Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [English]
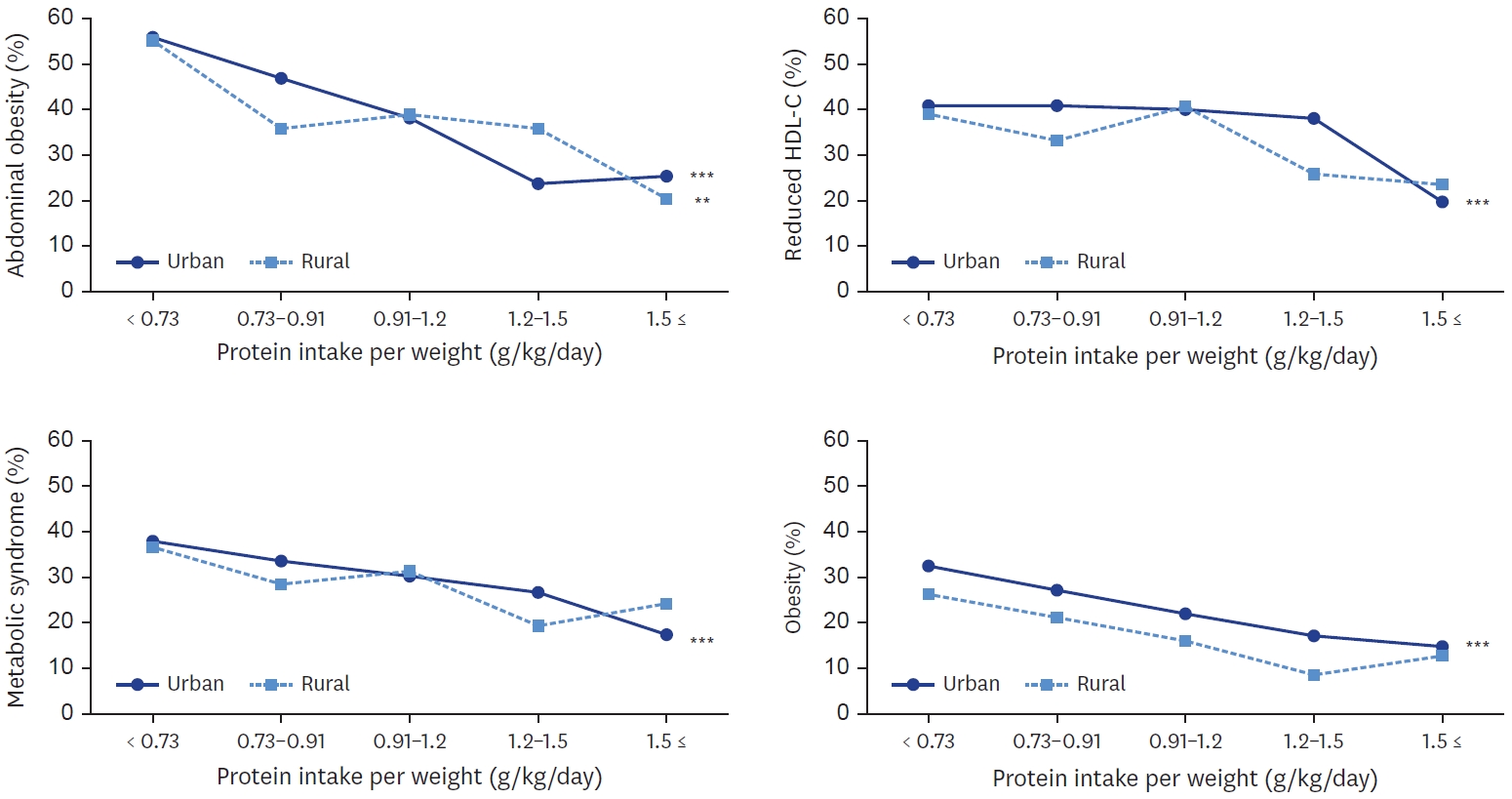
- Regional differences in protein intake and protein sources of Korean older adults and their association with metabolic syndrome using the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys: a cross-sectional study
- You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2024;29(3):173-188. Published online June 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2024.29.3.173
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The study aim was to analyze the regional differences in dietary protein intake and protein sources of Korean older adults and their association with metabolic syndrome.
Methods
Study participants were 1,721 older adults aged 65 and over who participated in 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Using 24-hour recall dietary intake data, protein intake and their food sources were examined. The association between protein intake and metabolic syndrome, obesity, and abdominal obesity were analyzed by multiple logistic regression.
Results
Total protein and animal protein intakes were higher in urban area (60.0 g, 24.4 g, respectively) than in rural area (54.6 g, 19.6 g, respectively). With increase of protein intake level, animal to total protein proportion was increased in both areas. Total protein and plant protein intake was negatively associated with the risk of obesity, abdominal obesity in both areas. Animal protein intake was negatively associated with the risk of obesity in both areas, and with abdominal obesity only in urban area. In urban area, plant protein intake was also negatively associated with the risks of metabolic syndrome, elevated triglyceride, and reduced high density lipoprotein-cholesterol. In urban area, the risk of metabolic syndrome was decreased when their protein intake was more than 0.91 g/kg and was lowest when their protein intake was more than 1.5 g/kg (P for trend < 0.001).
Conclusions
Korean older adults showed inadequate protein intake and those in rural area showed lower animal protein intake than in urban area. The risk of obesity and metabolic syndrome was decreased with the increase of protein intake level. These findings may help develop effective nutrition support strategy for older adults to reduce regional health disparity.
- 9,214 View
- 103 Download

- [Korean]
- Trends in Dietary Protein Intake and Its Adequacy among Korean Adults: Data from the 2010 ~ 2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES)
- Hyunji Ham, Kyungho Ha
- Korean J Community Nutr 2022;27(1):47-60. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2022.27.1.47
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate dietary protein intake and its adequacy among Korean adults during recent 10 years.
Methods
Based on the 2010 ~ 2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) data, a total of 51,296 adults aged 19 years old or more who participated in a one-day 24-hr dietary recall were included. Dietary protein intake was estimated as percentages of total energy (% of energy) and grams per body weight (g/kg/ day) and compared with the 2020 Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans to evaluate the adequacy of protein intake. In addition, proportions of people whose protein intakes were less than the estimated average requirement (EAR) and above the upper limit of the acceptable macronutrient distribution range (AMDR) (> 20% of energy) were calculated according to sociodemographic characteristics.
Results
Protein intake was increased from 14.7% of energy in 2010 to 15.6% of energy in 2019 among Korean adults. However, there was no increase in protein intake relative to the recommended nutrient intake (% RNI) during the recent 10 years. Protein intake relative to the RNI was decreased from 130.2% in 2010 to 121.1% in 2019 (P for trend < 0.0001) among total participants, and a significant decreasing trend was observed in all age groups except for over 65 years old. However, protein intake relative to the RNI was lowest in the elderly (98.6%). Proportions of low protein intake (< EAR) and high protein intake (> AMDR) increased in the past 10 years (P for trend < 0.0001 for all), and these were associated with socioeconomic statuses, such as education and household income levels.
Conclusions
These findings suggest that protein adequacy in Korean adults has not been improved over the past decade compared with recommended levels. Nutritional education and intervention programs should consider different intake levels according to sociodemographic characteristics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Status of Use of Protein Supplement Products according to the Health Concerns of Adults in Their 20s and 30s
Cho-In Oh, Bok-Mi Jung
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2025; 35(1): 9. CrossRef - Dietary Assessment of Older Korean Adults by Level of Plant Protein Intake
Yong-Seok Kwon, Ye-Jun Kim, Jeong-Hun Song, Yangsuk Kim
Nutrients.2025; 17(12): 1976. CrossRef - Trends in dietary amino acid intake and food sources among Korean adults: data from the 2010-2022 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Sumin Kim, Hyunji Ham, Kyungho Ha
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 773. CrossRef - Nutritional risk assessment using estimated usual nutrient intake in Korean adults: analysis of the 8th (2019–2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
Woojin Byeon, Cho-il Kim, Sung Ok Kwon, Jihyun Yoon, Linxi Huang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2025; 19(5): 799. CrossRef - High-Protein Products in 2013 and 2023: Shifts in Diverse Aspects Over the Last Ten Years
Hye Ran Lee, Ihyeon Cho, Hyejin Yi, Hee Jung Park
Food Supplements and Biomaterials for Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Regional differences in protein intake and protein sources of Korean older adults and their association with metabolic syndrome using the 2016–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys: a cross-sectional study
You-Sin Lee, Yoonna Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2024; 29(3): 173. CrossRef - Development of Protein Enhanced Diet for Socially Vulnerable Elderly
Jihye Hong, Hyung-Geun Jeon, Seulgi Kim, Gitae Park
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(1): 39. CrossRef - Consumption of protein supplements/protein-fortified foods among young adults in Jeju
Hyoju Lee, Youjeong Jang, Sumin Kim, Kyungho Ha
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2024; 57(2): 261. CrossRef - Association between Processed Meat Protein Consumption and Incident Osteoporosis in Adults Aged 50 Years and Older: A Prospective Cohort Study Based on Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study Data (2005–2020)
Dohee Lee, Soo Hyoung Lee, Ki Hyun Park, Kunhee Han, Eunjin Jeong
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2024; 45(5): 268. CrossRef - The Relationship of Pork Meat Consumption with Nutrient Intakes, Diet Quality, and Biomarkers of Health Status in Korean Older Adults
Ah-Jin Jung, Anshul Sharma, Mei Chung, Taylor Wallace, Hae-Jeung Lee
Nutrients.2024; 16(23): 4188. CrossRef - Higher Animal-Based Protein Intake Levels Show a Greater Likelihood of Having Metabolic Syndrome in Single-Person Households Among Korean Adults
Yeongin Lee, Hyojee Joung
Nutrients.2024; 16(23): 4239. CrossRef - Relationship between protein intake and grip strength in qualitative and quantitative aspects among the elderly in Korea: results from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Mi‑Hyun Kim, Mi‑Kyeong Choi, Yun‑Jung Bae
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Current status of nutrient intake in Korea: focused on macronutrients
Seung-Won Oh
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2022; 65(12): 801. CrossRef
- Status of Use of Protein Supplement Products according to the Health Concerns of Adults in Their 20s and 30s
- 6,876 View
- 194 Download
- 13 Crossref

- [English]
- Association of Low Hand Grip Strength with Protein Intake in Korean Female Elderly: based on the Seventh Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES VII), 2016-2018
- Won Jang, Ho Kyung Ryu
- Korean J Community Nutr 2020;25(3):226-235. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2020.25.3.226
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Decreasing muscle strength in old age has become a significant health problem because it increases the risk of falls or fractures and transfers to other diseases. The precise role of dietary protein intake in preventing or reducing muscle weakness is unclear. This study examined the relationship between handgrip strength and protein intake in Korean female elderly.
Methods
This was a cross-sectional study that used data from the Seventh Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (KNHANES) on female subjects aged 65 years and older. Low handgrip strength (LHGS) was defined as a handgrip strength below than 18 kg. Dietary intake data were obtained using the 1-day 24-hour recall method. Multiple regression was performed to test whether there is an independent relationship between the grip strength and protein intake, and the association between protein intake and LHGS was confirmed through multiple logistic regression.
Results
The mean age of the 2,083 elderly females was 73.3 ± 0.1 years, and the prevalence of LHGS was 35% (n=734). Elderly women with an LHGS consumed less energy, total protein, and animal-based protein than those in the normal group. A multiple regression analysis after adjusting for covariate revealed a significant positive association between the handgrip strength and energy, protein, and animal-based protein intake. Multiple logistic regression analysis showed that the odds ratio (OR) of LHGS in female elderly with the highest quartiles of consumption of energy [OR, 0.65; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.43- 0.82; P for trend=0.004], and animal-based protein [OR, 0.59; CI, 0.40-0.87; P for trend= 0.037] were significantly lower than those in the lowest quartiles.
Conclusions
The energy intake and animal-based protein intake were negatively associated with the LHGS. These results suggest that adequate energy intake and protein intake, particularly those from animal-based sources, for elderly women in Korea are beneficial in lowering the risk of LHGS. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship between dietary protein and amino acid intake and handgrip strength in Korean adults: data from the 2014–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyunji Ham, Sumin Kim, Kyungho Ha
Nutrition Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Protein Intake and Physical Activity on Hand Grip Strength in the Older Adults Aged over 65 Years of Age: Using Data from the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Do-Yeon Kim, Byung-Sun Choi
Korean Journal of Geriatrics & Gerontology.2025; 26(1): 23. CrossRef - Dietary Assessment of Older Korean Adults by Level of Plant Protein Intake
Yong-Seok Kwon, Ye-Jun Kim, Jeong-Hun Song, Yangsuk Kim
Nutrients.2025; 17(12): 1976. CrossRef - Association Between Protein Intake and Sarcopenia-Related Indicators Among Korean Older Adults: A Scoping Review
Minjee Han, Kyung-sook Woo, Kirang Kim
Clinical Nutrition Research.2025; 14(3): 216. CrossRef - Association Between Serum High Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein Levels and Low Muscle Strength Among Korean Adults
Bo-Hyun Choi, Sunhye Shin
Nutrients.2025; 17(16): 2698. CrossRef - Associations Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Sarcopenia in South Korean Adults: Based on the 2022 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Sunhye Shin, Mi Joung Kim
Nutrients.2025; 17(20): 3292. CrossRef - Development of Protein Enhanced Diet for Socially Vulnerable Elderly
Jihye Hong, Hyung-Geun Jeon, Seulgi Kim, Gitae Park
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(1): 39. CrossRef - Association Between Dietary Fiber Intake and Low Muscle Strength Among Korean Adults
Sunhye Shin
Clinical Nutrition Research.2024; 13(1): 33. CrossRef - Health Outcome Comparison Based on Dietary Inflammatory Levels among Sample of Korean Elderly
Seul-Ki Koo, Hee-Sook Lim
Healthcare.2024; 12(10): 1003. CrossRef - Low dietary vitamin C intake is associated with low muscle strength among elderly Korean women
Chan Yoon Park, Sunhye Shin
Nutrition Research.2024; 127: 75. CrossRef - The Relationship of Pork Meat Consumption with Nutrient Intakes, Diet Quality, and Biomarkers of Health Status in Korean Older Adults
Ah-Jin Jung, Anshul Sharma, Mei Chung, Taylor Wallace, Hae-Jeung Lee
Nutrients.2024; 16(23): 4188. CrossRef - Association of Protein Intake with Sarcopenia and Related Indicators Among Korean Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Minjee Han, Kyungsook Woo, Kirang Kim
Nutrients.2024; 16(24): 4350. CrossRef - Macronutrients intake and physical frailty in Korean older adults: A cohort‐based cross‐sectional study
Narae Yang, Yunhwan Lee, Mi Kyung Kim, Kirang Kim
Geriatrics & Gerontology International.2023; 23(7): 478. CrossRef - The effect of combining nutrient intake and physical activity levels on central obesity, sarcopenia, and sarcopenic obesity: a population-based cross-sectional study in South Korea
Jong Eun Park, Seulgi Lee, Kirang Kim
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between Anemia with Frailty and Nutritional Intake in Persons Age 65 and Older: The 2016–2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Heekyung Jeong, Chaeyoon Lee, So Yoon Han, Young-Jin Ko, Kyoung Jin Kim
Korean Journal of Family Practice.2023; 13(1): 15. CrossRef - Association between seafood intake and frailty according to gender in Korean elderly: data procured from the Seventh (2016–2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Won Jang, Yeji Choi, Jung Hee Cho, Donglim Lee, Yangha Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(2): 155. CrossRef - Association between plant protein intake and grip strength in Koreans aged 50 years or older: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016–2018
Sook-Hyun Jun, Jung Woo Lee, Woo-Kyoung Shin, Seung-Yeon Lee, Yookyung Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(5): 969. CrossRef - Trends in Seafood Consumption and Factors Influencing the Consumption of Seafood Among the Old Adults Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009~2019
Won Jang, Jung-Hee Cho, Donglim Lee, Yangha Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2022; 51(7): 651. CrossRef - Preparation of Mousse Type Pork Patties with Added Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae
Eunji Kim, Nami Joo
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2022; 32(1): 63. CrossRef - Dietary Essential Amino Acid Intake Is Associated with High Muscle Strength in Korean Older Adults
Jihyun Im, Hyoungsu Park, Kyong Park
Nutrients.2022; 14(15): 3104. CrossRef - Handgrip Strength Assessment and Its Associated Factors among Hospitalized Elderly in Klang Valley Hospitals
Khairunisar-E-Rashim Mohammed Yusufirashim, Noraida Omar, Shazli Illyani Mohamad Shafie, Siti Hazimah Nor’hisham
Malaysian Journal of Medicine and Health Sciences.2022; 18(6): 115. CrossRef - A study on the nutrient intake of the elderly in Korea based on activity limitations: data from the 2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Soyoung Kim, Youngmi Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(5): 543. CrossRef - Association between Sarcopenia and Energy and Protein Intakes in Community-dwelling Elderly
Woori Na, Dayoung Oh, Seohyeon Hwang, Bonghee Chung, Cheongmin Sohn
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(4): 286. CrossRef - Dietary phytochemicals as a promising nutritional strategy for sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Hye Yun Jeong, Oran Kwon
Applied Biological Chemistry.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Interaction between Obesity and Grip Strength on Health-Related Quality of Life in Elderly: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016-2018)
Seungjae Hyun, Darae Woo, Sangshin Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2021; 46(1): 28. CrossRef - Nutritional Status according to the Frailty Status of the Elderly at Home in Seo-gu, Gwangju, Korea
Ye Eun Kim, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 382. CrossRef
- Relationship between dietary protein and amino acid intake and handgrip strength in Korean adults: data from the 2014–2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,737 View
- 27 Download
- 26 Crossref

Original Articles
- [English]
- Effects of Low-Calorie Diet Including High Protein-Low Carbohydrate Protein Bar on Weight Loss and Serum Lipid Indicators in Overweight Women according to Dietary Compliance
- Dasom Park, Hyun Joo Lee, Sook Mee Son
- Korean J Community Nutr 2019;24(6):485-496. Published online December 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.6.485
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
This study was conducted to investigate the effect of a 6-week low-calorie diet (LCD) program including high protein-low carbohydrate protein bar on weight loss, blood pressure, and blood lipid profile in 40 overweight women according to dietary compliance.
METHODS
Subjects were 62 healthy overweight women (BMI ≥ 23.0 or body fat percentage ≥ 28%), aged 20~59 yrs who were provided a high protein-low carbohydrate protein bar (each 35 g, 154 kcal, protein energy %: 28.6%, carbohydrate energy %: 38.7%) as part of dinner for 6 weeks. Forty subjects who completed the whole diet program were categorized into high compliance (HC) group (days of eating protein bar ≥ 5 weeks) or low compliance (LC) group (days < 5 weeks).
RESULTS
Energy intake significantly decreased from 1,867.5 kcal at baseline to 1,137.4 kcal at 6 weeks for the HC group and from 1,971.7 kcal to 1,362.2 kcal for the LC group, respectively. On the other hand, a significant increase in protein energy percentage was observed in each group (HC group: 3.5%, LC group: 2.2%). Both groups showed significant decreases in weight (HC group: 1.8 kg, LC group: 1.1 kg), BMI, fat mass, systolic blood pressure, total cholesterol, and LDL-cholesterol. Reduction of body fat percentage and diastolic blood pressure were only observed in the HC group.
CONCLUSIONS
The inclusion of a high protein-low carbohydrate protein bar as part of a low-calorie diet for a short period can be effective to achieve weight loss and concomitantly improve blood cholesterol level without serious physiological side effects. More evident results can be achieved by eating a diet with low calorie diet including high protein-low carbohydrate protein bar for more than 5 weeks. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 규칙적 운동 수행에 따른 MZ세대의 고단백 식품 인식 및 섭취 패턴 비교 연구
지선 김, 영일 박, 나미 주
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2024; 40(5): 335. CrossRef
- 규칙적 운동 수행에 따른 MZ세대의 고단백 식품 인식 및 섭취 패턴 비교 연구
- 1,874 View
- 11 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Metabolic Syndrome Risk by Intake Ratio and Intake Pattern of Proteins in Middle-aged Men Based on the 2012-2013 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data
- Minkyoung Jang, Eunsil Her, Kyunghea Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2016;21(4):366-377. Published online August 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.4.366
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The purpose of the study was to compare intake of energy nutrients, physical characteristics, and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome according to protein intake group.
METHODS
Subjects were 827 men aged 40-65 years. The results presented were based on data from the 2012-2013 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey and analyzed using SPSS. The odds ratio (OR) of metabolic syndrome was assessed according to the protein intake group and intake pattern of protein-rich foods.
RESULTS
The mean of protein intake was 73.96 ± 0.71 g. According to level of protein intake, four groups (deficient, normal, excess 1, excess 2) were created and their percentages were 8.3%, 39.6%, 37.1%, and 15.0% respectively. The mean of daily energy intake was 2,312.33 ± 24.08 kcal. It was higher in excess group 2 than in the deficiency group (p < 0.001). Moreover, the intake of all energy nutrients increased significantly with protein intake group (p < 0.001). The main contribution to daily protein included mixed grains (10.96 ± 0.32 g), milled rice (7.14 ± 0.30 g), chicken (3.50 ± 0.21 g), and grilled pork belly (3.04 ± 0.16 g). With regard to physical characteristics, and blood pressure and blood test results, only body mass index increased significantly according to protein intake groups (p < 0.05). The prevalence of metabolic syndrome in subjects was 38.5%, and there was no significant correlation with protein intake group. The OR of metabolic syndrome increased with protein intake, and was higher 4.452 times in excess group 2 than in the normal group (p < 0.05). Conversely, the OR of metabolic syndrome according to the frequency of protein-rich food intake did not show a significant correlation.
CONCLUSIONS
The results of this study can be used as significant supporting data to establish guidelines for protein intake in middle-aged men. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of diet quality according to the eating-out patterns of preschoolers and school-aged children in South Korea: based on data from the 2016–2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yu-na Ju, Youngmi Lee, Kyunghee Song, Yujin Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2021; 54(2): 165. CrossRef - Dietary Safety Management Awareness and Competency for Healthcare among Adults in Daegu and Gyeongbuk Areas
Yunhwa Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2020; 25(2): 112. CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome Risk by Dietary Fat Energy Ratio in Middle-aged Men - Using the 2012~2013 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data -
Eun-Sil Her
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(6): 1030. CrossRef
- Evaluation of diet quality according to the eating-out patterns of preschoolers and school-aged children in South Korea: based on data from the 2016–2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,080 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

- [English]
- The Prevalence of Hypertension and Related Nutritional Risk Factors of Elderly Living in a Rural Area
- Mee Sook Lee
- Korean J Community Nutr 2015;20(4):291-300. Published online August 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2015.20.4.291
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
The prevalence of hypertension in Korean rural elderly was significantly higher than that of the general population. Determining the potential risk factors of hypertension would be useful for managing and improving the treatment and prevention of hypertension in rural areas.
METHODS
We studied 336 elderly individuals 110 males, 226 females) aged between 65 years and 95 years residing in the rural area, S-gun Jeonbuk. Health-related habits, frequency of intake of food groups, nutrient intakes, anthropometric and biochemical measurements were assessed. Subjects were defined as hypertensive if SBP was > or = 140 mmHg or if DBP was > or = 90 mmHg or take an antihypertensive drug.
RESULTS
The rate of prevalence of hypertension in the study group was 51.8% (male 40.0%, female 57.5%). The risk of occurrence of hypertension was higher among females (OR, 1.98), 75 years old or older (OR, 1.62), BMI > or = 25 kg/m2 (OR, 2.84), acceptable range (upper end) of body fat (OR, 2.29) and unhealthy (too high) range of body fat (OR, 3.28), hypertriglyceridemia (OR, 2.17) and hypercholesterolemia (OR, 5.42), low protein intakes (OR, 1.78). However, health related habits, frequencies of intake of food groups and most nutrient intakes except for protein did not show any significant relationship with the occurrence of hypertension.
CONCLUSIONS
To reduce the risk of occurrence of hypertension among elderly individuals in rural areas, it is needed to avoid increase of body fat, 25 or higher BMI (kg/m2) and hyperlipidemia and low intake of proteins. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health-related Behavior Affecting Hypertension in the Elderly Using Data from the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jongsuk LEE
Korean Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science.2024; 56(2): 163. CrossRef
- Health-related Behavior Affecting Hypertension in the Elderly Using Data from the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 976 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- [English]
- Blood Lipid Levels, Nutrient Intakes and Health-Related Lifestyles of Industrial Male Workers According to Apolipoprotein E Polymorphisms
- Yoo Kyoung Park, Sang Woon Cho, Ji Yeon Kang, Yun Mi Paek, Sook Hee Sung, Tae In Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 2008;13(5):713-722. Published online October 31, 2008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study was to investigate the association among nutrient intakes and health-related lifestyles with cardiovascular disease risk assessed by blood lipid profile according to Apolipoprotein E genotypes. Middle-aged industrial male workers who had completed their annual medical examination were recruited and data of 675 subjects who finished the nutrient survey were used in the analysis. Anthropometric parameters, dietary assessment (FFQ), health-related lifestyles and blood profiles were used for statistical analyses. Apo E genotype groups were classified into the following three genotypes: Apo E2 group (including E2/E2, E2/E3, E2/E4), Apo E3 group (including E3/E3), Apo E4 group (including E3/E4, E4/E4). The frequency of Apo E2, E3, and E4 allele were 13.3%, 75.0% and 11.7% respectively. There were no significant differences in the anthropometric parameters depending on different Apo E genotypes. Also, no significant differences in the nutrient intakes were found according to the genotype groups. The nutrient intakes of all subjects were similar to or higher than the level of KDRIs (Dietary Reference Intakes For Koreans) except for intakes of calcium (67.44% of KDRIs), vitamin A (73.83% of KDRIs) and vitamin B2 (78.02% of KDRIs). Also, there were no significant differences of health-related lifestyles according to Apo E genotype groups. As for the lipid profiles, Apo E4 group had significantly higher total and LDL-cholesterol concentrations than the Apo E2 group (p < 0.05). We confirmed that plasma total and LDL-cholesterol concentrations were greatly influenced by Apo E genotypes. However, nutrient intakes and health-related lifestyles were not associated with Apo E genotypes.
- 271 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Effect of Maengjong-Juk ( Phyllostachys Pubescens) Extract Coated Rice Diet on Antioxidative System of C57BL/6 Mice Fed Atherogenic Diet
- Eun Young Kim, Min Ja Lee, Young Ok Song, Gap Soon Moon
- Korean J Community Nutr 2004;9(4):536-544. Published online August 31, 2004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To evaluate the antioxidative effect of maengjong-juk (Phyllostachys pubescens) extract coated rice in vivo system, maengjong-juk extract coated rice diets were fed to C57BL/6 mice for 16 weeks. Plasma total antioxidative capacity, hepatic lipid peroxidation, protein oxidation, activities of antioxidative enzymes and total glutathione content were measured. Plasma total antioxidative capacity was elevated significantly in maengjong-juk extract diets supplemented group in a dose dependant manner. Hepatic TBARS contents were significantly decreased in maengjong-juk extract diets supplemented group compared to high cholesterol group. Maengjong-juk extract coated rice diets suppressed the protein oxidation significantly in liver. Activities of hepatic antioxidative enzymes such as total SOD, Cu,Zn-SOD, Mn-SOD, GSH-Px and catalase activities of maengjong-juk extract coated rice diets were significantly higher than those of high cholesterol diet. Total hepatic glutathione content was significantly increased by maengjong-juk extract coated rice diets administration. According to this study, numerous antioxidative materials and phytochemicals containing in maengjong- juk extracts appear to protect antioxidative systems in C57BL/6 mice fed bamboo extract coated rice diet.
- 245 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Effects of Isoflavone Supplementation on Serum Lipids in Hyperlipidemic Postmenopausal Women
- Da Hong Lee, Chung Ja Sung, Haeng Shin Lee, Mi Hyun Kim, Yu Lee Seo
- Korean J Community Nutr 2001;6(1):69-75. Published online February 28, 2001
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Intake of soy protein the fisk factors associated with cardiovascular disease in postmenopausal women. This study was designed to effects of isoflavone supplementation on serum lipids in 16 hyperlipidemic postmenopausal women . For this purpose, an intervention study was conducted for 12 weeks. Subjects were healthy, free-living women consuming habitual diets with 0.3g/d of isoflavone. Food and nutrient intake was obtained by 24-hr recall method and anthropometric measurement were made. Systolic and diastolic blood pressure, total serum cholesterol. HDL-cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol were determined before and after the isoflavone supplementation. The results were summarized as follows. The average age, hight, weight and BMI of the subject were 65.3 years, 151.4 cm, 62.2 kg and 27.1, respectively. The systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure were not reduced significantly with isoflavone supplementation. Total cholesterol (p<0.001), HDL-C(p<0.05), and LDL-C(p<0.01) were significantly increased after isoflavone concentration. In conclusion, isoflavone supplementation was not effective to modify risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
- 242 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- The Associations of Percent Body Fat with Dietary Intake, Plasma Lipids, Lipoprotein(a), and PAI-1 in Middle Aged Korean Adults
- Jean Chinock Kim Rim, Soon Ah Kang, Hiojung Wee
- Korean J Community Nutr 1998;3(5):695-706. Published online November 30, 1998
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was designed to investigate the associations of the percent body fat dietary intake, plasma lipoprotein profile, lipoprotein(a), and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1(PAI-1) concentrations of 1982 Korean subjects(men : 1000 and women : 982) between the ages of 40 and 59 years. The dietary assessment consisted of twenty-four hour dietary records and food frequency questionnaires. The subjects were identified into one of the five rating groups of % body fat : lean, underweight, normal, overweight and obese groups. The biochemical assessment included measurements of plasma total cholesterol(TC), HDL-cholesterol(HDL-C), LDL-cholesterol(LDL-C), triglyceride(TG), lipoprotin(a)(Lp(a)), and PAI-1. With respect to the ratio of percent energy intake of carbohydrate : protein : fat of the normal group of the women was 62% : 17% : 20%, respectively. Women apparently had a higher intake of carbohydrates than men(52% : 17 : 20%) did. There was a linear relationship between energy intake and % body fat in both mean and women(with the exception of the underweight group of women). The relationship of % body fat of men to the protein and fat intake was higher than that of the carbohydrate intake. Of the men in the study, intakes of energy, protein and alcohol were positively correlated to % body fat. In women, energy, carbohydrate and protein intake were positively correlated to % body fat, however, the fat, cholesterol and alcohol intake did not show any correlation to the % body fat in women. This study showed that % body fat was positively correlated with plasma TC, LDL-C, PAI-1 levels, and TG, but the % body fat was negatively correlated with plasma HDL-C level in both men and women. These results indicated that the high energy intake of obese or overweight subjects might contribute to several of the biochemical indices fo coronary heart disease(CHD) risk. In conclusion, increased energy intake is associated with overweight or obesity in middle aged Korean people. There was no relationship between % energy intake of fat and % body fat in the study, in middle-aged Korean men and women. The plasma lipid profile and PAI-1 level thought to be the risk factors of CHD were positively associated with percent body fat in middle aged Korean people.
- 262 View
- 1 Download

- [English]
- Effects of Dietary Protein and Calcium Levels on Iron and Zine Balance in Young Korean Women
- Kisun Nam, Kyungwon Kim, Jaoeok Koo, Haymie Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 1998;3(2):218-227. Published online May 31, 1998
- 279 View
- 0 Download

- [English]
- Intake/Balanc of Dietary Protein in Korean College Women
- Seung Ho Oh, In Seon Choi
- Korean J Community Nutr 1997;2(4):523-529. Published online October 31, 1997
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was conducted to obtain accurate data on the intake, digestibility and nitrogen balance of protein in Korean college women. Subjects were 8 female college students, aged from 21 to 23, and maintained their menu and life patterns regular during a 4-week study. The same amount of diet that the subjects had consumed, and feces and urine were collected and measured to extract their nitrogen content by Kjeldahl method. From this data, apparent digestibility and the body nitrogen balance were estimated by determing daily protein intake and excretion. The daily protein intake was 56.9+/-1.4g and daily fecal protein loss was 6.3+/-0.2g. The apparent digestibility of protein was 89.6+/-0.7%. The daily nitrogen intake measured by Kjeldahl method was 9.43+/-0.2g. The urinary nitrogen excretion was 7.64+/-0.23g and fecal nitrogen excretion was 1.02+/-0.03g. The nitrogen balance indicated a positive balance of 0.45+/-0.18g.
- 316 View
- 1 Download


 KSCN
KSCN

 First
First Prev
Prev



