Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [English]
- Psychosocial factors related to the stages of change in reducing sugar intake among adults in Seoul, Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Ju Young Lee, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2026;31(1):21-35. Published online February 28, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2026.00024
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study examined the factors associated with stages of change (SOC) in reducing sugar intake among adults, applying the theory of planned behavior.
Methods
An online survey was conducted among adults aged 19–49 years residing in Seoul, Korea. Based on their SOC in reducing sugar intake, participants (n = 380) were categorized into a pre-action group (45.3%) and an action group (54.7%). Statistical analysis was performed using χ2-test, analysis of covariance, and one-way analysis of variance with linear contrast.
Results
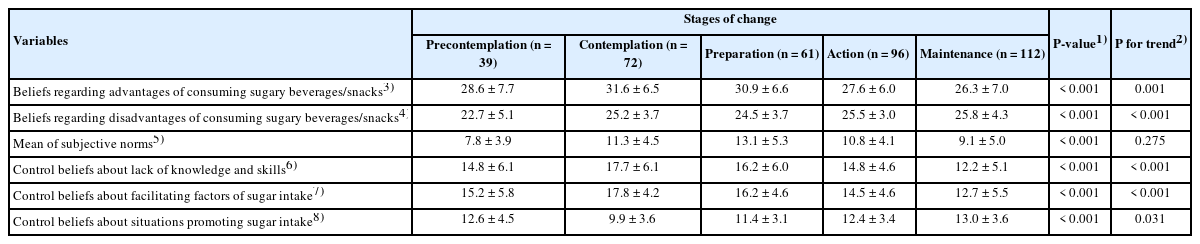
The consumption frequency of sugary foods was significantly higher in the pre-action group than in the action group (P < 0.001). Compared with the action group, participants in the pre-action group perceived the advantages of sugar intake more favorably (P < 0.001), perceived the disadvantages less strongly (P = 0.002), and reported greater influence from significant others (P = 0.004). In contrast, participants in the action group agreed less with insufficient knowledge/skills (P < 0.001), had greater control over the facilitating factors of sugar intake (P < 0.001), and had stronger control beliefs in situations promoting sugar intake (P < 0.001). Behavioral beliefs (P < 0.001) and control beliefs (P < 0.001) showed a significant linear trend across the five SOC, whereas subjective norms did not (P = 0.275).
Conclusion
Psychosocial factors related to sugar intake reduction clearly differed between the SOC groups. In the pre-action group, nutrition education should emphasize lowering the perceived benefits of sugar intake while increasing awareness of its adverse consequences. Strengthening the perception of control over sugar intake is important, despite the factors or situations promoting sugar intake. This can be achieved by providing practical tips and developing skills to reduce sugar intake. For the action group, it is necessary to maintain the reduced sugar intake through continual support and encouragement.
- 114 View
- 8 Download

- [English]
- Outcome expectations, self-efficacy, eating environment, and eating behaviors by the stages of change in adequate sodium intake among university students: a cross-sectional study
- Yeon Gyu Im, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(5):382-395. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00010

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated whether outcome expectations, self-efficacy, eating environment, and eating behaviors differed according to the stages of change in adequate sodium intake among university students. Methods: The participants were students recruited from nine universities in Seoul, Korea. An online survey was conducted, and data from 351 participants were analyzed. Participants were classified into pre-action and action stages based on adequate sodium intake. Data were analyzed using t-test, χ2-test, analysis of covariance, and correlation analysis. Results: Participants in the action stage (22.8%) felt fewer disadvantages of eating sodium adequately compared to those in the pre-action stage (77.2%, P < 0.001) and perceived more self-efficacy for healthy eating behaviors (P < 0.001) and controlling sodium intake (P < 0.01). The participants in the action stage also showed more desirable eating behaviors than those in the pre-action stage, including general eating behaviors, behaviors related to sodium intake, and sodium checks (P < 0.001). The physical environment in the action stage was more supportive of adequate sodium intake (P < 0.05). Eating behaviors, self-efficacy, and outcome expectations were significantly correlated with the stages of change; however, some differences were noticed in the correlation of the subscales of variables with the stages of change when examined by sex. Conclusion: We observed differences in factors according to the stages of change in adequate sodium intake. For the pre-action stage, nutrition education can be planned to modify negative expectations of eating adequate sodium, foster self-efficacy, and practice general eating behaviors and behaviors to gradually reduce sodium intake. It is also necessary to alter the physical environment to reduce sodium intake. In the action stage, support and reinforcement are needed to continually practice and maintain desirable eating behaviors. Nutrition education for women may be planned using multiple paths, whereas a simple strategy may be useful for men. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of a foodservice establishment manager’s willingness to perform duties on hygiene management levels and the mediating effects of extrinsic motivations: a cross-sectional study
Tae Yang Kim, Mi Young Lee, Young Eun Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2026; 31(1): 36. CrossRef - Psychosocial factors related to the stages of change in reducing sugar intake among adults in Seoul, Korea: a cross-sectional study
Ju Young Lee, Kyung Won Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2026; 31(1): 21. CrossRef
- Impact of a foodservice establishment manager’s willingness to perform duties on hygiene management levels and the mediating effects of extrinsic motivations: a cross-sectional study
- 2,785 View
- 48 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Status and Needs Assessment on Nutrition Management and Meal Service for Elementary · Middle · High School Athletes among Athlete's Parents
- Jung Hyun Hwang, Ji Yeon Kim, Kyung A Kim, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(1):47-59. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.1.47
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Young athletes require adequate nutrition to maintain their athletic performance, growth and health. This study examined the status and needs of nutrition management and meal services for student athletes among the athlete's parents.
METHODS
The subjects were parents of elementary, middle, and high school athletes (n=323) from 18 schools participating mainly in the Sports Food Truck. The questionnaire included general characteristics, status and needs on nutrition management and meal service for student athletes, and satisfaction with the Food Truck. The survey was done during 2018. The data were analyzed according to the school groups using a χ2-test or ANOVA.
RESULTS
Approximately 45% of subjects had difficulty in the nutrition management of athletes, and 87.1% had not received nutrition education. Approximately 74% wanted nutrition education held for athletes, and mainly wanted topics on nutrition management for health and eating for athletic performance. The preferred methods were lectures and cooking activity. The responses on the necessity of nutrition education for athletes, desired education topics, and desired times for education differed significantly according to the school groups (p < 0.05). Most subjects also wanted nutrition information mainly through SNS. In the athlete's meal, breakfast and snacks were highlighted as the meal to supplement. Approximately 90.3% responded that providing a meal service is necessary. The subjects preferred snacks before/after exercise and dinner if a meal service was provided. They preferred Korean food, followed by snacks, and a dish meal. As the meal type, the subjects wanted the Food Truck and packed meal. The responses on necessity of a meal service (p < 0.05), preferred food (p < 0.001), and meal type (p < 0.001) in the meal service differed significantly according to the school groups. Approximately 43% were satisfied with the Food Truck and 50.8% responded as average. They made suggestions for the Food Truck in terms of foods, operations and frequency.
CONCLUSIONS
Based on the study results, nutrition education and meal service may support nutrition for student athletes considering the needs of the parents according to the school groups.
- 1,216 View
- 4 Download

- [English]
- Nutrient Intakes of Male College Combat Sport Athletes by Weight Control Status
- Ji Yeon Kim, Ji Seon Lee, Seong Suk Cho, Hyon Park, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(6):495-506. Published online December 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.6.495
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Weight control practices are common in combat sport athletes. This study was performed to examine nutrient intakes of male college combat sport athletes (taekwondo, boxing, judo) by weight control (WC) status.
METHODS
Subjects were male combat sport athletes (n=90) from colleges in Gyeonggi Province. Survey was conducted during 2016. Questionnaire included general characteristics, weight control, and dietary intakes during the period of training, weight control, weigh-in ~ before competition and between competitions. Subjects were grouped into high- and normal WC groups. T-test, χ²-test, Fisher's exact test and ANCOVA were used to analyze the data.
RESULTS
During training, energy intake was 75.4% of EER and C:P:F ratio was 57.5:13.9:28.7. Iron and zinc intakes were different by WC groups (p<0.05). During weight control, energy intake was 44.7% of EER in normal WC and 30.5% in high WC group (p<0.05). C:P:F ratio was 69:11.1:19.5, and ratio from protein and fat was lower in the high WC group (p<0.05). Most nutrient intakes during weight control were less than 50% of 2015 KDRIs (RNI or AI), and intakes including thiamin (p<0.01), vitamin A, riboflavin, niacin, folate, calcium, potassium and zinc (p<0.05) were significantly lower in the high WC. Energy intake after weighing before the competition was 1,315 kcal, and energy (kcal/kg BW, p<0.05) and carbohydrate intakes (g/kg BW, p<0.01) were significantly higher in the high WC group. Energy intake between competitions was 691.1 kcal, with no difference by the WC group.
CONCLUSIONS
Nutrients intakes of combat sport athletes were inadequate. Dietary intakes during weight control were much below than the KDRIs, especially in the high WC group. It is needed to develop nutrition education programs for combat sport athletes to avoid severe energy restrictions and to apply specific dietary guides to each period of training and weight control. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Weight control practices, beliefs, self-efficacy, and eating behaviors in college weight class athletes
Ji Seon Lee, Seong Suk Cho, Kyung Won Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2020; 14(1): 45. CrossRef
- Weight control practices, beliefs, self-efficacy, and eating behaviors in college weight class athletes
- 1,429 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Perception on Optimal Diet, Diet Problems and Factors Related to Optimal Diet Among Young Adult Women Using Focus Group Interviews: Based on Social Cognitive Theory
- Hye Jin Kim, A Reum Lee, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(4):332-343. Published online August 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.4.332
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Study purpose was to investigate perception on diet, diet problems and related factors among young adult women using focus group interviews (FGI) based on the Social Cognitive Theory (SCT).
METHODS
Eight groups of FGI were conducted with 47 female undergraduate or graduate students. Guide for FGI included questions regarding perception on optimal diet, diet problems and cognitive, behavioral, and environmental factors of SCT. FGI were video, audio-taped, transcribed and analyzed by themes and sub-themes.
RESULTS
Subjects showed irregular eating habits (skipping breakfast, irregular meal time) and selection of unhealthy foods as the main diet problems. Regarding cognitive factors related to optimal diet, subjects mentioned positive outcome expectations (e.g., health promotion, skin health, improvement in eating habits, etc.) and negative outcome expectations (e.g., annoying, hungry, expensive, taste). Factors that promoted optimal diet were mainly received from information from mobile or internet and access to menu or recipes. Factors that prevented optimal diet included influence from friends, lack of time and cooking skills. Behavioral factors for optimal diet included behavioral capability regarding snacks, healthy eating and smart food selection. Subjects mentioned mass media (mobile, internet, TV) as the influential physical environment, and significant others (parents, friends, grandparents) as the influential social environment in optimal diet. For education topics, subjects wanted to learn about healthy meals, basic nutrition, disease and nutrition, and weight control. They wanted to learn those aspects by using mobile or internet, lectures (cooking classes), campaign and events.
CONCLUSIONS
Study results might be used for planning education regarding optimal diet for young adult women. Education programs need to focus on increasing positive outcome expectations (e.g., health) and behavioral capability for healthy eating and food selection, reducing negative outcome expectations (e.g., cost, taste) and barriers, making supportive environments for optimal diet, and incorporating topics and methods found in this study. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors affecting sugar intake in adults based on the social cognitive theory
Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(1): 120. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Need for Obesity Prevention Education Programs through Analysis of Factors Affecting Student Obesity Factors in Seoul during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Seoung Hi Kim, Seonyeong Baek, Min Jeong Choi, Sunny Ham
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2022; 32(3): 214. CrossRef - Focus Group Interviews with U.S. Americans with Respect to Recipe and Sensory Characteristics of Seolgitteok (Korean Rice-Flour Cake)
Han-Seok Seo, Sungeun Cho
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2018; 34(1): 15. CrossRef - Meal Types by Cooking Method Consumed by Korean Adults according to Meal Provision Place: Using 2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Mi-Kyung Choi
Korean Journal of Food & Cookery Science.2017; 33(3): 264. CrossRef - Utilization of Internet Dietary Information by University Students in Seoul and Gyeonggi Area
Young Eun Kang, Sim Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2016; 25(6): 811. CrossRef
- Factors affecting sugar intake in adults based on the social cognitive theory
- 1,442 View
- 6 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Status of Dietary Life Related Knowledge, Self-Efficacy, Food Preference and Dietary Behavior of Preschoolers in Kyunggi Area
- A Reum Lee, Ye Lee Yu, Hye Jin Kim, Kyung A Kim, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(3):274-283. Published online June 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.3.274
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of the study was to examine dietary life characteristics such as knowledge, self-efficacy and dietary behavior of preschoolers in Namyangju, Kyunggi-province, Korea.
METHODS
The survey questionnaire was developed based on literature review. Preschoolers aged 4-5 years (n=208) responded to the questionnaire to measure knowledge, self-efficacy, food preference, and dietary behavior. After excluding incomplete responses, the data of 197 subjects were used for analysis.
RESULTS
Mean score of dietary life knowledge was 8.0 out of 12, showing a low level of knowledge. Two out of 12 knowledge items were significantly different by gender. Percentage of correct answer on items of 'foods to make bones strong' and 'kinds of fast foods' was higher in girls than in boys (p<0.05). Total score of self-efficacy regarding dietary life was 40.1 (possible score: 12~48), on average. Compared to girls, boys had more confidence in 'not over-eating', and 'eating balanced meals with meat, fish and vegetables' (p<0.05). Boys scored higher on total score of food preference than girls (p<0.01). The preference for fruits was quite high. Among food items, boys scored higher on the preference for rice (p<0.01), fish (p<0.01), pork (p<0.05), beef (p<0.05), milk (p<0.01), and ice cream (p<0.05) than girls. Boys also liked fast foods more than girls did, showing preference for chicken (p<0.01) and soda (p<0.05). Compared to girls, boys showed more desirable behavior in 'eating breakfast everyday' (p<0.01). Dietary behavior was significantly correlated with self-efficacy (r=0.52, p<0.01), food preference (r=0.35, p<0.01), and knowledge (r=0.25, p<0.01) of subjects.
CONCLUSIONS
In this study, we observed differences in food preference by gender. Dietary behavior of preschoolers was correlated with several factors, including dietary life related knowledge, self-efficacy and food preference. Thus, it is needed to develop nutrition education programs focusing on increasing dietary life related knowledge and self-efficacy, and consider the differences in food preference of preschoolers by gender. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary Assessment and Trends Among Preschoolers in South Korea: Data from KNHANES 2012–2021
Yong-Seok Kwon, Ye-Jun Kim, Eun-Kyung Kim, Jin-Young Lee, Yangsuk Kim, Sohye Kim
Nutrients.2026; 18(2): 240. CrossRef - Dietary intake and nutritional status of Korean children and adolescents: a review of national survey data
Minji Kang, So Yoon Choi, Minyoung Jung
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics.2021; 64(9): 443. CrossRef - Study on the snack meal management for infants and toddlers and the demand for snack products according to the sustainable dietary style of mothers in Jeonbuk area
Ji-Eun Lee, Jeong-Ok Rho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(1): 39. CrossRef - Development of nutrition quotient for elementary school children to evaluate dietary quality and eating behaviors
Jung-Sug Lee, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sehyug Kwon, Hae-Rang Chung, Tong-Kyung Kwak, Myung-Hee Kang, Young-Sun Choi, Hye-Young Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(6): 629. CrossRef - Menu Recommendation System Using Smart Plates for Well-balanced Diet Habits of Young Children
Kwon Namgung, Tae-Hwan Kim, Youn-Sik Hong
Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Eating Behavior and Prosocial Behavior among Preschool Children in Kindergartens vs. Childcare Centers
So-Sun Sun, Ji-Young Ha, So Jung Seo
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2019; 29(2): 130. CrossRef - Fruit and vegetable intakes in relation to behavioral outcomes associated with a nutrition education intervention in preschoolers
Eun Byul Choi, Ji Eun Lee, Ji-Yun Hwang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2018; 12(6): 521. CrossRef - Dietary status of young children in Korea based on the data of 2013 ~ 2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Eun-kyung Kim, Byengchun Song, Se-Young Ju
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(4): 330. CrossRef - Evaluation of Dietary Behavior among Preschooler in Jecheon Area Using Nutrition Quotient for Preschoolers
Sung Hee Min
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2018; 34(4): 413. CrossRef
- Dietary Assessment and Trends Among Preschoolers in South Korea: Data from KNHANES 2012–2021
- 1,721 View
- 4 Download
- 9 Crossref

- [English]
- Status and Need Assessment on Nutrition & Dietary Life Education among Nutrition Teachers in Elementary, Middle and High Schools
- Na Gyeong Oh, Su Jin Gwon, Kyung Won Kim, Cheong Min Sohn, Hae Ryun Park, Jung Sook Seo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(2):152-164. Published online April 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.2.152
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to investigate the status and need for nutrition and dietary life education among nutrition teachers at schools. These characteristics were analyzed if they were different between elementary schools and middle-high schools.
METHODS
Subjects were 151 nutrition teachers from 70 elementary schools, 41 middle schools and 40 high schools in 17 cities nationwide selected by two-stage stratified cluster sampling process. Survey questionnaires included the items on general characteristics, status and need assessment for nutrition and dietary life education. Chi-square test or t-test was used for data analysis by school groups.
RESULTS
Nutrition education was implemented at 65.7% of elementary schools and 51.9% of middle-high schools. Nutrition education was mainly performed in 'discretionary activities·extracurricular activities' at elementary school and through 'newsletters, school homepage, foodservice bulletin board' at middle-high school (p<0.001). The most needed topic for nutrition education in nutrition teachers was 'healthy dietary habits and table manners' and this was not significantly different by school groups. Responses on adequate frequency (p<0.01), methods used for nutrition education (p<001), materials for nutrition education (p<0.001), information sources for nutrition education (p<0.001) were significantly different by school groups. Major tasks for activating nutrition education included 'securing the time for implementing nutrition education by reducing work loads' and 'developing standardized nutrition education materials' in schools.
CONCLUSIONS
Nutrition education at schools might be activated by improving working conditions of nutrition teachers and developing the practical programs that reflect the needs of nutrition teachers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutrition quotient for preschoolers and key impacting factors in Korea: a cross-sectional study on food literacy, social support, and the food environment of primary caregivers
Danbi Gwon, Ji-Yun Hwang, Jieun Oh
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(1): 16. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on the Necessity and Promoting Strategies for School-Based Dietary Education: Focus Group Interviews with Home Economics Teachers
Seung Jae Lee, Ji Eun Oh, Kyung Won Lee
Human Ecology Research.2025; 63(1): 41. CrossRef - Developing educational videos to inform rightly about school foodservice from kindergarten to high school: a case study
Gyoungok Gang, Chaewon Park, Haejin Kang, Wan Soo Hong, Yoo Kyoung Park, Sook Hee Choi, Seung Hye Kim, Jieun Choi, Jihyun Park, Hyeja Chang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 97. CrossRef - Nutrition teacher’s perception and current status of nutrition education for free learning semester program: a preliminary study
Mi Joo Park, Jeong-Hwa Choi, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(1): 24. CrossRef - 광주광역시 지역민의 영양교육 요구도 조사 분석
은평 양, 경윤 김, 승희 최, 금비 류, 옥경 김, 정미 윤
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(2): 100. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Need for Obesity Prevention Education Programs through Analysis of Factors Affecting Student Obesity Factors in Seoul during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Seoung Hi Kim, Seonyeong Baek, Min Jeong Choi, Sunny Ham
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2022; 32(3): 214. CrossRef - Awareness and Practice of Sugar Reduction in School Foodservice and the Practice of Nutrition Education in Daegu
Suhyang Jang, Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(3): 167. CrossRef - Analysis of the consumer perception and related education effect on the reduction of sugar for elementary school students in Seoul and Gyeonggi-do
Ki Nam Kim, Jung Sug Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Hae Kyung Chung, Hae Rang Chung, Moon-Jeong Chang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(3): 303. CrossRef - Evaluation of Dietary Quality and Nutritional Status according to the Use of Nutrition Labeling and Nutrition Claims among University Students in Chungbuk Area: Based on Nutrition Quotient
Yun-Jung Bae, Seo Young Park, Hye-Rin Bak
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(3): 179. CrossRef - What Are the Barriers at Home and School to Healthy Eating?: Overweight/Obese Child and Parent Perspectives
Hee Soon KIM, Jiyoung PARK, Yumi MA, Mihae IM
Journal of Nursing Research.2019; 27(5): e48. CrossRef - Effect of Dietary Education Experience (Home, School, and Mass Media) on Food Consumer Information literacy
Ji Eun Kim, Kyoung Sook Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(5): 363. CrossRef - Status and Needs Assessment on Nutrition Management and Meal Service for Elementary · Middle · High School Athletes among Athlete's Parents
Jung Hyun Hwang, Ji Yeon Kim, Kyung A Kim, Kyung Won Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(1): 47. CrossRef - Status and needs of nutrition education for children's sugars intake reduction in elementary school
Mi-Hyun Kim, Jee-Young Yeon
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(5): 433. CrossRef - Current status of dietary education in elementary, middle and high school in Gyeonggi province: Comparison according to school level and placement of nutrition teacher
Youngmi Lee, Soo Youn Kwon, Ji Hea Kim, Ok Sun Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(6): 645. CrossRef - Evaluation of educational school meal programs in Gyeonggi province, South Korea
Youngmi Lee, Oksun Kim, Uiok Lee, Sooyoun Kwon
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(1): 111. CrossRef - Needs Assessment for Dietary Education Program Focused on the Increase of HAN-SIK (Korean Food) Consumption in Children and Adolescents Living in Jeonbuk and Gyunggi Areas
Sang-Eun Lee, Yangsuk Kim, Eun Mi Ahn, Young Hwang, Young Kim
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2016; 27(S): 609. CrossRef
- Nutrition quotient for preschoolers and key impacting factors in Korea: a cross-sectional study on food literacy, social support, and the food environment of primary caregivers
- 1,647 View
- 10 Download
- 16 Crossref

- [English]
- Implementation and Evaluation of Nutrition Capacity Training Program for Dietitians and Related Professionals Working at Customized Home Visiting Health Services
- Sook Bae Kim, Jin Sook Yoon, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(1):71-83. Published online February 28, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.1.71
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of the study was to implement and evaluate a nutrition capacity training program for dietitians and other professionals working at customized home visiting health services (CHVHS). This program focused on nutrition services for hypertension or diabetes mellitus patients including topics regarding CHVHS, and composed of 10 sessions with lectures, discussion and practice. Dietitians (n = 54) and other professionals (n = 20) participated in the program and completed the questionnaire to assess their understanding of nutritional management, nutrition services and CHVHS before and after the program, and to examine program satisfaction and education needs. Subjects were mostly women (98.6%) and college or university graduates (93.2%). Total score (p < 0.001), as well as all items (p < 0.001 or p < 0.01) of understanding regarding nutritional management, nutrition services and CHVHS, were significantly increased after the program both in dietitians and in other professionals. Subjects were generally satisfied with the program, showing more satisfaction with items regarding subject's participation, acquiring new knowledge, usefulness of the program for CHVHS, and education materials. In future nutrition capacity training programs, subjects wanted to have classes regarding nutrition services for specific chronic diseases, development of education materials, methods for dietary life education, modifying eating habits and so on. Other professionals compared to dietitians, showed higher education needs in meal management (p < 0.01) and nutrition counseling skills (p < 0.05). This study showed the effectiveness of a nutrition capacity training program for home-visiting dietitians and other professionals, and suggests the need and direction for future nutrition capacity training programs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sodium Related Recognition, Dietary Attitude and Education Needs of Dietitians Working at Customized Home Visiting Health Service
Yun-Jeong Mo, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(6): 558. CrossRef - Evaluation of Nutrition Education for Hypertension Patients Aged 50 Years and Over
Eun Hye Moon, Kyung Won Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2011; 16(1): 62. CrossRef
- Sodium Related Recognition, Dietary Attitude and Education Needs of Dietitians Working at Customized Home Visiting Health Service
- 1,147 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Job Satisfaction, Work Performance, Work Satisfaction, Perceived Needs and Self-Evaluation of Knowledge and Skills of Nutrition Teachers in Gyeonggi Area
- Jae Yeon Lim, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(1):60-70. Published online February 28, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.1.60
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of the study was to examine job satisfaction, work performance, work satisfaction, perceived needs and self-evaluation of knowledge and skills of nutrition teachers. Survey questionnaire was administered to 106 nutrition teachers in schools of Gyeonggi area. Subjects were categorized into high- or low-job satisfaction group, and study variables were examined by job satisfaction group. Overall job satisfaction was high, with a mean score of 14.9 out of 20. High-job satisfaction group had more favorable perception regarding human relations and workplace atmosphere compared to the counterparts (p < 0.001). Work performance, examined by 12 items, was not significantly different between the two groups. However, satisfaction regarding specific work of nutrition teachers was significantly different by job satisfaction (p < 0.001). High-job satisfaction group responded that they had more knowledge and skills in areas such as food purchase management, food sanitation and safety management, equipment and facility management, nutrition education, nutrition counseling (p < 0.01), and general management & marketing (p < 0.05). High-job satisfaction group also indicated that nutrition teachers need to have more knowledge and skills than the counterparts, regarding food purchase management (p < 0.001), nutrition education (p < 0.01), nutrition counseling, general management and marketing, and teaching practices (p < 0.05). In addition, study results showed significant positive correlations among study variables. This study suggested that job satisfaction of nutrition teachers might be increased by having favorable human relations and workplace atmosphere, increasing satisfaction with specific work of nutrition teachers, and by increasing the knowledge and skills required for the work of nutrition teachers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of Job Description of Nutrition Teacher by the DACUM Method
Ji-Hee Kim, Jin-A Cha
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2016; 22(3): 193. CrossRef - Status and Need Assessment on Nutrition & Dietary Life Education among Nutrition Teachers in Elementary, Middle and High Schools
Na Gyeong Oh, Su Jin Gwon, Kyung Won Kim, Cheong Min Sohn, Hae Ryun Park, Jung Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(2): 152. CrossRef - Study on Current Nutrition Education and Effective Education Plan for Nutrition Teachers in Kyeonggi Region
Seong Yeong Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2016; 26(2): 181. CrossRef
- Development of Job Description of Nutrition Teacher by the DACUM Method
- 1,262 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Survey on Dietary Behaviors and Intakes of Instant Noodle (Ramyeon) Soup among College Students
- Hyung Sook Kim, Eun Young Lee, Kyungmin Kim, Kyung Won Kim, Jinwon Pyun, Sang Jin Chung, Young Hye Kwon, Ikhyun Yeo, Sangyun Lee, Kisun Nam
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(4):365-371. Published online August 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.4.365
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - High intakes of sodium may increase the risk of hypertension or cardiovascular diseases. According to the 2010 Korea National Health and Nutrition Survey, the average intake of sodium was 4,878 mg/day with salt, kimchi, soy sauce, fermented soybean paste and Ramyeon being the five main sources of sodium. In order to identify solutions to reduce the intake of sodium, we investigated the intake patterns and eating behaviors of Ramyeon among 347 college students (male 146, female 201) using survey questionnaires. The average age of study subjects was 23.7 years for males and 20.5 years for females. The average Body Mass Index (kg/m2) was 21.9 for males and 20.1 for females. The average frequency of Ramyeon intake was 2.0 times/week. The main reason for eating Ramyeon was convenience (56%), followed by good taste (27%), low price (11%) and other reasons (9%). The criteria for choosing Ramyeon were taste (72%), convenience (14%), price (7%), nutrition (1%), and the other factors (2%). Males' average intake of Ramyeon soup (61%) was higher than that of the females (36%). The estimated intake of Ramyeon soup by survey showed a positive correlation with the measured intake of Ramyeon soup. Sodium contents of Ramyeon were measured separately for the noodles and the soup, which were 1,185 mg/serving and 1,148 mg/serving each. Therefore, the amount of sodium intake can be reduced if students eat less Ramyeon soup. Also, we observed that dietary behaviors and soup intakes of Ramyeon between the sexes were different. Appropriate nutritional education for proper eating habits may help decrease the intake of sodium.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluating food portion estimation accuracy with multi-angle photographs
In-Young Choi, Mi-Hyun Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(4): 605. CrossRef - Comparison of the nutrition quotient by types of eating behavior among male and female university students in Gwangju
Geum-Bi Ryu, Young-Ran Heo
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(3): 277. CrossRef - Effects from the Use of Nutrition Labels and the Levels of Sodium-related Nutrition Knowledge on the Consumption of Instant Noodles (Ramyeon) by Middle School Students in the Incheon Area
Yang-Hee Kwon, Hyung-Sook Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(5): 397. CrossRef - A Qualitative Study on the Dietary Experience with the Children’s Meal Card : Focused on College Students Living in Busan
Soo Jin Lee, Ho Kyung Ryu
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2022; 33(2): 205. CrossRef - Flavor principle as an implicit frame: Its effect on the acceptance of instant noodles in a cross-cultural context
Meng Li, Seo-Jin Chung
Food Quality and Preference.2021; 93: 104293. CrossRef - Comparison of Sodium-Related Dietary Behavior and Low-Salt Dietary Attitude Based on the Gender and Salty Taste Assessment of Chinese International Students in the Jeonbuk Area
Qi Li, Ji Eun Lee, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2021; 31(2): 91. CrossRef - A Cross-National Study on Selection Attributes of Instant Noodle between China and Korea
Seong Soo Cha, Xiao-Wu Wang
Journal of Food Products Marketing.2020; 26(1): 1. CrossRef - Comparison of the sodium content of Korean soup-based dishes prepared at home, restaurants, and schools in Seoul
Yanghee Park, Jihyun Yoon, Sang-Jin Chung
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(6): 663. CrossRef - Development of a database of capsaicinoid contents in foods commonly consumed in Korea
Hoyoun Cho, Youngjoo Kwon
Food Science & Nutrition.2020; 8(8): 4611. CrossRef - Analysis of Sodium Content and Tastes of Ramyeon Cooked Using Different Recipes
Chang-Hwan Oh, Chung Ha-Yull
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2018; 34(5): 450. CrossRef - Development and User Satisfaction of a Mobile Phone Application for Image-based Dietary Assessment
Seo-Yoon Kim, Sang-Jin Chung
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(6): 485. CrossRef - Association of instant noodle intake with metabolic factors in Korea: Based on 2013~2014 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jee-Young Yeon, Yun-Jung Bae
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2016; 49(4): 247. CrossRef - Differences in Sodium-Intake Related Dietary Behaviors and Correlation Analysis According to Salty Taste Preference of University Students in Busan Area
Min-Ji Kang, Ki-Bo Choi, Eun-Soon Lyu
Korean journal of food and cookery science.2015; 31(4): 477. CrossRef - Study on Sodium Reduction: 'Healthy Restaurant for Sodium Reduction'
Soon Myung Hong, Jee Hye Lee, Hye-Kyung Kim, Rina Yu, Jeong Hee Seo, Eun Jeong Huh, Seong Suk Cho, Jeongah Yang
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2014; 20(3): 174. CrossRef - A Study on Food Habits and Nutrient Intakes according to BMI in Food and Nutrition Major and Non-major Female Students in Kyungnam University
Eun-Hee Seo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(4): 297. CrossRef - Diet-Related Health Risk Appraisal for Cardiometabolic Diseases of the College Students in Gyunggi-do
Hyung-Sook Kim
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2014; 25(1): 89. CrossRef
- Evaluating food portion estimation accuracy with multi-angle photographs
- 2,180 View
- 9 Download
- 16 Crossref

- [English]
- Implementation and Evaluation of Nutrition Education Programs Focusing on Increasing Vegetables, Fruits and Dairy Foods Consumption for Preschool Children
- Su Min Oh, Ye Lee Yu, Hye In Choi, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(5):517-529. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.5.517
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of the study was to implement and evaluate a nutrition education program for preschool children. Applying the PRECEDE-PROCEED model, the nutrition education program was developed and focused on changing beliefs, increasing nutrition knowledge and consumption of vegetables & fruits (V/F) and dairy foods. Subjects were children attending a childcare center in Seoulwho were grouped into education (n = 33) and control group (n = 32). Education group received four sessions of nutrition education during 2011 fall. Both groups completed the questionnaire at pretest and posttest, measuring nutrition knowledge, beliefs, and preferences of V/F and eating behaviors. Compared to control group, education group made significant gains in total score of nutrition knowledge after the education (p < 0.05). In addition, the pretest-posttest changes in total score of beliefs regarding V/F consumption and eating behaviors were higher in the education group than in the control group (p < 0.05). Two groups were significantly different in the pretest-posttest changes in specific beliefs regarding the benefits of V/F consumption and some eating behavior. However, there were no changes in the preferences of vegetables or fruits between the two groups after the education. The consumption of V/F and dairy foods was not significantly different after the education. This study revealed that nutrition education for preschoolers was effective in improving nutrition knowledge and perceived benefits regarding V/F consumption and specific eating behavior. This study suggested that more intensive education is needed to induce changes in eating behaviors. This program can be used in nutrition education of children at the childcare centers or kindergartens.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pilot evaluation of a cooking-based nutrition education program to promote vegetable intake among children in Seoul, South Korea: a single-group pre–post study
Sil-Ah Kim, Su-Jin Lee, Min-Ah Kim, Ji-Eun Oh, Sohyun Park, Hyun-Joo Ryou, Ji-Yun Hwang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(4): 249. CrossRef - Development and validation of an illustrated questionnaire on healthy eating practices among Korean preschool children
Dawon Park, Bo-Jeong Gong, Dahyeon Kim, Young-Hee Han, Saerom Shin, Eun Yeol Woo, Hye-Kyung Park, Taisun Hyun
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(6): 985. CrossRef - Changes in the importance and performance of low-sodium management among childcare center cooks in Yongin, South Korea, after salinometer support programs: a descriptive study
Jiwoo Min, Youngmi Lee, Yunhee Chang, Yujin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(4): 304. CrossRef - Development of a semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire for dietary intake of elementary school children: data from the Seventh Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Minji Jung, Eunhee Ha, Oran Kwon, Hyesook Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(4): 747. CrossRef - Preschoolers and Advertising: A Systematic Literature Review and Future Research Agenda on the Effects of Advertising on Preschool Children
Femke Loose, Liselot Hudders, Ini Vanwesenbeeck, Steffi De Jans
Journal of Advertising.2023; 52(3): 439. CrossRef - Effectiveness of nutrition education intervention focusing on fruits and vegetables in children aged six years and under: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Sumin An, Hyejin Ahn, Jeonghyeon Woo, Young Yun, Yoo Kyoung Park
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(5): 515. CrossRef - Development of nutrition quotient for elementary school children to evaluate dietary quality and eating behaviors
Jung-Sug Lee, Ji-Yun Hwang, Sehyug Kwon, Hae-Rang Chung, Tong-Kyung Kwak, Myung-Hee Kang, Young-Sun Choi, Hye-Young Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(6): 629. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Teacher-Led Nutritional Lessons in Altering Dietary Habits and Nutritional Status in Preschool Children: Adoption of a NASA Mission X-Based Program
Jieun Kim, Gilsook Kim, Jinah Park, Youfa Wang, Hyunjung Lim
Nutrients.2019; 11(7): 1590. CrossRef - Fruit and vegetable intakes in relation to behavioral outcomes associated with a nutrition education intervention in preschoolers
Eun Byul Choi, Ji Eun Lee, Ji-Yun Hwang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2018; 12(6): 521. CrossRef - Assessment of Foodservice and Cooking Program for Children Attending Community Child Centers in Korea
Sooyoun Kwon, Yoonjae Yeoh
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2016; 26(3): 223. CrossRef - The Development of Sugar Intake Reduction Test for Young Children
Nam-Hee Kim, Jee-Young Yeon, Mi-Hyun Kim
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(5): 818. CrossRef - Status of Dietary Life Related Knowledge, Self-Efficacy, Food Preference and Dietary Behavior of Preschoolers in Kyunggi Area
A Reum Lee, Ye Lee Yu, Hye Jin Kim, Kyung A Kim, Kyung Won Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(3): 274. CrossRef - Assessment on Dietary Diversity According to Korean Dietary Pattern Score of Korean Adolescents and Children: Using 2007~2013 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) Data
Yong-Suk Kwon, Yangsuk Kim
Korean journal of food and cookery science.2015; 31(5): 660. CrossRef - A Study on the Actual State of Nutrition Knowledge, Dietary Attitude, Eating Behavior, Physical Ability and Locomotion of Children Aged 5 Years in Siheung-city
Se-Hee Pyo, Hyun-Joo Kang
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(5): 760. CrossRef
- Pilot evaluation of a cooking-based nutrition education program to promote vegetable intake among children in Seoul, South Korea: a single-group pre–post study
- 1,737 View
- 8 Download
- 14 Crossref

- [English]
- Beliefs Regarding Vegetable Consumption, Self-Efficacy and Eating Behaviors according to the Stages of Change in Vegetable Consumption among College Students
- Yun Ahn, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(1):1-13. Published online February 29, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to examine beliefs, self-efficacy and eating behaviors by the stages of change in vegetable consumption among college students (n = 297). A survey was conducted to examine study variables, and subjects were categorized into three groups based on the stages of change: precontemplation/contemplation stage (PC/C), preparation stage (P), action/maintenance stage (A/M). Subjects had 3.7 servings of vegetables a day, and vegetable consumption was significantly different by stages of change (p < 0.001). The A/M group showed higher score on beliefs regarding vegetable consumption (p < 0.001) than the other groups, and perceived benefits of vegetable consumption (e.g. cancer prevention) more strongly (p < 0.05). The PC/C group felt more barriers than the A/M group, such as disliking cooking methods, texture of vegetables (p < 0.001), bad taste and bad experience of eating vegetables (p < 0.05). Self-efficacy score was 27.2, with decreasing self-efficacy from A/M to P, PC/C (p < 0.001). The A/M group showed more confidence in nine behaviors such as "eating vegetables during meals" and "replacing menu at home with more vegetable dishes" (p < 0.001) than the other groups. The A/M group had more desirable eating behaviors (e.g, having a variety of foods, eating regularly, consumption of food groups). This study suggests that target population for education and educational strategies be different based on the stages of change. For those in the PC/C stage, education might focus on reducing barriers and increasing self-efficacy. For those in the A/M stage, it is necessary to use strategies to maintain and reinforce behaviors for enough vegetable consumption.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Outcome expectations, self-efficacy, eating environment, and eating behaviors by the stages of change in adequate sodium intake among university students: a cross-sectional study
Yeon Gyu Im, Kyung Won Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(5): 382. CrossRef - Barriers influencing purchase behaviour of green personal care products – integrating innovation resistance theory perspective and stages of change model
Marta Szaban, Magdalena Stefańska
Economics and Environment.2023; 85(2): 420. CrossRef - Investigation of Millennials' Perception of Vegan Trends and Future Needs
Eun-Hye Song, Bok-Mi Jung
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(5): 373. CrossRef - Psychosocial factors and eating behaviors according to the stages of change in nutrition management among elementary and middle school athletes
Ji Yeon Kim, Seong Suk Cho, Kyung Won Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2021; 15(6): 732. CrossRef - Comparative Study of Eating Habits and Lifestyle by Gender among College Students in Pyeongtaek Region
Seo Hyeon Ahn, Seong Yeong Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2020; 30(2): 117. CrossRef - Dietary Life, Vitamin D Status and Blood Clinical Indices of University Laboratory Workers
Jung Hyun Hwang, Hong Mie Lee, Jung Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(3): 245. CrossRef - Factors affecting preference of vegetable in elementary school students: based on social cognitive theory
Su Hyeon Cha, Ho Kyung Ryu
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(3): 285. CrossRef - Relationship between Bone Density, Eating Habit, and Nutritional Intake in College Students
Hee-Sook Lim, Sung-In Ji, Hyeonji Hwang, Jeongmmok Kang, Yoon-Hyung Park, Hae-Hyeog Lee, Tae-Hee Kim
Journal of Bone Metabolism.2018; 25(3): 181. CrossRef - Factors affecting vegetable preference in adolescents: stages of change and social cognitive theory
Taejung Woo, Kyung-Hea Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2017; 11(4): 340. CrossRef - Coffee consumption behaviors, dietary habits, and dietary nutrient intakes according to coffee intake amount among university students
Sun-Hyo Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(3): 270. CrossRef - Gender Differences in Adolescents' Dietary Perceptions and Practices
Taejung Woo, Hye-Jin Lee, Kyoung Ae Lee, Seung Min Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(2): 165. CrossRef - Comparison of Dietary Self-efficacy, Obesity Stress, and Obesity-related Quality of Life According to BMI and Stages of Change in Vegetable Consumption for Nursing Students
Myoung Sook Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2015; 21(1): 65. CrossRef - A comparison of Dietary Habits and Influencing Factors for Vegetable Preferences of Adolescents in Gyeongnam Province
Suhyang Kwak, Taejung Woo, Kyoung Ae Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(4): 259. CrossRef - Factors associated with nutrition label use among female college students applying the theory of planned behavior
Hyun Jeong Lim, Min Ju Kim, Kyung Won Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2015; 9(1): 63. CrossRef - Nutrition knowledge, outcome expectations, self-efficacy, and eating behaviors by calcium intake level in Korean female college students
Min Ju Kim, Kyung Won Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2015; 9(5): 530. CrossRef - Nutrition knowledge, eating attitudes, nutrition behavior, self-efficacy of childcare center foodservice employees by stages of behavioral change in reducing sodium intake
Yun Ahn, Kyung Won Kim, Kyungmin Kim, Jinwon Pyun, Ikhyun Yeo, Kisun Nam
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(5): 429. CrossRef - Study on the Salt-Related Dietary Behaviors according to the Stage of Change Model for Salt-Related Intake of Middle School Students in Gyeongsangbuk-do Area
So-Young Park, Kyung-A Lee
Korean journal of food and cookery science.2014; 30(6): 687. CrossRef - Factors influencing on intention to intake fruit: moderating effect of fruit intake habit
Hyesoo Kim, Sunhee Seo
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2014; 47(2): 134. CrossRef - Comparison of practice of dietary guidelines and health beliefs according to stage of weight loss behavior change among male workers
Su Jeong Song, HongSeok Ahn, Jinmo Khil
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2013; 46(3): 276. CrossRef - Study on the Eating Habits and Practicability of Guidelines for Reducing Sodium Intake according to the Stage of Change in Housewives
So-Hyun Ahn, Jong-Sook Kwon, Kyungmin Kim, Jin-Sook Yoon, Baeg-Won Kang, Jong wook Kim, Seok Heo, Hea-Young Cho, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(6): 724. CrossRef
- Outcome expectations, self-efficacy, eating environment, and eating behaviors by the stages of change in adequate sodium intake among university students: a cross-sectional study
- 1,500 View
- 5 Download
- 20 Crossref

- [English]
- Evaluation of Nutrition Education for Hypertension Patients Aged 50 Years and Over
- Eun Hye Moon, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(1):62-74. Published online February 28, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.1.62
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was designed to implement and evaluate a nutrition education program for hypertensive patients aged between 50 and over. Nutrition education consisted of four sessions and, 35 out of 51 patients completed all education sessions at the public health center. To assess program effectiveness (effectively), data about blood pressure, blood cholesterol, anthropometry, nutrition knowledge, eating behavior and dietary intake were collected before and after nutrition education. Data were analyzed using SAS package (ver. 9.2) and significant difference was evaluated by paired t-test, x2-test and Wilcoxon signed rank test. Blood cholesterol was significantly reduced from 200.7 mg/dL to 188.7 mg/dL after nutrition education, although there were not significant changes in blood pressure or blood triglyceride level. Weight (p < 0.05), % body fat (p < 0.001), BMI (p < 0.05) were significantly reduced, especially in women, after nutrition education. Nutrition knowledge was increased significantly (p < 0.05), and some eating behaviors such as 'having fruits & vegetables for snack' and 'having brown rice, barley rice than white rice' were improved after nutrition education (p < 0.05). Sodium intake was reduced from 3,888.9 mg/day to 3,157.4 mg/day after nutrition education (p < 0.05). Except protein and iron intakes, the nutrient intake of hypertensive patients was much below the recommended level for Koreans. Dietary intakes of most of nutrients were not significantly different between pre-test and post-test. It appeared that nutrition education for the aged hypertensive patients was effective in reducing the percentage of % body fat and BMI, increasing the nutrition knowledge and some dietary behaviors. This nutrition education can be implemented at public health centers or senior centers for hypertensive patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pengaruh Pemberian Edukasi Terhadap Pengetahuan Hipertensi Peserta Prolanis Perempuan Di Puskesmas Brambang, Kabupaten Jombang
Finda Istiqomah, Ali Iqbal Tawakal, Chika Dewi Haliman, Dominikus Raditya Atmaka
Media Gizi Kesmas.2022; 11(1): 159. CrossRef - Effect of nutrition education in reducing sodium intake and increasing potassium intake in hypertensive adults
You-Sin Lee, Moo-Yong Rhee, Sim-Yeol Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2020; 14(5): 540. CrossRef - Effects of nutrition education on cardio-metabolic outcomes: A randomised clinical trial
Hildemar Dos Santos, W Lawrence Beeson, Gina Segovia-Siapco, Brenda Koranda, Tony Jehi
Health Education Journal.2020; 79(4): 458. CrossRef - Effect of a public health center-based nutrition education program for hypertension in women older than 50 years of age
Seoyun Park, Jong-Sook Kwon, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(3): 228. CrossRef - The Effect of Health Coaching Programs on Self-Efficacy, Health Behaviors, and Quality of Life in Hypertensive People Living in Poverty
Sun Ok Eom, Insook Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(3): 380. CrossRef - General Characteristics, Self-Efficacy, and Diet Control of Hypertension Patients at a Diabetes Admission Control Center in the Jeollanma-do Area
Su Jeong Yeo, In Woo Shin, Bok Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2015; 26(4): 731. CrossRef - Dietary Life related to Sodium of Participants in Hypertension and Diabetes Preventive Education at the Public Health Center
Hee-Ok Pak, Chun-Young Sohn, Jung-Hwa Park
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2015; 28(2): 219. CrossRef - Nutrition knowledge, eating attitudes, nutrition behavior, self-efficacy of childcare center foodservice employees by stages of behavioral change in reducing sodium intake
Yun Ahn, Kyung Won Kim, Kyungmin Kim, Jinwon Pyun, Ikhyun Yeo, Kisun Nam
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(5): 429. CrossRef - Sodium Related Recognition, Dietary Attitude and Education Needs of Dietitians Working at Customized Home Visiting Health Service
Yun-Jeong Mo, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(6): 558. CrossRef - The Effect of the Telemedicine Service System Application for the Patients with Hypertension at Community Health Practitioner Posts in Gangwon Province
Myung Soon Kwon, Ghee-Young Noh, Jounghwa Choi
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2014; 31(2): 55. CrossRef - The Effects of Low-sodium Diet Education Program on Dietary Habits, Diet Quality and Obesity Index in Overweight and Obese Middle-aged Women
Soo Bin Jeong, Seoyun Park, Sohyun Ahn, Jin Nam Kim, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(6): 513. CrossRef - Development of Nutrition Education Program for Consumers to Reduce Sodium Intake Applying the Social Cognitive Theory: Based on Focus Group Interviews
So-Hyun Ahn, Hye-Kyeong Kim, Kyung Min Kim, Jin-sook Yoon, Jong Sook Kwon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(4): 342. CrossRef - Effects of nutrition education on nutrition-related knowledge, dietary habits, and nutrient intakes of alcoholic patients
An Na Kim, Hyeon-Sook Lim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2014; 47(4): 277. CrossRef - Effects of Dietary Education on Low-sodium Diet Adaptation
Hae Young Kim, Juhyeon Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Culture.2014; 29(2): 212. CrossRef - An Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Nutrition Counseling for Adults with Risk Factors for Dyslipidemia
Tae Young Nam, Jung Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(1): 27. CrossRef - Blood Pressure, Sodium Intake and Dietary Behavior Changes by Session Attendance on Salt Reduction Education Program for Pre-hypertensive Adults in a Public Health Center
Eun-Jin Jung, Jong-Sook Kwon, So-Hyun Ahn, Sook Mee Son
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(6): 626. CrossRef - Effects of a Comprehensive Lifestyle Improvement Program for Middle-aged Women with Cardio-cerebrovascular Disease-related Risk Factors
Mi-Kyoung Park, Jeong-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2013; 24(2): 111. CrossRef - The Effect of Sodium Reduction Education Program of a Public Health Center on the Blood Pressure, Blood Biochemical Profile and Sodium Intake of Hypertensive Adults
Eun Jin Jung, Sook Mee Son, Jong-Sook Kwon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(6): 752. CrossRef - Development of Nutrition Education Program for Hypertension Based on Health Belief Model, Applying Focus Group Interview
Seoyun Park, Jong-Sook Kwon, Cho-il Kim, Yoonna Lee, Hye-Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2012; 17(5): 623. CrossRef - Effects of Nutritional Education Practice Program for Cardiocerebrovascular High-risk Group at the Education Information Center
Hang Me Nam, Seung Hee Woo, Young Ji Cho, Yun Jung Choi, Su Yeon Back, So Yeon Yoon, Jin Young Lee, Jung-Jeung Lee, Hye Jin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2011; 16(5): 580. CrossRef
- Pengaruh Pemberian Edukasi Terhadap Pengetahuan Hipertensi Peserta Prolanis Perempuan Di Puskesmas Brambang, Kabupaten Jombang
- 1,491 View
- 6 Download
- 20 Crossref

- [English]
- Nutrition Label Use, Self-Efficacy, Snacking and Eating Behavior of Middle School Students in Kyunggi Area
- Seo Yeon Ko, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(4):513-524. Published online August 31, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was designed to examine nutrition label use, self-efficacy, snacking and eating behaviors of middle school students, and to investigate if these characteristics were different by nutrition label use. A cross-sectional survey was conducted to 348 middle school students in Kyunggi, Korea. About a third of subjects read nutrition labels when they purchased snacks/packaged foods. Most nutrition label users were interested in reading information on calories, fat and trans-fat. Self-efficacy of eating/selecting snacks or general nutrition behavior was moderate (mean score: 44.4 out of 60), with significantly higher score in nutrition label users compared to nonusers (p < 0.001). Nutrition label users felt more confident in 9 items out of 15 items of self-efficacy, such as "taking fruits instead of cookies/candy for snack" (p < 0.001), "choosing milk instead of soft drink" (p < 0.01), "not having snacks after dinner" and "avoiding processed foods for snacks" (p < 0.05). Subjects had snacks 1.3 times a day, and nutrition label nonusers consumed snacks more frequently than the counterparts (p < 0.01). About 55% of nutrition label users and 64.7% of nonusers mainly purchased snacks for themselves (p < 0.05). Commonly purchased snacks by adolescents were ice cream, cookies/chips, breads and ramen. Major considerations in purchasing snacks were taste (46.9%) and price (34.6%). In selecting snacks, the influence of friends and parents was greater than the other sources. Based on eating frequency of snacks, nutrition label users were more likely to consume healthy snacks, such as fruit juices, vegetables, milk, yogurt, and potato/sweet potato than nonusers (p < 0.05). Eating behaviors measured by 15 items scored 33.6 out of 45. Nutrition label users showed better eating behaviors, such as "eating meals slowly", "eating foods cooked with plant oil", and "eating out less frequently" (p < 0.05). Study results showed that majority of adolescents did not read nutrition labels, selected snacks for themselves and had somewhat unhealthy foods for snacks. This study also showed the differences in self-efficacy, snacking and eating behaviors between nutrition label users and nonusers. In nutrition education, it is necessary to stress the importance and skills for reading nutrition labels. It is also needed to help adolescents to select healthy snacks and have desirable eating behaviors, as well as increasing self-efficacy.
- 437 View
- 6 Download

- [English]
- Intakes and Beliefs of Vegetables and Fruits, Self-Efficacy, Nutrition Knowledge, Eating Behavior of Elementary School Students in Kyunggi Area
- Soo Young Na, Seo Yeon Ko, Sun Hee Eom, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(3):329-341. Published online June 30, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to examine vegetable & fruit (V/F) intakes, beliefs and self-efficacy regarding V/F consumption, nutrition knowledge and eating behavior of elementary students. A survey was conducted to the 4th graders (n = 234) at two elementary schools in Guri, Kyunggi-do. About one-fourth of subjects were overweight or obese. Subjects had 4.2 servings of V/F a day, consuming 340.2 g of V/F. Girls consumed significantly more amounts of vegetables than boys (p < 0.05). Girls were more favorable regarding V/F consumption (p < 0.01), and believed more strongly on advantages of having V/F such as "good for skin", constipation prevention (p < 0.001) and cancer prevention (p < 0.05). Boys felt more strongly in disadvantages or barriers of eating V/F, including mother's cooking time constraints (p < 0.01), lack of past experience of eating V/F, and family members' disliking of V/F (p < 0.05). Girls felt more confident in eating V/F (p < 0.05) than boys; they also felt more confident in specific items of "eating fruits/salads instead of cookies/chips for snack" and "eating fruit juice/vegetable juice instead of soda" (p < 0.01). Subjects showed low level of nutrition knowledge, especially in items such as balanced meals, recommended servings of V/F and vitamin deficiency. Compared to boys, girls had more desirable eating behavior such as eating adequate amount of meals (p < 0.001), having a variety of foods, eating fruits daily, and having fatty foods less frequently (p < 0.05). Intakes of Ca and K were quite below the recommended level, while the intakes of protein, Na and vitamin A intake were much above the Dietary Reference Intakes (DRI) for 9-11 old children. Nutrient intakes expressed as %DRI was higher in girls for vitamin A (p < 0.01), energy and riboflavin (p < 0.05). High V/F consumption group (> or = 5 servings of V/F a day) compared to the counterparts showed higher self-efficacy and had better eating behaviors. Nutrition education for children should focus on increasing consumption of V/F, by helping them to increase self-efficacy for eating V/F and to recognize the benefits and reduce the barriers of eating V/F, especially in boys. It is also needed to provide nutrition information for balanced meals or increasing V/F consumption, and help the children to adopt desirable eating behavior.
- 452 View
- 2 Download

- [English]
- Evaluation of Nutrition Education for Diabetes Mellitus Management of Older Adults
- Hyun Joo Kang, Eun Mi Shin, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(6):734-745. Published online December 31, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Diabetes mellitus is the prevalent disease among older adults. The purpose of this study was to implement and evaluate the nutrition education program for diabetes mellitus patients aged 60 and over. The one group pretest and posttest design was employed to evaluate the program effectiveness. Nutrition education program for diabetes mellitus patients was carried out at the public healthy center in Guri city. The 38 out of 63 patients completed education program. They received four sessions of group education during four weeks. Nutrition education materials (booklet, leaflet) for older adults were provided to participants. Data about blood glucose, blood pressure, nutrition and diabetes mellitus knowledge, dietary behavior, dietary intake by 24-hour recalls were collected before and after nutrition education to evaluate the program effectiveness. All data were statistically analyzed using SAS package (ver.8.2) and significant difference was evaluated by chi-square-test, paired t-test and Wilcoxon signed rank test. Study results showed that blood pressure and blood glucose were slightly decreased after nutrition education but they did not reach statistical significance. There were positive changes in nutrition knowledge and dietary behavior. The total score of nutrition and diabetes knowledge increased significantly (p < 0.001), and the total score of dietary behavior was improved (p < 0.05) after nutrition education. Dietary intakes of most of nutrients examined were not significantly different between preand post-test. Based on study results, it appears that nutrition education program for the aged diabetes mellitus patients might effectively increase nutrition knowledge, dietary behavior and diet quality. This nutrition education program can be used at the public health centers or senior centers for the management of diabetes mellitus for older adults.
- 425 View
- 14 Download

- [English]
- Evaluation of a Nutrition Education Program for Elementary School Children
- Yun Ahn, Seo Yeon Ko, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(3):266-276. Published online June 30, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to implement and evaluate the nutrition education program for elementary school children. Subjects were 5th graders (n = 142) of an elementary school in Seoul, and 138 children completed four sessions of nutrition education during March-April, 2008. One group pretest-posttest design was used to evaluate the program effectiveness. Anthropometric measurements and measurements on nutrition knowledge, eating attitudes and eating behavior were done before and after education. Data were analyzed using paired t-test, t-test and chi-sqaretest. After completing nutrition education, body mass index (from 19.3 to 18.9), fat mass (from 10.9 kg to 10.1 kg), percent body fat (from 25% to 23.3%) of subjects decreased significantly (p< 0.001). Percentages of overweight or obese children were 24.6% at pretest and decreased to 20.3% at posttest, although it did not reach statistical significance. Total score of nutrition knowledge increased significantly from 11.9 (59.5/100) at pretest to 14.7 (73.5/100) at posttest (p< 0.001). After nutrition education, percentages of correct answers increased significantly in 10 knowledge items out of 20 items. These included items such as desirable weight control, energy requirements for boys, food groups, snack, and function of fat and balanced meals (p< 0.001). Total score of eating attitudes increased significantly from 35.1 to 36.9 (p< 0.001). Attitude of applying nutrition knowledge to daily life (p< 0.001), interest toward nutrition and health (p< 0.001), attitude of moderating food intake (p< 0.01), and attitude toward eating habit and future health (p< 0.05) were significantly different between pretest and posttest. Total score of eating behaviors increased significantly from 46.7 (possible score: 20-60) to 49.5 by nutrition education (p< 0.001). Improvement in eight eating behaviors were noticed after nutrition education. These included eating meals slowly, eat protein foods (p< 0.001), eating breakfast, eating meals regularly, eating meals with diverse foods, having dairy foods, eating foods using plant oils (p< 0.01), and having grains (p< 0.05). Subjects evaluated quite positively in attractiveness of program, understanding of program contents, helpfulness of program in improving nutrition knowledge and meal management. Study results show that the nutrition education program was effective in improving nutrition knowledge, eating attitudes and changing eating behaviors of children. This program can be used in nutrition education of children at school or at public health centers
- 502 View
- 19 Download

- [English]
- Nutrition Knowledge and Eating Behaviors of Elementary School Children in Seoul
- Na Young Jeong, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(1):55-66. Published online February 28, 2009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was aimed to examine nutrition knowledge, dietary attitudes, and eating habits of elementary school students and to examine if their characteristics differ by gender. Subjects were 5th and 6th graders of an elementary school (n = 317) in Seoul, and the survey was done during July 2007. Mean height, weight, BMI of subjects was 148.1 cm. 41.7 kg, 19.0, and 14.3% of subjects were categorized as the overweight/obese group. Anthropometric data were not significantly different by gender. Mean score of nutrition knowledge was 14.9 out of 20 showing moderate knowledge levels, and girls scored higher on nutrition knowledge than boys (p < 0.05). Subjects showed knowledge deficit in areas such as nutrients, food groups and specific weight control information. The percentages of correct answers regarding meals for brain function were significantly higher in girls than in boys (p < 0.05). They got nutrition information mainly from mass media and family/relatives. The mean score of dietary attitudes was 41.2 (possible score: 10-50) indicating somewhat positive attitudes, and the score of eating behaviors was 34.8 (possible score: 15-45). Subjects showed problems in eating habits such as having unbalanced diets and snack foods. 82.6% of subjects had unbalanced meals, and these percentages were higher in girls (87.2%) than in boys (78.1%, p < 0.05). Vegetables and fish/shellfish were the most disliked foods. Specific eating behaviors, such as eating slowly, eating grains and having processed foods less frequently, were better in girls than in boys (p < 0.05). Results also showed that majority of subjects need to improve specific behaviors including having diverse foods, eating meals slowly, having meals at regular times, having adequate foods in each food groups, and eating sweets or salty foods less frequently. Only 52.7% of subjects perceived their body images as normal, and 56.4% had experience of weight control. Reasons for weight control were different by gender (p< 0.05). Based on these findings, nutrition education for school children should focus on modifying eating habits or eating behaviors, by suggesting practically applicable methods and providing nutrition information that is interesting and suitable to school-aged children.
- 435 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Interview Survey of Elementary School Students'Nutrition Education and Practice
- Yu Jin Oh, Young Mee Lee, Jung Hyun Kim, Hong Seok Ahn, Jeong Weon Kim, Hae Ryun Park, Jung Sook Seo, Kyung Won Kim, O Ran Kwon, Hye Kyoung Park, Eun Ju Lee, Huy Ni Sung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2008;13(4):499-509. Published online August 31, 2008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated the experience and practice of elementary school students on nutrition education. The data were collected from 217 male and female students attending 5-6th grade elementary schools in Seoul and Kyunggi-Do from March to June 2007, interviewing face to face by a nutrition teacher and 3 interns of a nutrition teacher. The results were as follows: 86.5% of the subjects learned about 'Table etiquette', 'Reasons for eating fruits and vegetables'(78.7%), 'Food waste and environment'(72.3%), 'Healthy snacks'(55.7%), 'Food sanitation'(52.3%), 'Food culture of foreign countries'(48.1%). Nutrition education experience was significantly different by gender. A total of 43.5% boys responded that they never learned about 'basic food preperation'(p < 0.01). They had learned 'Nutrients for body'and 'Food waste and environment'in school, 'Healthy weight loss', 'Food culture of foreign countries', 'Food circulation'on television, Most content ('Table etiquette', 'Simple cooking', 'Food sanitation', 'Eating behaviors for health', 'Reasons for eating fruits and vegetables', 'Healthy snacks') was learned from parents. The practice after nutrition education was higher in 'Table etiquette'(2.14), 'Eating fruits and vegetables'(2.07) than others compared with education experience. The most reason of non-practice on nutrition information was 'Troublesome'. In 'Nutrients for body', a boy answered 'Difficult for practice'20.0%, a girl answered 'Difficult to understand'32.6%, showing a significant difference between the gender groups (p < 0.001). They remembered the 'Nutrients for body'(49.6%), 'Food sanitation'(44.5%) because of 'important content', 'Basic food preparation'(40.6%), 'Food culture of foreign countries'(36.3%) because of 'interesting content', 'Healthy weight loss'(52.0%), 'Eating behavior for health'(44.5%) and 'Healthy snacks'(33.7%) because of 'need for my health'.
- 446 View
- 5 Download

- [English]
- Fast Food Consumption and Related Factors among University Students in Daejeon
- Kyung Won Kim, Yun Ahn, Hyung Mee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2004;9(1):47-57. Published online February 29, 2004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The study purpose was to investigate the factors related to fast food consumption of university students. Factors were identified using the Theory of Planned Behavior. Based on the pilot study, 18 behavioral beliefs, 7 normative beliefs and 19 control beliefs were identified. Data (n = 269) were analyzed using analysis of variance or chi-square tests. Subjects were categorized into non-users (27.9%), users (42%) and frequent users ( > or = 2 times/week, 30.1%). Regarding behavioral beliefs, users or frequent users responded more positively on advantages of eating fast foods including 'taste' (p < 0.001), 'making me feel full' (p < 0.001), 'diverse menus' (p < 0.05) than non-users. Compared to users, non-users responded more positively on the item that eating fast foods leads to eat vegetables less (p < 0.05), and negatively on 'making me eat more salt'(p < 0.05). Most of the referent groups, parents (p < 0.001), sisters/brothers (p < 0.01), relatives (p < 0.01), friends (p < 0.05), boy/girl friends (p < 0.05) were important sources of influence regarding subjects' fast food consumption. Users or frequent users felt less control over factors or situations that make it consume fast foods (9 out of 19 control beliefs). These factors included; availability issues (p < 0.001), 'not having other foods on hand'(p < 0.01), 'others eating together like fast foods', 'convenience', 'social increase in fast food use', 'easy to get fast foods anytime' (p < 0.05). In addition, users of fast foods were more likely to eat fast foods when they don't have time, when they do not like to cook, when they feel hungry (p < 0.05). These results suggest that interventions for university students include strategies to moderate fast food use by modifying behavioral beliefs, suggesting alternative menus and behavior modification techniques, increasing perception of control, and eliciting social support.
- 483 View
- 18 Download

- [English]
- Psychosocial Factors Related to Dairy Product Consumption among Female University Students in Daejeon
- Eun Mi Shin, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2003;8(6):867-875. Published online December 31, 2003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate the psychosocial factors influencing dairy product consumption of female university students in Daejeon. The Theory of Planned Behavior provided the basis for this study. As a result of the pilot-study, 18 behavioral beliefs, 8 normative beliefs, and 12 control beliefs were identified. The subjects (n = 236) were grouped into a high-consumption group (1 serving / day, n = 117) and a low consumption group (< 1 serving / day, n = 119). The data were analyzed using t-tests or chi-square-tests. Among the general characteristics, there were significant differences in the amount of pocket money spent per month, residence type (p < 0.01), weight, frequency of exercise and perceived health status (p < 0.05) of the subjects. With respect to the 18 behavioral beliefs, the high consumption group responded less negatively on 'eating dairy foods would not be convenient' than the low consumption group (p < 0.05). None of the subjective normative items were significantly different between the two groups. However, notable differences were found in regard to the control beliefs (8 out of 12 control beliefs). These included overall control over consuming dairy products (p < 0.001), as well as specific beliefs regarding barriers such as easy spoilage of dairy products, the cost, eating them for snacks and dislike for them (p < 0.05). In addition, specific situations, such as 'when I want them I get them' (p < 0.01), eating out and the availability of dairy foods at home (p < 0.05) were significantly different between the two groups. The high consumption group showed more control over these barriers or situations. These results suggest that nutritional education for young female adults should incorporate strategies to increase their perceived control over the consumption of dairy products by removing barriers and including environmental approaches which address the availability issues.
- 440 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Using the Theory of Planned Behavior to Explain Dairy Food Consumption among University Female Students
- Kyung Won Kim, Eun Mi Shin
- Korean J Community Nutr 2003;8(1):53-61. Published online February 28, 2003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was designed to explain the intentions and consumption of dairy foods among university female students. The factors related to intentions of consumption or actual consumption of dairy foods were identified within the theory of planned behavior. The survey questionnaire, developed using open-ended questions (n = 35), was administered to university female students (n = 184). Subjects completed information regarding attitudes, subjective norms, perceived control, intentions and consumption of dairy foods. Correlation analysis and multiple regression were used to study the association of factors with intentions and consumption of dairy foods. Subjects showed relatively low intention to consume dairy foods (- 0.4 +/- 1.6 from a scale of - 4 ~ + 4). They ate 1.2 +/- 0.9 servings of dairy foods a day and 52.2% of subjects had less than a serving a day, showing inadequate consumption of dairy foods. All three factors, attitudes, subjective norms and perceived control were significantly correlated to the intentions to take dairy foods regularly (r = 0.26 - 0.27). Multiple regression results, however, revealed that subjective norms (p < 0.01) and perceived control (p < 0.05) contributed to the model of explaining intentions, while attitudes did not (model R2 = 0.154). To predict and explain actual consumption of dairy foods, two regression models were examined. In the first model, perceived control was significant in predicting dairy foods consumption, while attitudes and subjective norms were not. In the second model, intentions and perceived control were significantly related to actual consumption of dairy foods, providing the empirical evidence of the theory (model R2 = 0.121). These results suggest that perceived control was significant in explaining actual behavior as well as intentions. This study suggests that nutrition education to increase dairy foods consumption for young adults should focus on increasing perception of control and eliciting social support from respected others.
- 458 View
- 3 Download

- [English]
- Development and Validation of a Computerized Semi-Quantitative Food Frequency Questionnaire Program for Evaluating the Nutritional Status of the Korean Elderly
- Hae Jeung Lee, Seon Joo Park, Jung Hee Kim, Cho Il Kim, Kyung Ja Chang, Kyeong Sook Yim, Kyung Won Kim, Hay Mie Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2002;7(2):277-285. Published online April 30, 2002
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to develop a semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire (SQ-FFQ) for subjects aged 50yr and over and to evaluate the validity of this SQ-FFQ. Dietary intake was assessed using SQ-FFQ that included 98 commonly consumed flood items selected from the results of the Korean Health and Nutritional Survey, 1998. Subjects (n = 2,660) aged 50yr and over were recruited from 7 metropolitan cities and 8 small cities. Each subject was interviewed using this SQ-FFQ developed in our laboratory and 24hr-recall method. Excluding incomplete data, Data from 1,149 subjects were used in this validity study. The nutrient intakes assessed by this SQ-FFQ were validated by comparing with the results from 1 day 24-hour recalls. Pearson's correlation coefficients between two methods were 0.71, 0.64, 0.53, and 0.43 for energy, carbohydrate, protein, and fat, respectively for all subjects. Spearman's correlation coefficients were higher than those of Pearson's correlation coefficients. Kappa values for energy, carbohydrate, protein, and fat were 0.79, 0.72, 0.70, and 0.64, respectively. The percentage for misclassification of the lowest quartile into the highest quartile or vice versa was 1.25-1.39% for all nutrients. Therefore, this SQ-FFQ seems to be useful in assessing the nutritional status of the middle-aged and elderly subjects in Korea.
- 396 View
- 9 Download

- [English]
- A Study on nutrition Knowledge, Nutritional Attitudes, Dietary Behavior and Dietary Intake by Weight Control Attempt among Middle School Female Students
- Kyung Won Kim, Eun Mi Shin
- Korean J Community Nutr 2002;7(1):23-31. Published online February 28, 2002
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate weight control attempts and related factors among 209 middle school female students in Daejeon. Variables examined were body satisfaction, beliefs regarding weight control, body image, nutrition knowledge, nutritional attitudes, dietary behavior and dietary intake. A cross-sectional survey was employed, and data was analyzed using t-test and chi-square teat (at alpha=0.05). The average height, weight, and body fat (%) of subjects were 160.2 cm, 52.4 kg, and 25.9%, respectively. Those who attempted weight control were 61.7% of the samples, suggesting that weight control was quite popular among adolescents. Students in the weight control attempt group were more satisfied with their body size (p<0.001), and showed more distorted body image than those in the no weight control attempt group (p<0.001). Most of beliefs regarding weight control were also different in the two groups. The attempt group believed more strongly in the advantages of weight control, and believed less strongly in the harmful effects or difficulties associated with weight control. Although there were no differences in nutrition knowledge in the two groups, nutritional attitudes were slightly more favorable in the attempt group (p<0.01). In contrast, eating behaviors, such as those related to caloric intake (p<0.001), body image (p<0.001), and specific situations (p<0.01) were more desirable in the no-attempt group than in the attempt group. In addition, dietary intake of the attempt group was less adequate than that of the no-attempt group for nutrients such as iron (p<0.01), vitamin A, thiamin, riboflavin, and vitamin C(p<0.05). This study suggests that adolescents who attempt control weight have a more distorted body image and inadequate diet and showed more undesirable eating behaviors. Students should be taught and practice desirable methods of weight control. Educational programs should also include strategies for changing beliefs regarding weight control, as well as modifying diets and eating behaviors.
- 376 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Development of a Website-Based Nutrition Education Program for Female College Students and Young Women
- Kyung Won Kim, Hyun Joo Kang, Kyung A Kim, Se Hwa Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2001;6(4):657-667. Published online October 31, 2001
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was designed to develop a website for providing nutrition information and education for college women and young women. The website focuses on two topics ; general nutrition and desirable weight control. This program is located at http : // www.ezydiet.co.kr. This program is composed of 5 major sections. The first two sections were designed to provide information ; one for general nutrition, and the other for providing information regarding weight control. The first section includes information regarding young adult women's diet, nutrition standards, such as the RDA or Korean Food Pyramid, drinking and smoking. The second section coveres information regarding desirable control, foods with high or low calories, eating disorders and popularly used dieting methods. The third section is for simple nutrition assessment, consisting of assessment of ideal body weight and obesity, energy requirements, and eating habits. The fourth section was designed to introduce and help users to apply behavioral modification techniques, such as monitoring, goal setting, stimulus control and reinforcement. The final section was designed for meal planning, by introducing a food exchange list and menu examples for one week. The characteristics of this web-based program are as follows ; 1) provide nutrition information systematically, 2) involve sections for the participation of the user, 3) include food pictures to help understanding of nutrition information, 4) include management modules for some sections to revise or update the information. One-hundred and ten female university students participated in the evaluation of this website. The evaluation results were favorable. About 90% of subjects rated that this program covers major topics 'well ' or 'very well', and that it was 'easy'to 'very easy'to understand the contents on website. Two-thirds of subjects rated quite positively on questions regarding attractiveness, overall quality and technical quality of website. In addition, about three-fourths of subjects answered that this website was helpful in increasing nutrition knowledge and in applying nutrition information into daily life. These results suggested the possibility of using a website as a means of providing nutrition information and education for young adult women.
- 358 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Dietary Intakes, Serum Lipids and Hematological Indices in Female Adolescent Smokers
- Jung Hee Kim, Hee Won Lee, Kyung Won Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 1999;4(2):149-156. Published online June 30, 1999
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was due to investigate the dietary intakes, serum lipids and other hematological indices in female adolescent smokers. The subjects were 85 smokers, whose average pack-year(smoking years on the basis of one pack of cigarettes per day) was 1.26 and 87 nonsmokers who were female high school students in Seoul. An anthropometric measreument was performed and % body fat was also analyzed by the Bioelectrical Impedance Fatness Analyzer(GIF-891). Dietary intakes and food habits were examined through questionnaires and nutrient intakes were analyzed by the Computer Aided. Nutritional analysis program for professional(CAN-pro). Serum TG, HDL-cholesterol and total-cholesterol levels were measured with test kits. Serum glucose, albumin, GOT and GPT were measured by automated dry chemistry system, SPOTCHEM 4410. Hemoglobin, hematocrit, RBC, WBC and MCV were determined by Semi Automated Microcell Counter(F-520). All data were statistically analyzed by SAS PC package program. There was no significant difference in the anthropometric measurements between smokers and nonsmokers. The caloric intake in adolescent smokers tended to be higher than that of nonsmokers but the difference was not statistically significant. In addition, there was no significant difference between smokers and nonsmokers in biochemical indices. Analysis of serum lipids showed that the serum levels of total-cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol of nonsmokers were unexpectedly significantly higher(p<0.05) than those of smokers. Overall results indicate that smoking itself with short pack-year in healthy female adolescent did not seem to influence apparent health and nutritional status.
- 414 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- A Study of the Obesity Index and Psychosocial Factors Influencing Obesity among Adolescent Girls
- Kyung Won Kim, Young Ah Kim, Jung Hee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 1997;2(4):496-504. Published online October 31, 1997
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate the dietary intake, obesity index and psychosocial factors influencing obesity among 200 high school girls in Seoul. The Social Cognitive Theory provided the Conceptual basis for this study. A cross-sectional survey was conducted to examine factors related to obesity, including self-efficacy for controlling overeating, social support for eating behavior, perception of body image and weight control, nutrition knowledge, and attitudes toward obesity. The data were analyzed using t-test and multiple logistic regression. The results of this study are as follows : 1) The mean age of the girls was 16.4 years, and the rate of overweight and obesity(measured by obesity index) was 27.0%. 2) The mean energy intake of subjects was 1832.3+/-384.0kcal. The energy derived from carbohydrates, proteins and fats was 62.7%, 13.8%, and 23.5%, respectively. There was no significant difference between the obese and the comparison group in energy intake. 3) The result of multivariate analysis indicated that obesity had a significant relation to the perception of ideal body image, social support for eating behavior, and self-efficacy for controlling overeating(p<0.01). As subjects preferred thinner body images(OR=0.39) and received less social support(OR=0.93), the odds of being classified as obese increased. The odds of being obese were also associated with self-efficacy, however, the relation was not strong(OR=1.04). 4) Specific social support was related to obesity among adolescent girls. As subjects received more support from family member, the odds of being obese decreased. The emotional support as well as family member's positive nutrition behavior plays a significant role. In addition, instrumental support from friends was associated with obesity. With repect to self-efficacy, the odds of being obese were increased as subjects felt less confident in controlling overeating when tempting food was placed in front of them or after an argument. In contrast, the obese group felt more confident in controlling overeating for the rest of the specific situations examined. These findings suggest that educational interventions for weight control should incorporate strategies to help participants realize their degree of obesity, to reduce the discrepancy between current and ideal body image, to elicit and maintain social support from friends and family, and to increase the self-efficacy for changing eating behaviors.
- 408 View
- 5 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



