Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [English]
- Ultra-processed food intake and dietary behaviors in Korean adolescents: a cross-sectional study based on the 2019–2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Jin-A Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(6):410-418. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00297
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
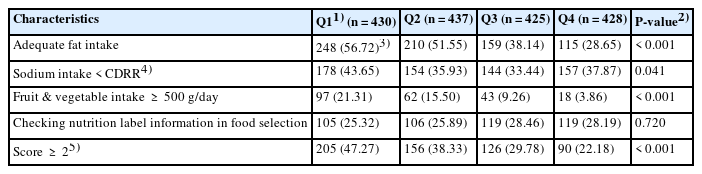
This study aimed to investigate the intake of ultra-processed foods (UPF) and dietary behaviors in Korean adolescents.
Methods
This study used 24-hour dietary recall data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2023). In total, 1,720 adolescents aged 12–18 years were included in this study and categorized into quartiles based on the percentage of energy intake from the UPF. Nutritional status, contributing subgroups of UPF intake, and healthy dietary practices were examined using Health Plan 2030 indicators across quartiles of UPF intake.
Results
The nutrient intake of protein, vitamins (A, B1, B2, niacin), and minerals (iron, potassium) was the lowest in the fourth quartile of UPF intake compared with the first quartile (P for trend < 0.001), whereas calcium intake increased across quartiles, from 47.68% in the first quartile to 58.51% in the fourth quartile (P for trend < 0.001). The main contributing subgroups to UPF intake differed across quartiles of UPF intake, and the highest contributing subgroups were ‘instant noodles and dumplings,’ ‘desserts, cakes, and ice cream,’ and ‘sauces and seasonings.’ Healthy dietary practices were the lowest in the fourth quartile (22.18%, P < 0.001), and the proportions of appropriate fat and fruit/vegetable intake were significantly lower in the higher quartiles of UPF intake (P < 0.001).
Conclusion
This study suggests that a lower UPF intake was associated with better nutritional status and healthy dietary practices in Korean adolescents. These findings provide fundamental evidence for promoting healthier food choices and balanced dietary practices.
- 162 View
- 9 Download

- [English]
- Healthy eating intentions among adults in China: a cross-sectional study of northern and southern regions and city tiers based on the theory of planned behavior
- Yi Jiang, Ji-Yun Hwang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2025;30(2):114-126. Published online April 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2025.00087
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The theory of planned behavior (TPB) has been widely employed to predict healthy eating intentions. Regional differences may affect dietary habits, health status, and personality traits, whereas variations in urbanization influence accessibility to fresh and healthy food, thereby impacting TPB components. This study aimed to explore whether regional differences between northern and southern China including city-tier development are associated with healthy eating intentions among Chinese adults.
Methods
The study included data from 2,114 Chinese adults aged 19–64 years collected between 2019 and 2023. Participants were categorized by geographic region (north or south) and city-tier status (first-tier or other).
Results
Compared to individuals from northern first-tier cities, those from southern regions exhibited stronger attitudes, perceived behavioral control (PBC), and intention to eat healthily. Participants from other cities in the north had more positive attitudes, subjective norms, PBC, and intentions to participate in healthy eating. Furthermore, residents of southern cities revealed weaker subjective norms than those of cities in the north. The adjusted odds ratio (OR) for compliance with intention to engage in healthy eating was higher among participants from other cities in both the north and south compared to those from northern first-tier cities (northern other cities: OR = 2.43, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.49–3.97, P < 0.001; southern other cities: OR = 1.95, 95% CI: 1.08–3.51, P = 0.027). No significant differences existed among the subjects from first-tier cities according to their geographic regions. These trends remained consistent even after including the interaction term between geographic regions and city-tier classification.
Conclusion
These findings underscore the complexity of regional variations influencing dietary intentions and indicate that tailored health promotion strategies should incorporate regional characteristics. Future research should explore underlying factors, including regional cultural influences, to better inform policies and interventions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Beyond taste: Unpacking the drivers of plant-based diet adoption
Md. Asaduzzaman Babu
Food and Humanity.2025; 5: 100779. CrossRef
- Beyond taste: Unpacking the drivers of plant-based diet adoption
- 1,656 View
- 31 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
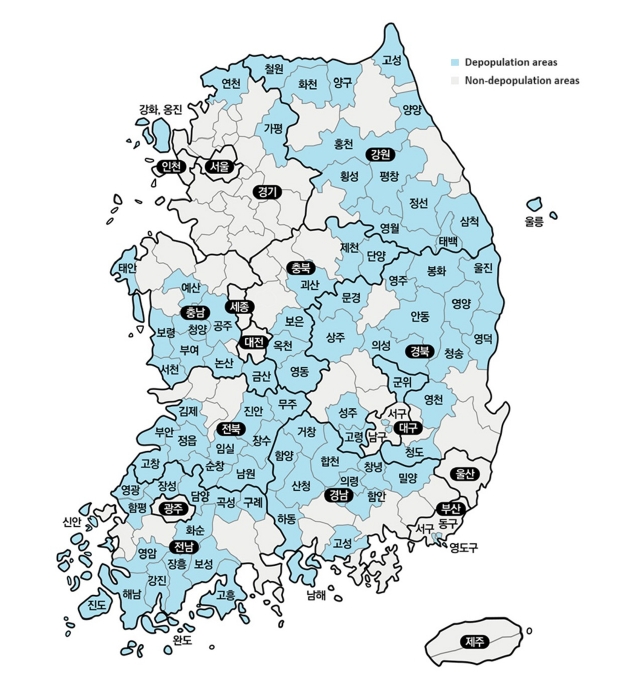
- Analysis of health behavior changes among residents in depopulation areas in Korea: a cross-sectional study based on Community Health Survey data from 2010 to 2019
- Miyong Yon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):348-357. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00001
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The total population of Korea began to decline in 2019; in particular, the population in rural areas has been rapidly decreasing and is aging. Therefore, the government has designated depopulation areas and is seeking ways to support them. To assess whether health disparities exist between areas with population decline and those without, this study used community health survey data to observe temporal changes in health behaviors between the two types of areas. Methods: The analysis used Community Health Survey data from 2010 to 2019, and regional classification was divided by depopulation areas designated by the Ministry of the Interior and Safety. Trends in health behavior and chronic disease prevalence between depopulation and non-depopulation areas were analyzed. All analyses were conducted using complex sample analysis procedures in SAS 9.4 software. Results: The smoking rate steadily decreased in both depopulation and non-depopulation areas, whereas the high-risk drinking rate increased slightly. The walking practice rate did not improve in depopulation areas compared to non-depopulation areas. Furthermore, nutritional labeling usage rate was consistently lower in depopulation areas than in non-depopulation areas, with the gap being the largest. The prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and hypertension showed that the gap between depopulation and non-depopulation areas is continuously increasing. Conclusions: Health behaviors in depopulation areas have not improved, and the prevalence of chronic diseases is increasing rapidly. Therefore, the demand for health care services that support healthy lifestyle practices and chronic disease management in these areas is expected to increase.
- 2,779 View
- 28 Download

- [Korean]
- Health behaviors and eating habits in people’s 20s and 30s according to food content usage level on social media: a cross-sectional study
- Seo-Yeon Bang, Bok-Mi Jung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(5):392-403. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.5.392
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was intended to investigate adults’ health behaviors and eating habits according to their levels of social media use.
Methods
From May 27 to July 11, 2022, an online survey was conducted of 452 male and female social media users in their 20s and 30s, and their eating habits and health behaviors were compared and analyzed according to their degree of social media use. For each of the three levels of food content use, the frequency of social media content use, and the total score range of average social media viewing time per day were divided into three parts, and a group with a score of less than 2 points was classified as low-use; a group with a score of 2 or more and less than 3 points was classified as middle-use; and a group with a score of 3 points or more was classified as high-use.
Results
The use of food content was higher in women than in men (P < 0.001), and higher in those in their 20s than in those in their 30s (P < 0.001). The group with a high level of food content use showed a higher rate of post-use hunger than the group with a low level (P < 0.01). The experience of eating after using food content was also higher in the group with a high level of use than in the group with a low level of use (P < 0.001). The group with a normal or high level of food content use had more negative eating habits than the group with a low level.
Conclusions
The study highlighted the need to provide desirable food content to people in their 20s and 30s with negative eating habits and to promote them so that they can use the right healthy nutrition–related content. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The relationship between smartphone usage and eating behavior for elementary school students in Gangneung, South Korea: cross-sectional study
Minji Kim, Meera Jang
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(4): 278. CrossRef
- The relationship between smartphone usage and eating behavior for elementary school students in Gangneung, South Korea: cross-sectional study
- 3,846 View
- 106 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- Association between health financial capacity of local governments and health behaviors of local residents: a cross-sectional study
- Miyong Yon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2023;28(2):95-103. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2023.28.2.95
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The budget gap in the health sector of local governments affects the supply of health services, which can cause the health gap. This study classified local governments according to their financial characteristics, such as local financial independence and health budget level. It analyzed the health behaviors and disease prevalence of local residents to examine the effect of local government financial investment on the health of local residents.
Methods
To classify types according to the financial characteristics of local governments, financial independence and the health budget data for 17 local governments were collected from the local fiscal yearbook of the Ministry of Public Administration and Security. The prevalence of chronic diseases and healthy behavior was compared using the 16,333 data of adults between the ages of 30 and 65 years among the original data of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016–2020).
Results
Cluster analysis was used to classify local governments into five clusters according to the health financial capacity type. A comparison of the prevalence of local residents by cluster revealed a similar prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, and hypercholesterolemia. On the other hand, the obesity rate (P < 0.01), high-risk drinking rate (P < 0.01), aerobic physical activity rate (P < 0.001), and healthy eating practice rate (P < 0.001) were significantly different. In addition, an analysis of the odds ratio based on the Seoul area revealed a higher risk of health behavior of non-Seoul residents.
Conclusions
It is necessary to review the universal health promotion project budget considering the degree of regional financial vulnerability from the viewpoint of health equity to narrow the health gap among regions.
- 1,315 View
- 25 Download

- [English]
- A Comparative Study of the Dietary Behavior of Adults Aged 20 and Over according to the Mukbang Viewing Time
- Ha-Yan Nam, Bok-Mi Jung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(2):93-102. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.2.93
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to investigate the relationship between watching Mukbang (eating broadcasts) and dietary and health behavior in adults who watch Mukbang Methods: The questionnaire was administered on a self-written basis through online and offline formats to 800 adults (400 men and 400 women). The contents of the survey consisted of general characteristics, Mukbang viewing time per week, breakfast intake frequency, preference for menus when viewing Mukbang , delivery food intake frequency per week, late meal intake frequency per week, and health behavior. The subjects were divided into three groups according to Mukbang viewing time.
Results
The body weight of viewers was significantly higher whenMukbang viewing time was over 14 hours for both men and women. In particular, based on the BMI (body mass index), those who watched Mukbang for more than 14 hours were found to be overweight. People with more than 14 hours of Mukbang viewing time per week were found to prefer mostly carbohydrate-rich food and meat, while those with less than 7 hours of Mukbang viewing time per week showed a higher preference for vegetables and fruits. An analysis of the frequency of breakfast eaten showed that the rate of skipping breakfast was the highest for those who watched Mukbang for more than 14 hours per week, and the rate of eating breakfast daily was the highest in the case of fewer than 7 hours of viewing. In the case of high Mukbang viewing time per week, the frequency of food delivery and night eating was high. When Mukbang viewing time was high, the viewer’s interest in health was low and the frequency of exercising too was low.
Conclusions
Viewers with high Mukbang viewing time showed undesirable health and eating behavior. Thus, it is believed that proper nutrition education on improving eating habits and raising the awareness of correct eating habits is necessary for such viewers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between food-related media content and the eating behaviors of Korean adults according to household type
Ahyoung Yun, Hyein Jung, Byungmi Kim, Yoonjoo Choi
Frontiers in Nutrition.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Addictive symptoms of mukbang watching: A qualitative interview study using directed content analysis
Kagan Kircaburun, Filipa Calado, Andrew Harris, Mark D. Griffiths
Emerging Trends in Drugs, Addictions, and Health.2024; 4: 100147. CrossRef - Mukbang and Cookbang watching and dietary behavior in Korean adolescents
Jimin Sung, Jae-Young Hong, Jihong Kim, Jihye Jung, Seoeun Choi, Ji Yun Kang, Mi Ah Han
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(4): 523. CrossRef - Effects of watching Mukbang and Cookbang videos on adolescents’ dietary habits and mental health: cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Seung-Hee Hong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(2): 156. CrossRef - Mukbang watching in Iran: a brief report validating the Persian version of the mukbang addiction scale and its relationship with disordered eating decisions and habits
Reza Shabahang, Sohee Kim, Xiuhan Chen, Mara S. Aruguete, Ágnes Zsila
Current Psychology.2024; 43(37): 29296. CrossRef - 성인 남녀의 먹방 시청시간에 따른 식행동에 대한 연구
하얀 남, 복미 정, 은례 전
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2024; 40(4): 275. CrossRef - Changes In the Activation of Supra-hyoid Muscles and Heart Rate of College Students During Food Intake According to Watching Mukbang
Byung-o Ahn, Sung-Min Son, Hyeong-Min Kim
American Journal of Health Behavior.2023; 47(4): 832. CrossRef - 밀키트 이용 고객의 식생활 양식과 밀키트 선택속성이 밀키트 제품의 만족도에 미치는 영향 분석
세은 김, 현주 배
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(3): 187. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Watching Mukbang (Eating Show), Eating Behaviors, and Anthropometric Parameters in Iranian Female Students
Fatemeh Manafi Anari, Shahryar Eghtesadi
Journal of Research in Health Sciences.2023; 23(1): e00574. CrossRef - Health behaviors and eating habits in people’s 20s and 30s according to food content usage level on social media: a cross-sectional study
Seo-Yeon Bang, Bok-Mi Jung
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(5): 392. CrossRef - Development and validation of Problematic Mukbang Watching Scale and Mukbang Watching Motives Scale: A cross-sectional study with adult mukbang watchers
Kagan Kircaburun, Andrew Harris, Filipa Calado, Mark D. Griffiths
Psychiatry Research Communications.2023; 3(3): 100138. CrossRef - Actual Status of Mukbang Viewing and Food Habits of University Students in Wonju Area
Seung-Lim Lee, Sun Hee Lee
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2022; 33(4): 631. CrossRef - Uses and gratifications of problematic mukbang watching – The role of eating and social gratification: A pilot study
Kagan Kircaburun, Mustafa Savcı, Emrah Emirtekin, Mark D. Griffiths
Journal of Psychiatric Research.2022; 146: 28. CrossRef - Problematic video-streaming: a short review
Maryam Rahat, Juliette Mojgani, Grace Lethbridge, Hashim Al-Bya, Beth Patterson, Carolina Goldman Bergmann, Michael Van Ameringen
Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences.2022; 48: 101232. CrossRef
- Association between food-related media content and the eating behaviors of Korean adults according to household type
- 2,343 View
- 56 Download
- 14 Crossref

- [English]
- The Study of Dietary Habits and Health Behaviors according to Physical Activity Type in Korean Adults -Based on the 2016~2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey-
- Jin-A Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(2):122-133. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.2.122
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study evaluated the dietary habits and health behaviors of Korean adults according to their physical activity. Methods: Adults aged 19~64 years, who participated in the 2016~2018 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, were enrolled in this study. The subjects were classified into the physical inactivity group, aerobic physical activity group, strength exercise group, and combined exercise group. Results: Significant differences in skipping breakfast, frequency of eating out, dietary supplements, and alcohol drinking status were observed among physical activity groups (P < 0.001). The combined exercise group had the highest % KDRI of protein, vitamin A, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, calcium, potassium, and iron (P < 0.001). The physical inactivity group had the highest obesity rate (35.1%), and they perceived their body image type to be obese. In the combined exercise group, 47.8% of respondents said they were in good health (P < 0.001). The health-related quality of life score of the physical inactivity group was the lowest, with a score of 0.94. The metabolic syndrome risk rate of the combined exercise group was lower at 0.62 times (95% CI, 0.51-0.75) than the physical inactivity group. Conclusions: The physical activity type was associated with metabolic syndrome. These results can be useful for supporting dietary education and physical activity programs for adults. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Dietary Habits, Physical Activity, and Perceived Health Status on Health‐Related Quality of Life by Household Characteristics of Patients With Chronic Diseases: The Korea Community Health Survey (KCHS)
Soyean Kang, Hae Sagong, Juyoung Lee
Public Health Nursing.2025; 42(3): 1182. CrossRef - The Association between the Type and Level of Physical Activity and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adults Aged 40 Years and over: Results from the Eighth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2021)
Namkuk Son
The Korean Journal of Sports Medicine.2024; 42(2): 145. CrossRef - Consumption of protein supplements/protein-fortified foods among young adults in Jeju
Hyoju Lee, Youjeong Jang, Sumin Kim, Kyungho Ha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(2): 261. CrossRef - 고령자의 신체건강 및 식생활 행태가 영양소 섭취량에 미치는 영향
하리 임, 다솔 김, 나미 주
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(6): 518. CrossRef - Association of Dietary Quality with Subjective Health-Related Perception and Chronic Diseases According to Age Segmentation of Korean Elderly
Sojeong Lee, Seungmin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 363. CrossRef
- Impact of Dietary Habits, Physical Activity, and Perceived Health Status on Health‐Related Quality of Life by Household Characteristics of Patients With Chronic Diseases: The Korea Community Health Survey (KCHS)
- 1,453 View
- 15 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Health and Nutrition Status of Elderly People with Multimorbidity: A Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013~2015)
- Na-Gyeong Oh, Jung-Sook Seo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(6):502-511. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.6.502
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated the health and nutritional status of the elderly according to the number of chronic diseases, using data obtained from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013~2015. Methods: Data from a total of 2,310 individuals, aged 65 years and over, were used for the analysis. The elders were divided into 0 (n=375), 1 (n=673), 2 (n=637) and 3 or more (n=625) groups, by considering the number of chronic diseases. Results: Compared to other groups, the elderly subjects who were living with their spouse had the highest ratio in group 0 (P < 0.05), whereas subjects without economic activities had highest ratio in 3 or more group (P < 0.05). The EQ-5D index of subjects in the 0 group (0.90 ± 0.01) was higher than that in the 3 or more group (0.86 ± 0.01) (P< 0.05). After adjusting for confounding factors, the energy intake of subjects was determined to be lowest in the 3 or more group (P < 0.05). Protein (P < 0.05) and riboflavin (P < 0.05) intakes of the 3 or more group were also lower than other groups. Conclusions: This study indicates that multimorbidity of the elderly is associated with their health and nutritional status. The nutrients intake of the elderly, especially energy, protein and riboflavin, tended to be lowest in the 3 or more group. Further research is required to elucidate the risk factors related to presence of multimorbidity in the elderly. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biochemical characteristics, nutrient intakes, and chronic disease risk according to the dietary fat energy ratio in middle-aged Korean: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ga-Hyeon Jeong, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(6): 528. CrossRef - Breastfeeding Duration Is Associated with the Risk of Tooth Loss, Chewing Difficulty, and Undernutrition among Older Korean Women: Results of the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2013–2015
Ye Rang Jo, Yoo Kyoung Park, Hee-Sook Lim
Nutrients.2023; 15(24): 5024. CrossRef - Nutritional Status according to the Frailty Status of the Elderly at Home in Seo-gu, Gwangju, Korea
Ye Eun Kim, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 382. CrossRef
- Biochemical characteristics, nutrient intakes, and chronic disease risk according to the dietary fat energy ratio in middle-aged Korean: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,244 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Consumption Behaviors of Energy Drinks and Comparison of Associated Factors Among College Students in Gwangju
- DaWun Seo, Bok Hee Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(4):289-301. Published online August 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.4.289
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The aim of this study was to examine the current status of consumption of energy drinks among college students and investigate the effects of general environmental factors, health behavior factors, caffeine knowledge levels, and perceived stress levels on consumption of energy drinks.
METHODS
A survey was conducted among a total of 479 college students in Gwangju, using self-administered questionnaires. The questionnaire consisted of items about general environmental factors, health behavior, caffeine knowledge, perceived stress, and energy drink consumption behaviors.
RESULTS
69.1% of participants experienced consumption of energy drinks, and specifically 82.8% of male students and 54.1% of female students experienced consumption of energy drinks (p < 0.001). The reasons for drinking energy drinks were found to be recovery from fatigue, curiosity, taste, habit, thirst relief, and stress relief. In addition, 40.7% of participants experienced drinking energy drinks mixed with alcohol, and specifically 48.6% of male students and 27.4% of female students reported drinking energy drinks with alcohol (p < 0.001). Moreover, 51.5% of participants responded that they experienced the effects of energy drinks, 31.9% reported experiencing adverse effects, and 41.1% were found to perceive the health risks. As a result of the assessment of caffeine knowledge, the participants showed a high level of knowledge of the arousal effect (77.7%) and the concentration increasing effect (70.8%) of caffeine, whereas they exhibited a low level of understanding of the health problems due to caffeine (32.6%) and adequate caffeine intake levels (24.4%). The higher levels of consumption experience of energy drinks was associated with higher body mass indexes (BMI) (p < 0.01), higher academic years (p < 0.01), lower levels of interest in health (p < 0.05), smoking (p < 0.001), alcohol consumption (p < 0.05), and higher levels of perceived stress (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
The risk groups related to consumption of energy drinks among college students were identified as male students rather than female students, students in the third or fourth year of study associated with increased stress levels, and students with negative health behaviors. Therefore, support for diverse health and nutrition education for college students is required along with the improvement of internal and external environments of schools in order for college students to manage increased stress levels due to the schoolwork and preparation for employment and maintain positive health behaviors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Caffeine Intake and Eating Disorders among College Students according to Whether an Examination was Imminent or Not
Eun-Ji Lee, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2023; 34(1): 47. CrossRef - 광주광역시 지역민의 영양교육 요구도 조사 분석
은평 양, 경윤 김, 승희 최, 금비 류, 옥경 김, 정미 윤
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(2): 100. CrossRef - A Study on the Perception and Intake of Caffeinated Beverages in Adults Aged 20 to 30 Years
Bo-Ra Seo, Sim-Yeol Lee
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2023; 33(6): 545. CrossRef
- Analysis of Caffeine Intake and Eating Disorders among College Students according to Whether an Examination was Imminent or Not
- 1,480 View
- 16 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- Health Behavior Factors Associated with Sugar-sweetened Beverage Intake among Adolescents
- Hyae Min Gu, Jong Park, So Yeon Ryu
- Korean J Community Nutr 2018;23(3):193-201. Published online June 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.3.193
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to measure the intake rate of SSBs (sugar sweetened beverages) and examine the relationship between health behavior factors and SSBs intake by adolescents.
METHODS
This study used data from the 2016 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey, which included 65,528 study participants. SSBs intake frequency was measured by asking respondents if they consumed soda, high-caffeinated beverages, and sugary drinks during the previous week. Type of intake was categorized into three groups according to the number of consumed drinks [SSBs (0): None; SSBs (1–2): 1 or 2 consumed; SSBs (3): 3 consumed]. Multinomial logistic regression analysis was used to examine health behaviors that affected SSBs consumption.
RESULTS
Increased SSBs intake was significantly correlated with current smoking (OR=2.4, 95% CI=1.82–3.17), current drinking (OR=2.13, 95% CI=1.82–2.51), sedentary time increase (OR=1.31, 95% CI=1.15–1.49), three days or more physical activity per week (OR=1.12, 95% CI=1.02–1.24), < 8 hours sleep (OR=1.6, 95% CI=1.43–1.78), increased internet usage time (OR=1.44, 95% CI=1.25–1.65).
CONCLUSIONS
Sugar-sweetened beverages intake by Korean adolescents was associated with health behaviors such as smoking, drinking, sedentary time increase, more physical activity, poor sleeping time, and increased internet use time. Based on these results, it is necessary to recognize the influence of SSBs intake and to intervene to reduce consumption of SSBs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health-Related Behaviors and Perceived Health Status According to Water and Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Intake in Korean Adolescents
Yoon Sun Kim, Hyun Ja Kim
Nutrients.2024; 16(17): 3038. CrossRef - 성인 남녀의 먹방 시청시간에 따른 식행동에 대한 연구
하얀 남, 복미 정, 은례 전
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2024; 40(4): 275. CrossRef - Dietary behavior of school-going adolescents in Bhutan: Findings from the global school-based student health survey in 2016
Tshering Choeda, Kathiresan Jeyashree, Soundappan Kathirvel, Thinley Dorji, Kinley Dorjee, Karma Tenzin, Sangay Thinley, Tashi Tenzin, Mongal Singh Gurung
Nutrition.2021; 90: 111290. CrossRef - Association between Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Intake and Dietary Quality using Nutritional Quotient among Adults in Daegu, Korea
Kilye Kim, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 350. CrossRef - Sugar-sweetened beverage consumption and influencing factors in Korean adolescents: based on the 2017 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey
Ayoung Kim, Jinhee Kim, Seunghee Kye
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(5): 465. CrossRef
- Health-Related Behaviors and Perceived Health Status According to Water and Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Intake in Korean Adolescents
- 2,274 View
- 17 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Use of Dietary Supplements and Determinants of Taking Dietary Supplements by Gender in the Korean Population: Using the 4(th) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2007-2009)
- Yun Jung Lee, Minji Kang, Hee Young Paik, YoonJu Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(4):347-355. Published online August 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.4.347
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Although dietary supplements use in Korea has been rapidly increasing and women are more likely to take dietary supplements more than men, only a few studies have been conducted to investigate factors contributing to gender differences in dietary supplement use in the Korean population. The aim of this study is to evaluate the prevalence of dietary supplement use and also identify gender-specific key factors that contribute to it using the data of the 4th KNHANES.
METHODS
Subjects were divided into user and non-user groups according to the answer given to the question that asked whether they had used any dietary supplement for more than 2 weeks on a regular basis during the previous year. Factors related to dietary supplement use were examined by general characteristics, health behavior and eating behavior.
RESULTS
Prevalence of dietary supplement use was 13.6% for men and 20.6% for women. Users were more likely to be middle-aged, have higher income and education, have a spouse, or reside in dong areas in both men and women. Regarding health behaviors, men with desirable lifestyle behavior were more likely to take dietary supplements, while men who smoked were less likely to take dietary supplements. Regarding disease history, both men and women with a current disease had higher odds of taking supplements. With regard to dietary behavior, frequent eating out and nutrition attitude were associated with higher odds of taking supplements in both men and in women.
CONCLUSIONS
Health or dietary behavior related factors that were associated with taking supplements differed by gender. These findings can be useful for planning gender-specific dietary education and health programs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutritional risk assessment using estimated usual nutrient intake in Korean adults: analysis of the 8th (2019–2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Woojin Byeon, Cho-il Kim, Sung Ok Kwon, Jihyun Yoon, Linxi Huang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 799. CrossRef - Effect of Dietary Supplements on Vitamin and Mineral Intake Among Koreans: Data From the 2018-2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Moon Yeong Hwang, Jiyoun Hong
Food Supplements and Biomaterials for Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Weight management strategies and food supplement intake among Bulgarian adults: results of a national survey
Radiana Staynova, Vesselina Yanachkova
Pharmacia.2023; 70(4): 1119. CrossRef - A Study on the Dietary Behavior of Korean Adults: Focus on Dietary Supplement Intake, Household Size, and COVID-19
Jinkyung Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(6): 468. CrossRef - COVID-19 Salgını Sürecinde Yetişkinlerde Gıda Takviyesi Kullanımı ve İlişkili Etmenler
Kevser TARI SELÇUK, Nursel ŞAHİN
Turkish Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2021; 15(4): 751. CrossRef - Dietary supplements consumption and its association with socioeconomic factors, obesity and main non-communicable chronic diseases in the north of Iran: the PERSIAN Guilan Cohort Study (PGCS)
Marjan Mahdavi-Roshan, Arezoo Rezazadeh, Farahnaz Joukar, Yasaman Khorshidi, Mohammadreza Naghipour, Fariborz Mansour-Ghanaei
BMC Nutrition.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Nutritional Status of Vitamins and Minerals According to Consumption of Dietary Supplements in Korean Adults and the Elderly: Report Based on 2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Ji-Myung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(4): 329. CrossRef - Dietary Safety Management Awareness and Competency for Healthcare among Adults in Daegu and Gyeongbuk Areas
Yunhwa Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(2): 112. CrossRef
- Nutritional risk assessment using estimated usual nutrient intake in Korean adults: analysis of the 8th (2019–2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
- 1,441 View
- 6 Download
- 8 Crossref

- [English]
- Relationship between Snack Intake and Oral Health Behavior of Middle School Students in Gyeonggi Area
- Hyunsook Kang, Kyunghee Song
- Korean J Community Nutr 2017;22(4):336-346. Published online August 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.4.336
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The study was performed to investigate the relationship between snack intake and oral health behavior in middle school students in Gyeonggi-do area.
METHODS
The survey questionnaire was recorded by middle school students from July 6 to August 24, 2011. The questionnaire included items on general characteristics, snack intake status, and oral health behavior. Among collected survey questionnaire, a total of 620 questionnaires (320 males and 300 females) were analyzed using SPSS 15.0 program.
RESULTS
Frequencies of snack and beverage intakes were significantly higher in males than in females (p < 0.001). Oral health behavior was significantly higher in students with lower snack intake compared to those with higher or average snack intake (p < 0.05). Oral health behavior for tooth brushing and toothbrush care were significantly higher in females than in males (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
Oral health behavior score that reflected better oral health of the subjects were higher as the snack intake was lower. Oral health behavior score was higher in females than in males. We conclude that the contents for oral health and nutrition education focused on snack intake need to be developed to induce changes in oral health behavior in middle school students. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of night eating on oral health characteristics and symptoms of poor oral health in adolescents: a cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Seung–Hee Hong
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(2): 150. CrossRef - Evaluation of frequency of consumption of cariogenic snacks by freshmen versus the senior dental students in Tehran and the related factors: a cross-sectional study
Mahdia Gholami, Simin Z Mohebbi, Milad Mafakheri, Houra Shahhosseini
BMJ Open.2024; 14(9): e086041. CrossRef
- Effects of night eating on oral health characteristics and symptoms of poor oral health in adolescents: a cross-sectional study using the 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- 1,439 View
- 8 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Comparison of Health Belief Levels and Health Behavior Practices according to Lifestyle among Adults Residing in Seoul
- Na Hong Choi, Hong Seok Ahn, Seungmin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(6):683-696. Published online December 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.6.683
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study compared levels of health beliefs and health behavior practices according to lifestyle pattern among adults in Seoul. A self-administered survey questionnaire was collected from a total of 1,004 Seoul residents aged 30-59 years. The levels of perceived benefit, perceived barrier, and self-efficacy from health belief model and health behavior practices were measured across multiple health behavior areas including dietary behavior, drinking, smoking, exercise, functional food consumption, and weight control behavior. Factor analysis and subsequent cluster analysis based on 28 lifestyle questions divided the subjects into four lifestyles of society-, economy-, trend-, and health-oriented lifestyle. Some general characteristics were significantly different by lifestyles. The society-oriented lifestyle was significantly higher in proportions of men and overweight. The trend-oriented lifestyle was significantly younger and spent more monthly allowance. Health-oriented lifestyle was older. The levels of health belief variables and health behavior practices significantly differed by lifestyles. Overall the health-oriented lifestyle showed more desirable levels of health belief variables and health behavior practice in various health behavior areas compared to the other lifestyles, whereas the society-oriented lifestyle was found the other way. Health belief model variables including perceived benefit, perceived barrier, and self-efficacy were generally significant in predicting the levels of various health behavior practice, with somewhat differences by lifestyle pattern and health behavior type. The study findings suggest it may be useful to segment target subjects according to lifestyle pattern in planning and administering health education programs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of the factors that influence preschool children eating behavior by applying the health belief model: Seoul and Gyeonggi Province
Sung-Mi Cha, Soo-Youn Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(3): 541. CrossRef - Analysis of Dietary Behavior and Sustainable Dietary Life Competency in Families According to Parents’ Dietary Lifestyle: Using the 2021 Korea Consumer Behavior Survey for Food
Sun A Choi, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(11): 1179. CrossRef - Comparison of health care practice, dietary behavior, and nutrient intakes, considering the alcohol drinking status of industrial workers in the Chungnam area
Gun Hee Park, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(3): 277. CrossRef - Genetic Variations in Thiamin Transferase SLC35F3 and the Risk of Hypertension in Koreans
Ja-young Seo, Jeong-Hwa Choi
Clinical Nutrition Research.2021; 10(2): 140. CrossRef - Comparison of practice of dietary guidelines and health beliefs according to stage of weight loss behavior change among male workers
Su Jeong Song, HongSeok Ahn, Jinmo Khil
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2013; 46(3): 276. CrossRef - A Study on Dietary Behaviors, Health-Related Lifestyle of Adult Visitors at Public Health Centers in Gyeonggi Urban Area
Jong-Sook Kwon, Kyungmin Kim, Hyun-Chang Seo, Yoonna Lee, Seunggeon Lim, Young-Sug Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(6): 611. CrossRef
- Analysis of the factors that influence preschool children eating behavior by applying the health belief model: Seoul and Gyeonggi Province
- 1,297 View
- 0 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [English]
- Antioxidant Nutrient Intakes and Health Behaviors of Rheumatoid Arthritic Patients
- Ju Hee Lee, Eun Jung Chung, Young Ho Lee, Jong Dae Ji, Hong Seok Ahn
- Korean J Community Nutr 2008;13(2):253-262. Published online April 30, 2008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Previous studies have indicated that incidence of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is partly related to the damage of antioxidant systems, but etiology of RA is not fully identified. This study was performed to evaluate nutrient intakes including antioxidants, health related behaviors and food habits of RA patients and controls. RA patient group (n = 68) and sex-matched healthy controls (n = 68) were joined in this study. Nutrient intake was estimated using a semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire. As mean age of RA (52.9 +/- 13.8 years) was significantly higher than those of controls (48.7 +/- 5.9 years), data were analyzed by using Student's t-test, adjusted for age. There was no significant difference between two groups in body mass index. Compared with those of controls, frequencies of drinking (p < 0.001) and coffee consumption (p < 0.05) of RA groups were lower. RA groups had lower frequencies of fruit (p < 0.01), vegetable (p < 0.05) and fatty meat (p < 0.05) consumptions and balanced diet (p < 0.01), and higher frequencies of fried dishes (p < 0.01), and salty dishes (p < 0.01), compared to controls. The most nutrient intakes including energy intake of RA were tended to be lower than those of controls. Vitamin A, beta-carotene and vitamin C intakes were significantly lower in RA than controls (p < 0.001). Daily vitamin A, beta-carotene and vitamin C intakes of RA were lower than those of control (vitamin A: RA 360.6 +/- 252.23 microgram RE, control 844.5 +/- 426.2 microgram RE, p < 0.001; beta-carotene: RA 1450.9 +/- 1019.0 microgram, control 3968.8 +/- 2248.21 microgram, p < 0.001; vitamin C; RA 40.6 +/- 21.48 mg,control 84.7 +/- 40.29, p < 0.001) These results suggest sufficient consumption of antioxidant nutrients may prevent and improve RA status.
- 266 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Health-Related Behavioral Factors Associated with Nutritional Risks in Korean Aged 50 years and Over
- Kyeong Sook Yim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2007;12(5):592-605. Published online October 31, 2007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Undernutrition could be a significant deterrent to healthy aging and could negatively affect health outcomes in elderly. This study aimed to assess health-related factors which are associated with nutritional risks in middle-aged and elderly individuals by a cross-sectional study. Interviews were conducted with 2660 subjects (847 males, 1813 females), aged 50 years and over, in 15 cities in Korea. Data on food intake were obtained through a validated semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaires. Nutritional status were analyzed according to health-related factors including cigarette smoking, alcohol drinking, exercise, stress and depression level. Less regular exercise was associated with a higher likelihood of a poor nutrition [odds ratio (OR) 1.94; 95% confidence intervals (CI) 1.43-2.65] of middle-aged and elderly male subjects. Cigarette smoking (OR 1.84; 95% CI 1.24-2.71), less exercise (OR 2.58; 95% CI 2.07-3.21), stress (OR 1.73; 95% CI 1.36-2.22), and depression (OR 1.34; 95% CI 1.08-1.67) of middle-aged and elderly female subjects was associated with a higher likelihood of a poor nutrition. The results of the multiple regression analysis showed that less exercise proved to be the strongest predictors for the poor nutrition, followed by stress, smoking, and depression (model R2= 9.0%). It suggests that guidance to promote regular exercise, to quit smoking, to minimize stress and depression level might help to improve nutritional status of middle-aged and elderly in Korea. These findings also suggest that having recommendable health behaviors are beneficial to the good nutrition of subjects aged 50 years and over.
- 280 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- College Students' Dietary and Health Behaviors related to Their Myers-Briggs Type Indicator Personality Preferences
- Byung Sook Kim, Young Eun Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2002;7(1):32-44. Published online February 28, 2002
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The objective of this study was to evaluate college students' dietary and health behaviors in relation to their Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) personality preferences. Dietary and health behaviors were surveyed for 444 college students who performed the MBTI personality test. Only 6.1% of the subjects regularly had three meals a day, while 27.1% ate breakfast every day. Fifty-six point nine percent of the students took less than 15 minutes to eat a meal and had the habit of eating fast. The number of food groups they ate was, on average, 2.74 and was eaten mainly at dinner. This showed that college students did not eat a large variety of foods. Eighty-two percent of the subjects drank alcoholic beverages, 21.4% smoked, and 69.3% exercised. In addition, 73.9% of them were not satisfied with their body image, but they were not eager to try weight control. There were not many significant differences between Extraversion (E)-Introversion (I), Sensing (S)-iNtuition (N), and Thinking (T)-Feeling (F) in their dietary and heath behaviors, although some gender differences existed. Significantly better dietary and health behaviors were shown in subjects preferring Judging (J) rather than Perceiving (P). There behaviors included eating breakfast, regularly eating three meals a day, smoking less, exercising more and having a lower tendency to night-eating. The personality preference of J-P could be useful index for nutritional education and counseling or behavior modification programs for obese people.
- 327 View
- 5 Download

- [English]
- The Relationship between Ophthalmic Refractive Errors and Factors of Nutrition and Health
- Youngok Kim, Hae Jung Choi, Soon Young Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2000;5(4):608-614. Published online December 31, 2000
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to evaluate the relative importance among various biological and environmental factors on refractive errors. Various factors such as diseases, health related behavior such as drinking, smoking and exercise, as well as dietary factors were considered as a possible determinant. Surveys of 492 residents over 20 years of age in Kuri city were conducted during 1998. The survey included a refractive error test adopting a autokerato-refractometer, dietary survey using a 24 hour recall method, disease survey including blood and other diagnosis tests, and a health behavior survey using questionnaires with variables of smoking, drinking, and exercise. A stepwise logistic regression analysis was adopted to analyse the relative importance among independent variables of health behaviors, disease, and dietary factors on ametropias. As a result, in the case of myopia, liver dysfunction appeared to be the most important factors followed by the health related behavior of smoking and exercise as the second most important factors. Nutrient factors such as carotene and protein appeared to be the third most important factors. Similar results had been shown in the case of the hyperopia. In summary, liver dysfunction and the health related behaviors of drinking and smoking appeared to be more influential factors on abnormal eye sight of myopia and hyperopia than dietary factors.
- 275 View
- 7 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



