Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [English]
- Eating habits and dietary supplement utilization according to food-related lifestyle among Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
- EunJung Lee, Jin A Jang, Ji-Myung Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(4):253-264. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.00017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
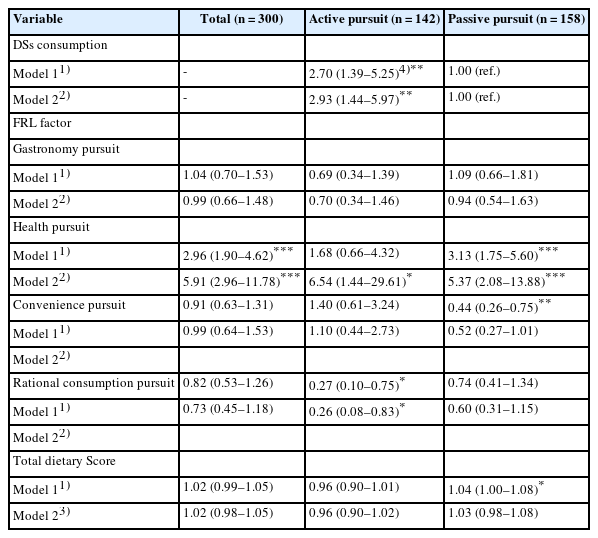
This study investigated the association between eating habits and the utilization of dietary supplements (DSs) according to food-related lifestyle (FRL) among Korean adults. Methods: This study included a total of 300 participants (150 men and 150 women) in their 20s to 60s living in Seoul and Gyeonggi Province. We identified two groups by factor and cluster analysis: an ‘active pursuit’ group and a ‘passive pursuit’ group. Differences in eating habits and DS utilization between the two groups were analyzed by chi-square test and t-test. Logistic regression analysis was used to analyze the effect of variables on DS consumption according to FRL. Results: There were significant differences between the two groups in terms of age, alcohol drinking frequency, total dietary score, change in DS consumption after coronavirus disease 2019, and current DS consumption (P < 0.05). The proportion who perceived many health benefits of DSs was higher in the ‘active pursuit’ group than in the ‘passive pursuit’ group (P = 0.003). The most commonly consumed type of DSs was multivitamins & minerals for the ‘active pursuit’ group, and omega-3 fatty acids for the ‘passive pursuit’ group. The ‘an active pursuit’ group consumed DSs 2.93 times more (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.44–5.97) compared to the ‘passive pursuit’ group, after adjusting for confounders. In the ‘active pursuit’ group, the health pursuit (odds ratio [OR] = 6.54, 95% CI: 1.44– 29.61) and rational consumption pursuit factors (OR = 0.26, 95% CI: 0.08–0.83) were associated with DS consumption, whereas only the health pursuit factor had a significant association (OR = 5.37, 95% CI: 2.08–13.88) within the ‘passive pursuit’ group. However, total dietary score and DSs consumption did not show a relationship. Conclusions: By understanding the consumption characteristics of DSs according to FRL, this can serve as basic data necessary for promoting health through the utilization of DSs and healthy behaviors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Discovering Vitamin-D-Deficiency-Associated Factors in Korean Adults Using KNHANES Data Based on an Integrated Analysis of Machine Learning and Statistical Techniques
Hongryul Ahn, Seungwon Kim, Jinmyung Jung, Chan Park
Nutrients.2025; 17(4): 618. CrossRef
- Discovering Vitamin-D-Deficiency-Associated Factors in Korean Adults Using KNHANES Data Based on an Integrated Analysis of Machine Learning and Statistical Techniques
- 4,975 View
- 94 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [Korean]
- A Study on the Dietary and Lifestyle Changes of Middle-Aged Women in the Gwangju Area in the COVID-19 Era
- Moon-Soon Kim, Bok-Mi Jung
- Korean J Community Nutr 2021;26(4):259-269. Published online August 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2021.26.4.259
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the changes in the eating habits and lifestyle of middle-aged women in Gwangju during the COVID-19 pandemic. Methods: A total of 428 middle-aged women aged between 40 and 60 participated in a survey relating to general information, food and lifestyle, health functional food, and menopausal symptoms. The correlation between the variables was analyzed. Results: In the positive habits, the intake of nutritional supplements for immunity enhancement increased the most, followed by the use of media to learn healthy eating tips, and diets including healthy food. Negative habits increased in the order of frequency of taking delivery orders, levels of stress or anxiety, and time spent sitting or watching movies. In the case of recommended foods, the intake increased the most in the order of eggs, fruits, vegetables, milk/dairy products, and seaweed. Non-recommended foods increased in the order of meat, bread, rice, and noodles. The awareness of health functional foods was in the increasing order of interest, knowledge, consumption experience, and purchase amount. The type of health functional food intake was in the increasing order of probiotics, multivitamin and mineral supplements, vitamin C, collagen, and omega-3. Menopausal symptoms were in the increasing order of bone and joint pain, poor sleep quality, emotional ups and downs, loneliness, and feeling of emptiness. In the correlation of major variables, positive habits showed a significant positive correlation with recommended food intake and the recognition of health functional foods. Negative habits showed a significant positive correlation with non-recommended food intake and a significant positive correlation with menopausal symptoms. Recommended food intake showed a significant positive correlation with health functional food recognition and intake and menopausal symptoms. Conclusions: This study suggests that it is necessary to establish social measures to reduce the negative effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on middle-aged women and to ensure effective self-management through a healthy lifestyle since the pandemic has a long-term impact. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Barley-Based Cereals Enhance Metabolic Health and Satiety in Overweight Korean Adults: A Randomized Trial
Ingyeong Kang, Hyunsook Jang, Minchul Gim, Sang Eun Bae, Yu Jin Lee, Chai Sun Leem, Yoo Kyoung Park
Nutrients.2025; 17(17): 2801. CrossRef - Comparative study on the health and dietary habits of Korean male and female adults before and after the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic: utilizing data from the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2021)
Chaemin Kim, Eunjung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(1): 65. CrossRef - Quality Characteristics of Staple Breads Based on Baking Methods
Eun-Hee Doo
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(1): 77. CrossRef - Changes in Ultra-Processed Food Consumption among Adolescents before and after the COVID-19 Pandemic : Using Data from the 7th (2018~2019) and 8th (2020~2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyun-Jin Hwang, Yoo Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Human Ecology.2024; 33(6): 981. CrossRef - Dietary guidelines adherence and changes in eating habits among college students in the post-COVID-19 period: a cross-sectional study
Eunyoung Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(3): 220. CrossRef - Changes in dietary habits and chronic diseases before and after COVID-19 by regions using data from the 2018-2020 Korea Community Health Survey and Consumer Behavior Survey for Foods: a cross-sectional study
Surim Park, Eun-hee Jang, Seungmin Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(2): 124. CrossRef - 광주광역시 지역민의 영양교육 요구도 조사 분석
은평 양, 경윤 김, 승희 최, 금비 류, 옥경 김, 정미 윤
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(2): 100. CrossRef - Consumers’ perceptions of dietary supplements before and after the COVID-19 pandemic based on big data
Eunjung Lee, Hyo Sun Jung, Jin A Jang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(3): 330. CrossRef - Self-rated health according to change of lifestyle after COVID-19: Differences between age groups
Dan Bi Lee, Jung Hyun Ahn, Jin Young Nam
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2022; 39(2): 1. CrossRef - Factors Related to Changes of Daily Life during COVID-19
Kyungjin Min, Pilhan Yun, Sangshin Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2022; 47(4): 297. CrossRef - Dietary Behavior and Diet Quality in the Korean Adult Population by Income Level before and after the COVID-19 Pandemic: Using the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019-2020)
Hye-Min Na, Bok-Mi Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2022; 33(3): 397. CrossRef
- Barley-Based Cereals Enhance Metabolic Health and Satiety in Overweight Korean Adults: A Randomized Trial
- 1,361 View
- 10 Download
- 11 Crossref

- [English]
- Dietary Life of Chinese International Students according to the Frequency of University Foodservice Use in Korea
- Yan Cui, Hye-Jong Yoo, Injoo Choi, Jihyun Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(4):291-302. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.4.291
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF
Objective
This study investigated the current use of university foodservice among Chinese international students in Korea, focusing on the relationship between the frequency of university foodservice use and their dietary life.
Methods
An online survey was conducted on 452 Chinese international students from February 6 to 12, 2020. The respondents were classified into “the Low-frequency group” (< one time/week; n=144), “the Mid-frequency group” (one-two times/week; n=133), and “the High-frequency group” (≥three times/week; n=175) according to their frequency of using university foodservice. The dietary life was compared among the three groups. Binominal logistic regression models were constructed to determine the associations between the frequency of university foodservice use and the changes in dietary life.
Results
More than 2/3 (68.1%) of the respondents used the university foodservice at least once per week. Chinese international students who were males and Han Chinese people, lived on campus, had stayed longer in Korea, and had no cooking facilities tended to use the university foodservice more often. The level of satisfaction with the university foodservice was not high (3.52 out of 5-points). Only 20% ate meals three times per day, and only 22% ate breakfast almost every day. The frequencies of overeating and skipping meals increased after studying in Korea. The frequency of university foodservice use, along with the length of residence in Korea, was associated with these negative changes in dietary life. Overeating (OR=2.11) and skipping meals (OR=1.79) were more likely to increase after studying in Korea in the Mid-frequency group than in the High-frequency group.
Conclusions
The frequency of university foodservice use was associated with the dietary life of Chinese international students in Korea. A high frequency (i.e. ≥three times/week) of using university foodservice may positively affect the dietary life of Chinese international students in Korea.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Sodium-Related Dietary Behavior and Low-Salt Dietary Attitude Based on the Gender and Salty Taste Assessment of Chinese International Students in the Jeonbuk Area
Qi Li, Ji Eun Lee, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2021; 31(2): 91. CrossRef
- Comparison of Sodium-Related Dietary Behavior and Low-Salt Dietary Attitude Based on the Gender and Salty Taste Assessment of Chinese International Students in the Jeonbuk Area
- 1,129 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- A study on the Utilization and Satisfaction of Commercially available Lunchbox by Dietary Lifestyle
- Hyosuk Kim, In-Joon Huh, Sim-Yeol Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(4):267-279. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.4.267
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF
Objective
This study investigated the utilization and satisfaction of lunchbox by considering the dietary lifestyle of the consumer, in order to refine the purchasing behavior of adults with experience in using lunchboxes, and to provide basic data for efficient menu configuration and direction towards improvement.
Methods
A total of 600 adults in Seoul and Gyeonggi-do answered a self-administered questionnaire designed to investigate general characteristics, utilization, menu preference, satisfaction, prospection, and improvement of lunchbox, according to the dietary lifestyle.
Results
The study subjects were classified into 5 groups: ‘taste seeking group’, ‘safety seeking group’, ‘health seeking group’, ‘economic seeking group’ and ‘convenience seeking group. Considering purchase value of the lunchbox, the ‘taste seeking group’ had a high utilization rate (35.1%) for prices less than 4,000 won (p < 0.05). Lunchboxes were mainly purchased at the lunchbox store (43.3%) and convenience store (37.7%). The important factor that contributed to purchasing a lunchbox was taste (61.3%), which was highest in the ‘taste seeking group’ (p < 0.01). The ‘health seeking group’ showed the highest preference for the low-salt diet lunchbox menu (26.0%) (p < 0.05). The satisfaction of ‘health seeking groups’ was lowest when considering addition of condiments (2.34%), origin of ingredient (2.59%), and provided calorie (2.81%) (p < 0.05). The overall response indicated future use of the lunchbox (69.6%) (p < 0.01); 35.8% respondents recommended the purchase of lunchbox, where convenience of purchase was the highest factor contributing to recommendation (50.2%) (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Taken together, our results indicate that taste was emphasized in every group purchasing the lunch box. Convenience of purchase was the highest factor contributing to satisfaction, which was relatively low when considering addition of condiments, nutrition and origin of ingredients. We propose that it is necessary to improve the development of various menus for increasing satisfaction by selecting the right ingredients contributing to good health of the consumer.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Survey on the Consumption Patterns and HACCP Awareness of Dosirak Customers
Ji-Won Ma, Hye-Yeon Lee, Hyun-Joo Bae
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2025; 35(3): 192. CrossRef - A Study on the Selection Attributes of Frozen Mandu (Korean Dumpling) for Adults in the Jeonbuk Area Using Conjoint Analysis
Da Eun Gong, Sun A Choi, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2024; 53(3): 297. CrossRef - Study on the Eating Out Behavior and the Status of Meal Delivery and Take-Out Consumption according to the Food-related Lifestyles of Adolescents : Using the Consumption Behavior Survey for Food in 2020
Eun Jung Lee, Hyeon Min Yang, Yeong Ju Lee, Sun A Choi, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(4): 284. CrossRef - Comparison of Eating Habits and Behaviors of Young Single-Person Households based on Food-Related Lifestyle
Dokyung Kim, Sim-Yeol Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2023; 23(3): 117. CrossRef - Beef Consumption Behavior amongst Korean Women: A Study Based on the Demographic Characteristics and Food-Related Lifestyle
Kyung-Ran Lee, EunJung Lee, Jung-Tak Lee, Jin A Jang
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(3): 323. CrossRef - How Does Adolescents’ Usage of Social Media Affect Their Dietary Satisfaction?
Harry Jeong, Kwangsoo Shin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(6): 3621. CrossRef - A Franchise Hamburger Menu for University Students Determined by Identifying Selection Attributes Using Conjoint Analysis
Yu-Ni Choi, Sung-Suk Chung, Jeong-Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2022; 32(4): 250. CrossRef - Studies of Selection Attributes for Lunch Boxes (Dosirak) Using Conjoint Analysis among Single Men
A Reum Han, Sung Suk Chung, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2021; 50(8): 884. CrossRef - E-commerce Food Purchases by Adult Women according to their Household Types
Yu-Jin Park, Yu-Mi Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(6): 464. CrossRef
- A Survey on the Consumption Patterns and HACCP Awareness of Dosirak Customers
- 1,390 View
- 13 Download
- 9 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Study on Middle and High School Students' Use of Convenience Foods at Convenience Stores in Incheon
- Seul Ki Lee, Mi Kyeong Choi, Mi Hyun Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(2):137-151. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.2.137
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The rapidly changing dietary environment requires a study that addresses the status of middle and high school students regarding their consumption of convenience food sold at convenience stores.
METHODS
This study examined adolescents' lifestyle patterns, dietary habits, and status of consuming convenience food at convenience stores. A total of 659 students (329 middle school students and 330 high school students) in Incheon participated in this questionnaire survey.
RESULTS
The mean age of the subjects was 13.7 years for the middle school students, and 16.6 years for the high school students. The gender and grade distributions in the middle and high school students were similar. The middle school students reported that they spent more time using electronic devices (p<0.001) or watching TV (p<0.001) than high school students. More than 60% of middle and high school students consumed convenience food at convenience stores without statistical difference between the two groups. The main reason for consuming convenience food from convenience stores was its convenience followed by taste in both groups. Despite the high frequency of consuming convenience food, the students rarely checked the nutrition labels at the time of purchase. On the other hand, they were still most concerned about the nutritional value of the convenience foods when they consumed convenience foods. The most frequently consumed convenience food was ramyon in both groups. Significant positive correlations were observed between the frequency of consuming convenience food at convenience stores and lifestyle factors for the middle school students, including monthly allowance, time for using electronic devices, and number of private lessons. For the high school students, however, the only monthly allowance had a significant positive correlation with the consumption.
CONCLUSIONS
Adolescents are increasingly exposed to convenience foods and relevant nutritional issues are a concern. Therefore, a dietary environment that is adequately formed for the healthy development of youth as well as systematic nutrient education that is appropriately designed for both middle and high school students is required. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Gen Z consumers’ expectations for smart convenience stores in the USA, South Korea, and Japan
Summer Dahyang Jung, Sahej Claire, Sohyeong Kim
Young Consumers.2024; 25(3): 400. CrossRef - Study on the Eating Out Behavior and the Status of Meal Delivery and Take-Out Consumption according to the Food-related Lifestyles of Adolescents : Using the Consumption Behavior Survey for Food in 2020
Eun Jung Lee, Hyeon Min Yang, Yeong Ju Lee, Sun A Choi, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(4): 284. CrossRef - The frequency of convenience food consumption and attitude of sodium and sugar reduction among middle and high school students in Seoul: a descriptive study
Seoyeon Park, Yeonhee Shin, Seoyeon Lee, Heejung Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(4): 269. CrossRef - Determination of the migration of plastic additives and non-intentionally added substances into food simulants and the assessment of health risks from convenience food packaging
Eun Chul Pack, Kyung Youn Lee, Jin Seop Jung, Dae Yong Jang, Hyung Soo Kim, Ye Ji Koo, Ho Geon Lee, Young Soon Kim, Kyung Min Lim, Seung Ha Lee, Dal Woong Choi
Food Packaging and Shelf Life.2021; 30: 100736. CrossRef - Association between breakfast and lifestyle, interest in beauty care, and attitude toward breakfast in high school girls in Incheon
Seolmi Lee, Mi-Hyun Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(3): 288. CrossRef - Convenience Store Use and the Health of Urban Adolescents in Seoul, South Korea
Nan-He Yoon, Changwoo Shon
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(18): 6486. CrossRef - Association between frequency of convenience foods use at convenience stores and dietary quality among high school students in Incheon
Eun-Mi Kim, Mi-Kyeong Choi, Mi-Hyun Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(4): 383. CrossRef
- Gen Z consumers’ expectations for smart convenience stores in the USA, South Korea, and Japan
- 2,622 View
- 21 Download
- 7 Crossref

- [English]
- Adulterated Food Management Characteristics according to Dietary Lifestyles among Adolescents
- Yunhwa Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(6):509-519. Published online December 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.6.509
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
Adulterated food education in adolescence period is very important because dietary management related to food safety is not made in a short period. This study aimed to identify dietary lifestyle factors which drive adulterated food management among middle and high school students.
METHODS
Data was collected from 270 middle and high school students in Daegu using a self-administered questionnaire in March and April of 2015. Data was analyzed using frequency analysis, one-way analysis of variance, χ²-test, factor analysis, reliability analysis, regression analysis, and cluster analysis.
RESULTS
The results of factor analysis indicated that adulterated food management awareness was classified into necessity, difficulty, and food purchasing anxiety. The adulterated food management capability was sub-grouped into environmental grasp, food identification, cooking hygiene, and situation management. The adulterated food management efficacy composed of management confidence, action intention, and knowledge. Dietary lifestyle comprised of gustation, family, and health factors after factor analysis, and it consisted of all seeking group, gustation seeking group, family seeking group, health seeking group, and family and health seeking group after cluster analysis. The gustation, family and health factors were significantly affected the factors of awareness, capability and efficacy of adulterated food management (p < 0.05). The frequency of health conditions, helping with meal preparation, and the times of eating out were significantly different according to seeking groups of dietary lifestyle (p < 0.01). The scores of awareness, capability and efficacy of adulterated food management of family and health seeking group were significantly higher than the other seeking groups (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
This study suggests that adulterated food management education programs should account for gustation, family and health factors of dietary lifestyle to be effective for adolescents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on the Eating Out Behavior and the Status of Meal Delivery and Take-Out Consumption according to the Food-related Lifestyles of Adolescents : Using the Consumption Behavior Survey for Food in 2020
Eun Jung Lee, Hyeon Min Yang, Yeong Ju Lee, Sun A Choi, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(4): 284. CrossRef - Dietary safety management competency for the sustainable health management of adolescents
Yunhwa Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(3): 406. CrossRef - Restaurant Meal Delivery and Take-Out Consumption Behavior according to Adolescents’ Food-Related Lifestyles
Yulee Shin, Minsook Kyung, Seonyeong Baek, Sunny Ham
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2021; 31(3): 172. CrossRef - Predicting adolescents’ behavioural intentions in adulterated food management
Yunhwa Kim
British Food Journal.2019; 122(1): 258. CrossRef - Survey on Foodservice Satisfaction and Dietary Education needs for Improvement of School Foodservice in Middle School Students in Seoul
Kyung-Hee Shin, Youngmee Lee, Wookyoun Cho
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(2): 127. CrossRef
- Study on the Eating Out Behavior and the Status of Meal Delivery and Take-Out Consumption according to the Food-related Lifestyles of Adolescents : Using the Consumption Behavior Survey for Food in 2020
- 1,162 View
- 0 Download
- 5 Crossref

- [English]
- Lifestyle, Diet, Self-care, and Diabetes Fatalism of Diabetic Patients with and without Diabetic Foot
- Jungha Choi, Juhee Kang, Hongmie Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2014;19(3):241-249. Published online June 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2014.19.3.241
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was to determine diabetes fatalism of diabetic patients with and without diabetic foot and its association with lifestyle, diet, and self-care.
METHODS
The subjects were diabetic patients with (male/female 48/21) and without diabetic foot (male/female 33/26). We administered the questionnaires which were designed to determine diabetes fatalism, lifestyle, diet, and self-care. Diabetes fatalism was determined by Diabetes fatalism scale (DFS), which consisted of total 12 items in three subscales namely, emotional stress, religiou.spiritual coping, and perceived self-efficacy.
RESULTS
The patients with diabetic foot had undesirable diets more frequently (1.37 and 0.91 days/week respectively) and their desirable diets (2.74 and 3.61 days/week respectively) and foot care (4.61 and 5.53 days/week respectively) were less frequent than those without diabetic foot (p < 0.05). An item analysis of the 12 DFS items revealed a Chronbach' alpha of 0.614 and 0.869, respectively in diabetic patients with and without diabetic foot. Perceived self-efficacy related DFS of subjects without diabetic foot was positively associated with smoking (r = 0.350, p < 0.01), undesirable diet (r = 0.295, p < 0.05), and drinking (r = 0.257, p < 0.05), while its negative association with exercise (r = -0.224, p < 0.088) and foot care (r = -0.247, p < 0.059) did not reach to statistical significance.
CONCLUSIONS
This work was the first study reporting the potential usefulness of DFS, especially perceived self-efficacy related subscale as a predictor of lifestyle, diet and self-care on the Korean diabetic patients, at least those without severe diabetic foot to screen those who should be the first target for diabetes education. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Influencing Glycemic Control by gender in Workers with Diabetes Mellitus
Eun Hee Jang
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2018; 21(2): 121. CrossRef - Association of selected health behaviors with perceived health, depressive symptom and fatalism among the aged 50-69 living in Seoul
Eun Jin Choi, Min Hye Kim
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2015; 32(2): 53. CrossRef
- Factors Influencing Glycemic Control by gender in Workers with Diabetes Mellitus
- 1,207 View
- 6 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- A Study on Dietary Behaviors, Health-Related Lifestyle of Adult Visitors at Public Health Centers in Gyeonggi Urban Area
- Jong Sook Kwon, Kyungmin Kim, Hyun Chang Seo, Yoonna Lee, Seunggeon Lim, Young Sug Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(6):611-625. Published online December 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2013.18.6.611
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate dietary behaviors and health-related lifestyles of adult visitors at a public health center in Gyeonggi urban area. A survey using questionnaire was conducted with 949 visitors at Seongnam public health centers from June to August, 2012. The data from 905 respondents were analyzed by gender, consisting of 322 males and 583 females, and age group, consisting of 243 low-age group (LA), 312 middle-age group (MA), 350 high-age group (HA), aged 20 to 30 years, 31 to 50 years, and 51 to 69 years, respectively. Average Body Mass Index was 23.0, which increased with age, and education level was high in LA. 59.0 percent of the subjects had various diseases, and the incidence of hypertension was the highest, followed by allergy, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, joint rheumatism. Incidence rates of chronic disease increased with age, which were lower than those from 2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Weekly drinking frequency rate and smoking rate decreased with age, and exercise performing rate was high at male and HA, which showed the same tendency as KNHANES. Female and HA showed more healthy dietary behaviors such as restricting salt, sugar, oily foods, foods containing food additives, calorie, caring for balanced diet, and referring to nutrition label. Subjects chose stress as the first factor, followed by diet, exercise, etc., among 13 suggested factors which strongly influence on human's life-span. In general, public health center visitors, especially female and HA, showed better dietary behaviors and health-related lifestyles compared with KNHANES.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary Safety Management Awareness and Competency for Healthcare among Adults in Daegu and Gyeongbuk Areas
Yunhwa Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(2): 112. CrossRef - Factors associated with the dietary quality and nutrition status using the Nutrition Quotient for adults focusing on workers in the manufacturing industry
Ji Suk Yim, Young Ran Heo
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(5): 488. CrossRef
- Dietary Safety Management Awareness and Competency for Healthcare among Adults in Daegu and Gyeongbuk Areas
- 1,137 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- [English]
- Status and Relationships among Lifestyle, Food Habits, and Stress Scores of Adults in Chungnam
- Yeon Ja Seo, Mi Hyun Kim, Myung Hee Kim, Mi Kyeong Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(5):579-588. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.5.579
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to investigate the association among demographic characteristics, lifestyle, food habits, and stress status of 437 males and females aged over 25 years in Chungnam. Overall, the stress status of the subjects was high showing an average of 103 points out of 156 points based on the something scale. Results of the study revealed that marital status, exercise status, and health status had significant relationships with food habits and stress scores. The subjects who were married, had a higher frequency of exercise, and were healthier, had a significantly higher food habit score but a significantly lower stress score compared with their counterparts. Also, food habit scores had a significantly negative relationship with stress scores. Thus, this research showed possible links among healthy food habits, desirable lifestyle, and low stress status. In other words, people who experience a high level of stress may be more likely to have unhealthy food habits, resulting in a poor healthy conditions. These results show that appropriate food habits and adequate dietary management are deemed necessary for people with a high degree of stress. Further in-depth studies are needed to clarify a direct relationship between stress and food habits and to determine the proper diet that may help relieve stress.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship between sweet food intake and stress among college students in Seoul and Gyeonggi areas
Jun-Gyeong Kim, Jounghee Lee, Kyunghee Song
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(4): 373. CrossRef - Association between stress and dietary habits, emotional eating behavior and insomnia of middle-aged men and women in Seoul and Gyeonggi
Onjeong Choi, Jiwon Kim, Yujin Lee, Youngmi Lee, Kyunghee Song
Nutrition Research and Practice.2021; 15(2): 225. CrossRef - Relationship between Dietary Habits, Life Stress and Nutrition Knowledge of High School Students in Gyeonggi Area
Kyung Ae Park, Hongmie Lee, Kyunghee Song
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(2): 126. CrossRef - Eating Habits of the University Students affected by Stress Levels in the Areas of Seoul and Gangwon Province
Jeongsill Lee
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2015; 28(5): 782. CrossRef - The Relationship between Stress, Social Support and Healthy Diet Score among Chinese University Students in Korea
Sunghee Lee, Zhen Feng, Youngmee Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(4): 273. CrossRef - Antioxidative Activity of Feral Haw (Crataegus pinnatifida BUNGE) Seed Extracts Using Various Solvents
Min-A Kim, Yishan Duan, Jong-Hwan Seong, Hun-Sik Chung, Han-Soo Kim
Korean journal of food and cookery science.2014; 30(1): 33. CrossRef - A comparative study on dietary behavior, nutritional knowledge and life stress between Korean and Chinese female high school students
Sohwan Son, Yoona Ro, Hwajin Hyun, Hongmie Lee, Kyunghee Song
Nutrition Research and Practice.2014; 8(2): 205. CrossRef - Antioxidative activities of various solvent extracts from haw (Crataegus pinnatifida Bunge)
Yishan Duan, Min-A Kim, Jong-Hwan Seong, Hun-Sik Chung, Han-Soo Kim
Korean Journal of Food Preservation.2014; 21(2): 246. CrossRef - A comparative study on dietary behavior, nutritional knowledge and life stress between Korean and Chinese female high school students
Sohwan Son, Yoona Ro, Hwajin Hyun, Hongmie Lee, Kyunghee Song
Nutrition Research and Practice.2014; 8(2): 205. CrossRef
- Relationship between sweet food intake and stress among college students in Seoul and Gyeonggi areas
- 1,097 View
- 3 Download
- 9 Crossref

- [English]
- Nutrient Intake, Lifestyle Factors and Prevalent Hypertension in Korean Adults: Results from 2007-2008 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Sle Koo, Youngok Kim, Mi Kyung Kim, Jin Sook Yoon, Kyong Park
- Korean J Community Nutr 2012;17(3):329-340. Published online June 30, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2012.17.3.329
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hypertension is a well-known risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Previous studies have shown that changes in diet and lifestyle factors can prevent the development of hypertension, but the combined effects of these modifiable factors on hypertension are not well established. The objective of this study is to investigate associations of diet and lifestyle factors, evaluated both individually and in combination, with prevalent hypertension among Korean adults. We analyzed data obtained from the 2007-2008 Korean National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey, a nationwide cross-sectional study using a stratified, multistage probability sampling design. The associations of 12 nutrient intakes and lifestyle factors with risk of hypertension were explored using restricted cubic spline regression and logistic regression models among 6,351 adults. Total energy and several nutrients and minerals, including, calcium, vitamin A, vitamin C, and sodium, showed non-linear relationships with the risk of prevalent hypertension. In multivariate logistic regression models, dietary score, obesity and alcohol intake were independently associated with the risk of prevalent hypertension, but smoking and physical activity were not. Overall, participants whose dietary habits and lifestyle factors were all in the low-risk group had 68% lower prevalence of hypertension (OR: 0.32, 95 CI: 0.14-0.74) compared to those who were at least one in the high-risk group of any dietary or lifestyle factors. The result suggests that combined optimal lifestyle habits are strongly associated with lower prevalence of hypertension among Korean adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Genetic Variations in Thiamin Transferase SLC35F3 and the Risk of Hypertension in Koreans
Ja-young Seo, Jeong-Hwa Choi
Clinical Nutrition Research.2021; 10(2): 140. CrossRef - Association of Soybean Food Intake and Cardiometabolic Syndrome in Korean Women: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2007 to 2011)
Sook-Hyun Jun, Woo-Kyoung Shin, Yookyung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 143. CrossRef - How Much Intake of Sodium Is Good for Frailty? : The Korean Frailty and Aging Cohort Study (KFACS)
S. Kim, M. Kim, J. Min, J. Yoo, M. Kim, J. Kang, Chang Won Won
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging.2019; 23(6): 503. CrossRef - Nutritional Status of Hypertensive Men in Gyeongnam Area
Hae-Jin Park, Ye-Ji Choi, Sung-Hee Kim
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2016; 26(4): 297. CrossRef - Nutrition knowledge, eating attitudes, nutrition behavior, self-efficacy of childcare center foodservice employees by stages of behavioral change in reducing sodium intake
Yun Ahn, Kyung Won Kim, Kyungmin Kim, Jinwon Pyun, Ikhyun Yeo, Kisun Nam
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(5): 429. CrossRef - Prevalence of Osteoarthritis and Related Risk Factors in the Elderly: Data from the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V), 2010~2012
Hye-Sang Lee
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2014; 20(2): 99. CrossRef - Excessive Sodium Intake and Related Factors According to Energy Intakes Among Korean Elderly: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study
Young-Jin Tak, Jeong-Gyu Lee, Yun-Jin Kim, Sangyeoup Lee, Dong-Wook Jung, Yu-Hyeon Yi, Young-Hye Cho, Eun-Jung Choi, Seung-Hun Lee, Hye-Lim Hwang, A-Ra Cho
Journal of the Korean Geriatrics Society.2014; 18(4): 185. CrossRef - The relationship of dietary sodium, potassium, fruits, and vegetables intake with blood pressure among Korean adults aged 40 and older
Mi Kyung Kim, Kirang Kim, Min-Ho Shin, Dong Hoon Shin, Young-Hoon Lee, Byung-Yeol Chun, Bo Youl Choi
Nutrition Research and Practice.2014; 8(4): 453. CrossRef - An Analysis of Food Consumption Patterns of the Elderly from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES Ⅴ-1)
Eun Mi Kim, Mi-Kyung Choi
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2013; 42(5): 818. CrossRef - Prevalence of Hypertension and Related Risk Factors in the Elderly: Data from the 4th Korean National Health & Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007~2009
Hye-Sang Lee
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2013; 19(1): 14. CrossRef - Association of Bone Mineral Density and Blood Pressure, Calcium Intake among Adult Women in Seoul · Kyunggi Area - Based on 2011 KNHANES -
Jae Ok Koo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(3): 269. CrossRef
- Genetic Variations in Thiamin Transferase SLC35F3 and the Risk of Hypertension in Koreans
- 1,179 View
- 1 Download
- 11 Crossref

- [English]
- The Antecedents of Coffee Satisfaction by Lifestyle Segments for Korean and Chinese University Students in Korea
- Hye Kyung Chung, Hye Young Kim, Hae Young Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(6):782-793. Published online December 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.6.782
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purposes of this study were to classify university students by their lifestyle and to investigate the relationships between lifestyle and coffee satisfaction. The survey had been undertaken for 360 Korean and Chinese university students in Daejeon from November to December 2009. A total of 242 usable questionnaires were received with 67.2% response rate. The statistical analysis was performed by the SPSS 18.0 package program. Lifestyles of subjects, based on AIO (Activities, Interests, Opinions) method and factor analysis, were segmented into 2 groups of "outgoing activity" (n = 137) and "introverted devotion" (n = 105). "Outgoing activity" group exhibited highly health-oriented (p < 0.001) and convenience-oriented (p < 0.001) characteristics, but "introverted devotion" group showed highly goal-oriented (p < 0.01) and safety-oriented (p < 0.01) features. Comparing to "introverted devotion" group, "outgoing activity" group showed higher intake of coffee (p < 0.01) and more expense for beverage (p < 0.01). Three factors were extracted from 15 coffee quality attributes by factor analysis; "fundamentals", "supplement" and "inducement". These factors were positively correlated with coffee satisfaction according to lifestyle groups (p < 0.01). For "outgoing activity" group, 'fundamentals' was independent factor for satisfaction on coffee in coffee house (beta = 0.268, p < 0.05) and canned or bottled coffee (beta = 0.314, p < 0.01), and "supplement" was independent factor for satisfaction on coffee in vending machine (beta = 0.235, p < 0.05). For "introverted devotion" group, "inducement" was independent factor for satisfaction on coffee in vending machine (beta = 0.238, p < 0.001). These results provide an understanding for lifestyles of coffee consumers and give an insight into differentiated marketing plans for coffee industry.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influences of atmospherics on customer satisfaction and behavioural intentions in the restaurant industry: Evidence from an emerging economy
Mananage Shanika Hansini Rathnasiri, Pawan Kumar, Bindu Aggarwal, Kiran Nair, Narayanage Jayantha Dewasiri, Yasuko Kawahata
PLOS ONE.2025; 20(4): e0319948. CrossRef - Health-related Factors and Nutritional Status in Shift-workers at Coffee Shops - Focused on Single Women in Twenties in Seoul -
Seung-Lim Lee, Soo-Jin Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(5): 467. CrossRef - Dietary habits score, nutrients intake and dietary quality related to coffee consumption of college students in Incheon
Yun Ju Lee, Jeong Soon You, Kyung Ja Chang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2013; 46(6): 560. CrossRef - Analysis of University Student' Perception of Coffee Shop Prices through Price Sensitivity Measurements
Hyun-Ah Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2012; 41(8): 1182. CrossRef
- Influences of atmospherics on customer satisfaction and behavioural intentions in the restaurant industry: Evidence from an emerging economy
- 1,366 View
- 3 Download
- 4 Crossref

- [English]
- Comparison of Health Belief Levels and Health Behavior Practices according to Lifestyle among Adults Residing in Seoul
- Na Hong Choi, Hong Seok Ahn, Seungmin Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(6):683-696. Published online December 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.6.683
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study compared levels of health beliefs and health behavior practices according to lifestyle pattern among adults in Seoul. A self-administered survey questionnaire was collected from a total of 1,004 Seoul residents aged 30-59 years. The levels of perceived benefit, perceived barrier, and self-efficacy from health belief model and health behavior practices were measured across multiple health behavior areas including dietary behavior, drinking, smoking, exercise, functional food consumption, and weight control behavior. Factor analysis and subsequent cluster analysis based on 28 lifestyle questions divided the subjects into four lifestyles of society-, economy-, trend-, and health-oriented lifestyle. Some general characteristics were significantly different by lifestyles. The society-oriented lifestyle was significantly higher in proportions of men and overweight. The trend-oriented lifestyle was significantly younger and spent more monthly allowance. Health-oriented lifestyle was older. The levels of health belief variables and health behavior practices significantly differed by lifestyles. Overall the health-oriented lifestyle showed more desirable levels of health belief variables and health behavior practice in various health behavior areas compared to the other lifestyles, whereas the society-oriented lifestyle was found the other way. Health belief model variables including perceived benefit, perceived barrier, and self-efficacy were generally significant in predicting the levels of various health behavior practice, with somewhat differences by lifestyle pattern and health behavior type. The study findings suggest it may be useful to segment target subjects according to lifestyle pattern in planning and administering health education programs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of the factors that influence preschool children eating behavior by applying the health belief model: Seoul and Gyeonggi Province
Sung-Mi Cha, Soo-Youn Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(3): 541. CrossRef - Analysis of Dietary Behavior and Sustainable Dietary Life Competency in Families According to Parents’ Dietary Lifestyle: Using the 2021 Korea Consumer Behavior Survey for Food
Sun A Choi, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(11): 1179. CrossRef - Comparison of health care practice, dietary behavior, and nutrient intakes, considering the alcohol drinking status of industrial workers in the Chungnam area
Gun Hee Park, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(3): 277. CrossRef - Genetic Variations in Thiamin Transferase SLC35F3 and the Risk of Hypertension in Koreans
Ja-young Seo, Jeong-Hwa Choi
Clinical Nutrition Research.2021; 10(2): 140. CrossRef - Comparison of practice of dietary guidelines and health beliefs according to stage of weight loss behavior change among male workers
Su Jeong Song, HongSeok Ahn, Jinmo Khil
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2013; 46(3): 276. CrossRef - A Study on Dietary Behaviors, Health-Related Lifestyle of Adult Visitors at Public Health Centers in Gyeonggi Urban Area
Jong-Sook Kwon, Kyungmin Kim, Hyun-Chang Seo, Yoonna Lee, Seunggeon Lim, Young-Sug Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(6): 611. CrossRef
- Analysis of the factors that influence preschool children eating behavior by applying the health belief model: Seoul and Gyeonggi Province
- 1,297 View
- 0 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [English]
- Dietary and Lifestyle Factors Associated with Hypertension in Korean Adolescents: Based on 2005 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Killye Kim, Sook Mee Son, Hye Kyeong Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2011;16(4):439-453. Published online August 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.4.439
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was performed to determine dietary and lifestyle factors associated with hypertension in Korean adolescents. Study subjects were 12~19 years (n = 521) adolescents who participated in the 2005 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES III). Subjects were divided into the hypertensive group (HG, n = 102) and normotensive group (NG, n = 419) by '2007 Korean children and adolescents growth standard' and the relationships between blood pressure and physical measurement, nutrients intakes, eating behaviors and health related factors were analyzed. HG showed significantly higher levels in weight, waist circumference and BMI than NG. The amount of nutrient intakes was not different between NG and HG. Index of nutritional quality (INQ) for phosphate was higher in HG compared with NG. In both male and female HG, INQ for iron was higher but INQ for vitamin B1 was lower than NG. HG revealed higher consumption frequencies of snack, yoghurt, and ice cream compared with NG. In eating and behavioral factors, 'dinner with family', 'eat proper amount', 'keep Korean traditional diet', alcohol drinking, and mean alcohol intake were significantly different between the two groups. By logistic regression method, risk factors for hypertension revealed in this study were gender (male), age (15~19 years), BMI (> or = 85 percentile), and not keeping Korean traditional diet. These results suggest that education program for hypertension prevention in adolescents should include eating habits improvement and lifestyle modification as well as weight control.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to Household Income Levels of Korean Adolescents: Using Data from the 6th (2013 ~ 2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yu-Kyeong Kwon, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(6): 467. CrossRef - Differences in SBP, BMI, and Stress with AUDIT Score in Adolescents
Mi-Kyoung Cho, Mi Young Kim
The Open Nursing Journal.2018; 12(1): 228. CrossRef - An analysis of long-term occurrence of renal complications following pediatric pyeloplasty
Hahn-Ey Lee, Kwanjin Park, Hwang Choi
Journal of Pediatric Urology.2014; 10(6): 1083. CrossRef - The Factors related to Dyslipidemia and Hypertension among Male Office Workers
Eun Kyung Lee, Ok Soo Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(4): 432. CrossRef - A Study on Classification of Obesity for Koreans based on the Articles in the Korean Journal of Community Nutrition - Articles Enlisted from 1996 to 2011 -
Youngnam Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(5): 525. CrossRef - Association of Bone Mineral Density and Blood Pressure, Calcium Intake among Adult Women in Seoul · Kyunggi Area - Based on 2011 KNHANES -
Jae Ok Koo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(3): 269. CrossRef
- Biochemical Characteristics and Dietary Intake according to Household Income Levels of Korean Adolescents: Using Data from the 6th (2013 ~ 2015) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,174 View
- 4 Download
- 6 Crossref

- [English]
- A Survey on the Breakfast Skipping Rate of Korean Adults Relative to Their Lifestyle and Breakfast Skipping Reasons and Dietary Behavior of Breakfast Skippers
- Sunju Yun, Hye Ryeon Jeong, Mi Hyun Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2010;15(2):191-205. Published online April 30, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated the rates and reasons for breakfast skipping according to gender, age, and lifestyle related factors in Korean adults. The survey was conducted using questionnaires and the subjects included 1148 male and female adults aged 19-64. The rate of breakfast skipping (frequency of eating breakfast under 4 times/week) was 41.20% of the total subjects. The breakfast skipping rate of the male subjects was significantly higher than that of the female subjects (p < 0.001). As age and household income decreased, the breakfast skipping rate increased. Residents in small cities more frequently skipped breakfast than those in larger cities. The main reason for breakfast skipping was "lack of time for the preparation and consumption of food" and this reason was especially higher for office workers and younger adults among the participants. In addition, the proportion of habitual breakfast skippers increased with age. Among the answers regarding the person who prepares breakfast in their households, the highest proportion was for "family members" in the males and "myself" for the females. Of breakfast skippers, 77.63% answered that they consumed breakfast substitutes such as breads, dairy and fruits/vegetables. To summarize the results, the gender, age and lifestyle factors of adults were significantly related to the rates and reasons for breakfast skipping. Therefore, to reduce breakfast skipping in Korean adults, a differentiated nutritional education approach relative to gender, age, and lifestyle is needed along with the development of balanced breakfast substitutes.
- 626 View
- 15 Download

- [English]
- Blood Lipid Levels, Nutrient Intakes and Health-Related Lifestyles of Industrial Male Workers According to Apolipoprotein E Polymorphisms
- Yoo Kyoung Park, Sang Woon Cho, Ji Yeon Kang, Yun Mi Paek, Sook Hee Sung, Tae In Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2008;13(5):713-722. Published online October 31, 2008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate the association among nutrient intakes and health-related lifestyles with cardiovascular disease risk assessed by blood lipid profile according to Apolipoprotein E genotypes. Middle-aged industrial male workers who had completed their annual medical examination were recruited and data of 675 subjects who finished the nutrient survey were used in the analysis. Anthropometric parameters, dietary assessment (FFQ), health-related lifestyles and blood profiles were used for statistical analyses. Apo E genotype groups were classified into the following three genotypes: Apo E2 group (including E2/E2, E2/E3, E2/E4), Apo E3 group (including E3/E3), Apo E4 group (including E3/E4, E4/E4). The frequency of Apo E2, E3, and E4 allele were 13.3%, 75.0% and 11.7% respectively. There were no significant differences in the anthropometric parameters depending on different Apo E genotypes. Also, no significant differences in the nutrient intakes were found according to the genotype groups. The nutrient intakes of all subjects were similar to or higher than the level of KDRIs (Dietary Reference Intakes For Koreans) except for intakes of calcium (67.44% of KDRIs), vitamin A (73.83% of KDRIs) and vitamin B2 (78.02% of KDRIs). Also, there were no significant differences of health-related lifestyles according to Apo E genotype groups. As for the lipid profiles, Apo E4 group had significantly higher total and LDL-cholesterol concentrations than the Apo E2 group (p < 0.05). We confirmed that plasma total and LDL-cholesterol concentrations were greatly influenced by Apo E genotypes. However, nutrient intakes and health-related lifestyles were not associated with Apo E genotypes.
- 288 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Relations Among Weight Control Behaviors, Health-related Lifestyles, and Diet Behaviors in Middle Aged Koreans
- Yoon Jung Choi, Eun Mi Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2008;13(2):176-188. Published online April 30, 2008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this study, we compared demographic anthropometric characteristic, health-related lifestyle and diet behavior among weight control behaviors of 1187 (555 male, 632 female) aged 40~69yrs in Ganghwa country. All the data were analyzed by chi-square test, trend test, student t-test using SPSS 12.0 version at p < 0.05. 'Attempting weight control (loss)' was more in women than that was found in men (36.6% vs 20.7%), and women attempting weight loss most were 40-50 yrs. The reasons of weight loss were 'health problem' and 'health promotion'. Physical activity and diet restriction were commonly employed as weight control methods. Both genders attempting weight loss had a higher education level, BMI, percentage of body fat, waist circumference and physical activity than those not attempting weight control (p < 0.05). In dietary habits like 'meal regularity', 'slow eating' and 'over eating', women attempting weight loss were superior than those who not attempting weight control group (p < 0.05). Eating pattern changes like 'decrease of fats and fatty foods intake', 'vegetable oil usage', 'increase of fruit and vegetables intake', 'decrease of sugar and salt intake' showed significant differences (p < 0.001) between the attempted weight control groups and nonattempted weight control groups. Salt taste was a preference in male non-attempted weight control group, while sour, hot and spicy taste were preference in female attempted weight control group (p < 0.05). Preference for processed foods, fried foods and snack were significant differences (p < 0.05) in women attempted weight control group. Those attempting weight loss tried to improve their eating patterns. However, those attempting weight loss were poorer than the others in health-related lifestyle and eating habit. Therefore, it is necessary to make an effort that improve healthrelated lifestyle and diet behavior in middle aged group.
- 324 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Perception of Foodservice Quality Attributes of Older Adults: Compared by Lifestyle and Dining Frequency in Continuing Care Retirement Communities
- Sunhee Seo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2006;11(2):261-270. Published online April 30, 2006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to identify the differences of older adults' perceptions of foodservice quality attributes of current offerings in Continuing Care Retirement Communities (CCRCs) in terms of their lifestyles (length of residency, special diet, housing option, travel frequency, dine out frequency), dining frequency, and demographics in the dining room of CCRCs. The survey was administered to residents in three CCRCs. Data was analyzed for 140 surveys using t-test, ANOVA, and factor analysis. This study found female older adults perceived the following attributes were more important than male ones: presentation of food, color and garnish, texture of vegetables, taste and flavor of food, and respectful attitude of serving staff. Older adults who have a special diet perceived the seasoning and bite sized pieces were more important than those who have a general diet. Also, there were significant differences between frequent visitors and occasional visitors in the dining room of CCRCs. By knowing the differences by residents' demographics and residential characteristics, the foodservice manager can establish strategies to increase the dining frequency of residents in the dining rooms of CCRCs.
- 308 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- A Study on the Defecation Pattern and Lifestyle Factors of Female High School and College Students in Gyeonggi Province
- Jong Hyun Lee, Ju Hwan O
- Korean J Community Nutr 2005;10(1):36-45. Published online February 28, 2005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The aim of this study was to investigate the dietary and lifestyle factors related to bowel pattern of female high school and college students in Gyeonggi Province. The total of 202 self-administered questionnaires (high school students 77;college students 125) were analyzed. All respondents were devided into four groups based on their self-reported pattern of defecation:18 subjects (9.0%) comprised the normal group, 73 (36.1%) the constipation group, 73 (36.1%) the constipation/diarrhea group, and 38 (18.8%) the diarrhea group. Regularity of exercise was significantly higher in the college students than high school students, and times spending on a chair were longer in the high school students than college students. Most students (72.7%) reported that they had stress. Fourty point six percent of the subjects reported that they had 3 meals per day, which tended to be higher in the normal and diarrhea group than constipation and constipation/diarrhea group. Most students (69.7) skipped breakfast which was lower in the normal group than the other groups. The most preferred dietary fiber food was korean cabbage kimchi. Fifty-eight point four percent of the subjects reported that they had irregular bowel movement. Bowel movement was more irregular in the high school students than college students, and in the constipation group than the other groups. Of the subjects, 77.7% had defecation frequency between three per week and three per day. Those who spent within 10 minutes for defecation were 79.6%, and those had difficulty in evacuating were 76.0%. High school students and those with constipation and constipation/diarrhea had a significantly lower defecation frequency, longer time spent at the toilet, and greater difficulty in evacuating than college students and normal and diarrhea group. The percentage of those who had feelings of residue in the intestine after defecation was 92.5%, and it was greater in the constipation or diarrhea group than in the normal group. Most students (93.5%) reported that they had abdominal pain or discomfort. These results suggest that decreasing times spending on a chair, decreasing stress, keeping 3 meal per day at regular hours, and increasing dietary fiber intake are associated with desirable bowel pattern.
- 422 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Dietary Habits and Factors Related to Lifestyles in Constipated Female Students
- Jeong Ran Shin, Sun Yung Ly
- Korean J Community Nutr 2003;8(5):675-688. Published online October 31, 2003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The aim of this study was to investigate the dietary habits and the factors related to lifestyles in female college students with constipation. A survey was conducted using a self-administered questionnaires. Two hundred ninety one subjects participated in this study. All respondents were divided into three groups based on their frequency of stool evacuation: 129 subjects (44.3%) comprised the normal group, 109 (37.5%) the mild constipated group and 53 (18.2%) the severely constipated group. Abdominal pain and ailment during evacuation were higher and the feeling of relief after evacuation was lower in the normal group than in the two constipated groups. The greater the symptoms of constipation, the more laxatives were taken. The prevalence of constipation was lower in students who lived at home than in those who lived in other types of residences. The more pocket money the subject had, the more complaints they had about constipation symptoms. Forty three percent of the subjects ate meals regularly. The less frequently they ate meals and the greater the rate of skipping breakfasts and dining-out, the greater were their constipation symptoms. Rice and most of the food items in the vegetable food group were consumed less frequently in the two constipated groups than in the normal group. The severely constipated group ate food items in the fat group less frequently than the normal and mildly costipated groups. The beverage intake of the normal group tended to be lower than those of the two constipated groups; the constipated groups consumed fruits and vegetable juices less frequently and coffee and tea more frequently. The severely constipated group ate the least number of food items in the vegetable & fruit and fat food groups. Therefore, dietary habits and factors related to lifestyles should be changed through nutrition education programs aimed at improving the symptoms of constipation in young women.
- 339 View
- 0 Download

Randomized Controlled Trial
- [English]
- A Study on the Anthropometry and Healh-Related Lifestyle Habits of Women College Students in Kunsan
- Hye Soon Chang, Mi Ra Kim
- Korean J Community Nutr 2003;8(4):526-537. Published online August 31, 2003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to compare the anthropometry and nutrition knowledge, food behaviour and lifestyle of women college students with different obesity indexes. The subjects were 251 women college students who were randomly selected from Kunsan National University. The height, body weight, soft/lean mass, fat mass, percentage of body fat, and fat distribution were measured, and health-related lifestyle habits were evaluated based on questionnaires. The subjects were assigned to one of the following groups based on their Body Mass Index (BMI): underweight, normal weight and overweight. The results were as follows. Their body weight, soft/lean mass, fat mass, percentage of body fat, and fat distribution were significantly higher in the overweight subjects when compared to the underweight or normal weight subjects. Standard of living, self-recognition of health status and duration of exercise were significantly correlated with their BMIs. Self-satisfaction with body weight decreased as the BMI increased. Most subjects had poor habits such as skipping meals and lack of exercises. The overweight and the underweight groups skipped meals more frequently than the normal weight group. There were no significant differences in the scores on the nutritional knowledge and the dietary behaviour of the subjects with different BMIs. Therefore, proper nutritional education on regular meals and intervention are required if women college students are to have normal weights and healthy lifestyles.
- 306 View
- 1 Download

Original Articles
- [English]
- Measuring Service Quality Perception of University Faculty Members & Staffs Towards Faculty Foodservice Based on Lifestyle Segmentation
- Moon Kyung Park, Il Sun Yang, Dong Hoon Kim, Seo Young Shin, Hae Young Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2003;8(4):556-565. Published online August 31, 2003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Market segmentation helps providers to find better marketing opportunities and allows foodservice managers to develop the right product for each target market. Therefore, this study, taking university faculty and staff as subject, is intended to diagnose the relative value of service quality attribute, on the basis service quality scenario of faculty foodservice; to suggest price for improving customer loyalty in market segments. A questionnaire was developed ar d mailed to 600 Yonsei university faculty and staffs. A total of 385 questionnaires were usable; resulting in a 58.7% of faculty and a 69.7% of staff response rate, respectively. Statistical data analysis was completed using the SAS/Win 6.12 for descriptive Analysis, ANOVA, principal factor analysis, cluster analysis, reliability test and discriminant analysis. The results of the study are as below. Eighteen questions were selected for measuring respondents' lifestyle by AIO method and the seven lifestyle factors derived from factor analysis and aggregated distinct 4 clusters. Service quality attributes of the scenario were determined with 'food quality', 'menu variety', 'atmosphere', 'fast service', and 'clean and sanitation'. 'Food quality', 'menu variety', 'atmosphere', 'fast service', and 'clean and sanitation', in decreasing order, were identified as improving customer loyalty. However, most faculty and staffs were satisfied with the present meal price. The result of this study indicates that the relative value of service quality was differed significantly among the various market segments. 'Food quality', 'menu variety', and 'atmosphere' were determined as major service quality attributes. Thus, customer loyalty could be increased by improving food taste and quality, atmosphere, and service delivery.
- 263 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Dietary Behaviors, Health-related Lifestyle and Blood Lipid Profile of Obese Children in Incheon
- Mi Young Lee, Soon Ki Kim, Kyung Ja Chang
- Korean J Community Nutr 2002;7(6):803-813. Published online December 31, 2002
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate the anthropometric and blood biochemical characteristics, the dietary behaviors and health-related lifestyles of obese children in Incheon. A cross-sectional survey was conducted using anthropometric measurements, biochemical assessments and questionnaire analysis. The subjects included 7,055 obese children residing in the Incheon area (from 106 elementary schools). The degree of obesity was classified using the Obesity Index (OI) as : light 20% < OI < 30% ; Medium 30% < OI < 50% ; Severe 50% > OI. The statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS 10.0 program. Most subjects fell within the medium range of obesity. Most subjects had dietary problems such as overeating, unbalanced meals and skipping breakfast. The ratio of boy subjects eating green and yellow vegetables was lower when compared to that of the girl subjects. The boy subjects exercised more frequently and longer than the girls. As the Obesity Index increased, hypercholesterolemia significantly increased. The blood cholesterol levels of the subjects were positively correlated with body fat, waist/hip ratio and BMI; HDL cholesterol levels of the subjects were negatively correlated with the anthropometric data and the LDL cholesterol levels of the subjects were positively correlated with body fat. The blood triglycerides levels of the subjects were positively correlated with body weight, body fat, waist/hip ratio and BMI. Therefore, proper nutritional education and intervention are required for an improvement of obese children's dietary behavior, heath-related factors and blood lipid profiles.
- 302 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- A Study of the Lifestyle Factors Related to Constipation among Food Habits of College Students in Seoul and Gyunggi
- Hea Jung Chung, Hye Won Park, Eun Jung Choi, Ji Jeung Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2002;7(5):654-663. Published online October 31, 2002
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study is to investigate how the lifestyles of food habits of college students relate to constipation. The results were as follows : 1) All the total respondents were 541 college students. 220 (40.8%) respondents were male and 321 (59.2%) respondents were female. Based on their BMIs, 55.5% of the female respondents were under-weight (BMI < 20), 16.8% of the male respondents were under-weight, as well. These results point out the fact that a high percentage of female college students are under-weight, compared to male of students. 2) Of the respondents, 59.0% reported having 1 or 2 meals per day, but their eating patterns were irregular. Of the respondents, 71.2% preferred white rice with their meals. Of the respondents, 51.2% reported that they skipped breakfast. The main reasons why these respondents skipped breakfast were either that they were in a busy (44.7%), or it was their habit (38.4%). The response that their meals were nutritionally balanced was 34.6%, and the student who thought that their own meal pattern was healthful was 8.0%. 3) This research also focused on body image among female college students, and the results indicate that the majority of female respondents (62.5%) felt that they were overweight (very fatty or fatty) and 90.1% of the female respondents indicated they were interested in dieting (interest or very interest). Most of the students were involved in light or medium activity (94.2%) or no exercise (75.6%). The ratio of those who exercised was everyday only 33.6%. 4) Of the respondents, 48.7% reported that they had difficulty evacuating (every time very difficult, every time difficult and sometimes difficult) and 50.3% of the students reported that their bowel movements were irregular. 5) Of the females, 8.2% and Of the males, 0.5% were regarded as constipated. 6) The life habit factors that influenced constipation were skipping breakfast, the amount of water intake and exercise.
- 330 View
- 2 Download

- [English]
- Association of Bone Densities with Anthropometric Indices and Lifestyles in Elderly People
- Sook Mee Son, Ye Na Chun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2002;7(3):327-335. Published online June 30, 2002
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was performed to investigate the relationships among bone mineral densities (BMD), anthropometric data and lifestyle factors in the elderly. Subjects included 138 elderly (male: 38, female: 100) aged over 65 years, who were home-dwelling in a low-income area of Puchon City. The BMDs of the lumbar spines (LS), femoral necks (FN), Ward's triangles (WT) and trochanters (TC) were measured by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry. The females showed significantly lower BMDs in four sites (p < 0.0001). The elderly aged over 75 revealed significantly more decreased femoral BMDs than the elderly aged 65 to 74. Female with BMIs of 20 to 25, showed significantly higher BMDs in LS, FN and trochanter than those with BMIs of less than 20. However, males displayed significantly higher BMDs in only LS, with increasing BMIs. THe BMDs of LS correlated with weights (r = 0.543, p < 0.001), heights (r = 0.477, p < 0.001), upper arm circumferences (r = 0.368, p < 0.01), waist circumferences (r = 0.367, p < 0.001), subscapular skinfold thicknesses (r = 0.363, p < 0.001) and hip circumferences (r = 0.231, p < 0.01). Non-smokers and non-drinkers showed significantly higher BMDs in trochanters only in the case of the males. Female milk-drinkers showed significantly elevated LS BMDs. Eighteen percent of the males were assessed as having osteoporosis, as compared to fifty percent of the females. Ninety-three percent of the females and 81.6% of the males responded that they often or always had "difficulty in standing for a long time".
- 311 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Comparison of Lifestyle and Nutrient Intake by Number of Components of Insulin Resistance Syndrome in the Daegu Community
- Hee Ja Lee, Jin Sook Yoon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2001;6(3):317-330. Published online August 31, 2001
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to figure out the characteristics of dietary habits and lifestyles related to the development of insulin resistance syndrome(IRS). The participants in this study were 595 adults with one or more abnormal data from a health examination and 215 normal adults. When IRS was defined as a condition in which the subjects have 2 or more abnormalities among obesity, hyperlipidemia, hypertension and hyperglycemia, the prevalence rate was 37.8%. We classified the 595 adults by the number of components of IRS components they had, the higher age and obesity index they had. Total cholesterol and glucose levels in the blood were also positively related to the number of IRS components. IRS subjects tended to practice less habitual drinking and more exercise and weight control. Coffee consumption and dining out frequency were also lower in the IRS group. An analysis of food habits by odds ratio indicated that total food score was better in the IRS group. However, it appeared that food habits such as \"frequent snacking\" and \"never rejecting offered foods\" need to be improved in IRS subjects. Other undesirable food habits were related to the consumption of eggs, dairy products, fried foods, garlic and onion. Dietary intake of Ca, Fe, riboflavin, Vit A, and energy were less than 75% of the Korean recommended allowance for more than half of the subjects. Nutrient intake was lower, Ca/P ratio from food intake was worse in the IRS group. Our results indicated that nutrition counseling for IRS need to be focused on balanced food intake to supply sufficient amount of each nutrient.
- 299 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- A Study on Nutritional Status, Maternal Factors, and Lifestyles according to BMD in Rural Postmenopausal Women
- Chung Ja Sung, Sun Hae Choi, Mi Hyun Kim, Yun Hee Choi, Da Hong Lee, Soo Kyung Baek, Hye Kyung Kim, Mi Kyeong Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2001;6(2):192-204. Published online May 31, 2001
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Osteoporosis and other related conditions pose a growing public health problem, especially in postmenopausal women. The main purpose of the study was to investigate the correlations among BMD, maternal factors, and life styles, and intake of nutrients in postmenopausal women. One hundred participants in Kyungge-do were divided into three groups according to their BMD measurements measured by DXA. Dietary analysis, anthropometric measurements, and questionares were administered to these women. The percentage of the osteoporosis, osteopenia(Osteopinia), and normal groups were 32%, 48%, and 20% respectively. The average age was significantly the highest in the osteoporosis group. The average age at menopause was 47.2. Osteoporosis group's age at menopause was significantly the lowest. The sleeping hours of the osteoporosis and osteopenia group were significantly longer than the normal group. The intake of vitamin B2 was positively correlated with the BMD of femoral neck. The BMD of these two sites was positively correlated with weight, BMI, waist, and hip size and negatively correlated with the length of the menstrual cycle, duration after menopause, the age at the last delivery, and sleeping hours. Spinal BMD positively correlated with hours of outdoor activity. Therefore, maternal factors, lifestyles, and intake of nutrients contribute to BMD.
- 302 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- The Relationship between Obesity, Lifestyle, and Dietary Intake and Serum Lipid Level in Male University Students
- Wha Jin Hyun
- Korean J Community Nutr 2001;6(2):162-171. Published online May 31, 2001
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was performed to investigate the relationship between obesity, health-related lifestyle, and dietary intake and serum lipid level in 96 male university students. Health-related lifestyle factors were obtained from questionnaires. Dietary intakes were evaluated with one-day 24-hr recall and two-day dietary record. Anthoropometric data were recorded and serum cholesterol and triacylglycerol concentrations were measured. 21.9%, 36.5%, 36.5%, and 6.2% of the subjects had levels beyond the normal range in serum total cholesterol(TC), HDL-cholesterol(HDL-C), LDL-cholesterol(LDL-C), and triacyglycerol respectively, and 57.3% of the subjects had more than one hyperlipidemic factor. TC was correlated positively with BMI(p<0.01), waist length(p<0.05), hip length(p<0.05), and the amount of smoking(p<0.05). HDL-C was correlated negatively with BMI(p<0.05) and hip lenghth(p<0.05). LTD-C was correlated positively with BMI(p<0.01), water length(p<0.05), hip length(p<0.01), and coffee consumption(p<0.05). TG was correlated positively with waist length(p<0.01), waist-to-hip ratio(p<0.05), and amount of smoking(p<0.01) and negatively correlated with frequence of exercise(p<0.05). Among nutrient intakes, only the ratio of protein to energy was correlated negatively with TC(p<0.05). Logistic regression analysis revealed that BMI, waist length, hip length, waist-to-hip ratio, and amount of cigarette smoking were associated with an increased risk of hyper-TC. BMI, waist length, and hip length were associated with an increased risk of hypo-HDL-C. BMI and coffee consumption were associated with an increased risk of hyper-LDL-C. Amount of cigarette smoking was associated with an increased risk of hyper-TG. In conclusion, a high prevalence of hyperlipidemia in subjects was observed. Also obesity, smoking, and coffee consumption were observed to be highly with the risk of hyperlipidemia in subjects. These findings imply that these factors should be primarily considered in planing the nutrition education program for the prevention of cardiovascular disease in male university students.
- 318 View
- 5 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



