Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Korean J Community Nutr > Volume 20(6); 2015 > Article
-
Research Article
- Effects of an Education Program on Sanitation Status at Centers for Children's Food Service Management: Focusing on Jung-gu and Dong-gu regions of Daejeon Metropolitan City
- Yu-Jin Seo, Min-Sun Jeon
-
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition 2015;20(6):447-459.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.6.447
Published online: December 31, 2015
Department of Food and Nutrition, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Min Sun Jeon. Department of Food and Nutrition, Chungnam National University, 99, Daehak-ro, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon 34134, Korea. Tel: 042-821-6836, Fax: (042) 821-8887, dearms@cnu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2015 The Korean Society of Community Nutrition
This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 1,125 Views
- 4 Download
- 12 Crossref
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- 일부 학교급식 위생관리 컨설팅을 통한 개선사항 도출 연구
해림 조, 서진 김, 중범 김, 수연 김
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2025; 41(3): 151. CrossRef - Relationship with the Perception of Foodservice, Nutritional Knowledge, and Foodservice Guidance of Day-Care Center Teachers in Gangwon Area
Seung-Lim Lee
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(3): 203. CrossRef - Relationship between the Nutrition Quotient, Sustainable Diets, and Meal Guidance of Day-Care Center Teachers according to the Type of Day-Care Center : Focus on the Gangwon Area
Seung-Lim Lee, Ji-Hye Kim, Hye-Ji Oh, Myeong-Jong Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(4): 262. CrossRef - A Study of Food Safety Knowledge for Sustainable Foodservice Management of Childcare Centers in South Korea Using Importance–Performance Analysis
Jeong-Sil Choi, Se-Young Ju
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(15): 9668. CrossRef - Evaluation of Food Safety Management Status of Children’s Foodservice Facilities Using Sanitary Check Scores and ATP Bioluminescence Assay in Gyoengbuk Area
Kyung-A Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2021; 50(2): 196. CrossRef - Comparison of Salinity and Sodium Content by the Salinity Measurement Frequency of Soups of Childcare Centers Enrolled in the Center for Children's Food Service Management in Daegu
Na-Yeong Lee, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(1): 13. CrossRef - Research trends in obesity & obesogenic environments in Korea
Myoungsook Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2019; 13(6): 461. CrossRef - Effects of Periodic Visiting Education Support on the Sanitation Management of Foodservice Facilities for Children in the Local Small City: A Focus on the Yecheon-gun Area
Hye-Jin Pak, Chan-Ick Cheigh
Food Engineering Progress.2019; 23(3): 200. CrossRef - Analysis of Sanitary Safety Management Improvement for Children’s Food service in Chilgok-gun Area
Suk-Hyeon Park, Hyeon-A Jung
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2018; 28(5): 345. CrossRef - The Effect of Personality Type and Job Performance on Emotional Exhaustion and Job Satisfaction - Staff of the Center for Children's foodservice management -
Kyung-Min Lee, Min-Sun Jeon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(6): 496. CrossRef - A study on the optimal variable transformation method to identify the correlation between ATP and APC
Hye-Kyung Moon, Jae-Kyoung Shin, Yang Sook Kim
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2016; 27(6): 1465. CrossRef - A Comparison of Hygiene and Safety Management Execution depending on the Characteristics of Children's Food Service Facilities
Jin-Young Lee
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(4): 573. CrossRef

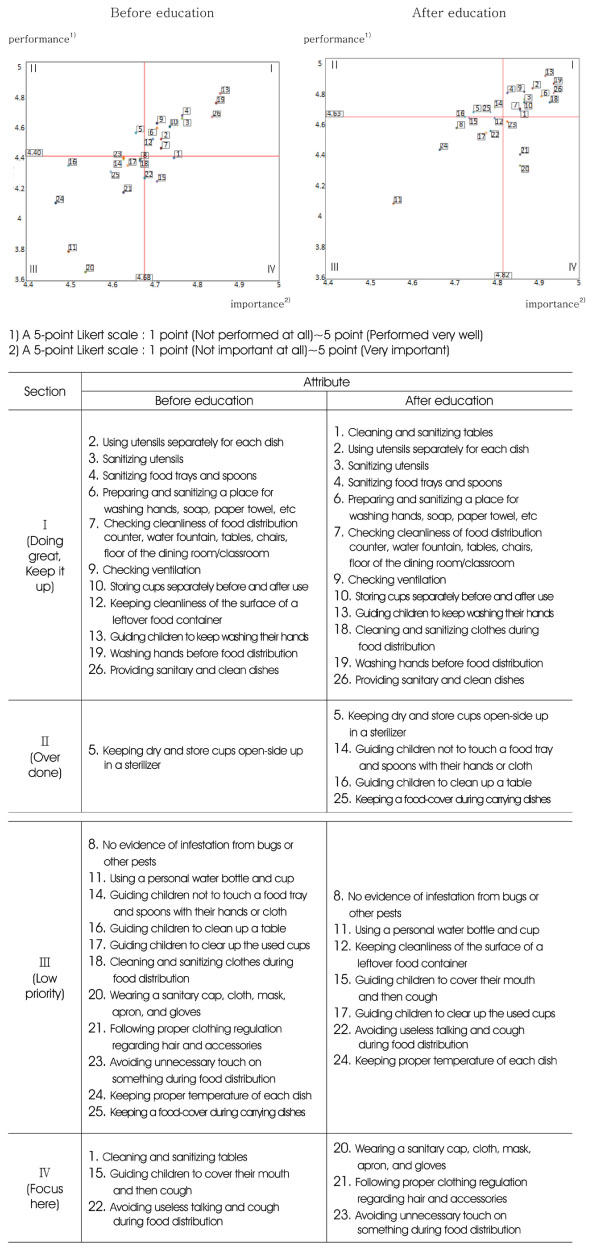
Fig. 1
Demographic information of the teachers
1) Multiple choice allowed
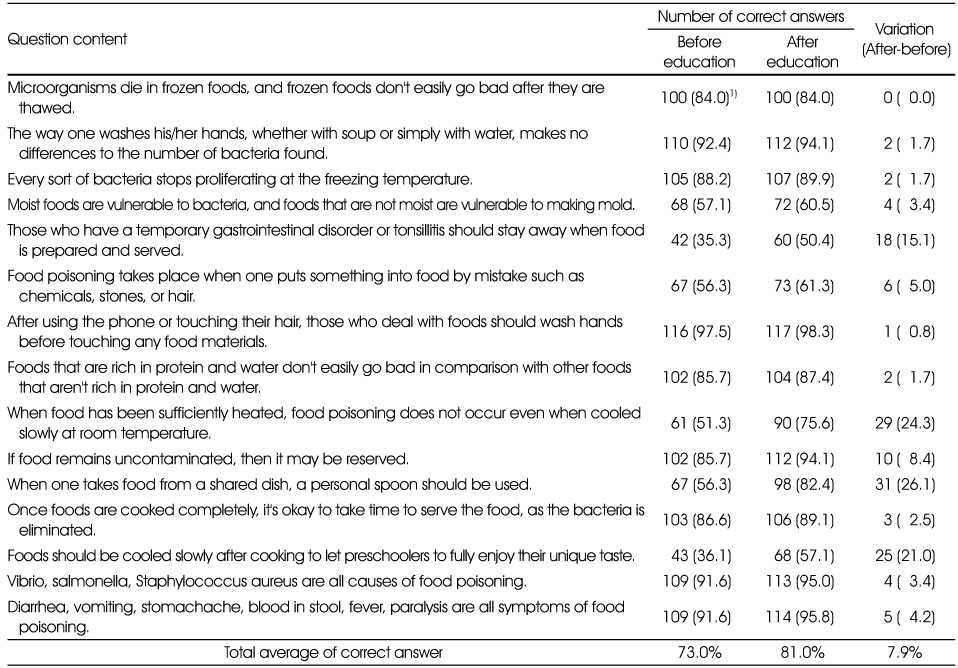
Levels of sanitation knowledge among the teachers
1) N (%)
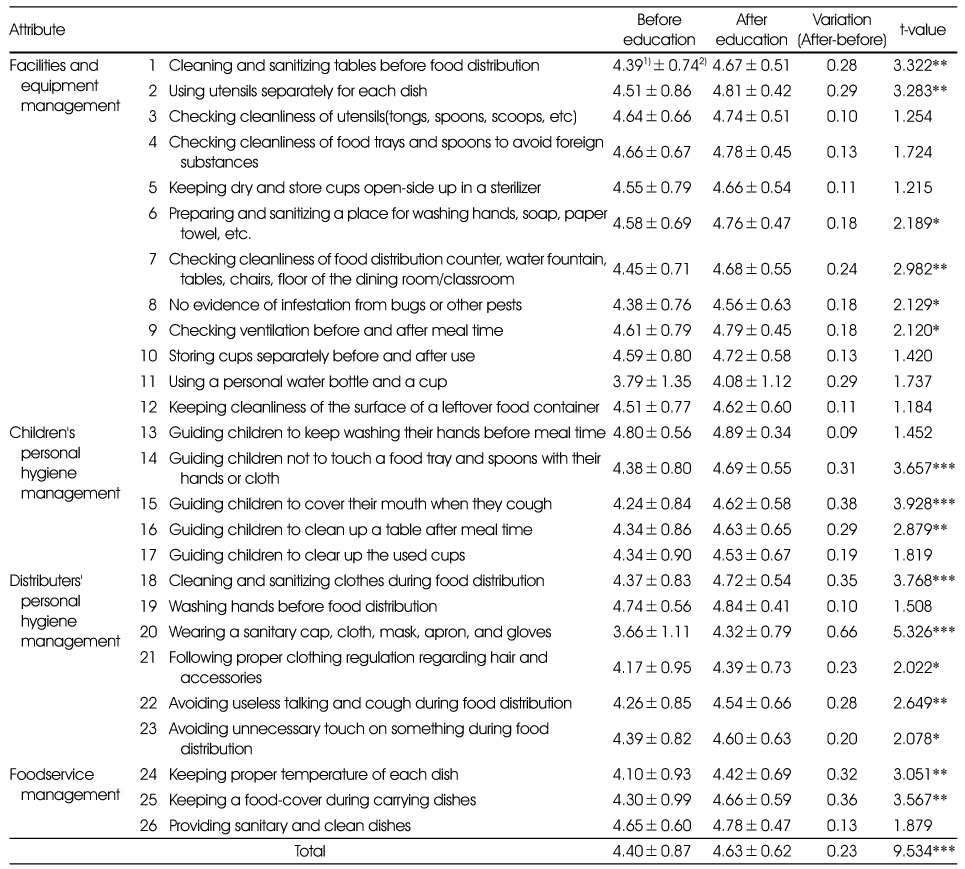
Levels of sanitation performance among teachers
1) A 5-point Likert scale : 1 point (Not performed at all)~5 point (Performed very well)
2) Mean±SD
*: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
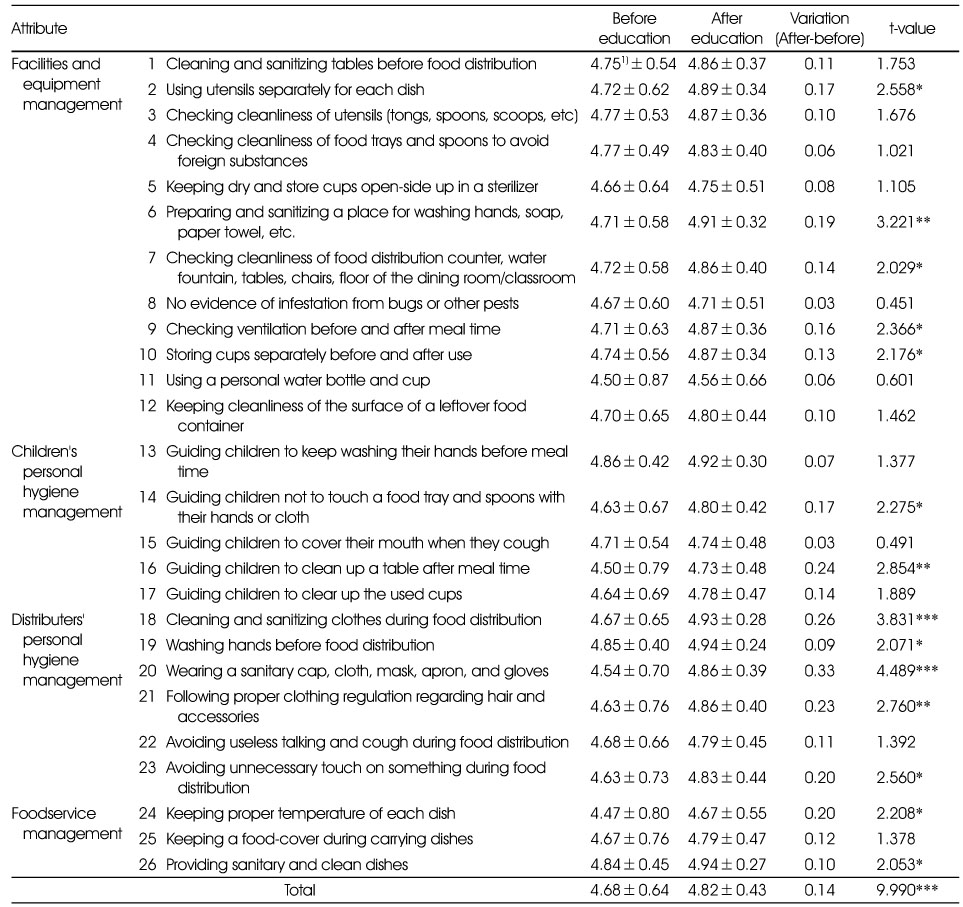
Levels of sanitation importance among teachers
1) A 5-point Likert scale : 1 point (Not important at all)~5 point (Very important)
2) Mean±SD
*: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
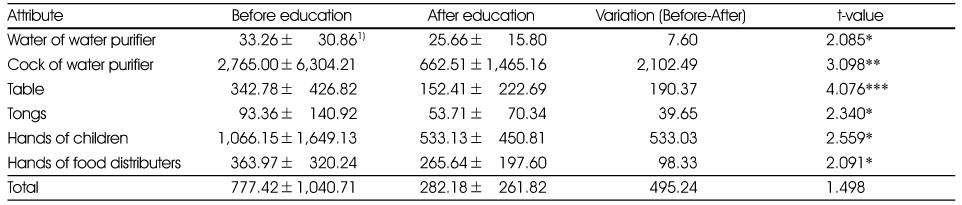
Microbiological qualities of the food distribution environment by ATP bioluminescence method (Unit : RLU/cm2)
1) Mean±SD
*: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
1) Multiple choice allowed
1) N (%)
1) A 5-point Likert scale : 1 point (Not performed at all)~5 point (Performed very well) 2) Mean±SD *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
1) A 5-point Likert scale : 1 point (Not important at all)~5 point (Very important) 2) Mean±SD *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001
1) Mean±SD *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001

 KSCN
KSCN

 Cite
Cite


