-8119, rwcho@khu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2012 The Korean Society of Community Nutrition
- 1,325 Views
- 19 Download
- 15 Crossref
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- The impact of carbohydrate quality index on menopausal symptoms and quality of life in postmenopausal women
Emine ELİBOL, Sevdenur Eski, Edanur Gez, Gizem Çamdeviren
BMC Women's Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of evaluation items for accessing practice and compliance with dietary guidelines among Korean adults
Min-Ah Kim, Sung-Min Yook, Jieun Oh, Jimin Lim, Hye Ji Seo, Young-Suk Lim, Ji Soo Oh, Hye-Young Kim, Ji-Yun Hwang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(2): 244. CrossRef - Comparison of Nutrient Intake and Diet Assessment according to the Subjective Health Perception and Disease Existence : The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data(2013~2017) Analysis
Yi-Na Yoon, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2021; 32(3): 395. CrossRef - Marine Healing, but Not Additional Intake of Undaria pinnatifida, Benefits Physical and Emotional Exhaustion Symptoms of Menopause
Hyunju Yun, Bora Lee, Sung Jae Lee, Clara Yongjoo Park
Clinical Nutrition Research.2020; 9(1): 1. CrossRef - Changes in Dietary Quality among Vietnamese Women Immigrants in Korea and Comparison with Korean Women
Young-Ah Cho, Do-Yeon Kim, Ryowon Choue, Hyunjung Lim
Clinical Nutrition Research.2018; 7(3): 178. CrossRef - Effects of Nutrition Education and Exercise Program on Obesity Index and Behavioral Modification in Moderate Obese Women
Myung-Hee Chang, Su-Jin Jung
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(4): 318. CrossRef - Effects of Nutrition Education at a Community Health Center on Overweight and Obese Middle-aged Women in Jeonbuk Area-Focused on Personalized Daily Energy Requirement and Food Exchange Units
Se-Yeon Kim, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(4): 307. CrossRef - Evaluation of Anthropometric Characteristics, Bone Density, Food Intake Frequency, Nutrient Intakes, and Diet Quality of Preand Postmenopausal Women : Based on 2008∼2011 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Soon Nam Choi, Kwang Hyun Jho, Nam Yong Chung
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2017; 27(5): 500. CrossRef - Use of the Menopause-Specific Quality of Life (MENQOL) questionnaire in research and clinical practice: a comprehensive scoping review
Beate C. Sydora, Hilary Fast, Sandy Campbell, Nese Yuksel, Jacqueline E. Lewis, Sue Ross
Menopause.2016; 23(9): 1038. CrossRef - Health Status Assessment Tool Development based on Dietary Patterns in Middle-Aged Women
Hye-Jin Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(1): 37. CrossRef - Influence of Customer, Foodservice Management and Competitor Environment on Quality of Customer’s Life in Contract Foodservice
Jin Young Lee, Kyung Soo Han
Journal of The Korean Society of Food Culture.2015; 30(5): 629. CrossRef - Effects of Inhalation of Essential Oil of Citrus aurantium L. var. amara on Menopausal Symptoms, Stress, and Estrogen in Postmenopausal Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Seo Yeon Choi, Purum Kang, Hui Su Lee, Geun Hee Seol, Ping Liu
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Dietary Habits and Climacteric Symptoms according to the Level of Food Supplement Use of Middle-aged Women
Mi Jeong Kim, Kyung-Hea Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2013; 42(7): 1054. CrossRef - Evaluation of Diet Quality according to Self-Rated Health Status of Korean Middle-Aged Women -Based on 2008~2009 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey-
Hye-Jin Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2013; 42(9): 1395. CrossRef - Characteristics of the Health Factors in 45~60 Year Old Korean Women related to Menopausal Stages - Based on 2008~2009 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey -
Hye-Jin Lee, Kwang-Hyun Cho, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(4): 450. CrossRef
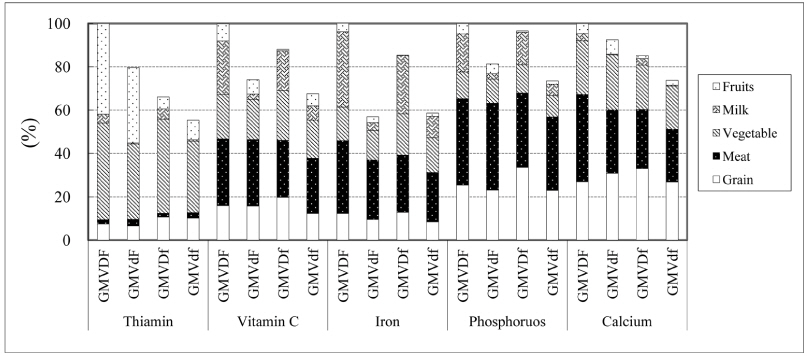
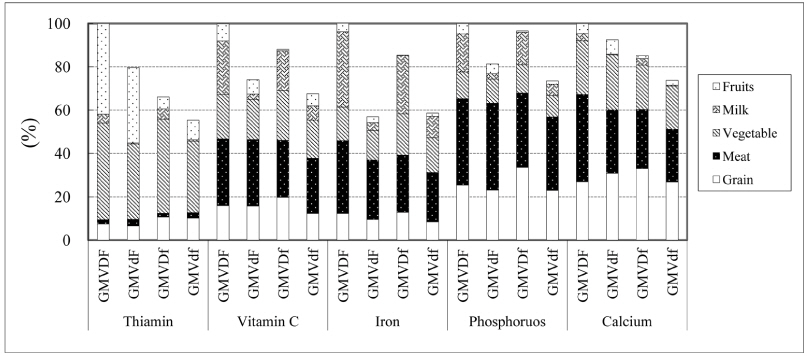
Fig. 1
Anthropometric and blood parameters according to the food group intake patterns
1) Waist Hip Ratio, 2) Systolic Blood Pressure, 3) Diastolic Blood Pressure, 4) Low Density Lipoprotein cholesterol, 5) High Density Lipoprotein cholesterol, 6) Grain, Meat, Vegetable, Dairy, and Fruit, 7) Values are Mean ± SD
†: Significantly different categorical variables by the chi-square test at p < 0.05
*: Means with different alphabetic letters within a raw are significantly different at p < 0.05 by Duncan's multiple range test after ANOVA
Nutrients intakes according to the food group intake patterns
1) Percentage ratio of carbohydrate : protein : fat in energy intake
2) Mean ± SD
3) Means with different alphabetic letters within a raw are significantly different at *: p < 0.05 by Duncan's multiple range test after ANOVA
INQ, NAR and MAR according to the food group intake patterns
1) INQ : Index of Nutritional Quality, 2) NAR : Nutrient Adequacy Ratio, 3) MAR : Mean Adequacy Ratio, 4) Mean ± SD, 5) Means with different alphabetic letters within a raw are significantly different at *: p < 0.05 by Duncan's multiple range test after ANOVA
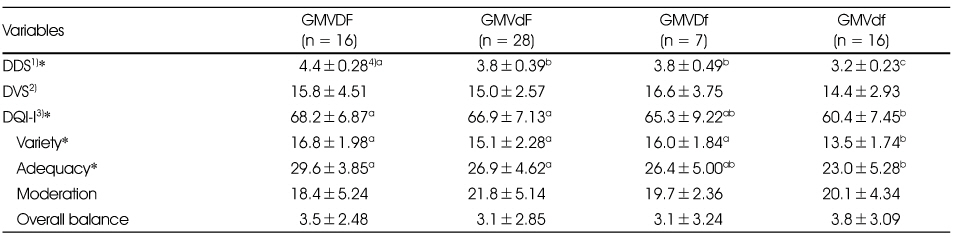
Total diet quality according to the food group intake patterns
1) DDS : Dietary Diversity Score, 2) DVS : Dietary Variety Score, 3) DQI-I : Dietary Quality of Index-international was composed with four domains, variety, adequacy, moderation, overall balance, 4) Mean ± SD, 5) Means with different alphabetic letters within a raw are significantly different at *: p < 0.05 by Duncan's multiple range test after ANOVA
Climacteric Symptoms according to the food group intake patterns
1) The scores of Kupperman's index were categorised as follows: normal < 20, moderate : 20 - 40, severe > 40. If a patient has a score of 20 she could be categorised as moderate
2) MENQoL : Menopause-specific quality of life questionnaire. The higher the scores of MENQoL were had, the worse the menopausal women's quality of life was had
3) Mean ± SD
4) Means with different alphabetic letters within a raw are significantly different at *: p < 0.05 by Duncan's multiple range test
1) Waist Hip Ratio, 2) Systolic Blood Pressure, 3) Diastolic Blood Pressure, 4) Low Density Lipoprotein cholesterol, 5) High Density Lipoprotein cholesterol, 6) Grain, Meat, Vegetable, Dairy, and Fruit, 7) Values are Mean ± SD †: Significantly different categorical variables by the chi-square test at p < 0.05 *: Means with different alphabetic letters within a raw are significantly different at p < 0.05 by Duncan's multiple range test after ANOVA
1) Percentage ratio of carbohydrate : protein : fat in energy intake 2) Mean ± SD 3) Means with different alphabetic letters within a raw are significantly different at *: p < 0.05 by Duncan's multiple range test after ANOVA
1) INQ : Index of Nutritional Quality, 2) NAR : Nutrient Adequacy Ratio, 3) MAR : Mean Adequacy Ratio, 4) Mean ± SD, 5) Means with different alphabetic letters within a raw are significantly different at *: p < 0.05 by Duncan's multiple range test after ANOVA
1) DDS : Dietary Diversity Score, 2) DVS : Dietary Variety Score, 3) DQI-I : Dietary Quality of Index-international was composed with four domains, variety, adequacy, moderation, overall balance, 4) Mean ± SD, 5) Means with different alphabetic letters within a raw are significantly different at *: p < 0.05 by Duncan's multiple range test after ANOVA
1) The scores of Kupperman's index were categorised as follows: normal < 20, moderate : 20 - 40, severe > 40. If a patient has a score of 20 she could be categorised as moderate 2) MENQoL : Menopause-specific quality of life questionnaire. The higher the scores of MENQoL were had, the worse the menopausal women's quality of life was had 3) Mean ± SD 4) Means with different alphabetic letters within a raw are significantly different at *: p < 0.05 by Duncan's multiple range test

 KSCN
KSCN




 Cite
Cite


